How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
Checkpoint Exam: Network Infrastructure Security Group Exam Answers
Modules 11 – 12 of the CyberOps Associate 1.0
1. What is an advantage of HIPS that is not provided by IDS?
- HIPS protects critical system resources and monitors operating system processes.
- HIPS deploys sensors at network entry points and protects critical network segments.
- HIPS monitors network processes and protects critical files.
- HIPS provides quick analysis of events through detailed logging.
Explanation: Network-based IDS (NIDS) sensors are typically deployed in offline mode. They do not protect individual hosts. Host-based IPS (HIPS) is software installed on a single host to monitor and analyze suspicious activity. It can monitor and protect operating system and critical system processes that are specific to that host. HIPS can be thought of as a combination of antivirus software, antimalware software, and a firewall.
2. Which statement describes a difference between RADIUS and TACACS+?
- RADIUS separates authentication and authorization whereas TACACS+ combines them as one process.
- RADIUS is supported by the Cisco Secure ACS software whereas TACACS+ is not.
- RADIUS uses TCP whereas TACACS+ uses UDP.
- RADIUS encrypts only the password whereas TACACS+ encrypts all communication.
Explanation: TACACS+ uses TCP, encrypts the entire packet (not just the password), and separates authentication and authorization into two distinct processes. Both protocols are supported by the Cisco Secure ACS software.
3. What are two disadvantages of using an IDS? (Choose two.)
- The IDS does not stop malicious traffic.
- The IDS works offline using copies of network traffic.
- The IDS has no impact on traffic.
- The IDS analyzes actual forwarded packets.
- The IDS requires other devices to respond to attacks.
Explanation: The disadvantage of operating with mirrored traffic is that the IDS cannot stop malicious single-packet attacks from reaching the target before responding to the attack. Also, an IDS often requires assistance from other networking devices, such as routers and firewalls, to respond to an attack. An advantage of an IDS is that by working offline using mirrored traffic, it has no impact on traffic flow.
4. Which statement describes one of the rules that govern interface behavior in the context of implementing a zone-based policy firewall configuration?
- An administrator can assign interfaces to zones, regardless of whether the zone has been configured.
- An administrator can assign an interface to multiple security zones.
- By default, traffic is allowed to flow among interfaces that are members of the same zone.
- By default, traffic is allowed to flow between a zone member interface and any interface that is not a zone member.
Explanation: An interface can belong to only one zone. Creating a zone is the first step in configuring a zone-based policy firewall. A zone cannot be assigned to an interface if the zone has not been created. Traffic can never flow between an interface that is assigned to a zone and an interface that has not been assigned to a zone.
5. Which technique is necessary to ensure a private transfer of data using a VPN?
- encryption
- virtualization
- scalability
- authorization
Explanation: Confidential and secure transfers of data with VPNs require data encryption.
6. What is the function of the distribution layer of the three-layer network design model?
- providing direct access to the network
- providing secure access to the Internet
- aggregating access layer connections
- providing high speed connection to the network edge
Explanation: The function of the distribution layer is to provide connectivity to services and to aggregate the access layer connections
7. What two components of traditional web security appliances are examples of functions integrated into a Cisco Web Security Appliance? (Choose two.)
- email virus and spam filtering
- VPN connection
- firewall
- web reporting
- URL filtering
Explanation: The Cisco Web Security Appliance is a secure web gateway which combines advanced malware protection, application visibility and control, acceptable use policy controls, reporting, and secure mobility functions. With traditional web security appliances, these functions are typically provided through multiple appliances. It is not a firewall appliance in that it only filters web traffic. It does not provide VPN connections, nor does it provide email virus and spam filtering; the Cisco Email Security Appliance provides these functions.
8. Which AAA component can be established using token cards?
- authentication
- accounting
- authorization
- auditing
Explanation: The authentication component of AAA is established using username and password combinations, challenge and response questions, and token cards. The authorization component of AAA determines which resources the user can access and which operations the user is allowed to perform. The accounting and auditing component of AAA keeps track of how network resources are used.
9. Which statement describes a VPN?
- VPNs use open source virtualization software to create the tunnel through the Internet.
- VPNs use dedicated physical connections to transfer data between remote users.
- VPNs use logical connections to create public networks through the Internet.
- VPNs use virtual connections to create a private network through a public network.
Explanation: A VPN is a private network that is created over a public network. Instead of using dedicated physical connections, a VPN uses virtual connections routed through a public network between two network devices.
10. What is a host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS)?
- It detects and stops potential direct attacks but does not scan for malware.
- It is an agentless system that scans files on a host for potential malware.
- It identifies potential attacks and sends alerts but does not stop the traffic.
- It combines the functionalities of antimalware applications with firewall protection.
Explanation:Accurrent HIDS is a comprehensive security application that combines the functionalities of antimalware applications with firewall protection. An HIDS not only detects malware but also prevents it from executing.
Because the HIDS runs directly on the host, itis considered an agent-based system.
11. Which two devices would commonly be found at the access layer of the hierarchical enterprise LAN design model? (Choose two.)
- modular switch
- Layer 3 device
- Layer 2 switch
- firewall
- access point
Explanation: While some designs do route at the access layer, the two devices that should always be placed at the access layer of the hierarchical design model are an access point and a Layer 2 switch. A modular switch is commonly used at the core layer. Routing by a Layer 3 device is commonly used in the distribution layer. The firewall is a device in the Internet edge network design.
12. Which two statements are true about NTP servers in an enterprise network? (Choose two.)
- There can only be one NTP server on an enterprise network.
- NTP servers at stratum 1 are directly connected to an authoritative time source.
- NTP servers control the mean time between failures (MTBF) for key network devices.
- NTP servers ensure an accurate time stamp on logging and debugging information.
- All NTP servers synchronize directly to a stratum 1 time source.
Explanation: Network Time Protocol (NTP) is used to synchronize the time across all devices on the network to make sure accurate timestamping on devices for managing, securing and troubleshooting. NTP networks use a hierarchical system of time sources. Each level in this hierarchical system is called a stratum. The stratum 1 devices are directly connected to the authoritative time sources.
13. In the data gathering process, which type of device will listen for traffic, but only gather traffic statistics?
- NetFlow collector
- NMS
- SNMP agent
- syslog server
Explanation: A NetFlow collector is the device that receives traffic statistics from networking devices. NetFlow only gathers traffic statistics, unlike syslog and SNMP which can collect various network events.
14. Which two protocols are link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.)
Explanation: ISIS and OSPF are link-state routing protocols. EIGRP and RIP are distance vector routing protocols. BGP is a path vector protocol.
15. What type of route is created when a network administrator manually configures a route that has an active exit interface?
- directly connected
- static
- local
- dynamic
Explanation: A static route is one that is manually configured by the network administrator.
16. Which characteristic describes a wireless client operating in active mode?
- must be configured for security before attaching to an AP
- broadcasts probes that request the SSID
- ability to dynamically change channels
- must know the SSID to connect to an AP
Explanation: A wireless client operating in active mode must know the name of the SSID. Probe requests are broadcast by a client across multiple channels and include the SSID name and supported standards. Active mode is used if an AP is configured to not broadcast beacon frames.
17. What are two types of addresses found on network end devices? (Choose two.)
Explanation: Intermediary devices use two types of addresses when sending messages to the final destination device, MAC and IP addresses. TCP and UDP are protocols used at Layer 4 to identify what port numbers are being used on the source and destination devices. A return address is used when mailing a letter, not in networking.
18. What is a characteristic of the WLAN passive discover mode?
- The client must know the name of the SSID to begin the discover process.
- The client begins the discover process by sending a probe request.
- The beaconing feature on the AP is disabled.
- The AP periodically sends beacon frames containing the SSID.
Explanation: In passive mode, the wireless clients learn what networks and APs are available. The client learns this information from beacon frames, sent by the APs, that contain the WLAN SSID, supported standards, and security settings.
19. What is a characteristic of a routed port that is configured on a Cisco switch?
- It supports subinterfaces.
- It is associated with a single VLAN.
- It runs STP to prevent loops.
- It is assigned an IP address.
Explanation: Routed ports on a Cisco switch behave similarly to those on a router. They are configured with an IP address and forward Layer 3 packets. Unlike Layer 2 switch interfaces, routed ports do not support STP, nor do they support subinterfaces as routers do.
20. What action does an Ethernet switch take when it receives a frame with an unknown Layer 2 source address?
- It forwards the frame out all interfaces except the interface on which it was received.
- It forwards the frame to the default gateway.
- It records the source address in the address table of the switch.
- It drops the frame.
Explanation: When an Ethernet switch receives a frame with an unknown Layer 2 address, the switch records that address in the address table.
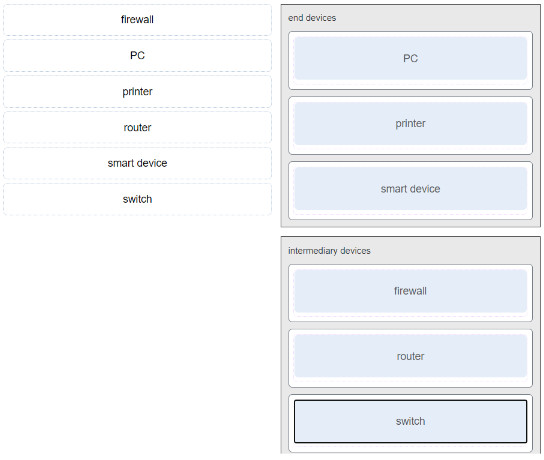
21.. Match each device to a category.
22. Which routing protocol is used to exchange routes between internet service providers?
Explanation: BGP is a path vector routing protocol and it is used by internet service providers to exchange routes.
23. What is the first step in the CSMA/CA process when a wireless client is attempting to communicate on the wireless network?
- The client sends an RTS message to the AP.
- The client sends a test frame onto the channel.
- The client listens for traffic on the channel.
- The AP sends a CTS message to the client.
Explanation: When a wireless client is attempting to communicate on the network, it will first listen to the channel to be sure it is idle. Next, the client sends an RTS message to the AP to request dedicated access to the network. The AP will then send a CTS message granting access to the client. The client will then transmit data.
24. What Wi-Fi management frame is regularly broadcast by APs to announce their presence?
- authentication
- beacon
- probe
- association
Explanation: Beacon frames are broadcast periodically by the AP to advertise its wireless networks to potential clients. Probing, association, and authentication frames are only sent when a client is associating to the AP.
25. What are the three parts of all Layer 2 frames? (Choose three.)
- source and destination IP address
- payload
- sequence number
- frame check sequence
- time-to-live
- header
Explanation: Layer 2 frames have three components: the header, the payload, and a frame check sequence at the end.
26. What is a function of SNMP?
- synchronizes the time across all devices on the network
- captures packets entering and exiting the network interface card
- provides a message format for communication between network device managers and agents
- provides statistical analysis on packets flowing through a Cisco router or multilayer switch
Explanation: SNMP is an application layer protocol that allows administrators to manage devices on the network by providing a messaging format for communication between network device managers and agents.
27. Which firewall feature is used to ensure that packets coming into a network are legitimate responses to requests initiated from internal hosts?
- application filtering
- stateful packet inspection
- packet filtering
- URL filtering
Explanation: Stateful packet inspection on a firewall checks that incoming packets are actually legitimate responses to requests originating from hosts inside the network. Packet filtering can be used to permit or deny access to resources based on IP or MAC address. Application filtering can permit or deny access based on port number. URL filtering is used to permit or deny access based on URL or on keywords.
28. In which memory location is the routing table of a router maintained?
Explanation: The routing table of a router is maintained in RAM, which is volatile memory. If a router loses power or is rebooted, the content of RAM is lost and the routing table must be rebuilt.
29. Lightweight access points forward data between which two devices on the network? (Choose two.)
- wireless router
- default gateway
- wireless LAN controller
- autonomous access point
- wireless client
Explanation: In a wireless deployment that is using lightweight access points (LWAPs), the LWAP forwards data between the wireless clients and the wireless LAN controller (WLC).
30. A Cisco router is running IOS 15. What are the two routing table entry types that will be added when a network administrator brings an interface up and assigns an IP address to the interface? (Choose two.)
- route that is manually entered by a network administrator
- local route interface
- route that is learned via OSPF
- directly connected interface
- route that is learned via EIGRP
Explanation: A local route interface routing table entry is found when a router runs IOS 15 or higher or if IPv6 routing is enabled. Whenever an interface is addressed and enabled (made active), a directly connected interface is automatically shown in the routing table.
31. Match the secunty service with the description.
Match the security service with the description.
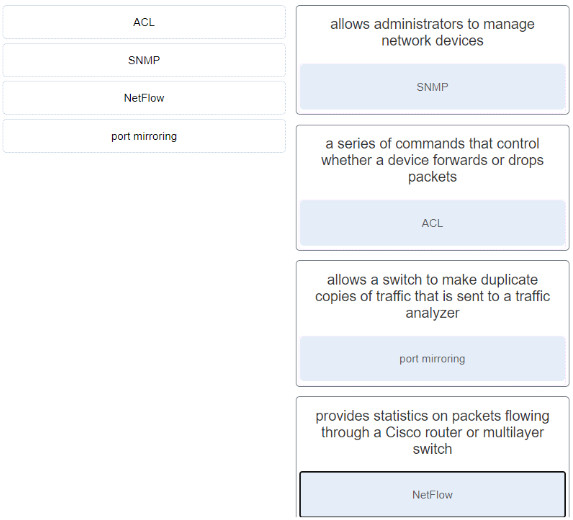
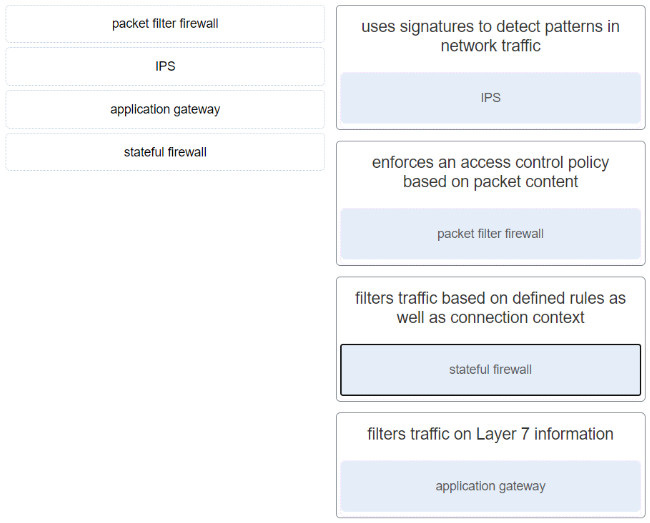
32. Match the network security device type with the descnption.
33. What is used on WLANs to avoid packet collisions?
Explanation: WLANs are half-duplex networks which means that only one client can transmit or receive at any given moment. WLANs use carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) to determine when to send data on the network to avoid packet collisions.
34. What information within a data packet does a router use to make forwarding decisions?
- the destination MAC address
- the destination host name
- the destination service requested
- the destination IP address
Explanation: A Layer 3 device like a router uses a Layer 3 destination IP address to make a forwarding decision.
35. What is a characteristic of a hub?
- operates at Layer 2
- regenerates signals received on one port out all other ports
- subdivides the network into collision domains
- uses CSMA/CA to avoid collisions
Explanation: A hub is a Layer 1 device that regenerates signals out all ports other than the ingress port. All ports on a hub belong to the same collision domain. Hubs use CSMA/CD to detect collisions on the network.
36. Match the network security device type with the description.
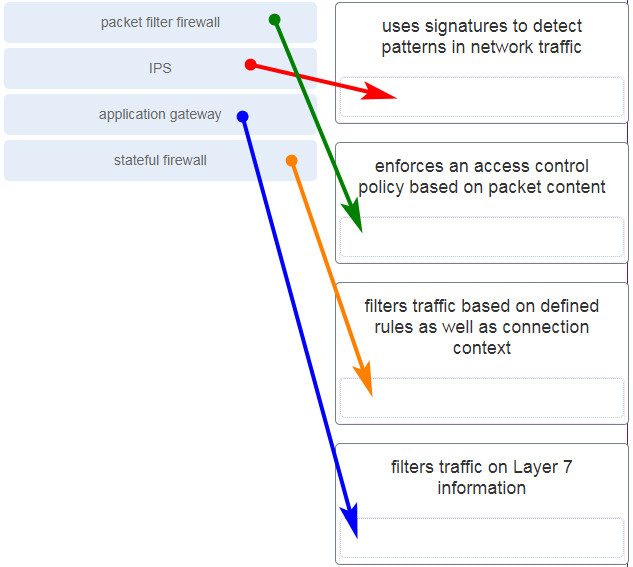





Question 31 is with a Error
The question is
Match the security service with the description.
What is used on WLANs to avoid packet collisions?
What information within a data packet does a router use to make forwarding decisions?