6.1.1.5 Lab – Task Manager in Windows 7 and Vista (Answers)
Introduction
In this lab, you will explore Task Manager and manage processes from within Task Manager.
Recommended Equipment
The following equipment is required for this exercise:
- A computer running Windows 7 or Vista
Step 1: Work in the Applications Tab of Windows Task Manager.
a. Log on to Windows as an administrator.
b. Open a browser and a folder.
c. Click the desktop and press Ctrl-Alt-Delete > Start Task Manager > Applications tab.
d. Select the open browser and then click Switch To.
What happened to the browser?
The browser became the active window.
e. Bring Windows Task Manager to the front of the desktop. Click New Task to open the Create New Task window.
f. In the Open field, type Notepad and click OK.
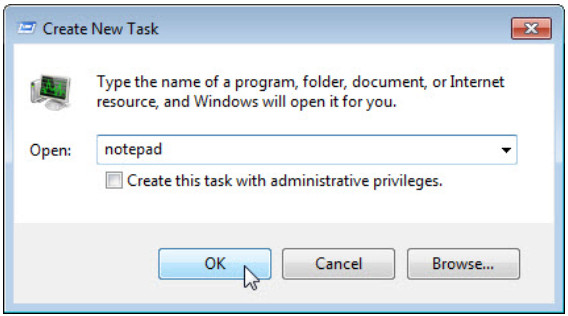
What happens?
Notepad opens.
g. Navigate back to the Windows Task Manager, select Notepad, and click End Task.
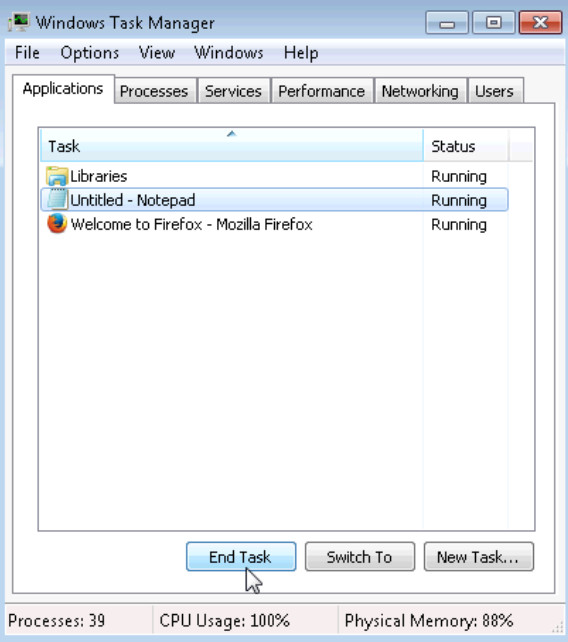
What happens?
Notepad closes.
Step 2: Work in the Services tab of Windows Task Manager.
a. Click the Services tab. Use the scroll bar on the right of the Services window to view all the services listed
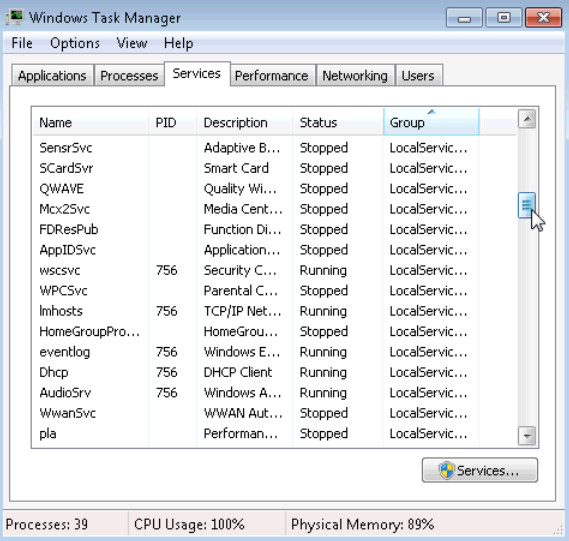
What are the statuses listed?
Stopped and Running.
Step 3: Work in the Performance tab of Windows Task Manager.
a. Click the Performance tab.
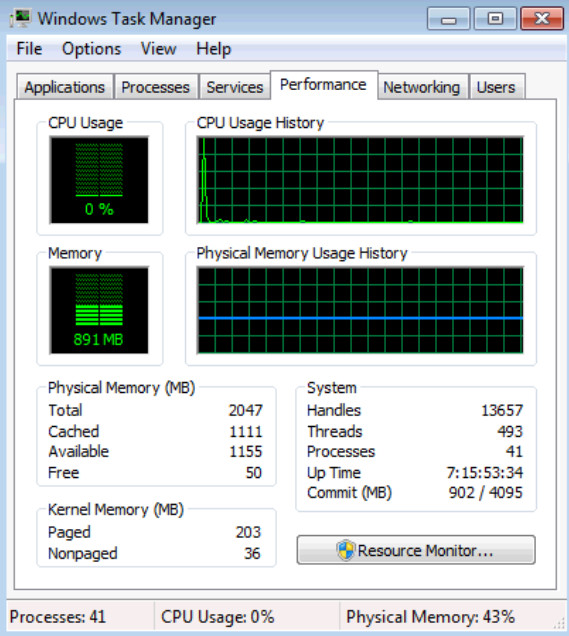
How many threads are running?
Answer may vary. The example displays 493.
How many processes are running?
Answer may vary. The example displays 41.
What is the total physical memory (MB)?
Answer may vary. The example displays 2047.
What is the available physical memory (MB)?
Answer may vary. The example displays 1155.
How much physical memory (MB) is being used by the system?
Answer may vary. This can be calculated by subtracting Free Physical Memory from Total Physical Memory. In the example the calculation would be 2047 – 50 = 1,997MB.
Step 4: Work in the Networking tab of Windows Task Manager.
a. Click the Networking tab.
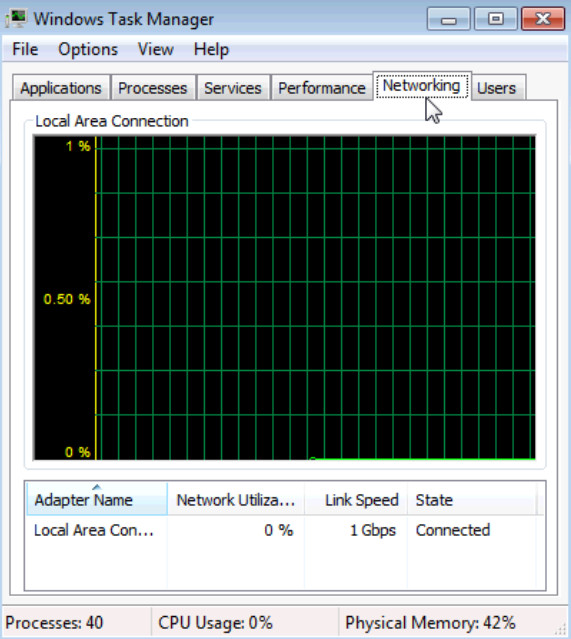
What is the link speed?
Answer may vary. The examples displays 1 Gbps.
Step 5: Work in the Users tab of Windows Task Manager.
a. Click the Users tab.
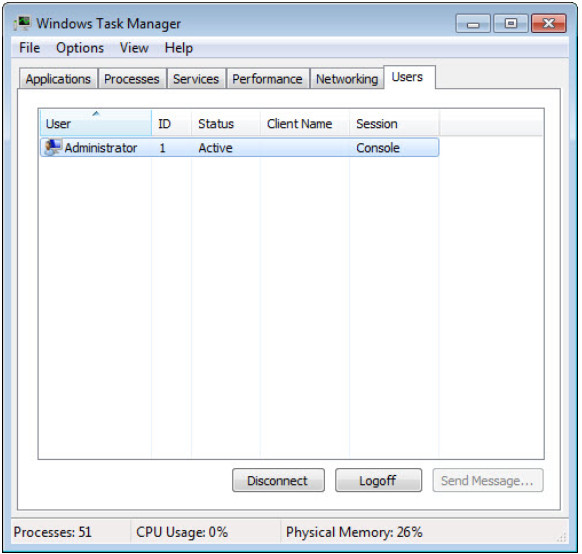
List all users and their status.
Answer may vary. The example displays one user, Administrator, with a status of active.
What actions can you perform on the user from this window?
Three actions are displayed: Disconnect, Logoff, and Send Message. But only Disconnect and Logoff can be performed on the user.
Step 6: Work in the Processes tab of Windows Task Manager.
a. Click the Processes tab.
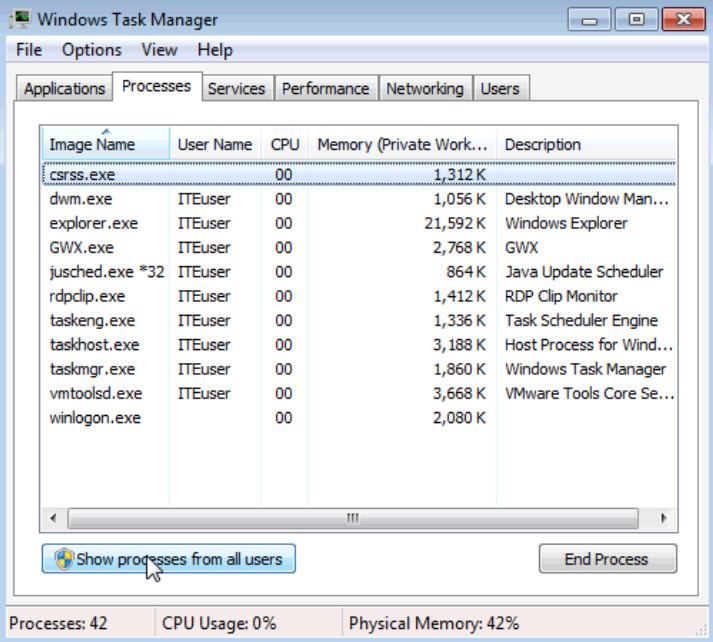
b. Check the checkbox Show processes from all users.
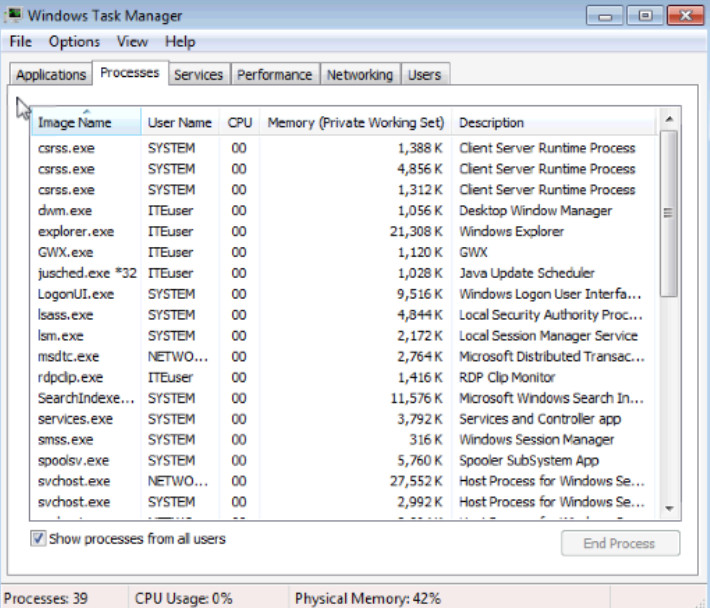
c. Double-click the white border around the Processes tab. This changes the view of Windows Task Manager to compact mode.
Note: The User Account Control window may open in Vista asking for permission to continue. Click Continue.
d. Click the heading Image Name. Click Image Name again.
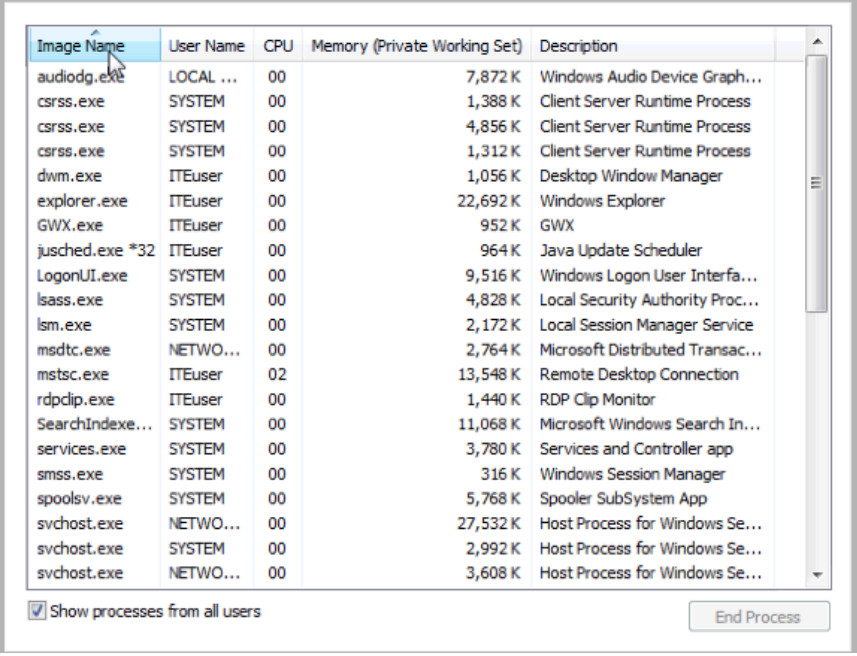
What effect does this have on the columns?
Places the names in alphabetical order. Each time you click the Image Name heading, it reverses the order (A to Z, then Z to A).
e. Click Memory (Private Working Set).
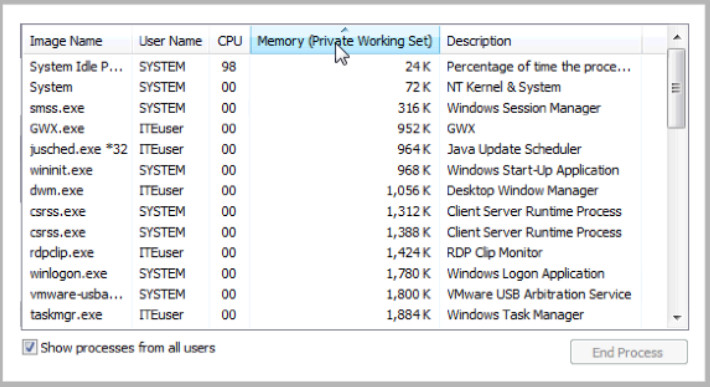
What affect does this have on the columns?
Places the numbers in ascending or descending order.
f. Double-click the outside border again to return to tabs mode.
g. Open a browser.
Note: Firefox is used in this lab. However, any browser will work. Just substitute your browser name whenever you see the word Firefox.
h. Return to the Windows Task Manager. Click Image Name so the list is in alphabetical order, then locate and select firefox.exe.
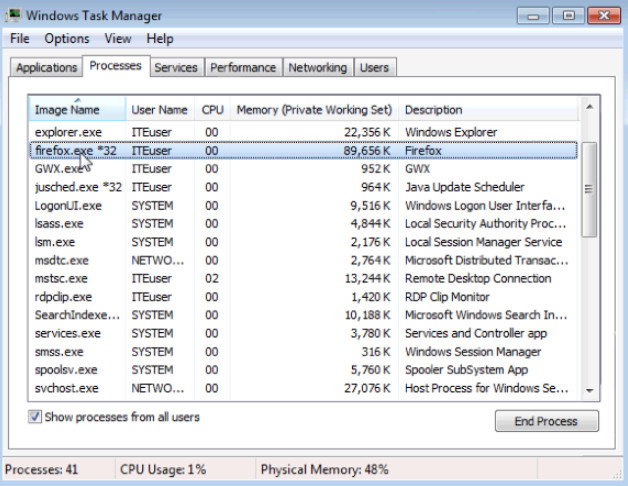
i. Right-click firefox.exe > Set Priority.
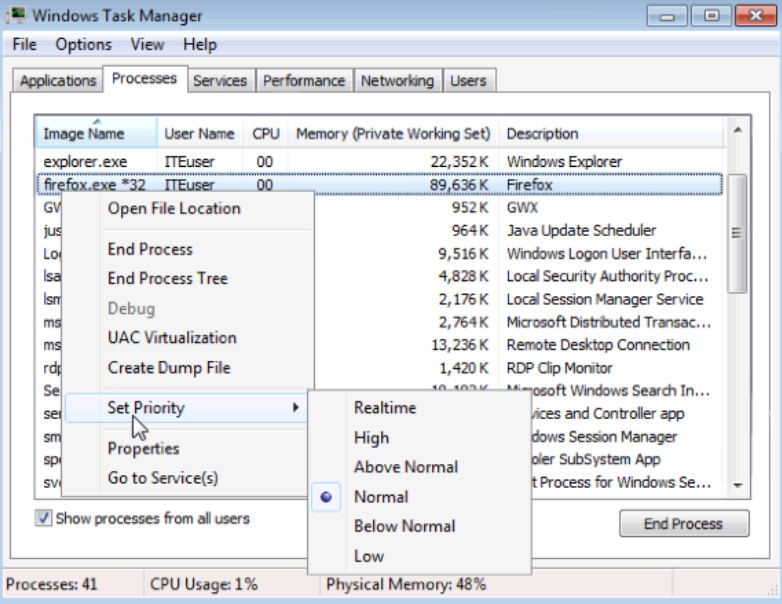
What is the default priority for the browser?
Normal.
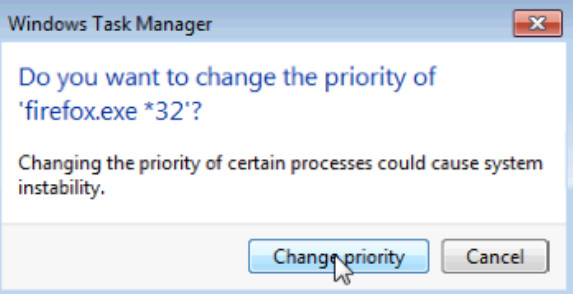
j. Set the priority to Above Normal. Then click Change priority in the Windows Task Manager warning message.
Step 7: Change the fields that are displayed in the Windows Task Manager.
a. Click View > Select Columns.
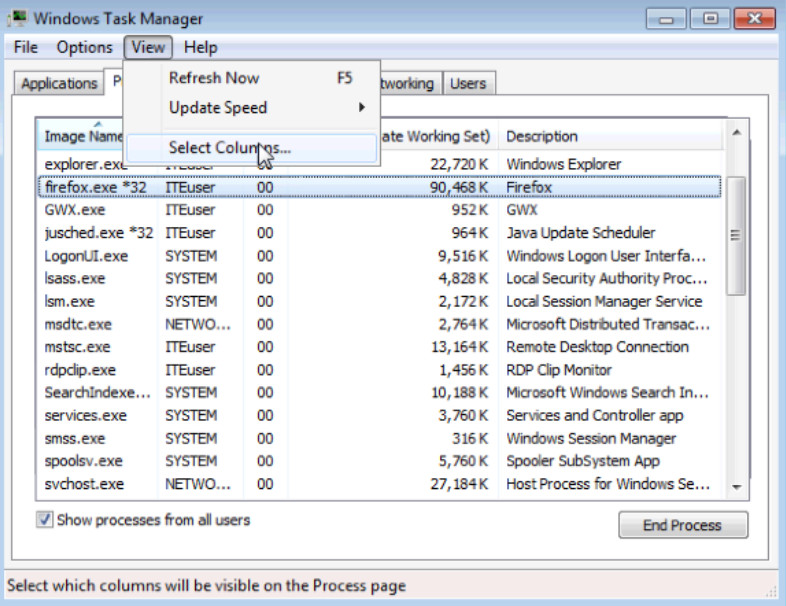
b. The Select Process Page Columns window opens. Check Base Priority and click OK.
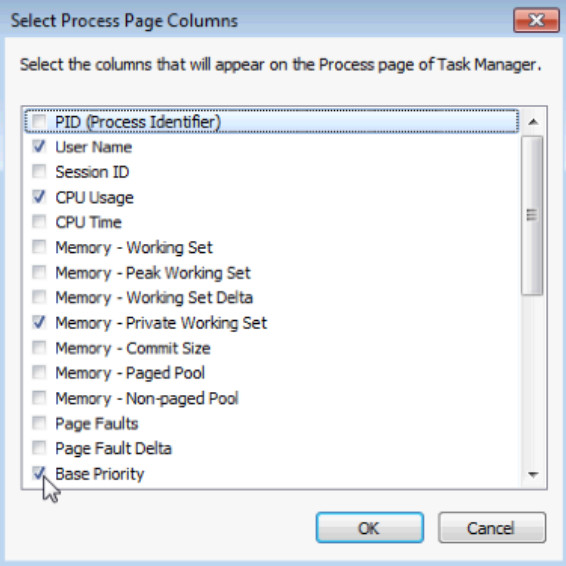
c. Expand the width of the Windows Task Manager so the Base Priority column is visible.
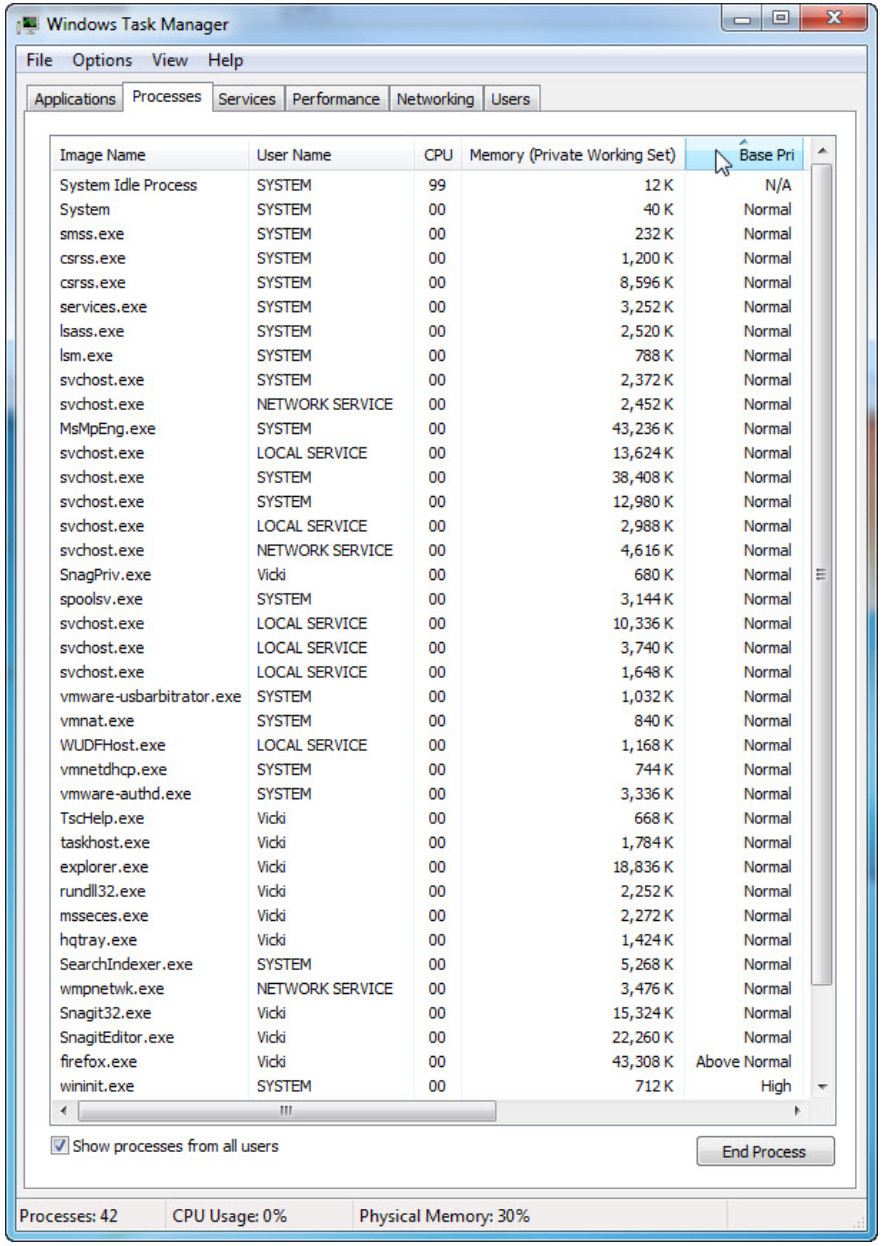
List the name of the image that has a base priority of Above Normal?
Firefox.exe.
Which image name has a base priority of N/A?
System Idle Process.
d. Reset Firefox.exe base priority to normal. To do this, right-click firefox.exe > Set Priority > Normal > Change priority.
e. Click View > Select Columns. Uncheck Base Priority and click OK.
f. Close Firefox.
Is Firefox listed as a process?
No, it is removed from the list of processes when it closes.
g. Close all open windows.
Reflection
Why is it important for an administrator to understand how to work within the Windows Task Manager?
Answers may vary. The Windows Task Manager can be a valuable tool for an administrator when troubleshooting problems with a Windows PC. It provides information about memory, CPU usage, and processes. It also allows the administrator to control process priority levels, and provides a way to end tasks or cancel processes.
