2.5.3 Packet Tracer – Propagate a Default Route in OSPFv2 (Instructor Version)
2.5.3 Packet Tracer – Propagate a Default Route in OSPFv2
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
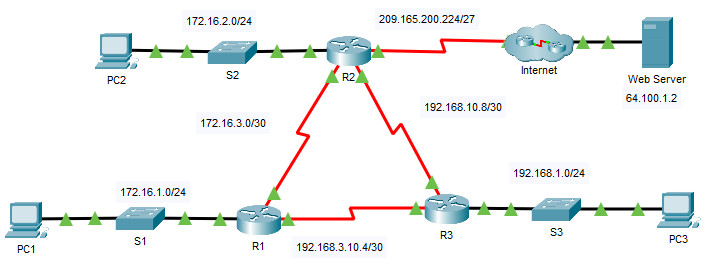
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IPv4 Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 172.16.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.16.3.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.10.5 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| R2 | G0/0 | 172.16.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.16.3.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.10.9 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/1/0 | 209.165.200.225 | 255.255.255.224 | ||
| R3 | G0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.10.6 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.10.10 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| PC1 | NIC | 172.16.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.1.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.16.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.2.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| Web Server | NIC | 64.100.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 64.100.1.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Propagate a Default Route
- Part 2: Verify Connectivity
Background
In this activity, you will configure an IPv4 default route to the Internet and propagate that default route to other OSPF routers. You will then verify the default route is in downstream routing tables and that hosts can now access a web server on the Internet.
Instructions
Part 1: Propagate a Default Route
Step 1: Test connectivity to the Web Server
a. From PC1, PC2, and PC3, attempt to ping the Web Server IP address, 64.100.1.2.
Were any of the pings successful?
What message did you receive, and which device issued the message?
b. Examine the routing tables on routers R1, R2, and R3.
What statement is present in the routing tables that indicates that the pings to the Web Server will fail?
Step 2: Configure a default route on R2.
Configure R2 with a directly attached default route to the Internet.
R2(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0/1/0
Note: Router will give a warning that if this interface is not a point-to-point connection, it may impact performance. You can ignore this warning because it is a point-to-point connection.
Step 3: Propagate the route in OSPF.
Configure OSPF to propagate the default route in OSPF routing updates.
R2(config)# router ospf 1 R2(config-router)# default-information originate
Step 4: Examine the routing tables on R1 and R3.
Examine the routing tables of R1 and R3 to verify that the route has been propagated.
R1> show ip route <output omitted> Gateway of last resort is 172.16.3.2 to network 0.0.0.0 <output omitted> O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 172.16.3.2, 00:00:08, Serial0/0/0 !------------------- R3> show ip route <output omitted> Gateway of last resort is 192.168.10.9 to network 0.0.0.0 <output omitted> O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 192.168.10.9, 00:08:15, Serial0/0/1
Part 2: Verify Connectivity
Verify that PC1, PC2, and PC3 can ping the web server.
Answer script
Router R2
enable config terminal ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0/1/0 router ospf 1 default-information originate
