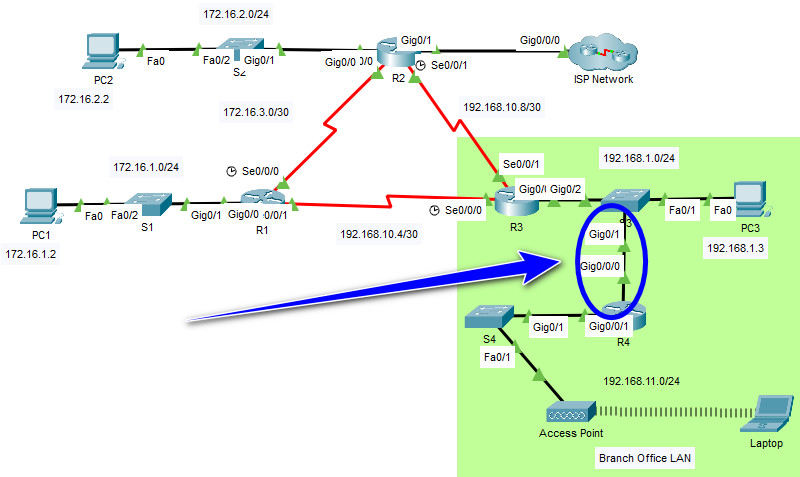
2.6.6 Packet Tracer – Verify Single-Area OSPFv2 (Instructor Version)
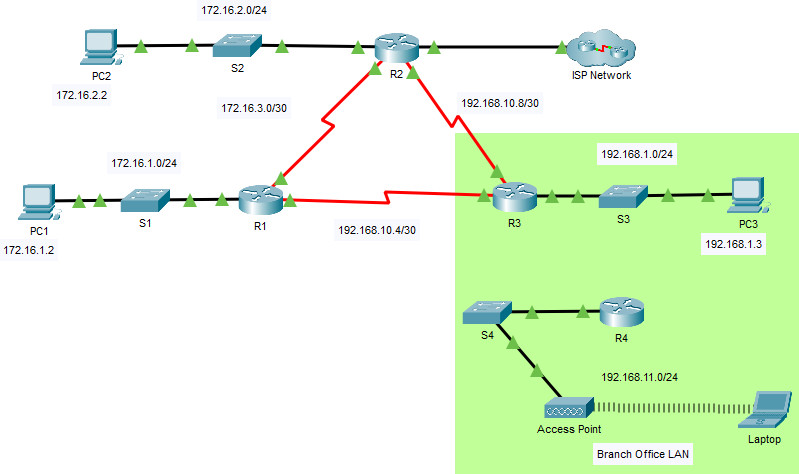
2.6.6 Packet Tracer – Verify Single-Area OSPFv2
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 172.16.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 64.100.54.6 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/0 | 172.16.3.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.10.5 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| R2 | G0/0 | 172.16.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.16.3.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.10.9 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| R3 | G0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 192.168.11.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.10.6 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.10.10 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| R4 | G0/0/0 | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| G0/0/1 | 192.168.11.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| ISP Router | NIC | 64.100.54.5 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| PC1 | NIC | 172.16.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.1.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.16.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.2.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| Laptop | NIC | DHCP | DHCP | DHCP |
Objectives
In this lab, you will use the CLI commands to verify the operation of an existing OSPFv2 network. In Part 2, you will add a new LAN to the configuration and verify connectivity.
- Identify and verify the status of OSPF neighbors.
- Determine how the routes are being learned in the network.
- Explain how the neighbor state is determined.
- Examine the settings for the OSPF process ID.
- Add a new LAN into an existing OSPF network and verify connectivity.
Background / Scenario
You are the network administrator for a branch office of a larger organization. Your branch is adding a new wireless network into an existing branch office LAN. The existing network is configured to exchange routes using OSPFv2 in a single-area configuration. Your task is to verify the operation of the existing OSPFv2 network, before adding in the new LAN. When you are sure that the current OSPFv2 LAN is operating correctly, you will connect the new LAN and verify that OSPF routes are being propagated for the new LAN. As branch office network administrator, you have full access to the IOS on routers R3 and R4. You only have read access to the enterprise LAN routers R1 and R2, using the username BranchAdmin, and the password Branch1234.
Instructor Note: The username Admin, password Cisco1234 has full privilege level 15 on routers R1 and R2.
Instructions
Part 1: Verify the existing OSPFv2 network operation.
The following commands will help you find the information needed to answer the questions:
show ip interface brief show ip route show ip route ospf show ip ospf neighbor show ip protocols show ip ospf show ip ospf interface
Step 1: Verify OSPFv2 operation on R1.
Wait until STP has converged on the network. You can click the Packet Tracer Fast Forward Time button to speed up the process. Continue only when all link lights are green.
a. Log into router R1 using the username BranchAdmin and the password Branch1234.Execute the show ip route command.
R1# show ip route
--- output omitted ----
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.3.2 to network 0.0.0.0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 3 masks
C 172.16.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 172.16.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
O 172.16.2.0/24 [110/65] via 172.16.3.2, 00:02:18, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.3.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 172.16.3.1/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.10.6, 00:02:18, Serial0/0/1
192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.10.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
L 192.168.10.5/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.10.8/30 [110/128] via 172.16.3.2, 00:02:18, Serial0/0/0
[110/128] via 192.168.10.6, 00:02:18, Serial0/0/1
O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 172.16.3.2, 00:02:18, Serial0/0/0
How did router R1 receive the default route?
From which router did R1 receive the default route?
How can you filter the output of show ip route to show only the routes learned through OSPF?
b. Execute the show ip ospf neighbor command on R1.
Which routers have formed adjacencies with router R1?
What are the router IDs and state of the routers shown in the command output?
Are all of the adjacent routers shown in the output?
c. Using the command prompt on PC1, ping the address of the ISP Router shown in the Address Table. Is it successful? If not, do a clear ospf process command on the routers and repeat the ping command.
Step 2: Verify OSPFv2 operation on R2.
a. Log into router R2 using the username BranchAdmin and the password Branch1234. Execute the show ip route command. Verify that routes to all the networks in the topology are shown in the routing table.
R2#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 64.100.54.5 to network 0.0.0.0
64.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 64.100.54.4/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 64.100.54.6/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 3 masks
O 172.16.1.0/24 [110/65] via 172.16.3.1, 00:15:37, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 172.16.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
C 172.16.3.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 172.16.3.2/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.10.10, 00:15:37, Serial0/0/1
192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
O 192.168.10.4/30 [110/128] via 192.168.10.10, 00:15:37, Serial0/0/1
[110/128] via 172.16.3.1, 00:15:37, Serial0/0/0
C 192.168.10.8/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
L 192.168.10.9/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 64.100.54.5
R2#
How did router R2 learn the default route to the ISP?
b. Enter the show ip ospf interface g0/0 on router R2.
R2#show ip ospf int g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is 172.16.2.1/24, Area 0
Process ID 10, Router ID 2.2.2.2, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 2.2.2.2, Interface address 172.16.2.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
What type of OSPF network is attached to this interface?
Are OSPF hello packets being sent out this interface? Explain.
c. Using the command prompt on PC2, ping the S0/0/1 address on router R3.
Is it successful?
Step 3: Verify OSPFv2 operation on R3.
a. Execute the show ip protocols command on router R3.
R3#show ip protocol
Routing Protocol is "ospf 10"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 3.3.3.3
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
192.168.10.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
192.168.10.8 0.0.0.3 area 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
1.1.1.1 110 00:23:53
2.2.2.2 110 00:23:58
3.3.3.3 110 00:23:57
Distance: (default is 110)
R3#
Router R3 is routing for which networks?
b. Execute the show ip ospf neighbor detail command on router R3.
What is the neighbor priority shown for the OSPF neighbor routers? This value is the default.
c. Using the command prompt on PC3, ping the address of the ISP Router shown in the Address Table.
Is it successful?
Part 2: Add the new Branch Office LAN to the OSPFv2 network.
You will now add the pre-configured Branch Office LAN to the OSPFv2 network.
Step 1: Verify the OSPFv2 configuration on router R4.
Execute a show run | begin router ospf command on router R4. Verify that the network statements are present for the networks that are configured on the router.
R4#show run | begin router ospf
router ospf 10
router-id 4.4.4.4
log-adjacency-changes
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
ip classless
!
ip flow-export version 9
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
line con 0
!
line aux 0
!
line vty 0 4
login
!
!
!
end
Which interface is configured to not send OSPF update packets?
Step 2: Connect the Branch Office router R4 to the OSPFv2 network.
a. Using the correct Ethernet cable, connect the G0/0/0 interface on router R4 to the G0/1 interface on switch S3. Use the show ip ospf neighbor command to verify that router R4 is now adjacent with router R3.
R4#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
3.3.3.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:32 192.168.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/0/0
R4#
What state is displayed for router R3?
b. Using the show ip ospf neighbor command on R3, determine the state of router R4. There may be a delay while OSPF converges.
Why is the state of router R4 different than the state of R1 and R2?
c. Using the command prompt on Laptop, ping the address of PC2.
Is it successful?