CyberOps Associate (Version 1.0) – CyberOps Associate 1.0 Practice Final exam answers
1. What are two problems that can be caused by a large number of ARP request and reply messages? (Choose two.)
- All ARP request messages must be processed by all nodes on the local network.
- A large number of ARP request and reply messages may slow down the switching process, leading the switch to make many changes in its MAC table.
- The network may become overloaded because ARP reply messages have a very large payload due to the 48-bit MAC address and 32-bit IP address that they contain.
- The ARP request is sent as a broadcast, and will flood the entire subnet.
- Switches become overloaded because they concentrate all the traffic from the attached subnets.
2. Refer to the exhibit. Which field in the Sguil application window indicates the priority of an event or set of correlated events?
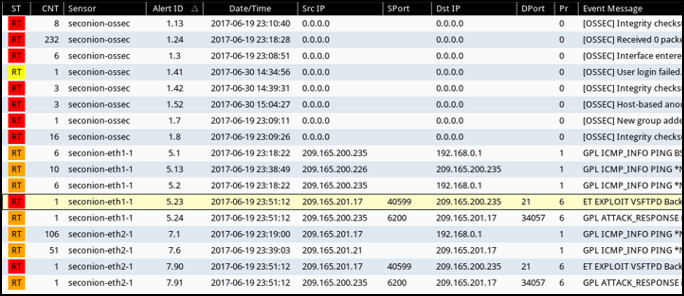
- ST
- AlertID
- Pr
- CNT
3. Match the job titles to SOC personnel positions. (Not all options are used.)
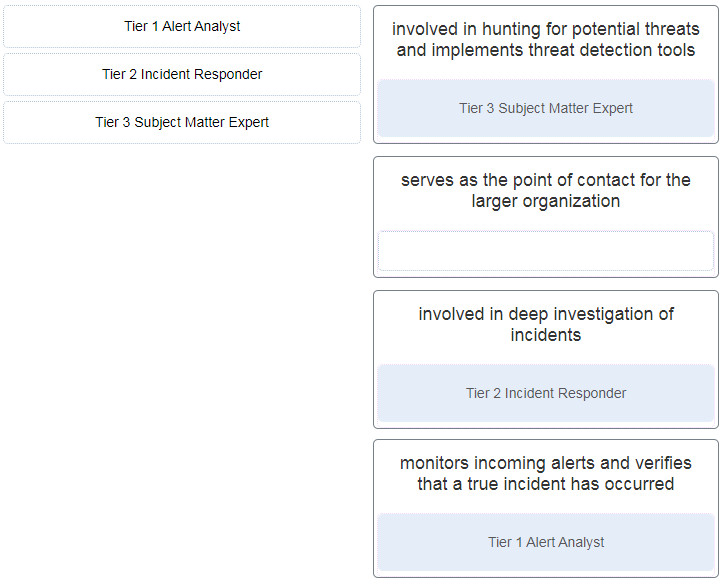
- Tier 1 Alert Analyst —> monitors incoming alerts & verifies that a true incident has occured
- Tier 2 Incident Responder –> involved in deep investigation of incident
- Tier 3 Subject Matter Expert –> involved in hunting for potential threads & implements thread detection tools
- (not use) –> serve as the point of contact for the large organitazion
4. If the default gateway is configured incorrectly on the host, what is the impact on communications?
- The host is unable to communicate on the local network.
- The host can communicate with other hosts on the local network, but is unable to communicate with hosts on remote networks.
- The host can communicate with other hosts on remote networks, but is unable to communicate with hosts on the local network.
- There is no impact on communications.
5. When a connectionless protocol is in use at a lower layer of the OSI model, how is missing data detected and retransmitted if necessary?
- Connectionless acknowledgements are used to request retransmission.
- Upper-layer connection-oriented protocols keep track of the data received and can request retransmission from the upper-level protocols on the sending host.
- Network layer IP protocols manage the communication sessions if connection-oriented transport services are not available.
- The best-effort delivery process guarantees that all packets that are sent are received.
6. What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
- /25
- /26
- /27
- /28
7. Which network monitoring tool saves captured network frames in PCAP files?
- NetFlow
- Wireshark
- SNMP
- SIEM
8. What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance?
- three-way handshake
- socket pair
- two-way handshake
- sliding window
9. What is the Internet?
- It is a network based on Ethernet technology.
- It provides network access for mobile devices.
- It provides connections through interconnected global networks.
- It is a private network for an organization with LAN and WAN connections.
10. Which protocol is used by the traceroute command to send and receive echo-requests and echo-replies?
- SNMP
- ICMP
- Telnet
- TCP
11. What are two ICMPv6 messages that are not present in ICMP for IPv4? (Choose two.)
- Neighbor Solicitation
- Destination Unreachable
- Host Confirmation
- Time Exceeded
- Router Advertisement
- Route Redirection
12. Match the network security testing technique with how it is used to test network security. (Not all options are used.)
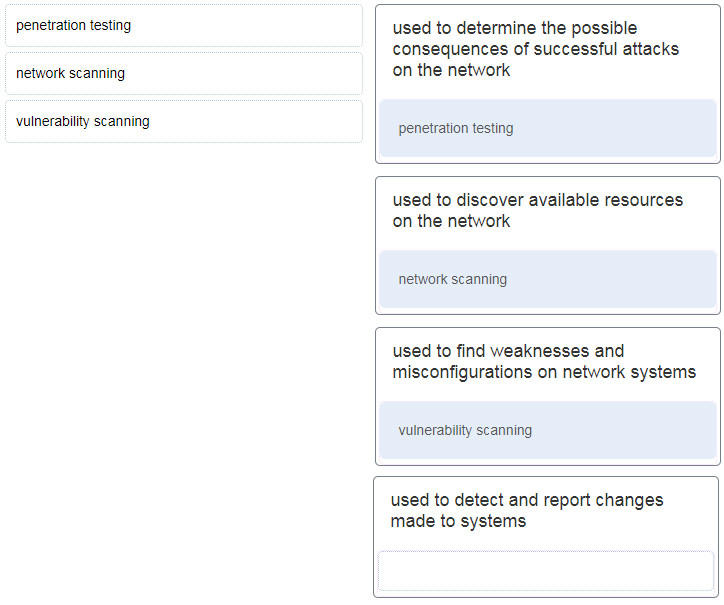
13. What are two monitoring tools that capture network traffic and forward it to network monitoring devices? (Choose two.)
- SPAN
- network tap
- SNMP
- SIEM
- Wireshark
14. Which network monitoring tool is in the category of network protocol analyzers?
- SNMP
- SPAN
- Wireshark
- SIEM
15. Based on the command output shown, which file permission or permissions have been assigned to the other user group for the data.txt file?
ls –l data.txt -rwxrw-r-- sales staff 1028 May 28 15:50 data.txt
- full access
- read, write
- read
- read, write, execute
16. What are three benefits of using symbolic links over hard links in Linux? (Choose three.)
- They can link to a directory.
- They can be compressed.
- Symbolic links can be exported.
- They can be encrypted.
- They can link to a file in a different file system.
- They can show the location of the original file.
17. A network security specialist is tasked to implement a security measure that monitors the status of critical files in the data center and sends an immediate alert if any file is modified. Which aspect of secure communications is addressed by this security measure?
- origin authentication
- data integrity
- nonrepudiation
- data confidentiality
18. A network administrator is configuring an AAA server to manage TACACS+ authentication. What are two attributes of TACACS+ authentication? (Choose two.)
- TCP port 40
- encryption for all communication
- single process for authentication and authorization
- UDP port 1645
- encryption for only the password of a user
- separate processes for authentication and authorization
19. In an attempt to prevent network attacks, cyber analysts share unique identifiable attributes of known attacks with colleagues. What three types of attributes or indicators of compromise are helpful to share? (Choose three.)
- IP addresses of attack servers
- changes made to end system software
- netbios names of compromised firewalls
- features of malware files
- BIOS of attacking systems
- system ID of compromised systems
20. Which two types of messages are used in place of ARP for address resolution in IPv6? (Choose two.)
- anycast
- broadcast
- neighbor solicitation
- echo reply
- echo request
- neighbor advertisement
21. What is indicated by a true negative security alert classification?
- An alert is verified to be an actual security incident.
- An alert is incorrectly issued and does not indicate an actual security incident.
- Normal traffic is correctly ignored and erroneous alerts are not being issued.
- Exploits are not being detected by the security systems that are in place.
22. Which statement describes the anomaly-based intrusion detection approach?
- It compares the antivirus definition file to a cloud based repository for latest updates.
- It compares the behavior of a host to an established baseline to identify potential intrusions.
- It compares the signatures of incoming traffic to a known intrusion database.
- It compares the operations of a host against a well-defined security policy.
23. Match the description to the antimalware approach. (Not all options are used.)
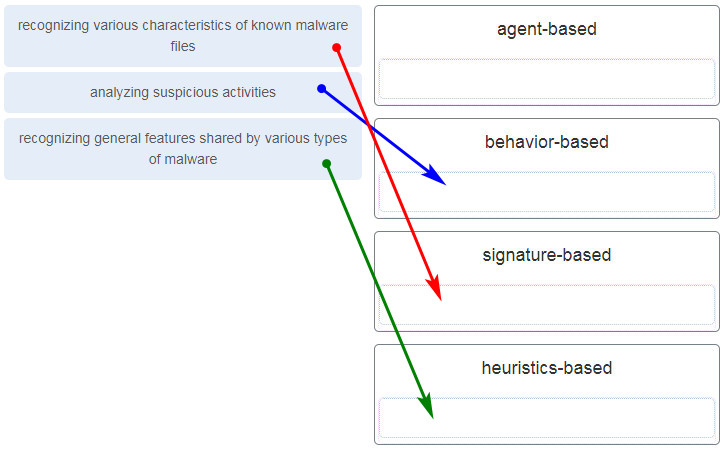
24. Which two protocols are associated with the transport layer? (Choose two.)
- ICMP
- IP
- UDP
- PPP
- TCP
25. A network administrator is creating a network profile to generate a network baseline. What is included in the critical asset address space element?
- the time between the establishment of a data flow and its termination
- the TCP and UDP daemons and ports that are allowed to be open on the server
- the IP addresses or the logical location of essential systems or data
- the list of TCP or UDP processes that are available to accept data
26. What are the three impact metrics contained in the CVSS 3.0 Base Metric Group? (Choose three.)
- confidentiality
- remediation level
- integrity
- attack vector
- exploit
- availability
27. What is a characteristic of DNS?
- DNS servers can cache recent queries to reduce DNS query traffic.
- All DNS servers must maintain mappings for the entire DNS structure.
- DNS servers are programmed to drop requests for name translations that are not within their zone.
- DNS relies on a hub-and-spoke topology with centralized servers.
28. What are two differences between HTTP and HTTP/2? (Choose two.)
- HTTP/2 uses a compressed header to reduce bandwidth requirements.
- HTTP/2 uses multiplexing to support multiple streams and enhance efficiency.
- HTTP/2 uses different status codes than HTTP does to improve performance.
- HTTP/2 issues requests using a text format whereas HTTP uses binary commands.
- HTTP has a different header format than HTTP/2 has.
29. Match the steps with the actions that are involved when an internal host with IP address 192.168.10.10 attempts to send a packet to an external server at the IP address 209.165.200.254 across a router R1 that is running dynamic NAT. (Not all options are used.)

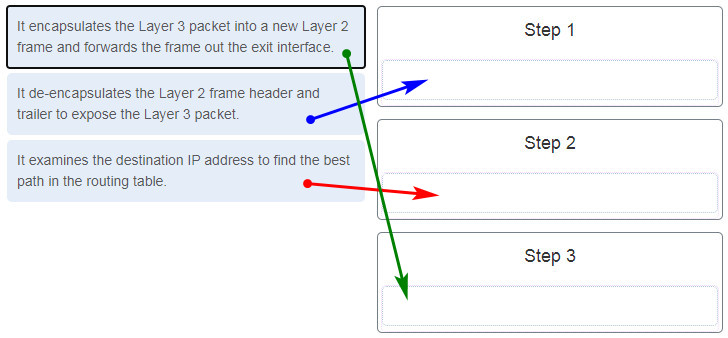
30. A router has received a packet destined for a network that is in the routing table. What steps does the router perform to send this packet on its way? Match the step to the task performed by the router.
31. What are two shared characteristics of the IDS and the IPS? (Choose two.)
- Both have minimal impact on network performance.
- Both are deployed as sensors.
- Both analyze copies of network traffic.
- Both use signatures to detect malicious traffic.
- Both rely on an additional network device to respond to malicious traffic.
32. Which statement describes a typical security policy for a DMZ firewall configuration?
- Traffic that originates from the DMZ interface is selectively permitted to the outside interface.
- Return traffic from the inside that is associated with traffic originating from the outside is permitted to traverse from the inside interface to the outside interface.
- Return traffic from the outside that is associated with traffic originating from the inside is permitted to traverse from the outside interface to the DMZ interface.
- Traffic that originates from the inside interface is generally blocked entirely or very selectively permitted to the outside interface.
- Traffic that originates from the outside interface is permitted to traverse the firewall to the inside interface with few or no restrictions.
33. After complaints from users, a technician identifies that the college web server is running very slowly. A check of the server reveals that there are an unusually large number of TCP requests coming from multiple locations on the Internet. What is the source of the problem?
- The server is infected with a virus.
- A DDoS attack is in progress.
- There is insufficient bandwidth to connect to the server.
- There is a replay attack in progress.
34. Which two statements describe access attacks? (Choose two.)
- Password attacks can be implemented by the use of brute-force attack methods, Trojan horses, or packet sniffers.
- To detect listening services, port scanning attacks scan a range of TCP or UDP port numbers on a host.
- Port redirection attacks use a network adapter card in promiscuous mode to capture all network packets that are sent across a LAN.
- Trust exploitation attacks often involve the use of a laptop to act as a rogue access point to capture and copy all network traffic in a public location, such as a wireless hotspot.
- Buffer overflow attacks write data beyond the allocated buffer memory to overwrite valid data or to exploit systems to execute malicious code.
35. Which two actions can be taken when configuring Windows Firewall? (Choose two.)
- Turn on port screening.
- Manually open ports that are required for specific applications.
- Allow a different software firewall to control access.
- Enable MAC address authentication.
- Perform a rollback.
36. Which statement describes the state of the administrator and guest accounts after a user installs Windows desktop version to a new computer?
- By default, the guest account is enabled but the administrator account is disabled.
- By default, both the administrator and guest accounts are enabled.
- By default, both the administrator and guest accounts are disabled.
- By default, the administrator account is enabled but the guest account is disabled.
37. What is a purpose of entering the nslookup cisco.com command on a Windows PC?
- to check if the DNS service is running
- to connect to the Cisco server
- to test if the Cisco server is reachable
- to discover the transmission time needed to reach the Cisco server
38. How is the event ID assigned in Sguil?
- All events in the series of correlated events are assigned the same event ID.
- Only the first event in the series of correlated events is assigned a unique ID.
- All events in the series of correlated events are assigned the same event group ID.
- Each event in the series of correlated events is assigned a unique ID.
39. Which two types of network traffic are from protocols that generate a lot of routine traffic? (Choose two.)
- routing updates traffic
- Windows security auditing alert traffic
- IPsec traffic
- STP traffic
- SSL traffic
40. What are two elements that form the PRI value in a syslog message? (Choose two.)
- facility
- timestamp
- severity
- header
- hostname
41. Which three pieces of information are found in session data? (Choose three.)
- default gateway IP address
- source and destination port numbers
- Layer 4 transport protocol
- source and destination MAC addresses
- user name
- source and destination IP addresses
42. What kind of ICMP message can be used by threat actors to perform network reconnaissance and scanning attacks?
- ICMP mask reply
- ICMP router discovery
- ICMP unreachable
- ICMP redirects
43. A flood of packets with invalid source IP addresses requests a connection on the network. The server busily tries to respond, resulting in valid requests being ignored. What type of attack has occurred?
- TCP session hijacking
- TCP SYN flood
- TCP reset
- UDP flood
44. An attacker is redirecting traffic to a false default gateway in an attempt to intercept the data traffic of a switched network. What type of attack could achieve this?
- DNS tunneling
- TCP SYN flood
- DHCP spoofing
- ARP cache poisoning
45. What is the most common goal of search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning?
- to increase web traffic to malicious sites
- to build a botnet of zombies
- to trick someone into installing malware or divulging personal information
- to overwhelm a network device with maliciously formed packets
46. Users report that a database file on the main server cannot be accessed. A database administrator verifies the issue and notices that the database file is now encrypted. The organization receives a threatening email demanding payment for the decryption of the database file. What type of attack has the organization experienced?
- man-in-the-middle attack
- DoS attack
- ransomware
- Trojan horse
47. What two kinds of personal information can be sold on the dark web by cybercriminals? (Choose two.)
- city of residence
- Facebook photos
- name of a bank
- name of a pet
- street address
48. What three services are offered by FireEye? (Choose three.)
- blocks attacks across the web
- creates firewall rules dynamically
- identifies and stops latent malware on files
- subjects all traffic to deep packet inspection analysis
- deploys incident detection rule sets to network security tools
- identifies and stops email threat vectors
49. After containment, what is the first step of eradicating an attack?
- Change all passwords.
- Patch all vulnerabilities.
- Hold meetings on lessons learned.
- Identify all hosts that need remediation.
50. Which activity is typically performed by a threat actor in the installation phase of the Cyber Kill Chain?
- Install a web shell on the target web server for persistent access.
- Harvest email addresses of user accounts.
- Open a two-way communication channel to the CnC infrastructure.
- Obtain an automated tool to deliver the malware payload.
51. When dealing with a security threat and using the Cyber Kill Chain model, which two approaches can an organization use to help block potential exploitations on a system? (Choose two.)
- Collect email and web logs for forensic reconstruction.
- Conduct full malware analysis.
- Train web developers for securing code.
- Build detections for the behavior of known weaponizers.
- Perform regular vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
52. How might corporate IT professionals deal with DNS-based cyber threats?
- Limit the number of simultaneously opened browsers or browser tabs.
- Monitor DNS proxy server logs and look for unusual DNS queries.
- Use IPS/IDS devices to scan internal corporate traffic.
- Limit the number of DNS queries permitted within the organization.
53. How does using HTTPS complicate network security monitoring?
- HTTPS adds complexity to captured packets.
- HTTPS cannot protect visitors to a company-provided web site.
- Web browser traffic is directed to infected servers.
- HTTPS can be used to infiltrate DNS queries.
54. Match the security concept to the description.

55. What are the two important components of a public key infrastructure (PKI) used in network security? (Choose two.)
- intrusion prevention system
- digital certificates
- symmetric encryption algorithms
- certificate authority
- pre-shared key generation
56. Which three algorithms are designed to generate and verify digital signatures? (Choose three.)
- 3DES
- IKE
- DSA
- AES
- ECDSA
- RSA
57. Which section of a security policy is used to specify that only authorized individuals should have access to enterprise data?
- statement of authority
- identification and authentication policy
- campus access policy
- Internet access policy
- statement of scope
- acceptable use policy
58. Refer to the exhibit. A cybersecurity analyst is viewing captured packets forwarded on switch S1. Which device has the MAC address d8:cb:8a:5c:d5:8a?
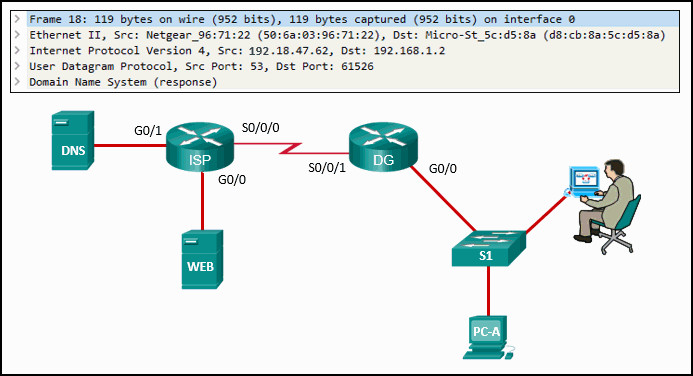
- PC-A
- DNS server
- web server
- router DG
- router ISP
59. What kind of message is sent by a DHCPv4 client requesting an IP address?
- DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message
- DHCPDISCOVER unicast message
- DHCPOFFER unicast message
- DHCPACK unicast message
60. Place the evidence collection priority from most volatile to least volatile as defined by the IETF guidelines.

61. What is the responsibility of the human resources department when handling a security incident?
- Coordinate the incident response with other stakeholders and minimize the damage of the incident.
- Perform actions to minimize the effectiveness of the attack and preserve evidence.
- Apply disciplinary measures if an incident is caused by an employee.
- Review the incident policies, plans, and procedures for local or federal guideline violations.
62. How does a security information and event management system (SIEM) in a SOC help the personnel fight against security threats?
- by integrating all security devices and appliances in an organization
- by analyzing logging data in real time
- by combining data from multiple technologies
- by dynamically implementing firewall rules
63. At which OSI layer is a source IP address added to a PDU during the encapsulation process?
- network layer
- transport layer
- data link layer
- application layer
64. What is the purpose of CSMA/CA?
- to prevent loops
- to isolate traffic
- to filter traffic
- to prevent collisions
65. Why is DHCP preferred for use on large networks?
- Hosts on large networks require more IP addressing configuration settings than hosts on small networks.
- It prevents sharing of files that are copyrighted.
- It is a more efficient way to manage IP addresses than static address assignment.
- Large networks send more requests for domain to IP address resolution than do smaller networks.
- DHCP uses a reliable transport layer protocol.
66 Which NIST incident response life cycle phase includes continuous monitoring by the CSIRT to quickly identify and validate an incident?
- postincident activities
- detection and analysis
- containment, eradication, and recovery
- preparation
67. What will a threat actor do to create a back door on a compromised target according to the Cyber Kill Chain model?
- Add services and autorun keys.
- Collect and exfiltrate data.
- Obtain an automated tool to deliver the malware payload.
- Open a two-way communications channel to the CnC infrastructure.
68. Which type of evidence supports an assertion based on previously obtained evidence?
- direct evidence
- corroborating evidence
- best evidence
- indirect evidence
69. A technician is configuring email on a mobile device. The user wants to be able to keep the original email on the server, organize it into folders, and synchronize the folders between the mobile device and the server. Which email protocol should the technician use?
- POP3
- MIME
- IMAP
- SMTP
70. What is the goal of an attack in the installation phase of the Cyber Kill Chain?
- Break the vulnerability and gain control of the target.
- Establish command and control (CnC) with the target system.
- Create a back door in the target system to allow for future access.
- Use the information from the reconnaissance phase to develop a weapon against the target.

if this isn’t for 200-201, what is it for please?
A technician is configuring email on a mobile device. The user wants to be able to keep the original email on the server, organize it into folders, and synchronize the folders between the mobile device and the server. Which email protocol should the technician use?
Added, thanks for sharing!
Which type of evidence supports an assertion based on previously obtained evidence?
Thanks for sharing!
What will a threat actor do to create a back door on a compromised target according to the Cyber Kill Chain model?
Thanks for sharing!