2.4.11 Packet Tracer – Modify Single-Area OSPFv2 (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or green highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
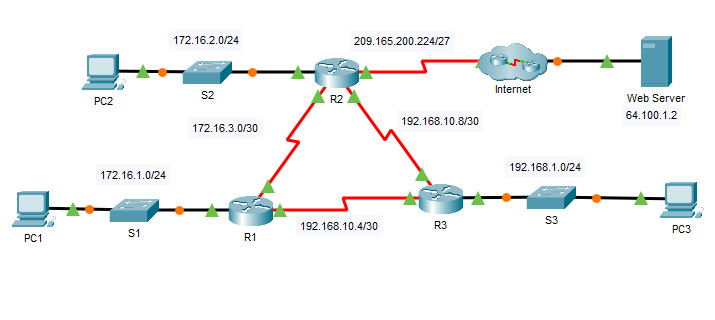
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IPv4 Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 172.16.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.16.3.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.10.5 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| R2 | G0/0 | 172.16.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.16.3.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.10.9 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/1/0 | 209.165.200.225 | 255.255.255.224 | ||
| R3 | G0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.10.6 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.10.10 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| PC1 | NIC | 172.16.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.1.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.16.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.2.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| Web Server | NIC | 64.100.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 64.100.1.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Modify OSPF Default Settings
- Part 2: Verify Connectivity
Scenario
In this activity, OSPF is already configured and all end devices currently have full connectivity. You will modify the default OSPF routing configurations by changing the hello and dead timers and adjusting the bandwidth of a link. Then you will verify that full connectivity is restored for all end devices.
Instructions
Part 1: Modify OSPF Default Settings
Step 1: Test connectivity between all end devices.
Before modifying the OSPF settings, verify that all PCs can ping the web server and each other.
Step 2: Adjust the hello and dead timers between R1 and R2.
a. Enter the following commands on R1.
R1(config)# interface s0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval 15 R1(config-if)# ip ospf dead-interval 60
b. After a short period of time, the OSPF connection with R2 will fail, as shown in the router output.
00:02:40: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 209.165.200.225 on Serial0/0/0 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired 00:02:40: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 209.165.200.225 on Serial0/0/0 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached
Both sides of the connection need to have the same timer values in order for the adjacency to be maintained. Identify the interface on R2 that is connected to R1. Adjust the timers on the R2 interface to match the settings on R1.
R2(config)# interface s0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval 15 R2(config-if)# ip ospf dead-interval 60
After a brief period of time you should see a status message that indicates that the OSPF adjacency has been reestablished.
00:21:52: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.10.5 on Serial0/0/0 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done
Step 3: Adjust the bandwidth setting on R1.
a. Trace the path between PC1 and the web server located at 64.100.1.2. Notice that the path from PC1 to 64.100.1.2 is routed through R2. OSPF prefers the lower cost path.
C:\> tracert 64.100.1.2 Tracing route to 64.100.1.2 over a maximum of 30 hops: 1 1 ms 0 ms 8 ms 172.16.1.1 2 0 ms 1 ms 0 ms 172.16.3.2 3 1 ms 9 ms 2 ms 209.165.200.226 4 * 1 ms 0 ms 64.100.1.2 Trace complete.
b. On the R1 Serial 0/0/0 interface, set the bandwidth to 64 Kb/s. This does not change the actual port speed, only the metric that the OSPF process on R1 will use to calculate best routes.
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 64
c. Trace the path between PC1 and the web server located at 64.100.1.2. Notice that the path from PC1 to 64.100.1.2 is redirected through R3. OSPF prefers the lower cost path.
C:\> tracert 64.100.1.2 Tracing route to 64.100.1.2 over a maximum of 30 hops: 1 1 ms 0 ms 3 ms 172.16.1.1 2 8 ms 1 ms 1 ms 192.168.10.6 3 2 ms 0 ms 2 ms 172.16.3.2 4 2 ms 3 ms 1 ms 209.165.200.226 5 2 ms 11 ms 11 ms 64.100.1.2 Trace complete.
Part 2: Verify Connectivity
Verify that all PCs can ping the web server and each other.
Answer scripts
Router R1
interface s0/0/0 ip ospf hello-interval 15 ip ospf dead-interval 60 bandwidth 64
Router R2
interface s0/0/0 ip ospf hello-interval 15 ip ospf dead-interval 60
