1. What are two roles of the transport layer in data communication on a network? (Choose two.)
- tracking the individual communication between applications on the source and destination hosts
- performing a cyclic redundancy check on the frame for errors
- identifying the proper application for each communication stream
- providing the interface between applications and the underlying network over which messages are transmitted
- providing frame delimiting to identify bits making up a frame
2. During a TCP session, a destination device sends an acknowledgment number to the source device. What does the acknowledgment number represent?
- the last sequence number that was sent by the source
- one number more than the sequence number
- the total number of bytes that have been received
- the next byte that the destination expects to receive
3. Which two services or protocols use the preferred UDP protocol for fast transmission and low overhead? (Choose two)
- DNS
- HTTP
- FTP
- POP3
- VoIP
4. Which transport layer feature is used to guarantee session establishment?
- TCP port number
- UDP ACK flag
- TCP 3-way handshake
- UDP sequence number
5. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function of TCP or UDP in this situation? (Choose three.)
- The TCP source port number identifies the sending host on the network.
- The source port field identifies the running application or service that will handle data returning to the PC.
- UDP segments are encapsulated within IP packets for transport across the network.
- The UDP destination port number identifies the application or service on the server which will handle the data.
- TCP is the preferred protocol when a function requires lower network overhead.
- The TCP process running on the PC randomly selects the destination port when establishing a session with the server.
6. What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
- to end communication when data transmission is complete
- to request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data
- to inform a source to retransmit data from a specific point forward
- to ensure that segments arrive in order at the destination
7. What happens if part of an FTP message is not delivered to the destination?
- The message is lost because FTP does not use a reliable delivery method.
- The part of the FTP message that was lost is re-sent.
- The entire FTP message is re-sent.
- The FTP source host sends a query to the destination host.
8. Which two flags in the TCP header are used in a TCP three-way handshake to establish connectivity between two network devices? (Choose two.)
- FIN
- SYN
- ACK
- PSH
- RST
- URG
9. Which tool is used to provide a list of open ports on network devices?
- Tracert
- Nmap
- Whois
- Ping
10. Which two fields are included in the TCP header but not in the UDP header? (Choose two.)
- destination port
- checksum
- sequence number
- window
- source port
11. Refer to the exhibit. Which three lines represent the TCP three-way handshake?
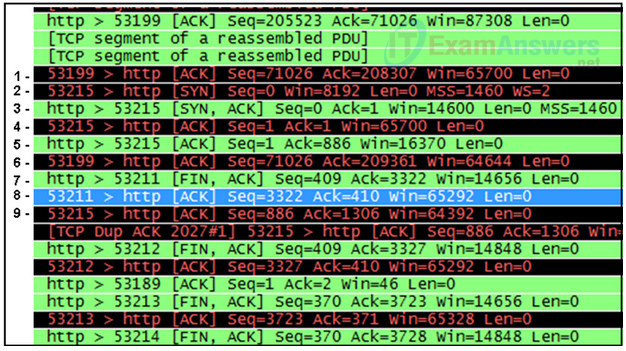
- lines 6, 7, and 8
- lines 2, 3, and 4
- lines 2, 8, and 9
- lines 1, 2, and 3
- lines 4, 5, and 6
12. What is a characteristic of a TCP server process?
- A host running two different applications can have both configured to use the same server port.
- There can be many ports open simultaneously on a server, one for each active server application.
- An individual server can have two services assigned to the same port number within the same transport layer services.
- Every application process running on the server has to be configured to use a dynamic port number.
