3.3.12 Packet Tracer – VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
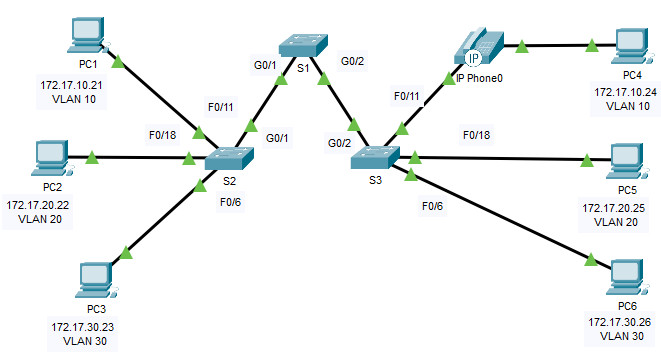
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | VLAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | NIC | 172.17.10.21 | 255.255.255.0 | 10 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.17.20.22 | 255.255.255.0 | 20 |
| PC3 | NIC | 172.17.30.23 | 255.255.255.0 | 30 |
| PC4 | NIC | 172.17.10.24 | 255.255.255.0 | 10 |
| PC5 | NIC | 172.17.20.25 | 255.255.255.0 | 20 |
| PC6 | NIC | 172.17.30.26 | 255.255.255.0 | 30 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Verify the Default VLAN Configuration
- Part 2: Configure VLANs
- Part 3: Assign VLANs to Ports
Background
VLANs are helpful in the administration of logical groups, allowing members of a group to be easily moved, changed, or added. This activity focuses on creating and naming VLANs, and assigning access ports to specific VLANs.
Part 1: View the Default VLAN Configuration
Step 1: Display the current VLANs.
On S1, issue the command that displays all VLANs configured. By default, all interfaces are assigned to VLAN 1.
S1#show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8
Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12
Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16
Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20
Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
Gig0/1, Gig0/2
1002 fddi-default active
1003 token-ring-default active
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trnet-default active
S1#
Step 2: Verify connectivity between PCs on the same network.
Notice that each PC can ping the other PC that shares the same subnet.
- PC1 can ping PC4
- PC2 can ping PC5
- PC3 can ping PC6
Pings to hosts on other networks fail.
What benefits can VLANs provide to the network?
Part 2: Configure VLANs
Step 1: Create and name VLANs on S1.
a. Create the following VLANs. Names are case-sensitive and must match the requirement exactly:
• VLAN 10: Faculty/Staff
S1#(config)# vlan 10 S1#(config-vlan)# name Faculty/Staff
b. Create the remaining VLANS.
• VLAN 20: Students
• VLAN 30: Guest(Default)
• VLAN 99: Management&Native
• VLAN 150: VOICE
S1(config-vlan)#vlan 20
S1(config-vlan)#name Students
S1(config-vlan)#vlan 30
S1(config-vlan)#name Guest(Default)
S1(config-vlan)#vlan 99
S1(config-vlan)#name Management&Native
S1(config-vlan)#vlan 150
S1(config-vlan)#name VOICE
Step 2: Verify the VLAN configuration.
Which command will only display the VLAN name, status, and associated ports on a switch?
S1#show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8
Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12
Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16
Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20
Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
Gig0/1, Gig0/2
10 Faculty/Staff active
20 Students active
30 Guest(Default) active
99 Management&Native active
150 VOICE active
1002 fddi-default active
1003 token-ring-default active
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trnet-default active
Step 3: Create the VLANs on S2 and S3.
Use the same commands from Step 1 to create and name the same VLANs on S2 and S3.
S2
S2(config)#vlan 10 S2(config-vlan)#name Faculty/Staff S2(config-vlan)#vlan 20 S2(config-vlan)#name Students S2(config-vlan)#vlan 30 S2(config-vlan)#name Guest(Default) S2(config-vlan)#vlan 99 S2(config-vlan)#name Management&Native S2(config-vlan)#vlan 150 S2(config-vlan)#name VOICE
S3
S3(config)#vlan 10 S3(config-vlan)#name Faculty/Staff S3(config-vlan)#vlan 20 S3(config-vlan)#name Students S3(config-vlan)#vlan 30 S3(config-vlan)#name Guest(Default) S3(config-vlan)#vlan 99 S3(config-vlan)#name Management&Native S3(config-vlan)#vlan 150 S3(config-vlan)#name VOICE
Step 4: Verify the VLAN configuration.
show vlan brief
Part 3: Assign VLANs to Ports
Step 1: Assign VLANs to the active ports on S2.
a. Configure the interfaces as access ports and assign the VLANs as follows:
• VLAN 10: FastEthernet 0/11
S2(config)# interface f0/11 S2(config-if)# switchport mode access S2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10
b. Assign the remaining ports to the appropriate VLAN.
• VLAN 20: FastEthernet 0/18
• VLAN 30: FastEthernet 0/6
S2(config-if)#interface f0/18
S2(config-if)#switchport mode access
S2(config-if)#switchport access vlan 20
S2(config-if)#interface f0/6
S2(config-if)#switchport mode access
S2(config-if)#switchport access vlan 30
S2(config-if)#
Step 2: Assign VLANs to the active ports on S3.
S3 uses the same VLAN access port assignments as S2. Configure the interfaces as access ports and assign the VLANs as follows:
• VLAN 10: FastEthernet 0/11
• VLAN 20: FastEthernet 0/18
• VLAN 30: FastEthernet 0/6
S3(config)#interface f0/11
S3(config-if)#switchport mode access
S3(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10
S3(config-if)#interface f0/18
S3(config-if)#switchport mode access
S3(config-if)#switchport access vlan 20
S3(config-if)#interface f0/6
S3(config-if)#switchport mode access
S3(config-if)#switchport access vlan 30
Step 3: Assign the VOICE VLAN to FastEthernet 0/11 on S3.
As shown in the topology, the S3 FastEthernet 0/11 interface connects to a Cisco IP Phone and PC4. The IP phone contains an integrated three-port 10/100 switch. One port on the phone is labeled Switch and connects to F0/4. Another port on the phone is labeled PC and connects to PC4. The IP phone also has an internal port that connects to the IP phone functions.
The S3 F0/11 interface must be configured to support user traffic to PC4 using VLAN 10 and voice traffic to the IP phone using VLAN 150. The interface must also enable QoS and trust the Class of Service (CoS) values assigned by the IP phone. IP voice traffic requires a minimum amount of throughput to support acceptable voice communication quality. This command helps the switchport to provide this minimum amount of throughput.
S3(config)# interface f0/11 S3(config-if)# mls qos trust cos S3(config-if)# switchport voice vlan 150
Step 4: Verify loss of connectivity.
Previously, PCs that shared the same network could ping each other successfully.
Study the output of from the following command on S2 and answer the following questions based on your knowledge of communication between VLANS. Pay close attention to the Gig0/1 port assignment.
S2# show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9
Fa0/10, Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14
Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/19
Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23
Fa0/24, Gig0/1, Gig0/2
10 Faculty/Staff active Fa0/11
20 Students active Fa0/18
30 Guest(Default) active Fa0/6
99 Management&Native active
150 VOICE active
Try pinging between PC1 and PC4.
Although the access ports are assigned to the appropriate VLANs, were the pings successful? Explain.
What could be done to resolve this issue?
Answer Scripts
Switch S1
vlan 10 name Faculty/Staff vlan 20 name Students vlan 30 name Guest(Default) vlan 99 name Management&Native vlan 150 name VOICE
Switch S2
vlan 10 name Faculty/Staff vlan 20 name Students vlan 30 name Guest(Default) vlan 99 name Management&Native vlan 150 name VOICE interface fa0/11 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 interface fa0/18 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 20 interface fa0/6 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 30
Switch S3
vlan 10 name Faculty/Staff vlan 20 name Students vlan 30 name Guest(Default) vlan 99 name Management&Native vlan 150 name VOICE interface fa0/11 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 mls qos trust cos switchport voice vlan 150 interface fa0/18 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 20 interface fa0/6 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 30

file not found on pdf file