6.1.4.2 Lab – Hard Drive Maintenance in Windows 8 (Answers)
Introduction
In this lab, you will examine the results of using Disk Check and Disk Defragmenter on a hard drive.
Recommended Equipment
- A computer running Windows 8
- Two or more partitions on the hard drive.
Step 1: Run the Error-checking Tool on a disk volume.
a. Log on to Windows as an administrator.
b. Open Windows Explorer. Right-click New Volume (G:) > Properties > Tools > Check Now.
Note: Substitute the volume name and drive (G:) for those used in your computer.
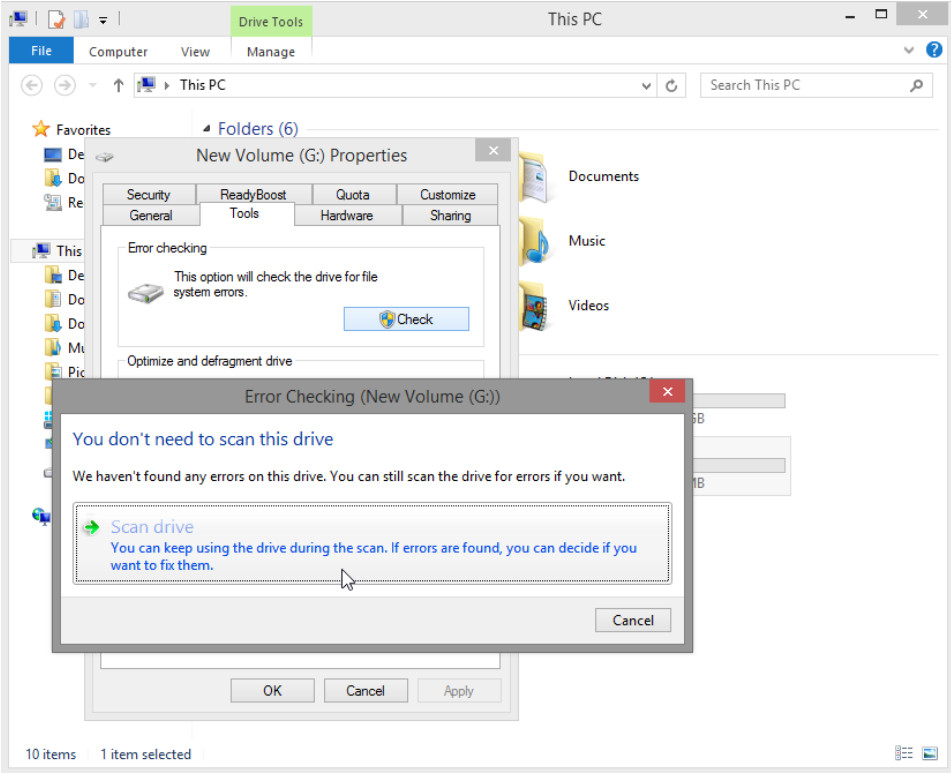
c. Because Windows monitors the drives and runs automatic scheduled scans, you may see a message saying that You don’t need to scan this drive. Click Scan drive.
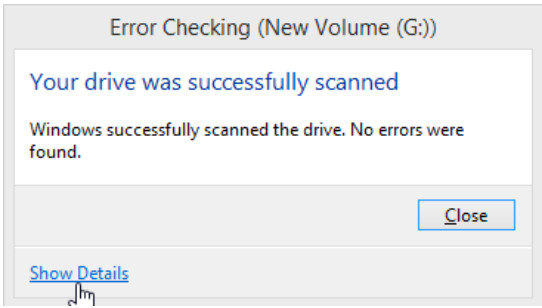
d. The Your drive was successfully scanned window opens. Click Show details.
e. The Event Viewer opens to display the Chkdsk event. Double click the Information event in the middle pane.
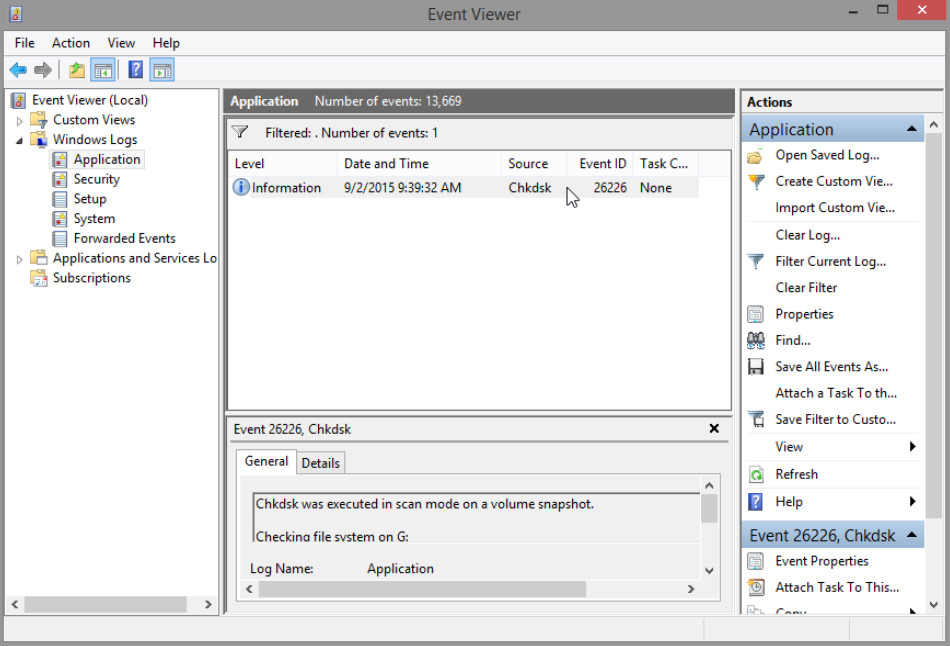
How many stages were processed?
Answers may vary. 3 stages if no problems occurred during check.
Were any problems found with the volume?
Yes or No.
If so what are they?
Answers may vary.
f. Click Close.
g. Close all open windows.
Step 2: Use the Disk defragmenter tool.
Note: Do not perform this step if your computer has an SSD drive. It is unnecessary to defragment SSD drives.
a. Open Windows Explorer. Right-click drive (C:) > Properties. Click the Tools tab > Optimize.
b. The Optimize Drives window opens. Click (C:) > Analyze.
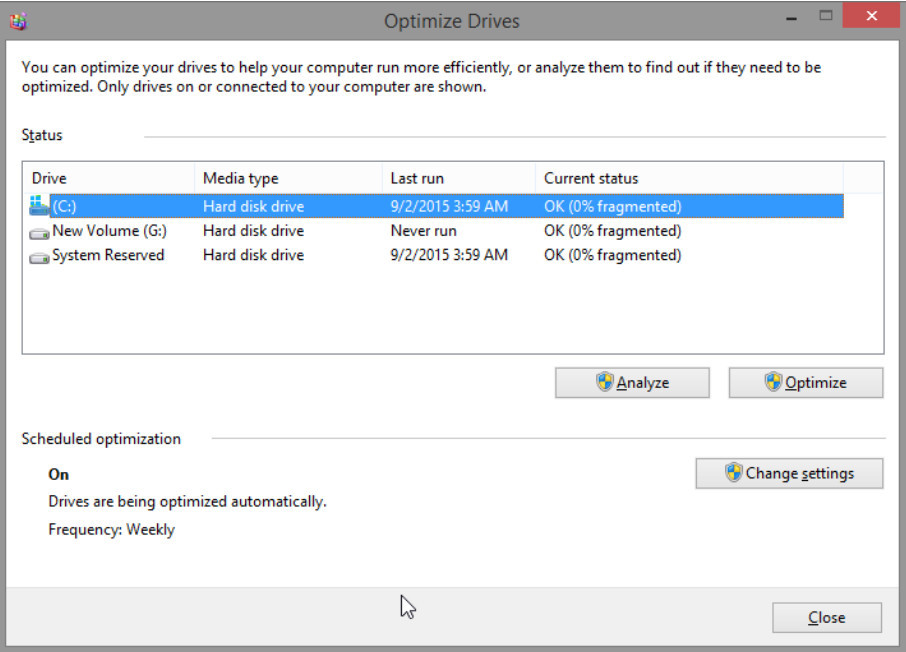
What percentage of the disk is fragmented?
Answers may vary
c. Click Optimize to start defragmenting the disk.
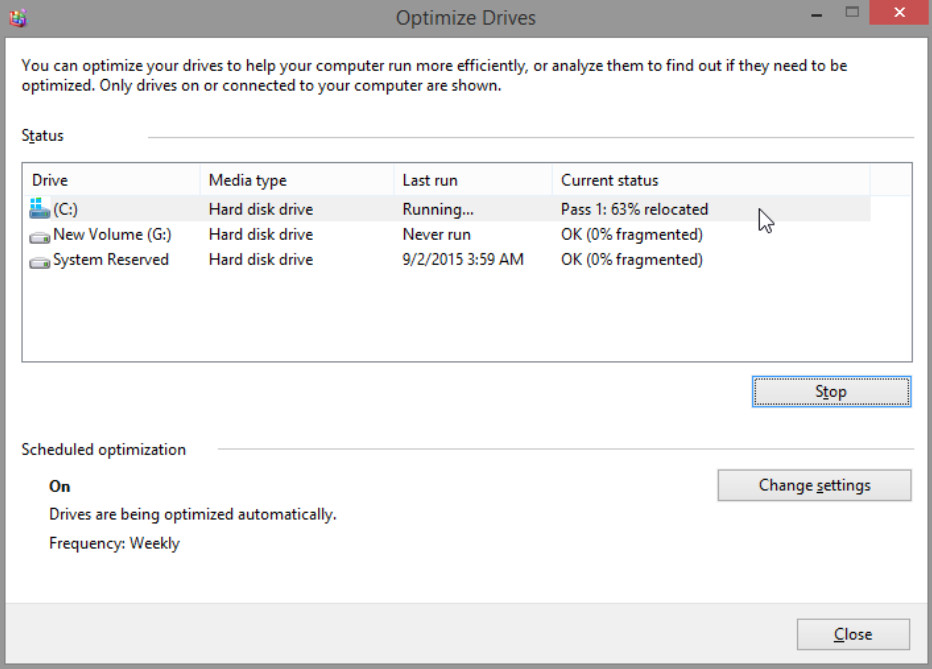
What is the first process during defragmenting (See Current status column)?
Analyzed.
What are the four tasks performed for each pass (See Current status column)?
Relocated, defragmented, and consolidated.
How many passes did it take to defragment drive C:?
Answers may vary. 6 passes.
d. When defragmenting is complete, click Close.
e. Close all windows.
Note: It is not possible to view the detail of the defragmented hard drive through the GUI version of defragmenter.
