11.1.4.11 Lab – Working with File Explorer
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Instructor copy only.
Introduction
In this lab, you will explore and use the File Explorer (Windows Explorer) to navigate the Windows file system.
Required Resources
- Windows PC
Instructions
Step 1: Explore File Explorer
File Explorer is a file management application in Windows 8.x and 10. Windows 7 has a similar file management application called Windows Explorer. The main difference between the two is that Windows Explorer does not have the Ribbon menu bar.
In the File Explorer, you could use the Ribbon menu bar to copy, move, delete, or create new folders.
a. Click Start. Search for File Explorer or Windows Explorer.
b. Click Desktop on the left panel.
c. In the right panel, right-click New > Folder to create a new folder on the Desktop. Name this new folder, Folder1.
d. Create another folder and name it Folder2.
e. Move Folder2 into Folder1. Click Folder2 and select Move to > Choose location in the Ribbon Home menu to move Folder2 into Folder1 or you can use your mouse to drag-and-dropFolder2 into Folder1.
Question:
What happened with Folder1 and Folder2 on the Desktop?
The new folders are displayed on the Desktop. After moving Folder2 into Folder1, only Folder1 on the Desktop.
f. Create a new text document in Folder1. Right-click New > Text Document. Name the new text document.
g. The file extension is hidden by default. In Windows 10 and 8.x, select File name extensions in the View tab in the Ribbon in File Explorer. Another way to show the file extension is to navigate to the Control Panel. In the small icon view, click Folder Explorer Options (Windows 10) or Folder Options (Windows 8.x and 7). Click the View tab and unselect Hide extensions for known file types. Click OK to continue.
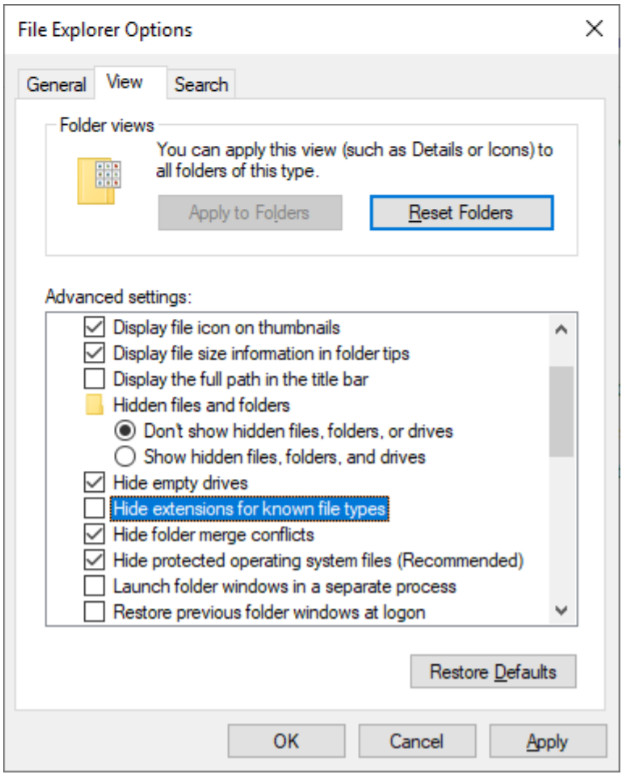
Question:
What is the file extension for the text document?
The file extension is .txt.
h. Make a copy of the text document and place it in Folder2.
Question:
How would you do it?
Answer may vary. Right-click the text document > click Copy. Open Folder2 and right-click Paste. Or click the text document, click Copy to in the Ribbon Home menu, and click Choose location and select Folder2.
i. Right-click the text document > click Properties. Click the Details tab.
What are the attributes associated with this file?
A for Archive.
j. Now create a folder named Folder3 inside Folder2.
Questions:
What is the complete path to Folder3? (Hint: One way to find this information is in the folder properties.)
Answer will vary. For example, 10.5 GB free out of 24.4GB.
In Windows 8.x and 10, which directories are listed under Folders? (Note: There is no Folders heading in Windows Explorer.)
Answer may vary. The folders are Desktop, Downloads, Documents, Pictures, Music, and Videos.
k. Navigate to the Desktop within File Explorer or Windows Explorer.
l. Drag and drop Folder1 onto Quick Access (Windows 10) or Favorites (Windows 7 and 8.x).
Question:
What happened? Why would you want to do this?
The folder is now listed under the headings Quick Access or Favorites. This provides a link to the folder and allows for quick access to a nested folder from File Explorer or Windows Explorer.
m. Within the File Explorer or Windows Explorer, navigate to the Local Disk (C:).
Question:
What are folders listed in the Local Disk (C:)?
Answer may vary. The listed folders are PerfLogs, Program Files, Program Files (x86), Users, and Windows.
n. Open the Users folder. List all the folders in the directory.
o. Open the folder associated with your username.
Question:
Were you able to open it? Explain.
Yes. You have the permission to access folder owned by you.
p. Open the folder associated with another username if it is available on the PC.
Question:
Were you able to open it? Explain. (Note: Windows 7 does not display other users’ folders.)
Answer may vary. If the user account has administrative privileges, you may be able to open the user folder of a standard user. A standard user cannot open the folder of administrative privileges without the credentials of the administrative user.
q. Notice the Public folder. This folder is accessible to any local users on the PC. Furthermore, it can be configured to be accessible for networked users.
Question:
Open the Public folder. List all the folders in the directory.
Answer will vary. Some of the folders in the directory are Public Documents, Public Downloads, Public Music, Public Pictures, and Public Videos.
Step 2: Windows Libraries
Windows Libraries is a centralized location for related files from different locations on the PC or network. For example, the Videos library is a collection of all the videos from different locations on your PC and on a network drive. This acts as a short cut to all those videos.
a. To access the library, click Start Open File Explorer or Windows Explorer.
b. For Windows 8.x and 10, right-click the left panel. Click Show libraries.
c. Expand the Libraries.
Question:
Which folders or files listed under the Libraries heading?
Answer may vary. Documents, Music, Pictures, and Videos.
d. A new library can also be created. Right-click Libraries > click New > click Library. Provide a name for the new library.
e. Include Folder1 in the new library, Folder1 on the Desktop can be added to the Libraries. Navigate to the Desktop. Right-click Folder1 > click Include in library > select the new library you created
Select the library you created in the left panel. Click the Library Tools tab and select Manage library.
Question:
How would you remove the directory of Folder1 from the library without deleting Folder1 and its contents from the computer?
Answer may vary. Select the Folder1 library location and click Remove and then click OK.
