Lab – Configure CDP, LLDP, and NTP (Instructor Version)
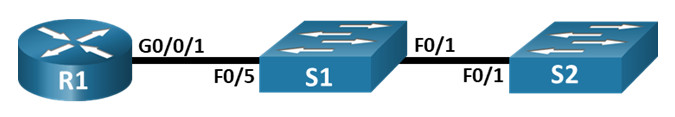
Topology
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Loopback1 | 172.16.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| G0/0/1 | 10.22.0.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| S1 | SVI VLAN 1 | 10.22.0.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.22.0.1 |
| S2 | SVI VLAN 1 | 10.22.0.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 10.22.0.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 2: Network Discovery with CDP
- Part 3: Network Discovery with LLDP
- Part 4: Configure and Verify NTP
Background / Scenario
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol for network discovery on the data link layer. It can share information such as device names and IOS versions with other physically connected Cisco devices. Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is vendor-neutral protocol using on the data link layer for network discovery. It is mainly used with network devices in the local area network (LAN). The network devices advertise information, such as their identities and capabilities to their neighbors.
Network Time Protocol (NTP) synchronizes the time of day among a set of distributed time servers and clients. NTP uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as its transport protocol. By default, NTP communications use Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
An NTP server usually receives its time from an authoritative time source, such as an atomic clock attached to a time server. It then distributes this time across the network. NTP is extremely efficient; no more than one packet per minute is necessary to synchronize two machines to within a millisecond of each other.
In this lab, you must document the ports that are connected to other switches using CDP and LLDP. You will document your findings in a network topology diagram.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Ensure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 1 Router (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 2 Switches (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 1 PC (Windows with a terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings on the router and switches.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Configure basic settings for the router.
a. Assign a device name to the router.
router(config)# hostname R1
b. Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were host names.
R1(config)# no ip domain lookup
c. Assign class as the privileged EXEC encrypted password.
R1(config)# enable secret class
d. Assign cisco as the console password and enable login.
R1(config)# line console 0 R1(config-line)# password cisco R1(config-line)# login
e. Assign cisco as the VTY password and enable login.
R1(config)# line vty 0 4 R1(config-line)# password cisco R1(config-line)# login
f. Encrypt the plaintext passwords.
R1(config)# service password-encryption
g. Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited.
R1(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $
h. Configure interfaces as listed in the table above
R1(config-if)# interface g0/0/1 R1(config-if)# ip address 10.22.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# end
i. Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
R1# copy running-config startup-config
Step 3: Configure basic settings for each switch.
a. Assign a device name to the switch.
switch(config)# hostname S1 switch(config)# hostname S2
b. Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were host names.
S1(config)# no ip domain-lookup S2(config)# no ip domain-lookup
c. Assign class as the privileged EXEC encrypted password.
S1(config)# enable secret class S2(config)# enable secret class
d. Assign cisco as the console password and enable login.
S1(config)# line console 0 S1(config-line)# password cisco S1(config-line)# login S2(config)# line console 0 S2(config-line)# password cisco S2(config-line)# login
e. Assign cisco as the VTY password and enable login.
S1(config)# line vty 0 15 S1(config-line)# password cisco S1(config-line)# login S2(config)# line vty 0 15 S2(config-line)# password cisco S2(config-line)# login
f. Encrypt the plaintext passwords.
S1(config)# service password-encryption S2(config)# service password-encryption
g. Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device sees the banner message “Authorized Users Only !”.
S1(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $ S2(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $
h. Shut down all unused interfaces.
S1(config)# interface range f0/2-4, f0/6-24, g0/1-2 S1(config-if-range)# shutdown S1(config-if-range)# end S2(config)# interface range f0/2-24, g0/1-2 S2(config-if-range)# shutdown S2(config-if-range)# end
i. Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
S1# copy running-config startup-config S2# copy running-config startup-config
Part 2: Network Discovery with CDP
On Cisco devices, CDP is enabled by default. You will use CDP to discover the ports that are currently connected.
a. On R1, use the appropriate show cdp command to determine how many interfaces are CDP enabled, and of those how many are up and how many are down.
R1# show cdp interface | include interfaces cdp enabled interfaces : 5 interfaces up : 4 interfaces down : 1
How many interfaces are participating in the CDP advertisement? Which interfaces are up?
Answers will vary. In the output above, five interfaces are participating in CDP. Four are up, one is down.
b. On R1, use the appropriate show cdp command to determine the IOS version used on S1.
R1# show cdp entry S1 ------------------------- Device ID: S1 Entry address(es): Platform: cisco WS-C2960+24LC-L, Capabilities: Switch IGMP Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1, Port ID (outgoing port): FastEthernet0/5 Holdtime : 125 sec Version : Cisco IOS Software, C2960 Software (C2960-LANBASEK9-M), Version 15.2(4)E8, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc3) Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport Copyright (c) 1986-2019 by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Fri 15-Mar-19 17:28 by prod_rel_team advertisement version: 2 VTP Management Domain: '' Native VLAN: 1 Duplex: full
What IOS version is S1 using?
Answers may vary. S1 in this example is using IOS Version 15.2(4)E8
c. On S1, use the appropriate show cdp command to determine how many CDP packets have been output.
S1# show cdp traffic
CDP counters :
Total packets output: 179, Input: 148
Hdr syntax: 0, Chksum error: 0, Encaps failed: 0
No memory: 0, Invalid packet: 0,
CDP version 1 advertisements output: 0, Input: 0
CDP version 2 advertisements output: 179, Input: 148
How many packets has CDP output since the last counter reset?
Answers may vary. In this example, CDP has output 179 packets
d. Configure the SVI for VLAN 1 on S1 and S2 using the IP addresses specified in the Addressing Table above. Configure the default gateway on each switch based on the Address Table.
S1(config)# interface vlan 1 S1(config-if)# ip address 10.22.0.2 255.255.255.0 S1(config-if)# no shutdown S1(config-if)# exit S1(config)# ip default-gateway 10.22.0.1 S2(config)# interface vlan 1 S2(config-if)# ip address 10.22.0.3 255.255.255.0 S2(config-if)# no shutdown S2(config-if)# exit S2(config)# ip default-gateway 10.22.0.1
e. On R1, issue the show cdp entry S1 command.
What additional information is now available?
The output includes the management IP address for VLAN 1 SVI on S1 that was just configured.
R1# show cdp entry S1 ------------------------- Device ID: S1 Entry address(es): IP address: 10.22.0.2 Platform: cisco WS-C2960+24LC-L, Capabilities: Switch IGMP Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1, Port ID (outgoing port): FastEthernet0/5 Holdtime : 133 sec Version : Cisco IOS Software, C2960 Software (C2960-LANBASEK9-M), Version 15.2(4)E8, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc3) Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport Copyright (c) 1986-2019 by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Fri 15-Mar-19 17:28 by prod_rel_team advertisement version: 2 VTP Management Domain: '' Native VLAN: 1 Duplex: full Management address(es): IP address: 10.22.0.2
f. Disable CDP globally on all devices.
R1(config)# no cdp run S1(config)# no cdp run S2(config)# no cdp run
Part 3: Network Discovery with LLDP
On Cisco devices, LLDP maybe enabled by default. You will use LLDP to discover the ports that are currently connected.
a. Enter the appropriate lldp command to enable LLDP on all devices in the topology.
R1(config)# lldp run S1(config)# lldp run S2(config)# lldp run
b. On S1, issue the appropriate lldp command to give you detailed information on S2.
S1# show lldp entry S2
Capability codes:
(R) Router, (B) Bridge, (T) Telephone, (C) DOCSIS Cable Device
(W) WLAN Access Point, (P) Repeater, (S) Station, (O) Other
------------------------------------------------
Local Intf: Fa0/1
Chassis id: c025.5cd7.ef00
Port id: Fa0/1
Port Description: FastEthernet0/1
System Name: S2
System Description:
Cisco IOS Software, C2960 Software (C2960-LANBASEK9-M), Version 15.2(4)E8, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc3)
Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Copyright (c) 1986-2019 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Fri 15-Mar-19 17:28 by prod_rel_team
Time remaining: 109 seconds
System Capabilities: B
Enabled Capabilities: B
Management Addresses:
IP: 10.22.0.3
Auto Negotiation - supported, enabled
Physical media capabilities:
100base-TX(FD)
100base-TX(HD)
10base-T(FD)
10base-T(HD)
Media Attachment Unit type: 16
Vlan ID: 1
Total entries displayed: 1
What is the chassis ID for switch S2?
Answers will vary. In this example, the chassis ID for S2 is c025.5cd7.ef00.
c. Console into all the devices and use the LLDP commands necessary for you to draw the physical network topology from only the show command output.
Answers will vary, but the main command to use is show lldp neighbor. The idea is for the student to visualize the network topology from only the LLDP outputs.
Part 4: Configure NTP
In Part 4, you will configure R1 as the NTP server and S1 and S2 as NTP clients of R1. Synchronized time is important for syslog and debug functions. If the time is not synchronized, it is difficult to determine what network event caused the message.
Step 1: Display the current time.
Issue the show clock detail command to display the current time on R1. Record the information regarding the current time displayed in the following table.
| Date | Time | Time Zone | Time Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Answer will vary. | Answer will vary. | Answer will vary, usually the Time Zone is not set. | Answer will vary, usually Time Source is not set. |
Step 2: Set the time.
Use the appropriate command to set the time on R1. The time entered should be in UTC.
R1# clock set 19:45:00 19 September 2019
Step 3: Configure the NTP master.
Configure R1 as the NTP master with a stratum level of 4.
R1(config)# ntp master 4
Step 4: Configure the NTP client.
a. Issue the appropriate command on S1 and S2 to see the configured time. Record the current time displayed in the following table.
| Date | Time | Time Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Answer will vary. | Answer will vary. | Answer will vary. |
b. Configure S1 and S2 as NTP clients. Use the appropriate NTP commands to obtain time from R1’s G0/0/1 interface, as well as to periodically update the calendar or hardware clock on the switch.
S1(config)# ntp server 10.22.0.1 S1(config)# ntp update-calendar S2(config)# ntp server 10.22.0.1 S2(config)# ntp update-calendar
Step 5: Verify NTP configuration.
a. Use the appropriate show command to verify that S1 and S2 are synchronized with R1.
Note: It could take a few minutes before the switches are synchronized with R1.
S1# show ntp status | include Clock Clock is synchronized, stratum 5, reference is 10.22.0.1 S2# show ntp associations address ref clock st when poll reach delay offset disp *~10.22.0.1 127.127.1.1 4 4 64 3 3.194 4.629 63.914 * sys.peer, # selected, + candidate, - outlyer, x falseticker, ~ configured
b. Issue the appropriate command on S1 and S2 to see the configured time and compare the time recorded earlier.
Reflection Question
Within a network, on which interfaces should you not use discovery protocols? Explain.
Discovery protocols should not be used on interfaces that are facing the external networks because these protocols provide insights about the internal network. This information allows attackers to gain valuable information about the internal network and can be used to exploit the network.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 4221 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 4300 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
Device Configs – Final
Router R1
R1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1651 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! vrf definition Mgmt-intf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! enable secret 5 $1$eLNA$ep.HFs8Pvv4rfDFXkbHHF/ ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode none ! lldp run no cdp run ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 no ip address negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 10.22.0.1 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! interface Serial0/1/0 no ip address ! interface Serial0/1/1 no ip address ! interface GigabitEthernet0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-intf no ip address negotiation auto ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server ip http secure-server ip tftp source-interface GigabitEthernet0 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C ! line con 0 password 7 045802150C2E login transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password 7 045802150C2E login ! ntp master 4 ! end
Switch S1
S1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1832 bytes ! version 15.2 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname S1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 5 $1$7eu1$pupMzRuJZXnwBeb2vcW2p0 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending lldp run no cdp run ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ! interface FastEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 ! interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/7 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/19 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 ip address 10.22.0.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip default-gateway 10.22.0.1 ip http server ip http secure-server ! banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C ! line con 0 password 7 02050D480809 login line vty 0 4 password 7 02050D480809 login line vty 5 15 password 7 02050D480809 login ! ntp update-calendar ntp server 10.22.0.1 end
Switch S2
S2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1842 bytes ! version 15.2 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname S2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 5 $1$Uajv$IGsyRs/8vTPBk6R9tmJ0Q0 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup ! ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending lldp run no cdp run ! ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ! interface FastEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/7 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/19 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 ip address 10.22.0.3 255.255.255.0 ! ip default-gateway 10.22.0.1 ip http server ip http secure-server ! banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C ! line con 0 password 7 030752180500 login line vty 0 4 password 7 030752180500 login line vty 5 15 password 7 030752180500 login ! ntp update-calendar ntp server 10.22.0.1 end

GRACIAS
thanks
ntp update-calendar doesn’t work