1. Refer to the exhibit. What three types of routes are displayed in this routing table? (Choose three).
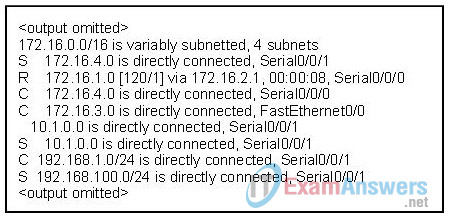
- networks local to this router
- the default route for this router
- static routes on this router
- mobile routes
- routes learned from dynamic routing protocols
- routes learned from non-cisco router
2. Which characteristic can be used to determine if a route is an ultimate route?
- The route displays a subnet mask.
- The route is a parent route.
- The route was configured by an administrator.
- The route includes an exit interface.
3. Refer to the exhibit. Which two routes are considered parent routes? (Choose two.)

- 172.16.0.0/24
- 172.16.4.0
- 172.16.1.0
- 10.0.0.0/16
- 192.168.1.0/24
- 192.168.100.0/24
4. Router R1 is configured with R1(config)# ip classless and R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0. What will R1 do with a packet that matches a parent route but does not match any associated child routes?
- forward the packet using the longest parent route match
- forward the packet via the default route
- return the packet with an icmp “destination unreachable” message to the source address
- drop the packet
5. What action will enable classful routing behavior on a router?
- configuring RIPv1 or IGRP
- configuring a link-state routing protocol
- using only classful netmasks on all networks
- issuing the no ip classless command
6. In the route lookup process, what constitutes the preferred route?
- the ultimate route
- the longest match of left-most bits
- the shortest prefix length
- the first route that resolves to an exit interface
7. If a packet matches a level 1 parent route in the routing table, what occurs next in the lookup process?
- The router will drop the packet since level 1 requires an exit interface.
- The router will look for the level 2 child route with an exit interface.
- The router will send the packet out all interfaces except the one in which it was recieved.
- The router will ARP all connected networks to find the interface with destionation on it.
8. What do the ip classless and no ip classless commands do?
- determine the address lookup behavior of the routing process
- specify whether the router will accept subnet masks in routing updates
- restrict the use of classful or classless routing protocols
- allow the router to accept or not accept VLSM for interface addresses
9. Router R1 is configured with R1(config)# no ip classless and R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0. What will R1 do with a packet that matches a parent route but does not match any associated child routes?
- forward the packet using the longest parent route match
- forward the packet via the default route
- return the packet with an icmp “destination unreachable” message to the source address
- drop the packet
10. Refer to the exhibit. Router C is running version 12.3 of the IOS. The router receives a packet with a destination of 172.16.1.130. Which route will router C use to forward the packet?
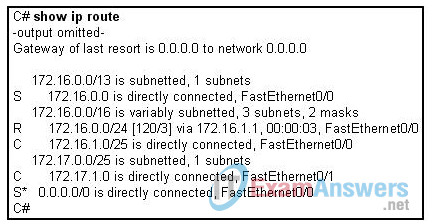
- 172.16.1.0/25
- 172.16.0.0/16
- 172.16.0.0/24
- 172.16.0.0/13
- the default route
- none, it will drop the packet
