1. Refer to the exhibit. Host A is unable to obtain an IP address from the DHCP server. Which procedure would solve this problem?
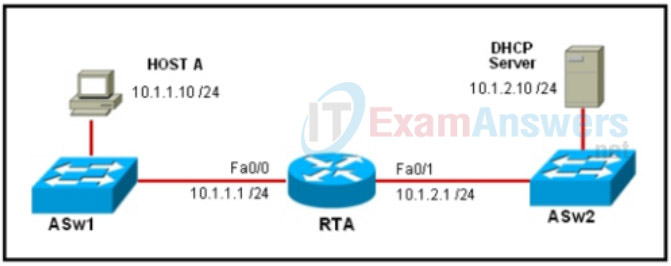
- Use the command ip helper-address 10.1.2.1 on interface Fa0/0 of router RTA.
- Use the command ip helper-address 10.1.2.10 on interface Fa0/0 of router RTA.
- Use the command ip forward-protocol 68 on interface Fa0/1 of router RTA.
- Use the command ip forward-protocol 67 on interface Fa0/1 of router RTA.
- Use the command ip helper-address 10.1.2.10 on interface Fa0/1 of router RTA.
- Use the command ip forward-protocol 67 on interface Fa0/0 of router RTA.
2. Refer to the exhibit. What additional configuration is required for host A to receive IP configuration from the DHCP server?
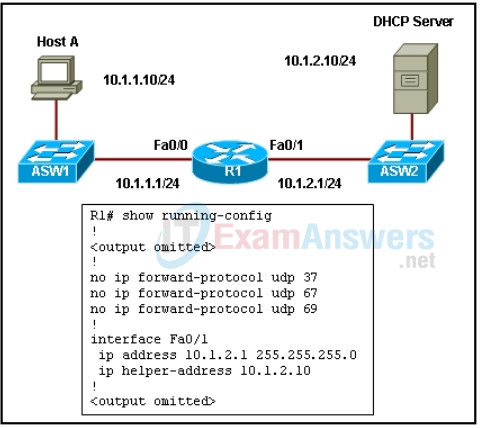
- The ip forward-protocol 67 global configuration command is required to forward DHCP requests to IP address 10.1.2.10.
- The ip dhcp information option command is required on interface Fa0/1.
- The ip forward-protocol 37 global configuration command is required to forward DNS requests to IP address 10.1.2.10.
- The ip forward-protocol 37 global configuration command is required to forward DNS requests to IP address 10.1.2.10.
- The ip helper-address 10.1.2.10 command is required on interface Fa0/0.
- The ip forward-protocol 69 global configuration command is required to forward TFTP requests to IP address 10.1.2.10.
3. Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true regarding the diagram and show ip route command output?
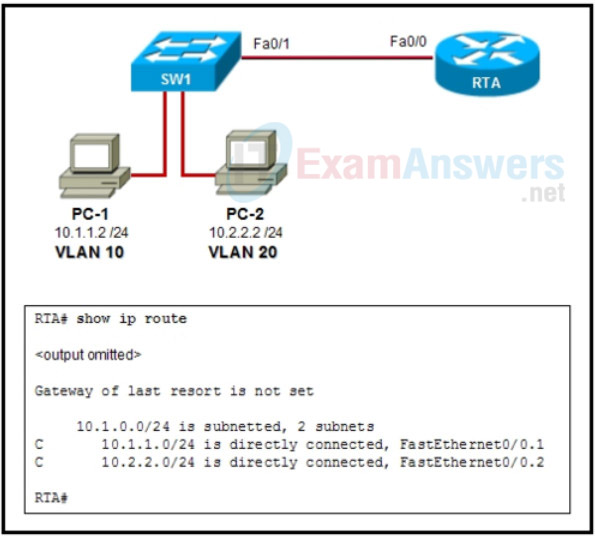
- The default gateway for hosts on VLAN 10 should be the Fa0/0 IP address of the router.
- The default gateway for hosts on VLAN 10 should be the Fa0/0.2 IP address of the router.
- Because their packets are being trunked, hosts on VLAN 10 do not need a default gateway.
- Because no routing protocol has been configured, the router will not forward packets between workstations.
- The default gateway for hosts on VLAN 10 should be the Fa0/0.1 IP address of the router.
4. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator attempts to ping the IP address 172.16.20.1 from RouterA. What will the router output be?
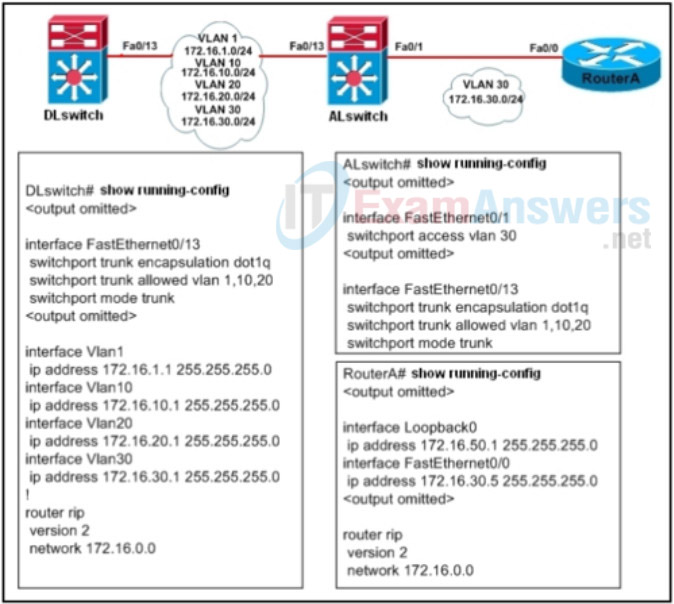
- %network or host unreachable, TTL exceeded
- Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!! - %Unrecognized host or address, or protocol not running
- Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
….. - %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/13, changed state to down
- Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
U.U.U
5. Which statement describes what occurs when a DHCP request is forwarded through a router that has been configured with the ip helper-address command?
- The router replaces the source MAC address included in the DHCP request with its own MAC address.
- The router replaces the source IP address of the DHCP request with the IP address that is specified with the ip helper-address command.
- The router replaces the unicast destination IP address of the DHCP request with the unicast IP address that is specified with the ip helper-address command.
- The router replaces the broadcast destination IP address of the DHCP request with the unicast IP address that is specified with the ip helper-address command.
6. A DHCPREQUEST message has been sent from the client to the DHCP server. What information is included in the message?
- denial message to reject the first offer from the DHCP server
- initial message to locate a DHCP server
- confirmation that the IP address has been allocated to the client
- formal request for the offered IP address
7. A client sends a request for an IP address to a DHCP server. Which DHCP message to the client will provide the configuration parameters that include an IP address, a domain name, and a lease for the IP address?
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
8. A client computer is set up for DHCP and needs an IP configuration. During the DHCP client configuration process, which response will enable the client to begin using the assigned address immediately?
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPACK
9. Which message will be sent back to the client by the DHCP server to confirm that the IP address has been allocated to the client?
- DHCPOFFER unicast
- DHCPREQUEST broadcast
- DHCPOFFER broadcast
- DHCPACK unicast
- DHCPREQUEST unicast
- DHCPDISCOVER unicast
- DHCPDISCOVER broadcast
10. Refer to the exhibit. The router has been properly configured for the trunking interface. Which statement is true about the routing table on the router?
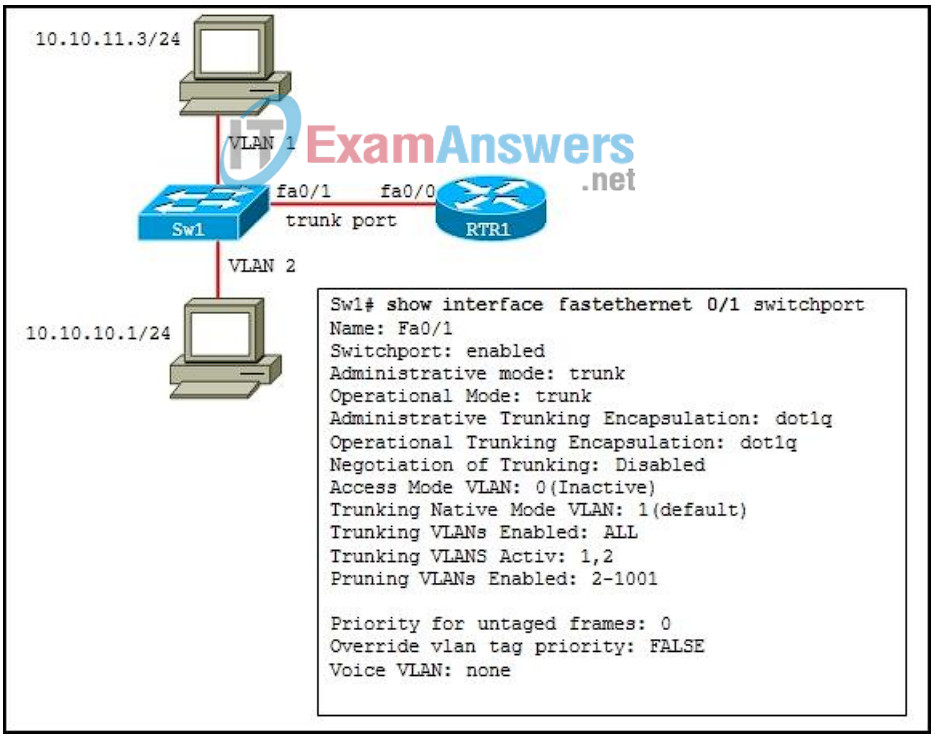
- Because the switch is not configured properly to trunk VLAN 1 and VLAN 2, the routing table of the router will not show routes to either VLAN .
- It will show one trunking route to 10.0.0.0/8.
- Because the switch port fa0/1 is in access mode, the routing table of the router will not show any routes.
- It should contain routes to the 10.10.10.0/24 and the 10.10.11.0/24 networks.
- It will show a next hop address of the switch for both VLANs.
11. Refer to the exhibit and the partial configuration taken on router RTA. Users on VLAN 5 cannot communicate with the users on VLAN 10. What should be done to fix the problem?
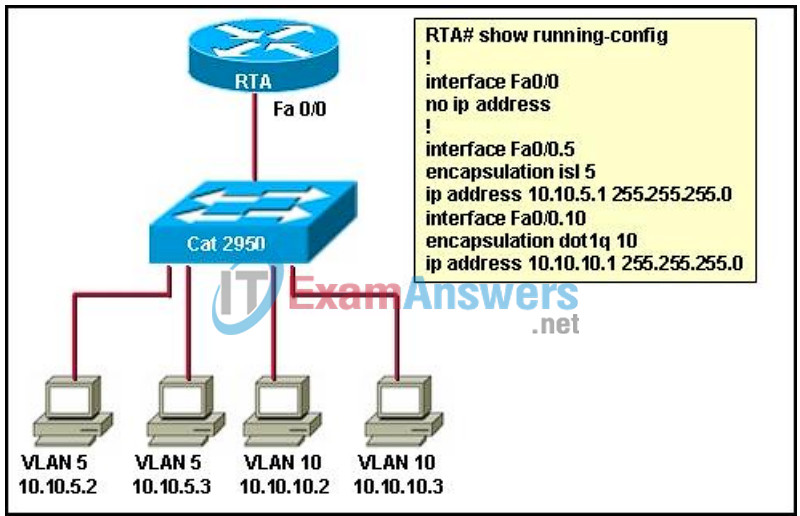
- Two static routes should be configured on the router, each pointing to each subnet.
- A dynamic routing protocol should be configured on the router.
- The Fa0/0 interface should be configured with a primary IP address of 10.10.5.1/24 and a secondary IP address of 10.10.10.1/24.
- The subinterfaces of the router should be configured with 802.1Q encapsulation.
12. Which two statements are true about routed ports on a multilayer switch? (Choose two.)
- A routed port is a physical switch port with Layer 2 capability.
- The interface vlan global configuration command is used to create a routed port.
- A routed port behaves like a regular router interface and supports VLAN subinterfaces.
- A routed port is not associated with a particular VLAN.
- To create a routed port requires removal of Layer 2 port functionality with the no switchport interface configuration command.
13. How is the Layer 2 functionality restored to a port configured for Layer 3 operation?
- no switchport
- switchport mode access
- switchport
- switchport access vlan
14. What is an advantage to using a trunk link to connect a switch to an external router that is providing inter-VLAN routing?
- provides redundancy to the VLANs
- lowers latency
- works with any switch that supports VLANs and trunking
- reduces CPU overhead
15. Which two statements are true about switched virtual interfaces (SVI) on a multilayer switch?
- An SVI is a physical switch port with Layer 3 capability.
- An SVI behaves like a regular router interface but does not support VLAN subinterfaces.
- To create an SVI requires removal of Layer 2 port functionality with the no switchport interface configuration command.
- Only one SVI can be associated with a VLAN.
- By default, an SVI is created for the default VLAN (VLAN1).
16. Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration should be applied on router R1 in order for host 1 to receive its IP configuration from the DHCP server?
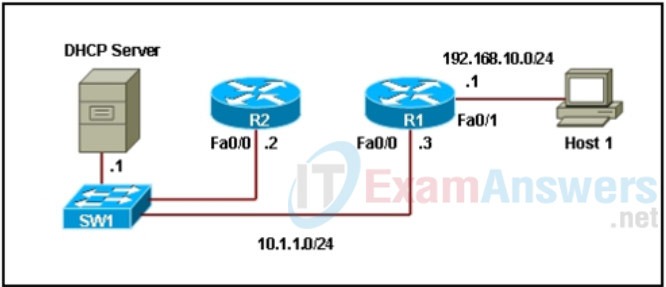
- ip helper-address 10.1.1.3 applied to the Fa0/1 interface
- ip helper-address 192.168.10.1 applied to the Fa0/0 interface
- ip helper-address 10.1.1.3 applied to the Fa0/0 interface
- ip helper-address 192.168.10.1 applied to the Fa0/1 interface
- ip helper-address 10.1.1.2 applied to the Fa0/0 interface
- ip helper-address 10.1.1.1 applied to the Fa0/1 interface
17. Which three statements about a routed port are true? (Choose three.)
- A routed switch port is created by entering VLAN interface configuration mode and assigning an IP address.
- A routed switch port can serve as a default gateway for devices.
- A routed switch port provides an interface that may provide a Layer 3 connection to a next-hop router.
- A routed switch port is a virtual Layer 3 interface that can be configured for any VLAN that exists on a Layer 3 switch.
- A routed switch port is created by configuring a Layer 2 port with the no switchport interface configuration command and assigning an IP address.
- A routed switch port is a physical device that is associated with several VLANs.
18. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the debug ip dhcp server packet output, which statement is true?
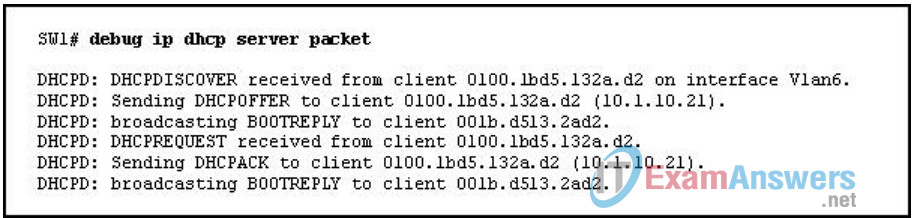
- The client accepts the offer from the DHCP server for the 10.1.10.21 IP address.
- The client sends a DHCPREQUEST that contains IP address 10.1.10.21 to the DHCP server.
- The client sends a DHCPDISCOVER that contains IP address 10.1.10.21 to the DHCP server.
- The client sends the BOOTREPLY broadcast message to inquire for a new IP address.
19. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator attempts to ping the IP address 172.16.20.1 from RouterA. What will the router output be?
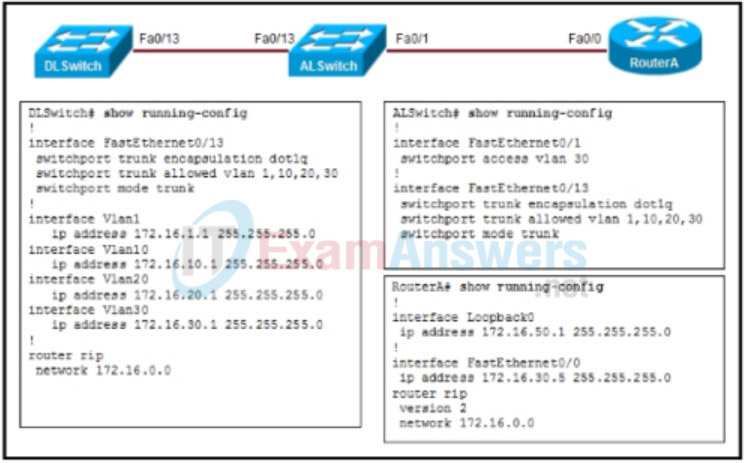
- %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/13, changed state to down
- Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
U.U.U - %Unrecognized host or address, or protocol not running
- Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
….. - Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!! - %Source quench: destination or port unreachable
20. Refer to the exhibit and the partial configuration taken on routers RTA and RTB. All users can ping their gateways, but users on VLAN 5 and VLAN 10 cannot communicate with the users on VLAN 20. What should be done to solve the problem?
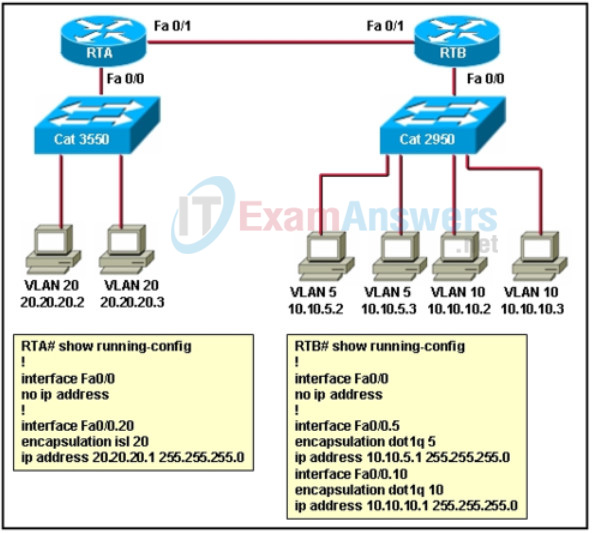
- RTA interface Fa0/1 and RTB Fa0/1 should be configured with three subinterfaces, each with 802.1Q encapsulation.
- RTA interface Fa0/1 and RTB Fa0/1 should be configured with three subinterfaces, each with ISL encapsulation.
- A dynamic routing protocol or static routes should be configured on the routers.
- A trunk should be configured between routers RTA and RTB.

Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration should be applied on router R1 in order for host 1 to receive its IP configuration from the DHCP server?
wrong asnwer:
ip helper-address 192.168.10.1 applied to the Fa0/1 interface
Correct answer:
FeedbackThe correct answer is: ip helper-address 10.1.1.1 applied to the Fa0/1 interface
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator attempts to ping the IP address 172.16.20.1 from RouterA. What will the router output be?
Wrong Answer:
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
U.U.U
Correct:
The correct answer is: Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
…..