1. Match the network type to the definition.
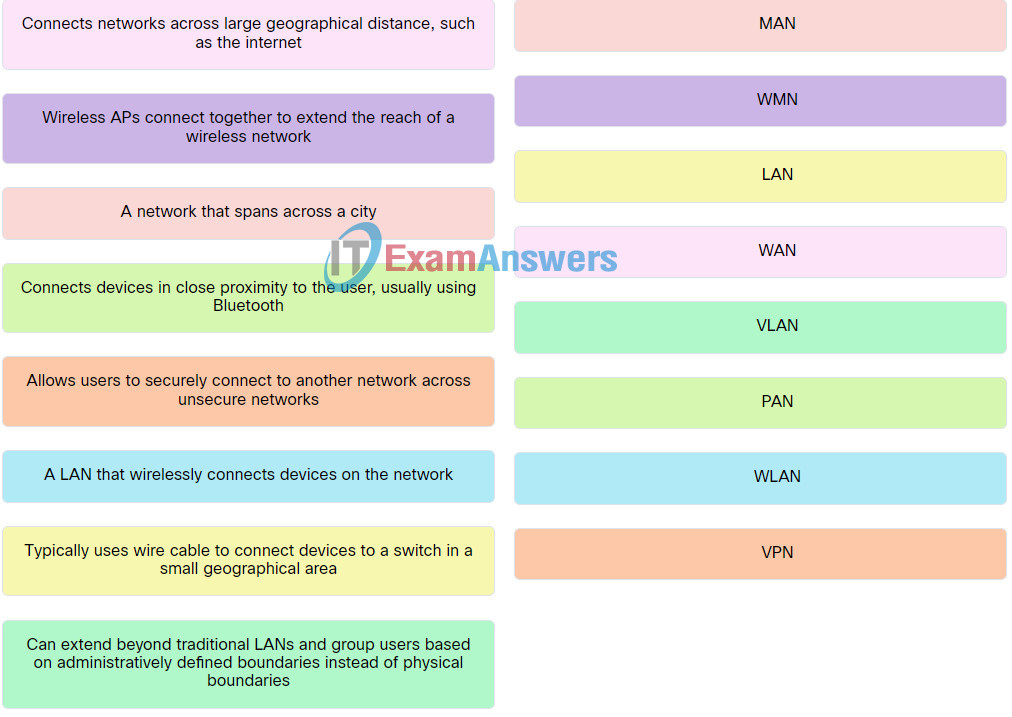
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| A network that spans across a city. |
MAN |
| A LAN that wirelessly connects devices on the network. |
WLAN |
| Connects devices in close proximity to the user, usually using Bluetooth. |
PAN |
| Wireless APs connect together to extend the reach of a wireless network. |
WMN |
| Connects networks across large geographical distance, such as the internet. |
WAN |
| Allows users to securely connect to another network across unsecure networks |
VPN |
| Typically uses wire cable to connect devices to a switch in a small geographical area. |
LAN |
| Can extend beyond traditional LANs and group users based on administratively defined boundaries instead of physical boundaries. |
VLAN |
2. Match internet connection type to the definition.
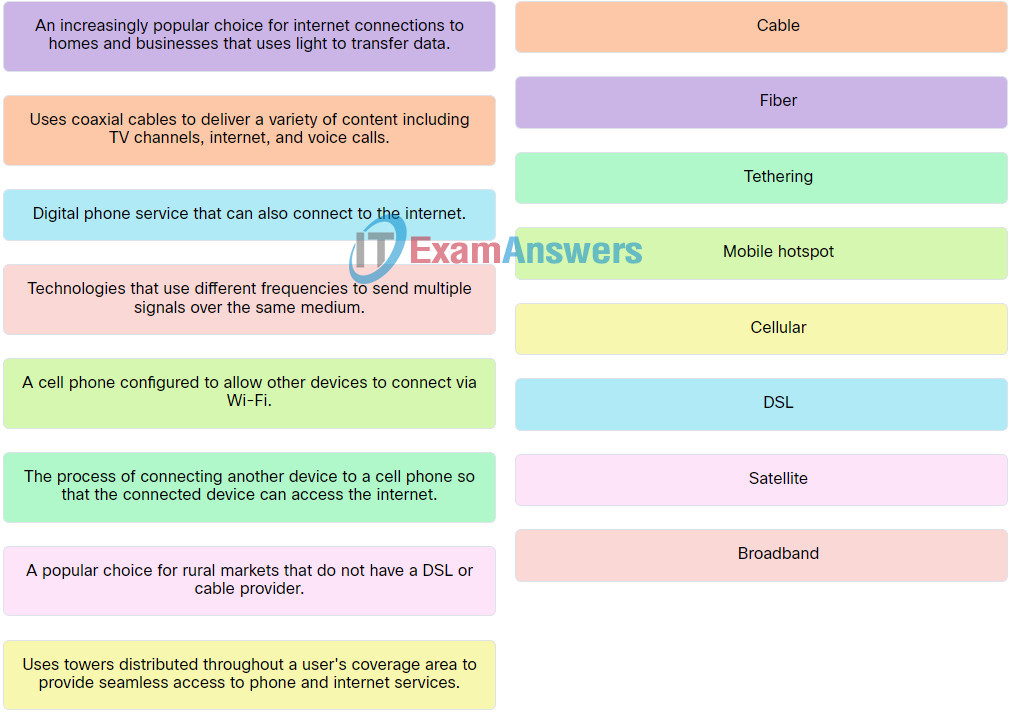
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| A network that spans across a city. |
MAN |
| Technologies that use different frequencies to send multiple signals over the same medium. |
Broadband |
| Digital phone service that can also connect to the internet. |
DSL |
| A cell phone configured to allow other devices to connect via Wi-Fi. |
Mobile hotspot |
| An increasingly popular choice for internet connections to homes and businesses that uses light to transfer data. |
Fiber |
| A popular choice for rural markets that do not have a DSL or cable provider. |
Satellite |
| Uses coaxial cables to deliver a variety of content including TV channels, internet, and voice calls. |
Cable |
| Uses towers distributed throughout a user’s coverage area to provide seamless access to phone and internet services. |
Cellular |
| The process of connecting another device to a cell phone so that the connected device can access the internet. |
Tethering |
3. Choose whether the following statements are true or false.
- The transport layer has only one protocol, like the internet layer. – False
- Some application layer protocols use only UDP. – True
- Some application layer protocols can use both TCP and UDP. – True
- Some application layer protocols use neither TCP nor UDP. – False
4. Which two statements apply to the Transport Layer protocols, TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- TCP provides reliability and data acknowledgement.
- TCP resends lost data and has low overhead.
- UDP is fast and delivers data as it arrives.
- UDP has low overhead and acknowledges packets received.
- Both TCP and UDP use port numbers and are considered to be reliable.
Explanation: TCP provides reliability, data acknowledgement, and resends lost data. UDP is fast, delivers data as it arrives, and has low overhead. Both TCP and UDP use port numbers
5. Match application and ports to the Transport Layer protocol used.
| port 20-FTP (data) |
TCP |
| port 21-FTP (control) |
TCP |
| port 22-SSH |
TCP |
| port 23-Telnet |
TCP |
| port 25-SMTP |
TCP |
| port 53-DNS |
Both |
| port 80-HTTP |
Both |
| port 67-DHCP (server) |
UDP |
| port 68-DHCP (client) |
UDP |
| port 69-TFTP |
UDP |
| port 110 – POP3 |
TCP |
| ports 137-139 – NetBIOS NetB |
Both |
| port 143 – IMAP |
TCP |
| port 161/162 – SNMP (data) |
Both |
| port 389 – LDAP (control) |
TCP |
| port 427 – SLP |
Both |
| port 443 – HTTPS |
Both |
| port 445 – SMB/CIFS |
Both |
| port 548 – AFP |
TCP |
| port 3389 – RDP |
Both |
6. Match the wireless protocol to the description.
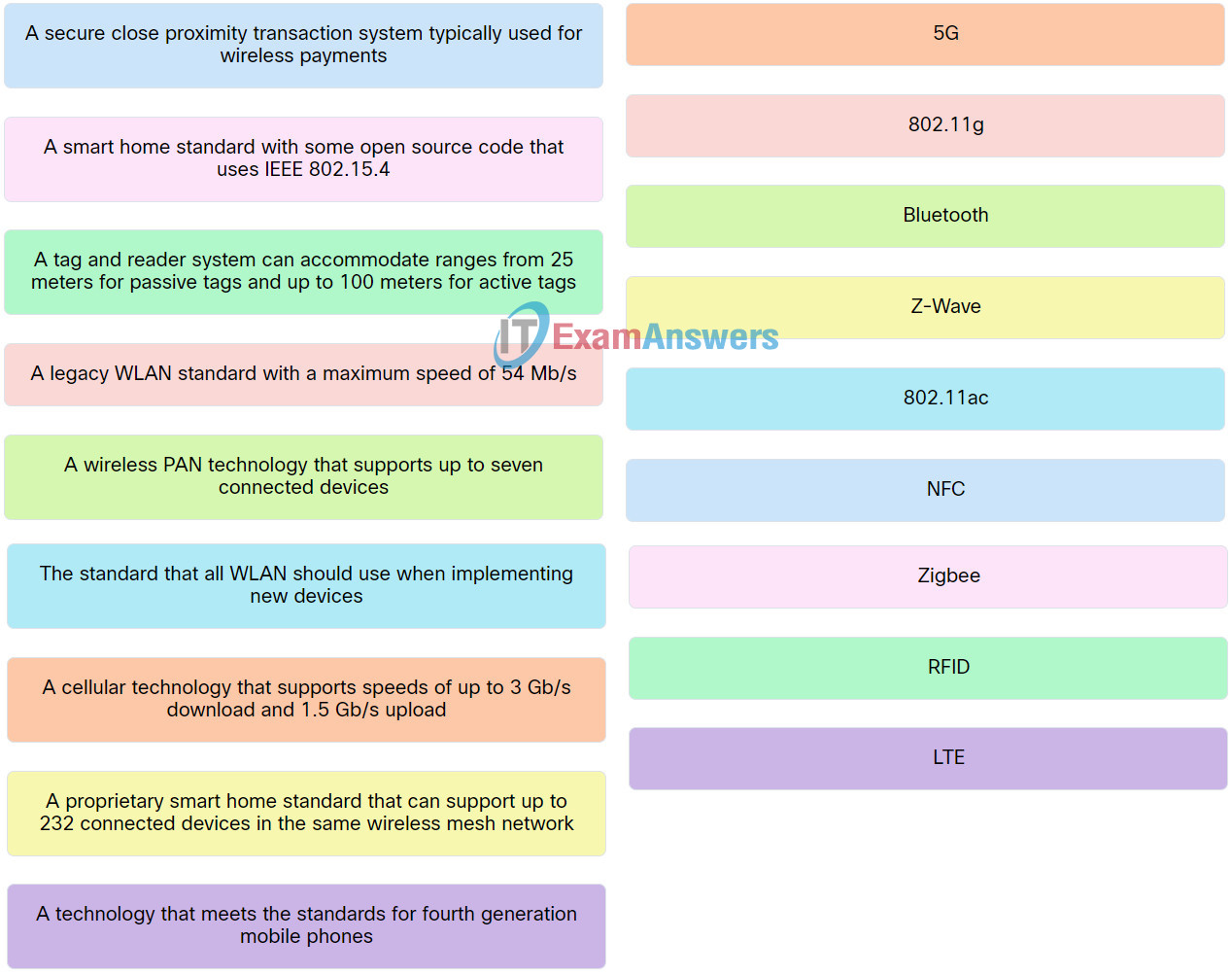
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| A legacy WLAN standard with a maximum speed of 54 Mb/s. |
802.11g |
| The standard that all WLAN should use when implementing new devices. |
802.11ac |
| A wireless PAN technology that supports up to seven connected devices. |
Bluetooth |
| A technology that meets the standards for fourth generation mobile phones. |
LTE |
| A smart home standard with some open source code that uses IEEE 802.15.4. |
Zigbee |
| A cellular technology that supports speeds of up to 3 Gb/s download and 1.5 Gb/s upload. |
5G |
| A proprietary smart home standard that can support up to 232 connected devices in the same wireless mesh network. |
Z-Wave |
| A tag and reader system can accommodate ranges from 25 meters for passive tags and up to 100 meters for active tags. |
RFID |
| A secure close proximity transaction system typically used for wireless payments. |
NFC |
7. Match network server to the description.
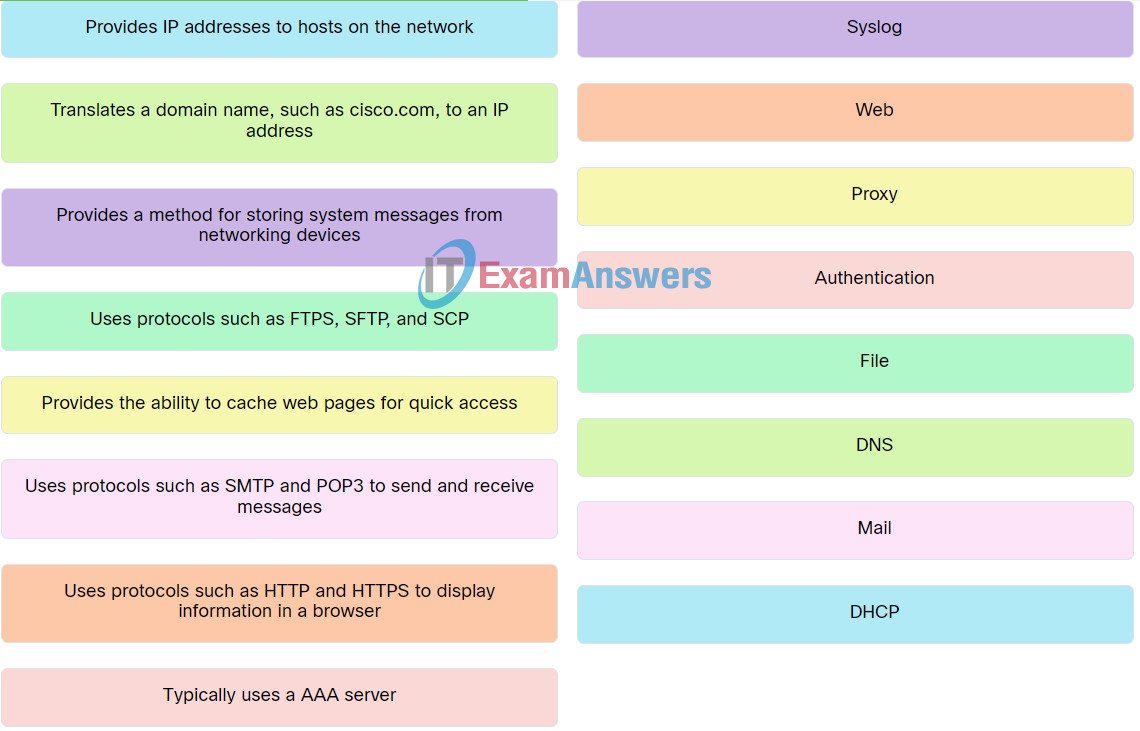
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| Typically uses a AAA server. |
Authentication |
| Provides IP addresses to hosts on the network. |
DHCP |
| Translates a domain name, such as cisco.com, to an IP address. |
DNS |
| Provides a method for storing system messages from networking devices. |
Syslog |
| Uses protocols such as SMTP and POP3 to send and receive messages. |
Mail |
| Uses protocols such as HTTP and HTTPS to display information in a browser. |
Web |
| Provides the ability to cache web pages for quick access. |
Proxy |
| Uses protocols such as FTPS, SFTP, and SCP. |
File |
8. Match network device to the characteristic.
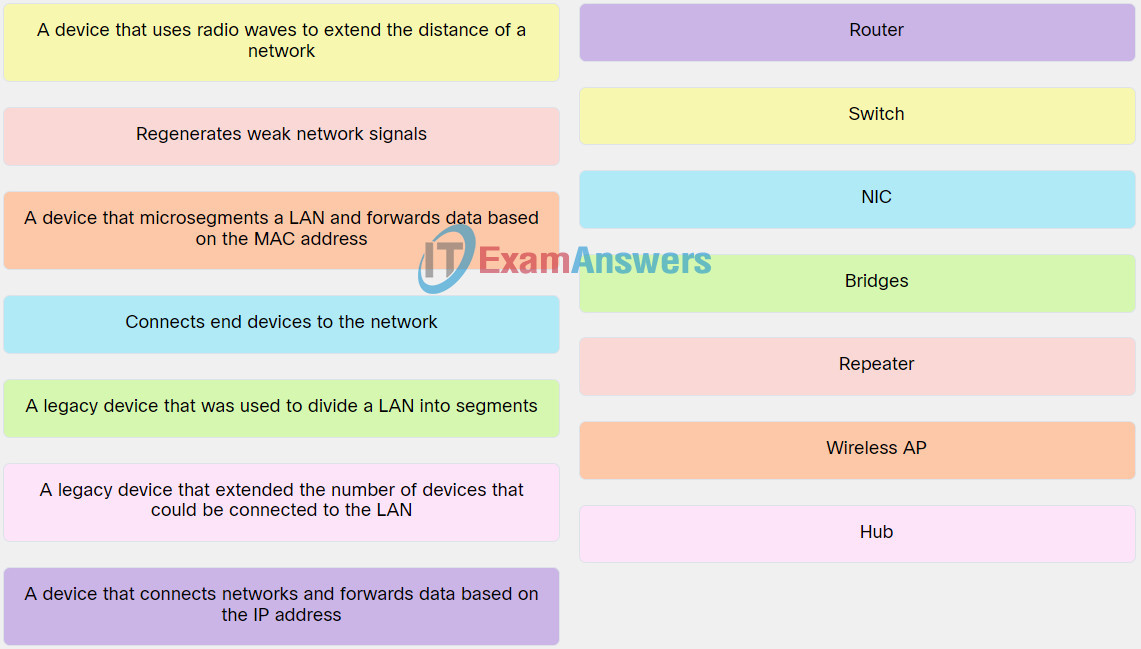
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| Regenerates weak network signals. |
Repeater |
| Connects end devices to the network. |
NIC |
| A legacy device that was used to divide a LAN into segments. |
Bridges |
| A device that connects networks and forwards data based on the IP address. |
Router |
| A legacy device that extended the number of devices that could be connected to the LAN. |
Hub |
| A device that microsegments a LAN and forwards data based on the MAC address. |
Wireless AP |
| A device that uses radio waves to extend the distance of a network. |
Switch |
9. Match security device to the characteristic.
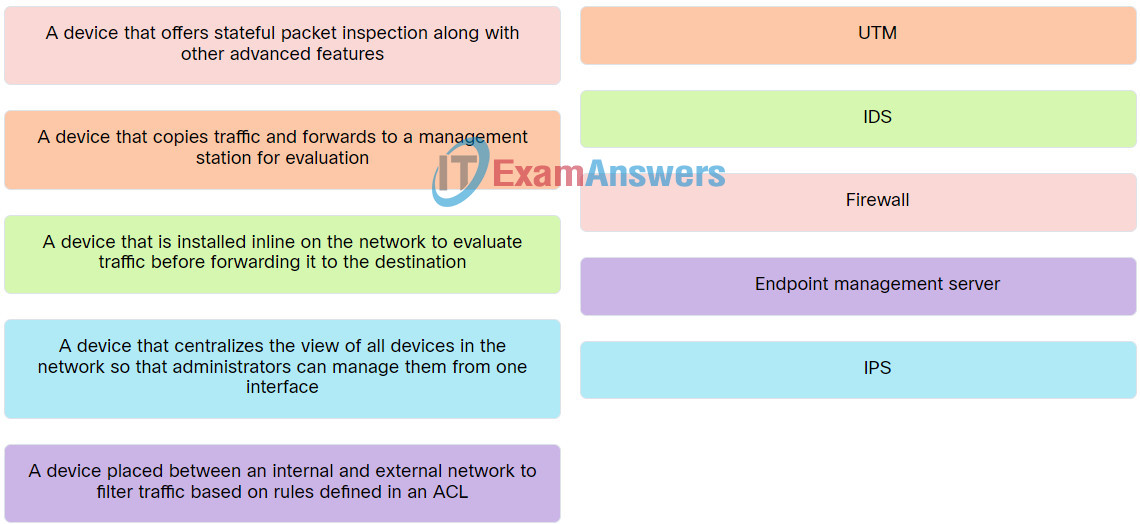
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| A device that offers stateful packet inspection along with other advanced features. |
Firewall |
| A device that centralizes the view of all devices in the network so that administrators can manage them from one interface. |
IPS |
| A device that is installed inline on the network to evaluate traffic before forwarding it to the destination. |
IDS |
| A device placed between an internal and external network to filter traffic based on rules defined in an ACL. |
Endpoint management server |
| A device that copies traffic and forwards to a management station for evaluation. |
UTM |
10. Match the term to the respective description.
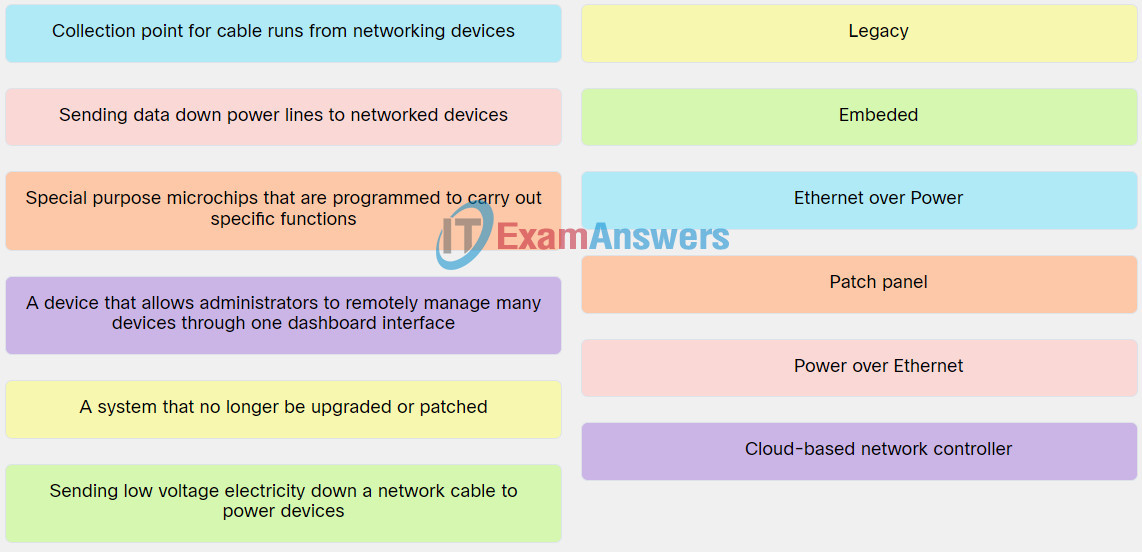
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| Sending data down power lines to networked devices. |
Power over Ethernet |
| Collection point for cable runs from networking devices. |
Ethernet over Power |
| Sending low voltage electricity down a network cable to power devices. |
Embeded |
| A device that allows administrators to remotely manage many devices through one dashboard interface. |
Cloud-based network controller |
| A system that no longer be upgraded or patched. |
Legacy |
| Special purpose microchips that are programmed to carry out specific functions. |
Patch panel |
11. Match network tool to the description
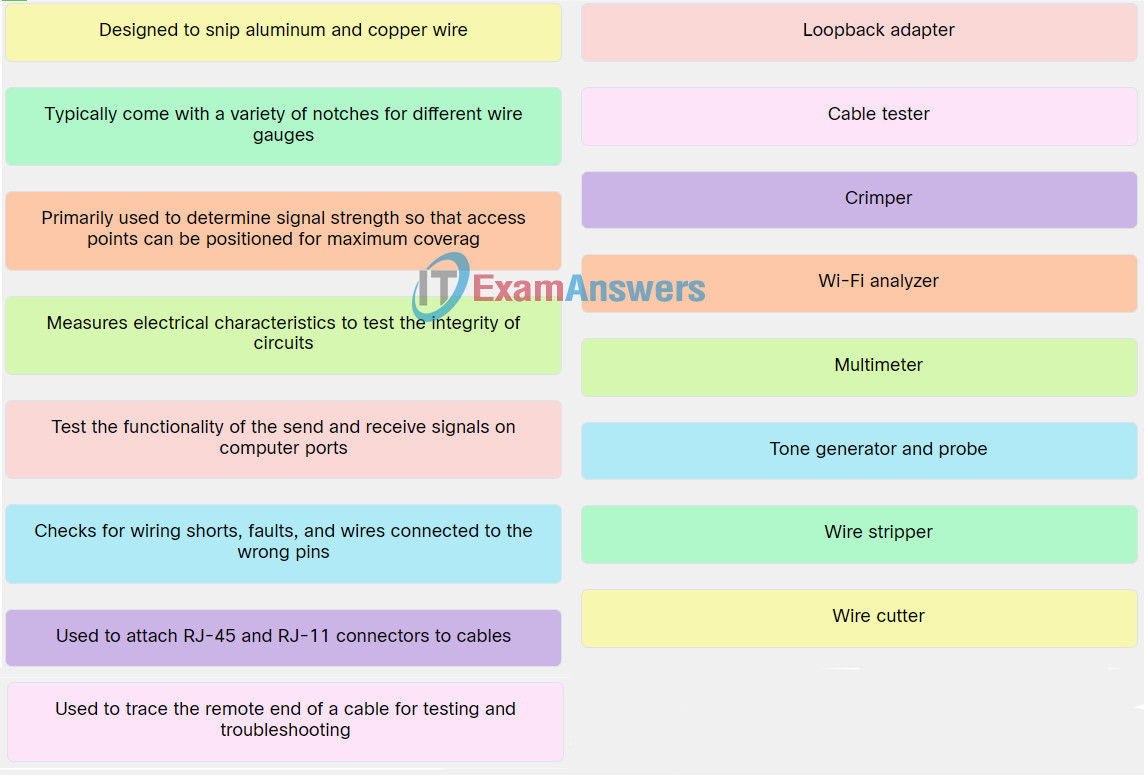
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| Test the functionality of the send and receive signals on computer ports. |
Loopback adapter |
| Checks for wiring shorts, faults, and wires connected to the wrong pins. |
Tone generator and probe |
| Measures electrical characteristics to test the integrity of circuits. |
Multimeter |
| Used to attach RJ-45 and RJ-11 connectors to cables. |
Crimper |
| Used to trace the remote end of a cable for testing and troubleshooting. |
Cable tester |
| Primarily used to determine signal strength so that access points can be positioned for maximum coverag. |
Wi-Fi analyzer |
| Designed to snip aluminum and copper wire. |
Wire cutter |
| Typically come with a variety of notches for different wire gauges. |
Wire stripper
|
12. Match fiber cabling term to the definition.

Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| Uses LED emitters and popular for LANs and runs up to 550 meters. |
Multimode fiber |
| Technology used to send and receive on a single strand of fiber. |
WDM |
| Uses a laser and popular for long distance runs FONTning hundreds of kilometers. |
Single-mode fiber |
| Element in a fiber optic cable through which light pulses travel. |
Core |
| Acts like a mirror reflecting light to keep it traveling down the fiber. |
Cladding |









