CCNP Enterprise: Advanced Routing ( Version 8.0) – CCNP ENARSI 8 Final Exam
1. Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has performed a partial configuration to prevent routes from being reinjected. What is the next configuration that should be issued?
- An access list with a deny statement must be created and used with redistribution.
- A distribute list with a deny statement must be created and used with redistribution.
- A route map with a deny statement must be created and used with redistribution.
- A prefix list with a deny statement must be created and used with redistribution.
2. In which two situations is a metric not required for performing redistribution into the EIGRP routing process? (Choose two.)
- when redistributing routes from OSPF
- when redistributing routes from RIP
- when redistributing static routes
- when redistributing routes from BGP
- when redistributing routes from another EIGRP autonomous system
3. Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has issued the commands shown on a boundary router. What are two results of the network engineer issuing this command? (Choose two.)

- The internal administrative distance for EIGRP AS 66 has been changed to 66.
- The internal administrative distance has changed to 66 and the external administrative distance has changed to 90 for routes sourced from the router with IP 172.16.55.1.
- The router has created the EIGRP autonomous system of 66.
- The network 172.16.55.0 has a modified internal metric of 66.
- The internal administrative distance has been changed to 66 for routes sourced from the router with IP 172.16.55.1 and matching ACL 90.
4. What type of BGP message precedes the successful formation of a BGP peering session?
- keepalive
- established
- withdraw
- open
- update
5. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring BGP on a router. Which configuration step is needed in order to establish the BGP session with the neighbor router?

- Configure the keepalive timer.
- Initialize and activate the address family.
- Advertise the networks attached to the router.
- Restart the BGP process.
6. Which two statements describe the BGP weight attribute? (Choose two.)
- It is advertised to neighbor routers.
- It correlates to the AS hop count.
- It is an 8-bit value.
- It is the first step in selecting the BGP best path.
- It is a Cisco-defined attribute.
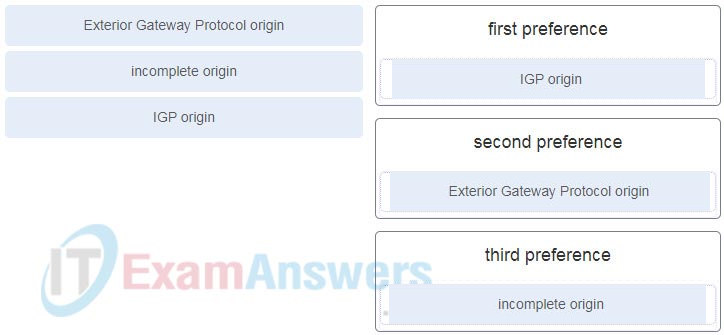
7. Match the preference, that is used by the BGP origin attribute in best path calculation, to the order.
8. A network administrator is configuring BGP multipathing for paths learned from iBGP advertisement. What is a condition for additional paths to be considered equal to the best path?
- The AIGP attribute must match.
- The neighbor IP address must match.
- The originated attribute must match.
- The IGP cost must match for IBGP and EBGP.
9. A network administrator is troubleshooting an issue with a DMVPN tunnel. From the output of the show dmvpn command, the administrator notes that the tunnel is in the IPsec state. What problem does this state indicate?
- The line protocol of the DMVPN tunnel is down.
- The DMVPN spoke router has not registered.
- IPsec tunnels have not established IKE sessions.
- IPsec security associations are not established.
10. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring Phase 1 DMVPN. The hub router RH1 and the spoke router RS2 are already configured and the administrator is finalizing configurations on spoke router RS3 by mapping the NHRP and NHS addresses for the DMVPN hub. Which configuration should the administrator use for the ip nhrp map command?
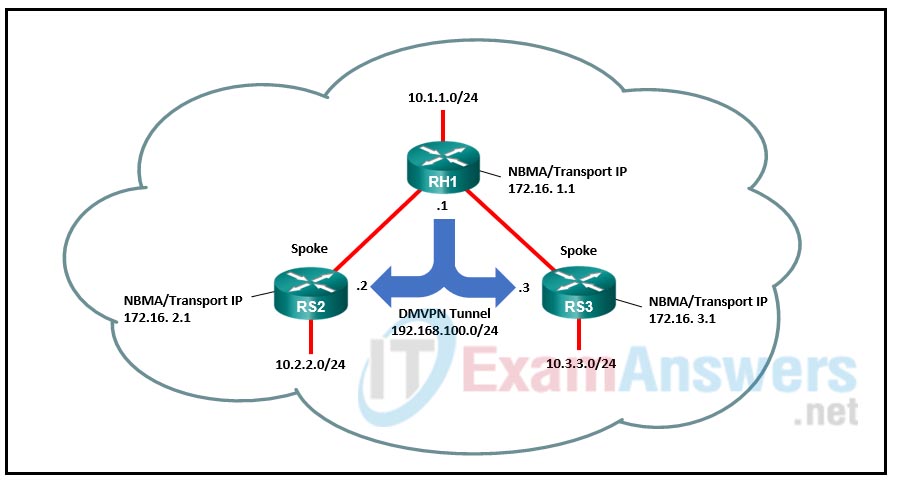
- ip nhrp map 192.168.100.1 172.16.1.1
- ip nhrp map 192.168.100.1 172.16.3.1
- ip nhrp map 192.168.100.3 172.16.3.1
- ip nhrp map 192.168.100.3 172.16.1.1
11. Which NHRP message type notifies routers of routes used by NHRP that are no longer available?
- purge
- registration
- redirect
- resolution
12. What information is maintained in the CEF adjacency table?
- MAC address to IPv4 address mappings
- the IP addresses of all neighboring routers
- IP address to interface mappings
- Layer 2 next hops
13. Refer to the exhibit. All networks are active in the same EIGRP routing domain. When the auto-summary command is issued on R3, which two summary networks will be calculated on R3? (Choose two.)
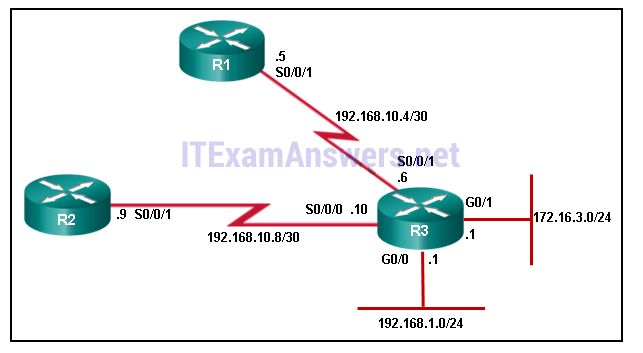
- 172.16.0.0/16
- 172.16.3.0/24
- 192.168.1.0/30
- 192.168.10.0/30
- 192.168.10.0/24
14. Refer to the exhibit. Which two routes will be advertised to the router ISP if autosummarization is disabled? (Choose two.)
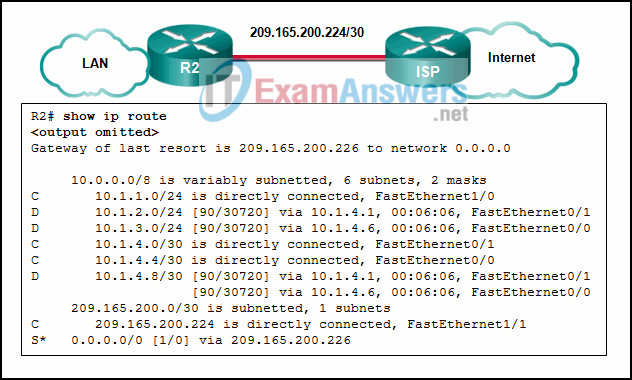
- 10.1.0.0/1
- 10.1.2.0/24
- 10.1.4.0/24
- 10.1.4.0/28
- 10.1.4.0/30
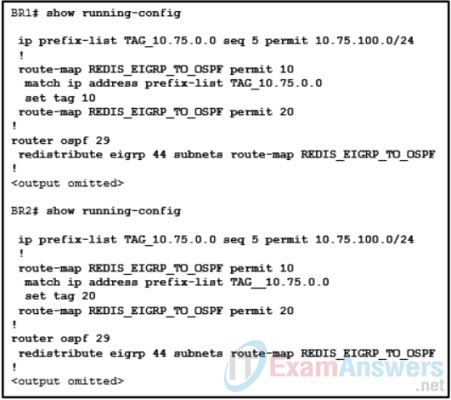
15. Which is a characteristic of policy based routing (PBR)?
- Packets originating from a router can be identified through local PBR policies.
- PBR examines packets as they exit a router interface.
- PBR policies are universal for all packets and modify the RIB.
- Next-hop addresses defined in set statements are automatically placed in the routing table.
16. Which two statements are true of policy-based routing (PBR) as a path control tool? (Choose two.)
- It can be applied only to link-state routing protocols.
- It is applied only in the inbound direction.
- Configured route map entries will have default sequence number increments of 5.
- Packets that do not match any match statements will be dropped.
- It provides a mechanism to specify one or more next hops for packets that match criteria.
17. A network administrator is writing a standard ACL that will deny any traffic from the 172.16.0.0/16 network, but permit all other traffic. Which two commands should be used? (Choose two.)
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 permit any
- Router(config)# access-list 95 host 172.16.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255
- Router(config)# access-list 95 172.16.0.0 255.255.255.255
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny any
18. Refer to the exhibit. Considering that R2, R3, and R4 are correctly configured, why did R1 not establish an adjacency with R2, R3, and R4?
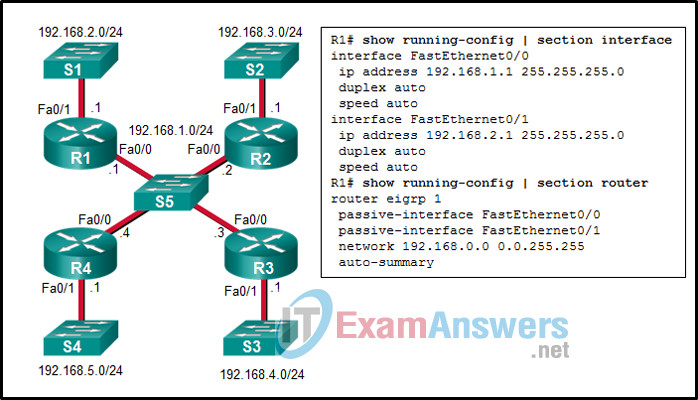
- because the automatic summarization is enabled on R1
- because the IPv4 address on Fa0/0 interface of R1 is incorrect
- because the Fa0/0 interface of R1 is declared as passive for EIGRP
- because there is no network command for the network 192.168.1.0/24 on R1
19. Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 were configured with EIGRP message authentication, but the routers cannot exchange EIGRP messages. Which two problems are causing the EIGRP authentication failure between R1 and R2 in this configuration? (Choose two.)
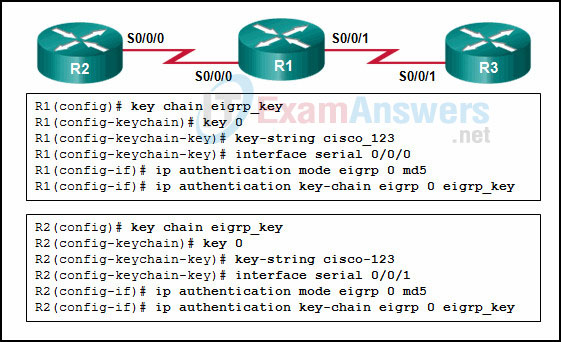
- The key ID is invalid, because its value has to be in the range from 1 to 2147483647.
- The EIGRP message authentication is being configured on the wrong interface on R2.
- The key chain name must be in upper case.
- The routers have a different value for the key-string.
- At least two keys had to be created for each key chain.
20. Refer to the exhibit. Why did R1 and R2 not establish an adjacency?
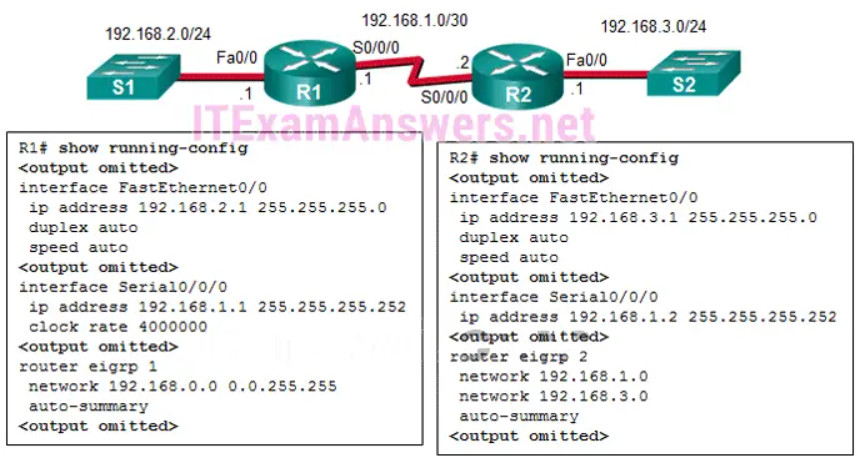
- The IPv4 address of Fa0/0 interface of R1 has a wrong IP address.
- The AS number does not match on R1 and R2.
- The automatic summarization is enabled on R1 and R2.
- There is no network command for the network 192.168.1.0/24 on R1.
21. Match the IPsec function with its description. (Not all options are used.)

22. Match the IPsec function with the description.

23. Which three statements describe the IPsec protocol framework? (Choose three.)
- AH provides integrity and authentication.
- ESP provides encryption, authentication, and integrity.
- AH uses IP protocol 51.
- AH provides encryption and integrity.
- ESP uses UDP protocol 50.
- ESP requires both authentication and encryption.
24. A network administrator is configuring an ACL to match networks for BGP route filtering. The administrator creates an ACE permit ip 10.0.32.0 0.0.31.0 255.255.255.0 0.0.0.192 . Which network matches the ACE?
- 10.0.32.0/27
- 10.0.66.0/24
- 10.0.62.0/25
- 10.0.31.0/26
25. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting BGP configuration and wants to display only routes that originated in AS 40. Which regular expression should the administrator use in the command show bgp ipv4 unicast regex regex-pattern ?
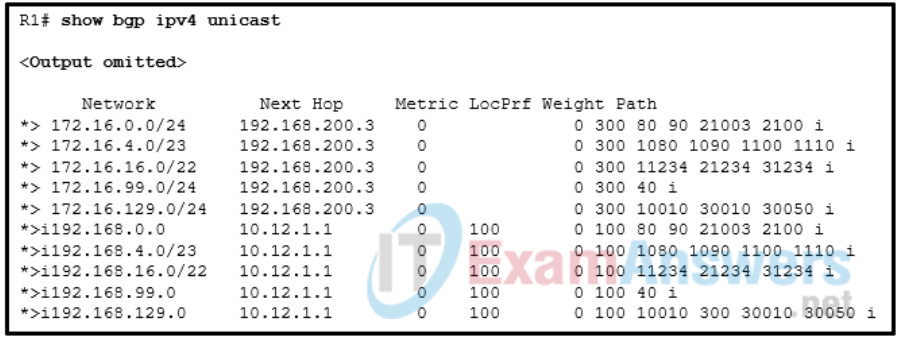
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regex ^40_
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regex *40_
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regex _40$
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regex .40.
26. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast 172.16.0.0 command to check the route information in the BGP table. Which statement describes the characteristic of the advertisement of this route?
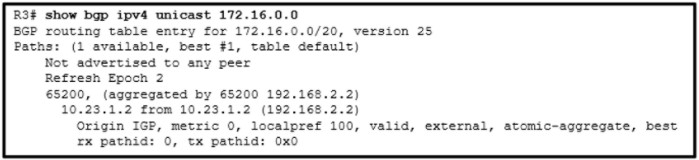
- The route is advertised for networks directly connected to the BGP router 192.168.2.2.
- The route is advertised with the aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.240.0 summary-only command.
- The route is advertised through an IGP.
- The route is advertised through a static route.
27. What OSPF LSA type is used to advertise routes redistributed into an OSPF domain?
- type 3
- type 4
- type 5
- type 7
28. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured two-way redistribution on router R1. What metrics will be used for redistributed routes?
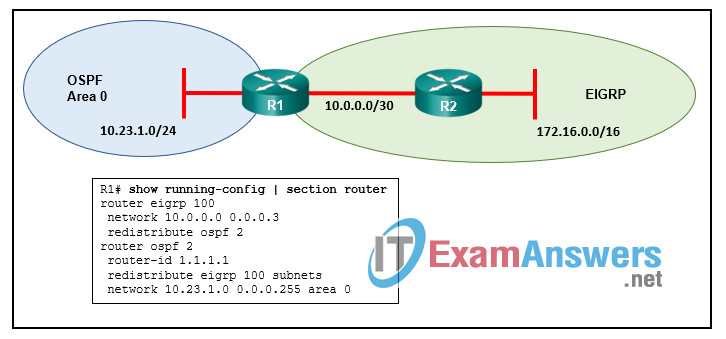
- EIGRP routes will have a metric of 1 and OSPF routes will have a metric of infinity.
- EIGRP routes will have a metric of infinity and OSPF routes will have a metric of 20.
- EIGRP routes will have a metric of 170 and OSPF routes will have a metric of 20.
- EIGRP routes will have a metric of infinity and OSPF routes will have a metric of 1.
29. Refer to the exhibit. Which route will appear in the routing table of R3 as a result of the redistribution configuration issued on R2?
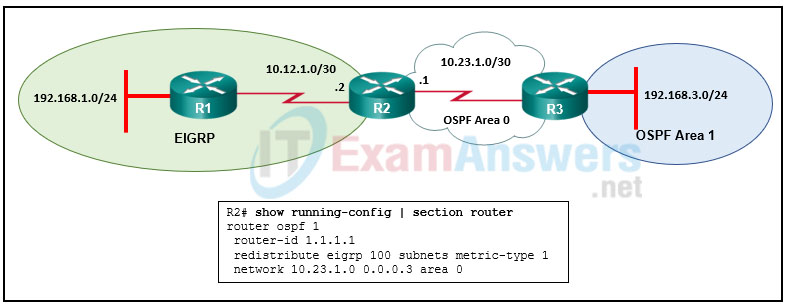
- O E2 192.168.1.0/24 [110/20] via 10.23.1.1, 00:04:42, Serial0/0/1
- O IA 10.23.1.0/30 [110/20] via 10.23.1.1, 00:04:42, Serial0/0/1
- O E1 192.168.1.0/24 [110/86] via 10.23.1.1, 00:04:42, Serial0/0/1
- D EX 10.23.1.0/30 [170/3072] via 10.12.1.2, 00:09:07, Serial0/0/1
30. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured OSPFv2 on the two Cisco routers. The routers are unable to form a neighbor adjacency. What should be done to fix the problem on router R2?
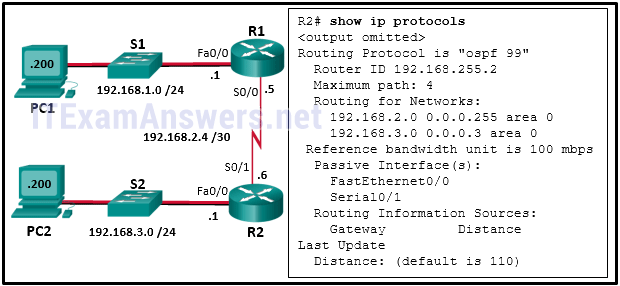
- Implement the command no passive-interface Serial0/1.
- Implement the command network 192.168.2.6 0.0.0.0 area 0 on router R2.
- Change the router-id of router R2 to 2.2.2.2.
- Implement the command network 192.168.3.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 on router R2.
31. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a recent OSPF stub configuration between R3 and R4. The only routes that should appear on the routing table for R4 are intra-area routes and the default route. However, interarea routes are also appearing. What must the administrator do to fix this problem?
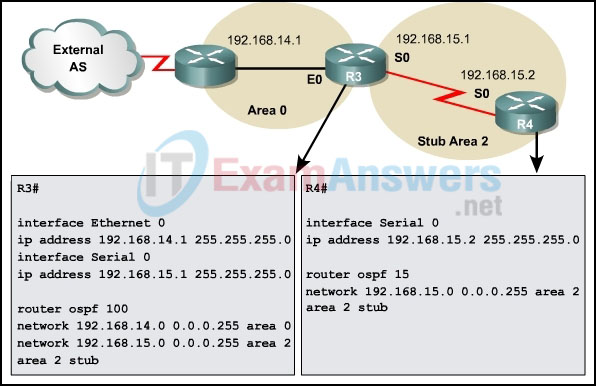
- Issue the keyword nssa on R3.
- Issue the keyword nssa on R4.
- Issue the keyword stub on R4.
- Issue the keyword no-summary on R4.
- Issue the keyword no-summary on R3.
- Issue the keyword stub on R3.
32. Refer to the exhibit. Router R0-A is not learning all of the OSPF routes from the remote sites that connect to router R0-B and R0-C. What are two issues the network engineer should consider? (Choose two.)
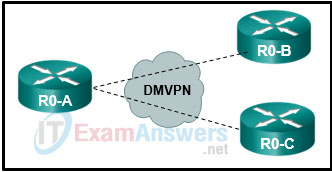
- routes not going from the LSDB to the routing table because of ACL
- DR selection
- missing default route(s)
- neighbor adjacency
- SSH misconfiguration
33. Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 are configured as shown. However, the show ipv6 ospf neighbor command reveals that there are no OSPFv3 neighbors established. What error in the configuration is preventing neighbor relationship from forming between the two routers?
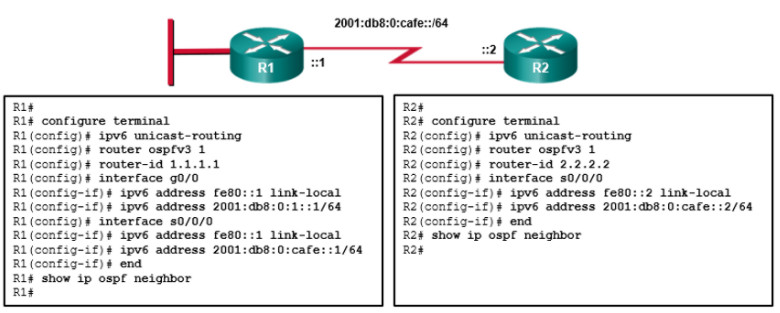
- OSPFv3 is not enabled on the interfaces.
- The IPv6 routing process is not enabled.
- There is a link-local address conflict between the serial and gigabit interfaces on R1.
- The IPv6 address family is not initialized on either router.
34. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator has entered the command default-information originate in OSPFv3 global configuration mode on R1, but R2 is not receiving a default route. What is the problem?
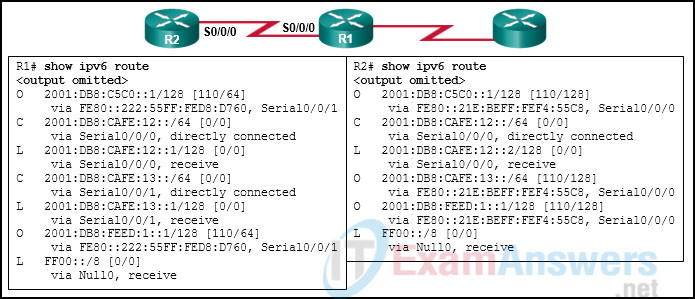
- The default-information originate command is only used for OSPFv2.
- R1 and R2 are on different subnets.
- OSPFv3 is not running on R2.
- R1 does not have a default route configured.
35. An administrator is troubleshooting an OSPFv3 network. Router A and router B are configured with IPv6 addressing and basic routing capabilities using OSPFv3. While debugging the routing process, the administrator discovers that the networks that are advertised from router A do not show in the routing table of router B. Why is the routing information not being learned by router B?
- Router A has a stub interface.
- IPv6 unicast routing is not enabled on Router B.
- The OSPFv3 timers on both routers were adjusted for fast convergence.
- An IPv6 traffic filter is blocking the networks from entering the interface on router B that is connected.
36. Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 enable EIGRP on all of their interfaces. Which two conclusions can the field engineer draw from the outputs of the show ip route eigrp command on each router? (Choose two.)
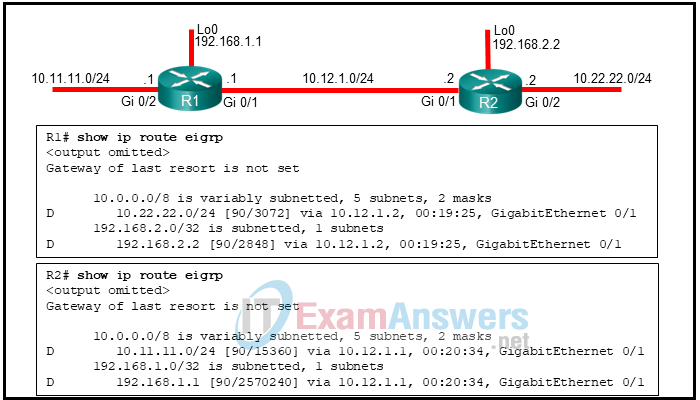
- Both routers are using the same path metric calculation method.
- The path metric calculation used in R2 addresses the scalability with higher-capacity interfaces.
- R1 and R2 are using the same K factors to calculate the path metric.
- An adjacency will be allowed between the routers, as long as all the K factors in both routers are set to default values.
- The EIGRP configuration mode of R1 uses wide metrics calculation.
- R2 is using EIGRP classic configuration mode.
37. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator wants EIGRP on Router1 to load balance traffic to network 2001:db8:11:10::/64 across two interfaces. Currently traffic is using only interface GigabitEthernet0/1. A second route, not in the routing table, is available with a metric of 264000. What value is needed in the variance command to make EIGRP put the second route into the routing table?
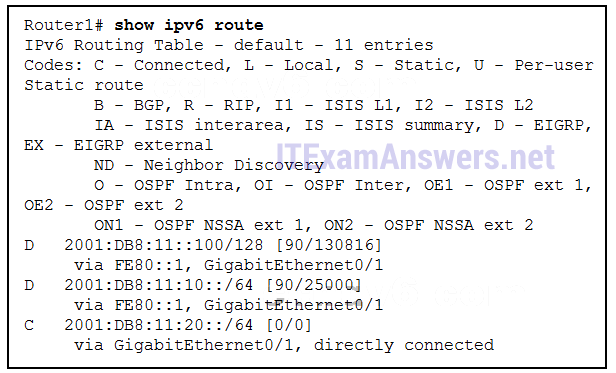
- 4
- 10
- 1
- 11
38. Refer to the exhibit. Router R2 has recently been configured and connected via interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 to router R1. R1 is configured correctly, but fails to establish a neighbor relationship with R2. What is the problem?
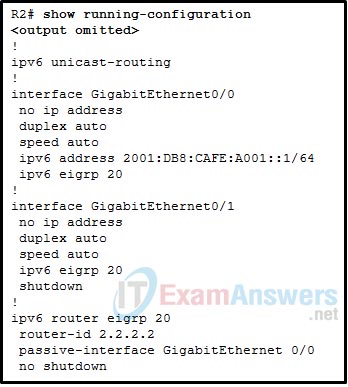
- The EIGRPv6 process has not been activated on interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/0.
- The passive-interface command is preventing hello packets from being sent.
- The command ipv6 unicast-routing should be implemented in the router configuration mode.
- The command ipv6 unicast-routing has not been implemented.
39. An administrator wants to configure EIGRPv6 in an IPv6 network. Which three statements are valid for the configuration of EIGRPv6? (Choose three.)
- Split horizon needs to be enabled on all EIGRPv6 hub routers.
- The network statement must be configured for the EIGRPv6 process.
- EIGRPv6 has to be directly configured on the interfaces over which it runs.
- There is no network statement configuration for EIGRPv6.
- When using a passive-interface configuration, EIGRPv6 does not have to be configured for that interface.
- EIGRPv6 needs to be directly configured on an interface that has been made passive.
40. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator configured a class map as shown, but the traffic is not being classified as desired. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?

- The traffic would be subject to the implicit default class.
- The ACL-EIGRP is permitting the wrong IP multicast address.
- The traffic would never match the CoPP-CLASS class map.
- The ACL-ICMP access-list should be in a separate class map because it is not a routing protocol.
41. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator configures AAA authentication on router R1. The ACS servers are configured and running. The administrator tests the configuration by telneting to R1. What will happen if the administrator attempts to authenticate through the RADIUS server using incorrect credentials?
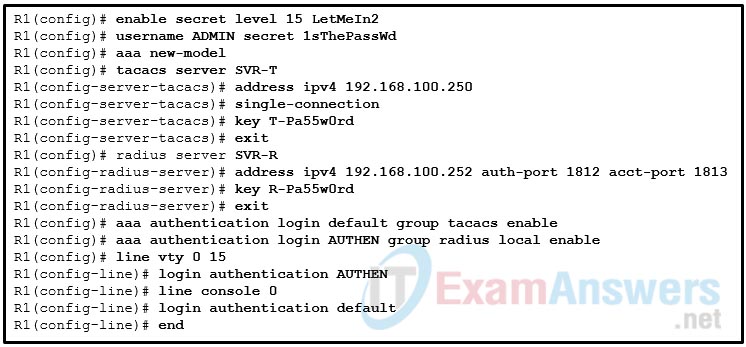
- The enable secret password and a random username could be used in the next login attempt.
- The authentication process stops.
- The enable secret password could be used in the next login attempt.
- The username and password of the local user database could be used in the next login attempt.
42. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show run | section username|aaa|line|radius command to verify an AAA configuration on a Cisco router. Which two conclusions can be drawn from the command output? (Choose two.)
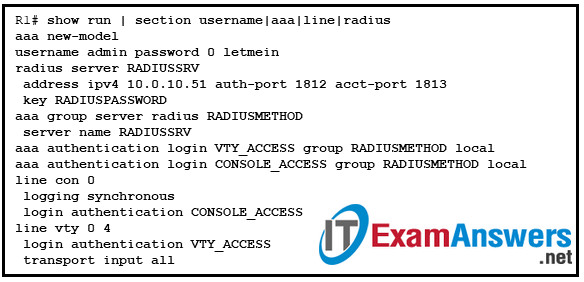
- The router must use Cisco default ports for authentication and accounting to connect to a RADIUS server.
- Authentication for the vty lines is using the default authentication method.
- Authentication for the console line will use local authentication as a fallback method if the RADIUS server is not available.
- A missing ip radius source-interface command on RADIUS server settings may prevent the router from using the services of the server.
- The Cisco router can use the radiuspassword pre-shared key to connect to a RADIUS server.
43. From the routing tables shown from routers within a multiarea OSPF network, which routing table would be from an internal router that is within a totally stub area?
A.
Gateway of last resort is 10.1.1.1 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 8 subnets, 4 masks O IA 10.0.0.0/30 [110/4] via 10.1.1.1, 01:17:40, GigabitEthernet0/1 O IA 10.0.0.4/30 [110/3] via 10.1.1.1, 01:17:50, GigabitEthernet0/1 O IA 10.0.0.8/30 [110/66] via 10.1.1.1, 01:17:50, GigabitEthernet0/1 O 10.1.0.0/24 [110/2] via 10.1.1.1, 01:18:00, GigabitEthernet0/1 C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 O IA 10.2.0.0/25 [110/5] via 10.1.1.1, 01:17:40, GigabitEthernet0/1 O IA 10.2.0.128/25 [110/6] via 10.1.1.1, 01:17:40, GigabitEthernet0/1 O*IA 0.0.0.0/0 [110/3] via 10.1.1.1, 01:17:50, GigabitEthernet0/1
B.
Gateway of last resort is 10.1.1.1 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks O 10.1.0.0/24 [110/2] via 10.1.1.1, 01:26:37, GigabitEthernet0/1 C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 O*IA 0.0.0.0/0 [110/3] via 10.1.1.1, 01:26:27, GigabitEthernet0/1
C.
Gateway of last resort is 10.0.0.5 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 10 subnets, 4 masks O 10.0.0.0/30 [110/2] via 10.0.0.5, 01:42:33, GigabitEthernet0/1 C 10.0.0.4/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.0.0.6/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 C 10.0.0.8/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L 10.0.0.9/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 C 10.1.0.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 L 10.1.0.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 O 10.1.1.0/24 [110/2] via 10.1.0.2, 01:42:38, GigabitEthernet0/0 O IA 10.2.0.0/25 [110/3] via 10.0.0.5, 01:42:33, GigabitEthernet0/1 O IA 10.2.0.128/25 [110/4] via 10.0.0.5, 01:42:33, GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks O E2 192.168.0.0/30 [110/20] via 10.0.0.5, 01:42:33, GigabitEthernet0/1 O E2 192.168.0.64/26 [110/20] via 10.0.0.5, 00:47:20, GigabitEthernet0/1 O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 10.0.0.5, 01:42:33, GigabitEthernet0/1
D.
Gateway of last resort is not set 1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 1.1.1.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback0 S 10.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 203.0.113.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 203.0.113.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L 203.0.113.1/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
44. How does Cisco implement interarea OSPF summarization?
- It must be configured manually on ASBRs.
- The summarized route metric is equal to the lowest cost of all subnets within the summary address range.
- Multiple routes inside the area are summarized by more than one LSA.
- It is performed automatically by OSPF.
45. What are the two purposes of an OSPF router ID? (Choose two.)
- to uniquely identify the router within the OSPF domain
- to facilitate router participation in the election of the designated router
- to enable the SPF algorithm to determine the lowest cost path to remote networks
- to facilitate the establishment of network convergence
- to facilitate the transition of the OSPF neighbor state to Full
46. How is the flooding scope of link state advertisements denoted within OSPFv3 LSAs?
- The outer IPv6 OSPFv3 header uses three bits to determine LSA scope.
- Three bits of the 16-bit LS type field of OSPFv3 LSAs set the scope.
- ABR LSAs include scope information as part of the routing information payload.
- LSA scope is specified by the area area-ID range prefix-length command.
47. A network technician is verifying the OPSFv3 address families configuration on a Cisco router. What would the technician expect to see displayed when the show ospfv3 database router adv-router 4.4.4.4 command is issued?
- the LSAs created by the router on which the command is executed and sent to the router with RID 4.4.4.4
- all area LSAs in the LSDB of the DR router on which the command is executed with RID 4.4.4.4
- all LSAs in the LSDB of the router with RID 4.4.4.4
- the LSAs received from the router with RID 4.4.4.4 that exist in the LSDB of the local router
48. Refer to the exhibit. Both routers R1 and R2 are configured for OSPFv3 and are routing for both IPv4 and IPv6 address families. Which two destination addresses will R1 use to establish a full adjacency with R2? (Choose two.)
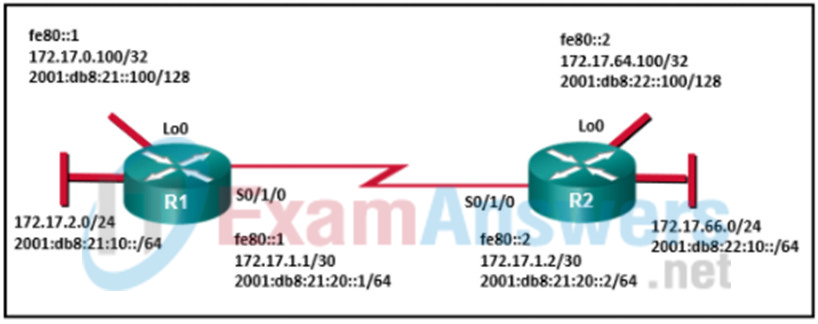
- ff02::5
- fe80::2
- 2001:db8:22::100
- 172.17.66.1
- 2001:db8:21:20::2
49. Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 was configured by a network administrator to use SNMP version 2. The following commands were issued:
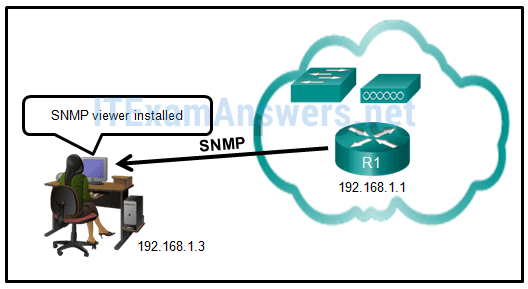
R1(config)# snmp-server community batonaug ro SNMP_ACL
R1(config)# snmp-server contact Wayne World
R1(config)# snmp-server host 192.168.1.3 version 2c batonaug
R1(config)# ip access-list standard SNMP_ACL
R1(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.10.3
Why is the administrator not able to get any information from R1?
- The snmp-server enable traps command is missing.
- There is a problem with the ACL configuration.
- The snmp-server community command needs to include the rw keyword.
- The snmp-server location command is missing.
50. Refer to the exhibit. The total number of packet flows is not consistent with what is expected by the network administrator. The results show only half of the flows that are typically captured for the interface. Pings between the router and the collector are successful. What is the reason for the unexpected results?
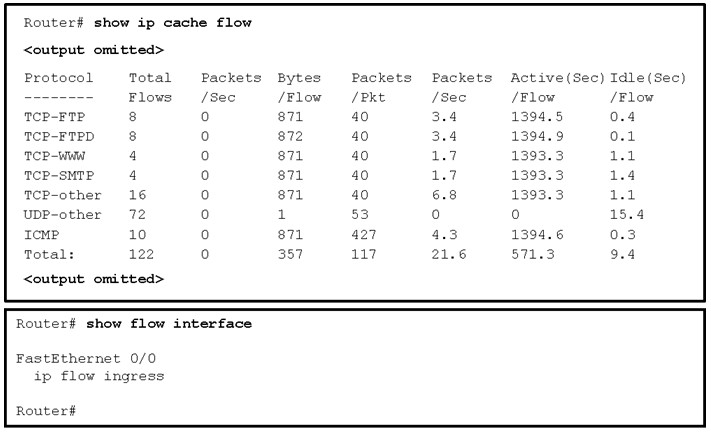
- Interface Fa0/0 is not configured as the source of the packets sent to the collector.
- The interface is shutdown.
- The Netflow collector IP address and UDP port number are not configured on the router.
- The router is not configured to monitor outgoing packets on the interface.
51. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring the syslog service on a Cisco router. Which command should be used to configure an IPv4 address of 192.168.10.254 as the source address on the syslog packets as they exit the router R1?
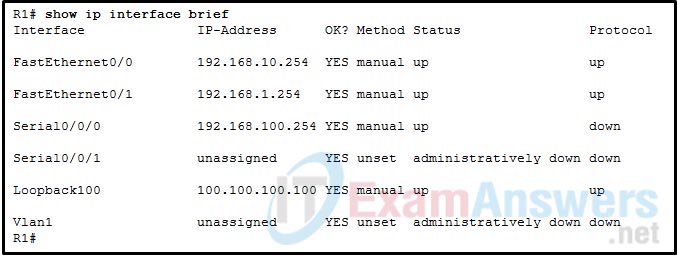
- R1(config)#logging host 192.168.10.254
- R1(config)#logging origin-id ip
- R1(config)#logging source-interface fa0/0
- R1(config)# logging 192.168.10.254
52. Which three implicit access control entries are automatically added to the end of an IPv6 ACL? (Choose three.)
- deny ip any any
- deny ipv6 any any
- permit ipv6 any any
- deny icmp any any
- permit icmp any any nd-ns
- permit icmp any any nd-na
53. Which two networks would match the following prefix list? (Choose two.)
ip prefix-list MATCHTHIS seq 5 deny 10.1.0.0/16 ge 24 le 30
- 10.0.0.0/16
- 10.1.1.0/30
- 10.1.0.0/24
- 10.1.0.0/16
- 10.0.0.0/24
54. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator has configured the IPv6 ACL that is in the exhibit to permit outbound Telnet traffic to any destination, and block TCP connections from 2001:db8:1::1 to any destination. All other packets should be denied and logged. After implementing the ACL, all IPv6 traffic, including Telnet from the 2001:db8::/32 subnet is denied. What is the problem?

- The deny ipv6 any any log ACE is preventing NDP from functioning.
- The eq telnet parameter should appear immediately after the IPv6 address in the first ACE.
- The ACEs are in the wrong order.
- The wildcard mask is missing from the first ACE.
55. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the command show bgp ipv6 unicast | begin Network to check the BGP table. Which statement describes the routes with an unspecified address (::) in the Next Hop column?
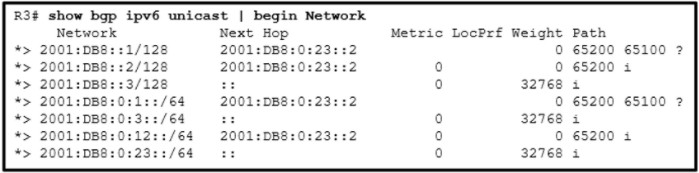
- They are learned through an IGP.
- They are locally generated network prefixes.
- They indicate routes created by static route configuration.
- They are learned through BGP advertisements from the next neighbor.
56. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast 10.1.1.128 command on router R2 to verify the network 10.1.1.128 in the BGP table. The administrator notices that there are two paths to reach the network. Which BGP factor is used to determine the best-path?
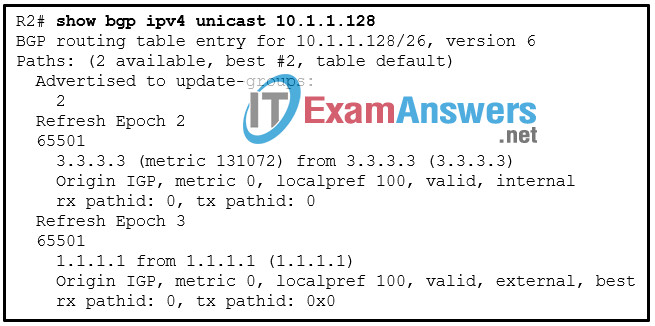
- the value of the BGP RID
- the value of the lowest multi-exit discriminator attribute
- whether the path is being learned via IBGP or EBGP
- the value of the weight attribute
57. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring BGP route advertisement on router R1. The network 10.1.0.0/24 is subnetted into four 10.1.0.0/26 subnets that are attached to the 4 interfaces of R1 respectively. The administrator issues the show ip route command and notices that the network 10.1.0.0/24 is not advertised by BGP. What is a possible cause for this issue?
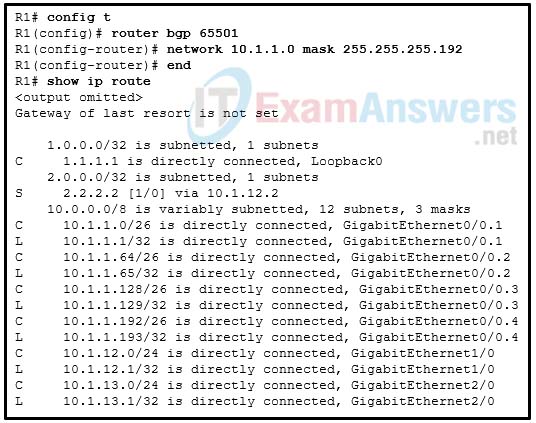
- Not all four interfaces are up/up.
- The network mask command does not match the network/prefix in the routing table.
- The BGP slit-horizon rule prevents the network from being advertised.
- The network command is missing the summary-only keyword.
58. Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol is used by R2 and R5 to exchange Layer 3 routes?
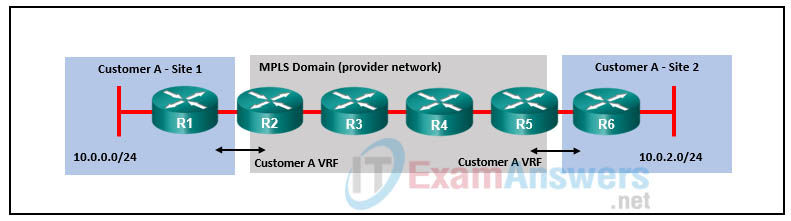
- EIGRP
- MP-BGP
- LDP
- OSPF
59. When an unlabeled packet arrives at an MPLS-enabled router interface, which database is used to make a forwarding decision on the packet?
- IP routing table (RIB)
- IP forwarding table (FIB)
- label information base (LIB)
- label forwarding table (LFIB)
60. Match the MPLS router type to its characteristic.
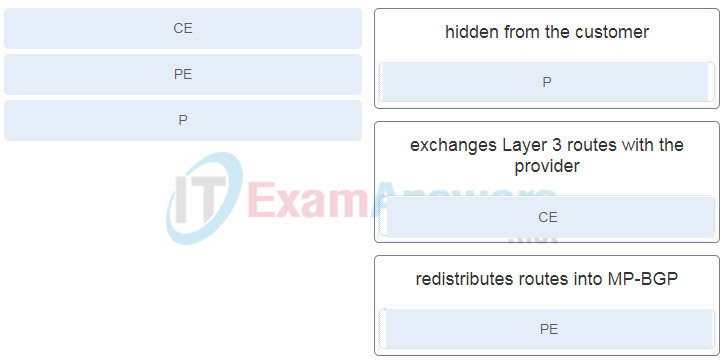
61. What is the order in determining the BGP router ID?
- statically defined, the highest IP address of any active interfaces, and the highest IP address of any active loopback interfaces
- statically defined, the highest IP address of any active loopback interfaces, and the highest IP address of any active interfaces
- the highest IP address of any active interfaces, statically defined, and the highest IP address of any active loopback interfaces
- the highest IP address of any active loopback interfaces, statically defined, and the highest IP address of any active interfaces
62. A network engineer is troubleshooting OSPFv2 routing issues on two connected routers. Which two requirements to form an adjacency need to be verified? (Choose two.)
- Verify that one of the interfaces that connects the two routers is active and the other passive.
- Verify that one of the routers is the DR or BDR and the other router a DRother.
- Verify that the interfaces that connect the two routers are in the same subnet.
- Verify that the interfaces that connect the two routers are in the same area.
- Verify that both routers are using the same OSPFv2 process ID.
63. Router RTRA is adjacent to RTRB through a WAN link. RTRB can be seen in the output of the show cdp neighbors command issued on RTRA, can be pinged from RTRA, but is not showing OSPF routes from RTRA. What are two potential issues? (Choose two.)
- There are duplicate IP addresses on the interfaces that connect RTRA and RTRB.
- One or both routers are missing or have a misconfigured network statement.
- Each interface that connects the routers has been set to priority 0.
- A clock rate has not been installed on the DCE side of the link.
- A distribute list is denying routes from being installed in the routing table.
64. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a GRE tunnel between two corporate sites terminating on routers CE1 and CE2. The router CE2 is already configured. What set of commands should the administrator configure on router CE1?
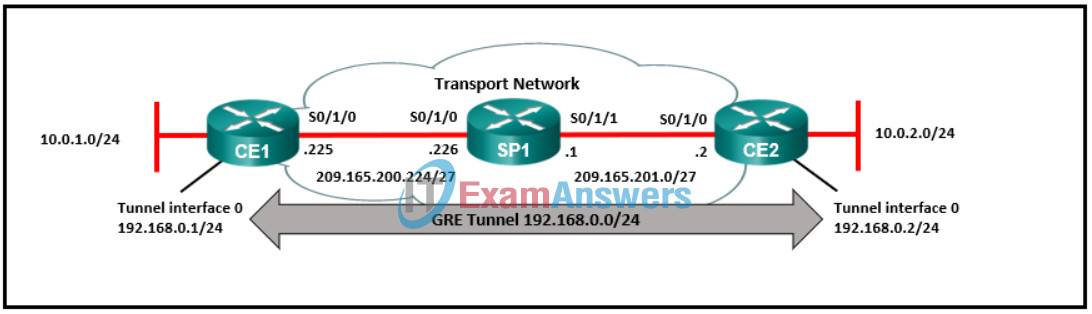
- interface tunnel 0
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
tunnel source S0/1/0
tunnel destination 209.165.201.2 - interface tunnel 0
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
tunnel source 192.168.0.1
tunnel destination 209.165.201.2 - interface tunnel 0
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
tunnel source S0/1/0
tunnel destination 209.165.200.224 - interface tunnel 0
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
tunnel source S0/1/0
tunnel destination 192.168.0.2
65. Refer to the exhibit. What is the function of the Null0 route in the outputs displayed for R1 and R2?
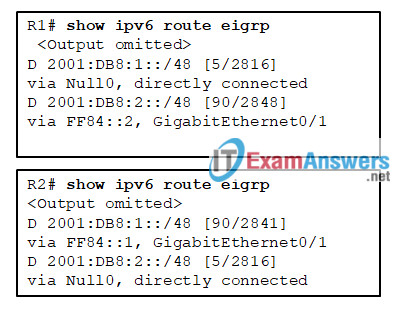
- to advertise the local /48 summary route
- to force advertisements of only the /64 route entries to the neighbor routers
- to force advertisements of only the /128 route entries to the neighbor routers
- to invoke the split horizon rule to prevent routing loops
66. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show ipv6 eigrp neighbors command. Which conclusion can be drawn based on the output?
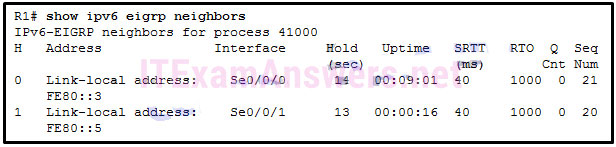
- The link-local addresses of neighbor routers interfaces are configured manually.
- R1 has two neighbors. They connect to R1 through their S0/0/0 and S0/0/1 interfaces.
- The neighbor with the link-local address FE80::5 is the first EIGRP neighbor that is learned by R1.
- If R1 does not receive a hello packet from the neighbor with the link-local address FE80::5 in 2 seconds, it will declare the neighbor router is down.
67. Which ACE will permit a packet that originates from any network and is destined for a web server at 192.168.1.1?
- access-list 101 permit tcp any host 192.168.1.1 eq 80
- access-list 101 permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 eq 80 any
- access-list 101 permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 any eq 80
- access-list 101 permit tcp any eq 80 host 192.168.1.1
68. An administrator is troubleshooting two routers in an OSPFv3 network. They are trying to establish an OSPFv3 adjacency over an Ethernet link, but the adjacency is not forming. What are two possible reasons for this issue? (Choose two.)
- mismatched Area IDs
- mismatched network types
- mismatched global OSPV3 PID and the PID configured on the Ethernet interface
- mismatched link-local addresses
- mismatched global unicast addresses
- mismatched subnet masks
69. Refer to the exhibit. R1 and R2 are connected to the same LAN segment and are configured to run OSPFv3. They are not forming a neighbor adjacency. What is the cause of the problem?
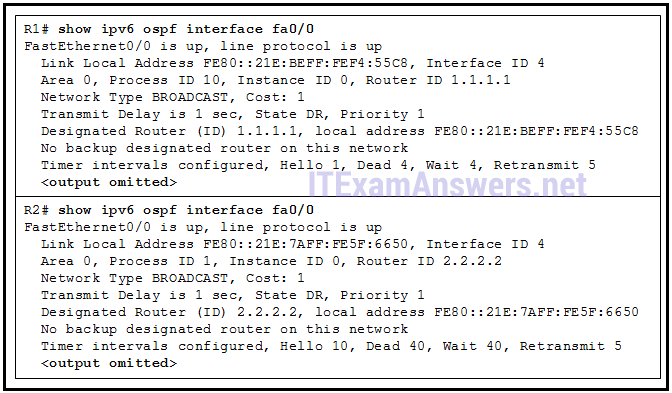
- The IPv6 addresses of R1 and R2 are not in the same subnet.
- The priority value of both R1 and R2 is 1.
- The timer intervals of R1 and R2 do not match.
- The OSPFv3 process IDs of R1 and R2 are different.
70. Refer to the exhibit. A SNMP manager is using the community string of snmpenable and is configured with the IP address 172.16.10.1. The SNMP manager is unable to read configuration variables on the R1 SNMP agent. What could be the problem?
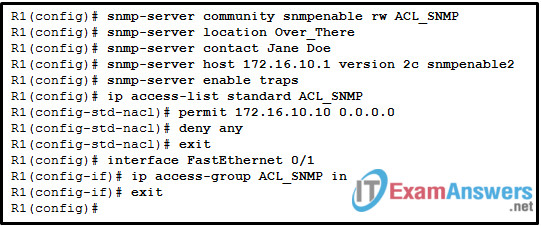
- The incorrect community string is configured on the SNMP manager.
- The community of snmpenable2 is incorrectly configured on the SNMP agent.
- The ACL is not permitting access by the SNMP manager.
- The SNMP agent is not configured for read-only access.
71. In which two situations would a company consider using an OSPF virtual link? (Choose two.)
- when merging with another company and needing to connect the two backbone areas
- when connecting discontiguous areas
- when allowing corporate telecommuters to connect to corporate OSPF network resources
- when importing a non-OSPF routing protocol into an ABR or backbone OSPF router
- when importing a non-OSPF routing protocol into an internal OSPF router
72. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator verifies on an enterprise network that EIGRP query packets are delayed because of packet loss. The administrator issues the show ip protocols | include Active command to see the EIGRP active timer on a router. What can the administrator conclude from this output?

- EIGRP waits 120 seconds before sending a SIA query to neighbors that did not respond.
- The SIA state is declared for a neighbor without receiving an SIA reply after 4 minutes.
- Upon receipt of an SIA query from a neighbor router, the router needs to respond within 60 seconds to avoid being SIA state.
- This is the default value of the active timer.
73. Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is troubleshooting a configuration for EIGRP and OSPF mutual redistribution. Why is the OSPF process not receiving all of the redistributed EIGRP routes?
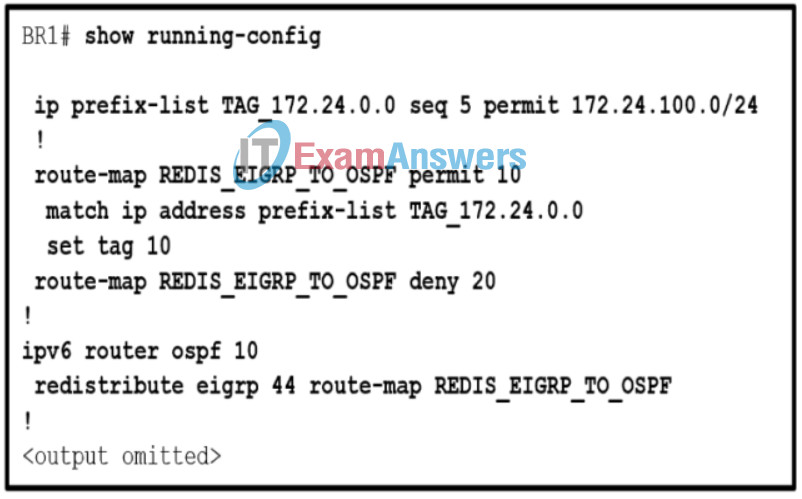
- The route map REDIS_EIGRP_TO_OSPF does not reference a correct prefix-list.
- The 172.24.100.0 network is the only network receiving a tag during the redistribution process.
- Because of the deny keyword on sequence 20, only the 172.24.100.0 network is being allowed in the redistribution process.
- The match command is referencing an ip keyword and should be referencing an ipv6 keyword.
74. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has attempted to implement a default route from R1 to the ISP and propagate the default route to EIGRP neighbors. Remote connectivity from the EIGRP neighbor routers to the ISP connected to R1 is failing. Based on the output from the exhibit, what is the most likely cause of the problem?
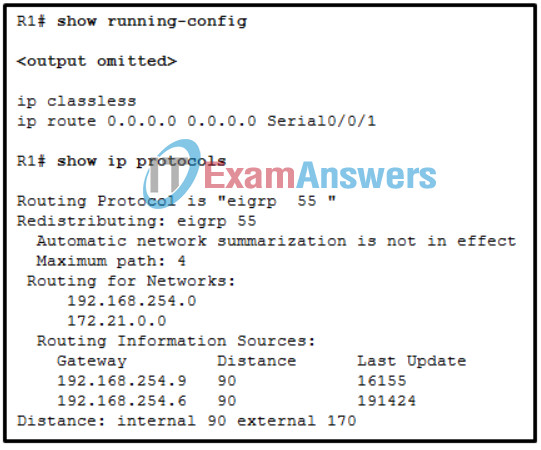
- The ip route command must specify a next-hop IP address instead of an exit interface when creating a default route.
- The command redistribute static has not been issued on R1.
- The network statement for the ISP connection has not been issued.
- The command default-information originate has not been issued on R1.
- There are no EIGRP neighbor relationships on R1.
75. Which two network prefixes match the prefix match pattern 172.16.0.0/12 ge 16? (Choose two.)
- 172.20.0.0/15
- 172.31.0.0/12
- 172.17.1.0/24
- 172.16.0.0/30
- 172.30.0.0/12
76. What is the purpose of the BGP maximum prefix feature?
- to restrict the number of routes received from a peer
- to restrict the bandwidth used for a specific set of routes
- to restrict the number of peers that will advertise the same route
- to restrict the number of routes sent to a peer with low bandwidth
77. What is the purpose of the BGP maximum prefix feature?
- to restrict the bandwidth used for a specific set of routes
- to preserve the router memory for a set of important routes
- to restrict the number of peers that will advertise the same route
- to ensure that the BGP table does not overwhelm the router
78. Refer to the exhibit. Router R2 is configured for 2-way redistribution between OSPF and EIGRP. When the network administrator views the EIGRP topology table on R1, no redistributed routes from OSPF are present. What corrective action on R2 should the administrator take to resolve this issue?
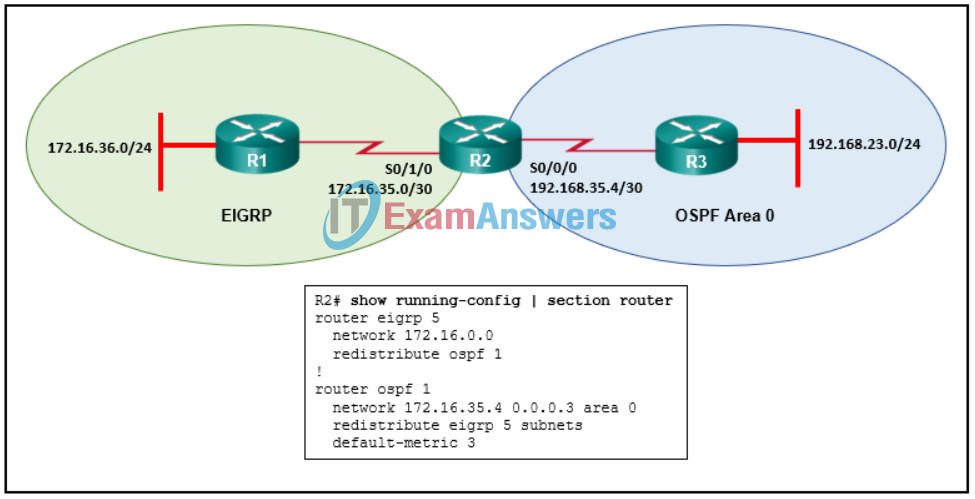
- Remove the subnets keyword from the OSPF configuration.
- Apply a seed metric to OSPF routes.
- Change the OSPF metric type to 1.
- Change the EIGRP process to 1.
79. Which three statements describe the default operation of route redistribution? (Choose three.)
- Routes redistributed into EIGRP have an AD of 190.
- Routes redistributed into OSPF have an AD of 20.
- OSPF external routes are not included in OSPF to BGP redistribution.
- BGP only redistributes EBGP routes into IGP protocols.
- BGP weight for redistributed routes is set to 4096.
- Routes redistributed into OSPF from BGP have a seed metric of 1.
80. Which two elements of security are ensured by data integrity? (Choose two.)
- Data is available wherever it it needed.
- Data is accurate and has not been changed in transit.
- Data is always available to users.
- Data is viewable to only authorized users.
- Data can only be modified by authorized users.
81. Which feature of IPsec validates the source of data transmitted through the Internet?
- authentication
- confidentiality
- anti-replay protection
- data integrity
82. What is used on PE routers in an MPLS Layer 3 VPN deployment to isolate the routes of multiple customers?
- BGP communities
- MP-BGP address families
- VRF instances
- DMVPN tunnels
83. Refer to the exhibit. While configuring a multiarea OSPF topology, a network administrator implements the network 10.254.254.0 0.0.0.255 area 99 command. Which type of OSPF router is being configured?
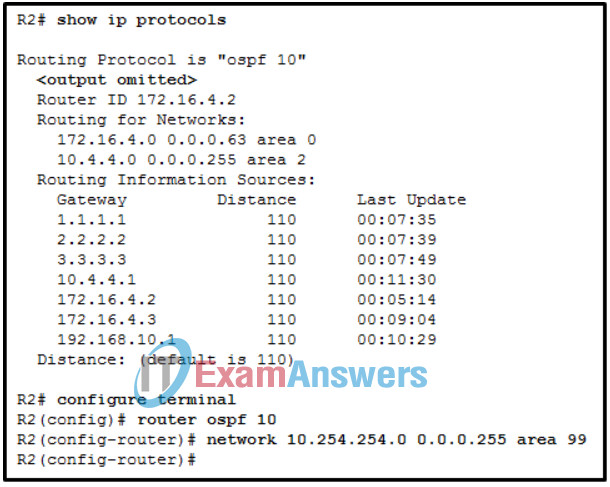
- ASBR
- internal backbone
- internal
- ABR
84. A network administrator is configuring IPv6 route summarization on a BGP router with the command aggregate-address 2001:db8::/60 summary-only . Which two component networks match the aggregated route? (Choose two.)
- 2001:db8:0:24::/64
- 2001:db8:0:12::/64
- 2001:db8:0:15::/64
- 2001:db8:0:0::/64
- 2001:db8:0:e::/64
85. In addition to no shutdown , which two commands must a network technician issue on the interface of a Cisco router to enable OSPFv3 address families for IPv6 on that interface? (Choose two.)
- ipv6 address 2001:DB8:0:1::1/64
- router ospfv3 1
- ipv6 unicast-routing
- ospfv3 1 area 0 ipv6
- ipv6 router ospf 1
- ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
86. Which forwarding address is used by OSPFv3 address families learned routes to forward data packets to the next hop router?
- the IPv6 link-local address of the neighboring router
- FF02::5
- the outgoing interface IPv6 link-local address
- FF02::6
87. Which two classes of BGP path attributes are advertised between autonomous systems? (Choose two.)
- well-known mandatory
- optional transitive
- well-known non-transitive
- well-known discretionary
- optional nontransitive
88. Multiple paths exist in the BGP table. Assuming the weights are the same, what will the next determining factor be?
- lowest origin type
- highest local preference
- locally originated
- lowest MED
- shortest AS_Path
89. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast summary command on a router to check the adjacency state with a neighbor router. The value under the State/PfxRcd field shows Idle. Which statement describes the status of adjacency between the two routers?
- A three-way TCP handshake is complete but the adjacency has not formed because the neighbor router has not responded to the open message.
- Because there is no Layer 3 connectivity between the two routers, the adjacency is not formed.
- The adjacency is successfully formed and the router is waiting for messages from the neighbor router.
- The adjacency is formed, but no prefix has been received from the neighbor router.
90. Refer to the exhibit. A user has configured a NIC on the PC as shown but finds that the PC is unable to access the Internet. What is the problem?
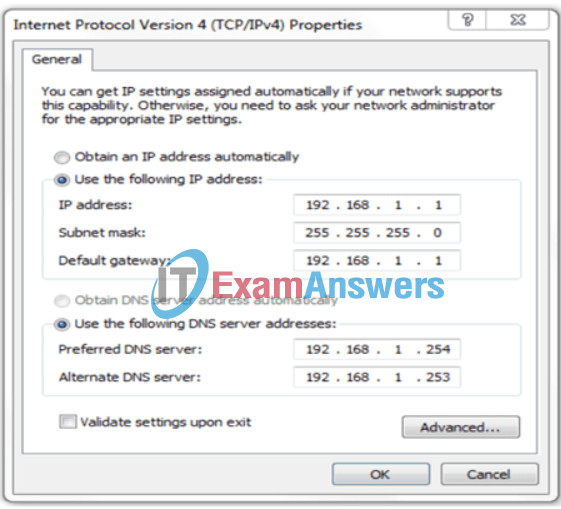
- There should not be an alternate DNS server.
- The preferred DNS address is incorrect.
- The default gateway address is incorrect.
- The settings were not validated upon exit.
91. Refer to the exhibit. For the given topology, what are three results of the OSPF DR and BDR elections ? (Choose three.)
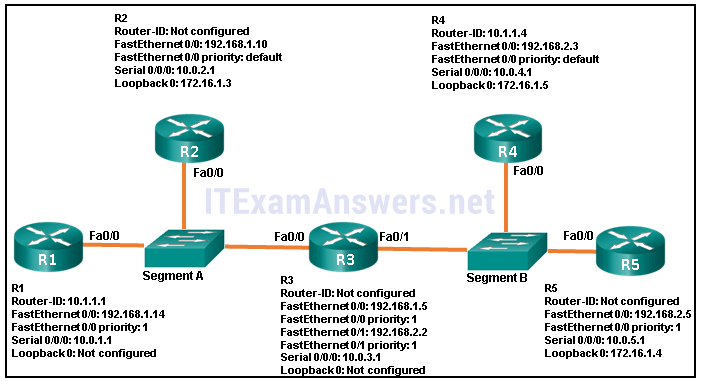
- R1 is BDR for segment A.
- R4 is DR for segment B.
- R2 is DR for segment A.
- R5 is BDR for segment B.
- R3 is DR for segment B.
- R3 is DR for segment A.
92. Consider the following access list that allows IP phone configuration file transfers from a particular host to a TFTP server:
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit udp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 range 1024 5000 R1(config)# access-list 105 deny ip any any R1(config)# interface gi0/0 R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out
Which method would allow the network administrator to modify the ACL and include FTP transfers from any source IP address?
- R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# no ip access-group 105 out
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 21
R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out - R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 21 - R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# no ip access-group 105 out
R1(config)# no access-list 105
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit udp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 range 1024 5000
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 21
R1(config)# access-list 105 deny ip any any
R1(config)# interface gi0/0
R1(config-if)# ip access-group 105 out - R1(config)# access-list 105 permit udp host 10.0.70.23 host 10.0.54.5 range 1024 5000
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 20
R1(config)# access-list 105 permit tcp any host 10.0.54.5 eq 21
R1(config)# access-list 105 deny ip any any
93. What is the reason for a network engineer to alter the default reference bandwidth parameter when configuring OSPF?
- to force that specific link to be used in the destination route
- to more accurately reflect the cost of links greater than 100 Mb/s
- to enable the link for OSPF routing
- to increase the speed of the link
94. Refer to the exhibit. A network technician issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast summary command on router R1 to verify the BGP state with the neighbor. Which scenario would cause a neighbor relationship to fail?

- There is no route in the routing table to reach the neighbor on one or both routers.
- The path to the neighbor at 10.1.13.3 is through the default route.
- The BGP table has not been exchanged.
- The AS number used in the neighbor configuration is wrong.
95. Which capability is supported by all three DMVPN phase models?
- direct spoke-to-hub communication
- spoke-to-spoke between DMVPN networks
- direct spoke-to-spoke communication
- on-demand VPN tunnels between spokes
96. What characterizes an EIGRP stub site feature?
- The stub functionality can be passed to a branch site that has multiple edge routers.
- It prevents downstream routers from receiving and advertising network prefixes across the WAN.
- It works by identifying the Ethernet interfaces and then setting an EIGRP stub site identifier.
- EIGRP neighbors on WAN links send EIGRP queries to the remote site when a route becomes active.
97. Refer to the exhibit. Why did R1 and R2 not establish an adjacency?
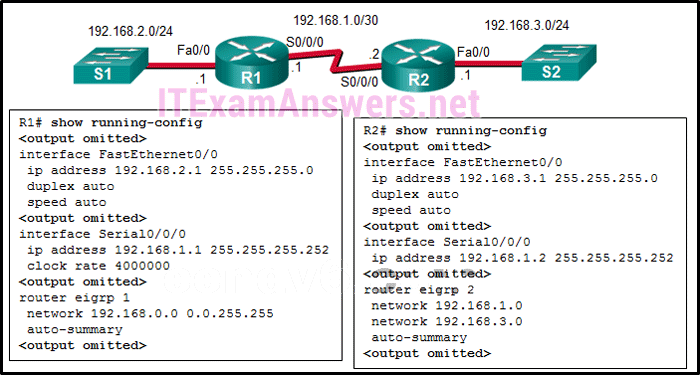
- The no shutdown command is misapplied on both routers.
- The AS number must be the same on R1 and R2.
- The router ID must be the same on both routers.
- R1 S0/0/0 and R2 S0/0/0 are on different networks.
- The link-local address must be the same on both routers.
98. An administrator needs to configure a router to perform conditional forwarding of packets based on packet characteristics in addition to the destination IP address. Which technology does the administrator need to configure?
- Multiprotocol Label Switching
- route redistribution
- policy based routing
- virtual routing and forwarding
99. What is a requirement for member routers in a BGP peer group?
- They must use a loopback interface to establish a BGP session.
- They must be of the same model.
- They must form a fully meshed connection.
- They must be of the same BGP session type.
100. In order to limit spoofed packets on a network, a network administrator is configuring uRPF on a Cisco router interface with the ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx command. After the configuration is completed, the administrator observes that valid packets are being dropped. What may be causing this packet discard?
- The uRPF is configured with loose mode and asymmetric routing occurs.
- The uRPF is configured with strict mode and symmetric routing occurs.
- The return traffic used a different path to that used by the source traffic.
- The same path is used for the source traffic and the return traffic.
101. A device has been assigned the IPv6 address of 2001:0db8:cafe:4500:1000:00d8:0058:00ab/64. Which is the network identifier of the device?
- 2001:0db8:cafe:4500:1000
- 2001:0db8:cafe:4500:1000:00d8:0058:00ab
- 1000:00d8:0058:00ab
- 2001:0db8:cafe:4500
- 2001
102. A network administrator is teaching a junior network engineer about EIGRP stub routers. Which two explanations can be given to the junior engineer about the subject? (Choose two.)
- An EIGRP stub router advertises only connected routes by default.
- An EIGRP stub router receives queries from EIGRP when a route goes active.
- An EIGRP stub router does not advertise routes that it learns from other EIGRP peers.
- An EIGRP stub router announces that it is a stub router within the EIGRP query packet.
- An EIGRP stub router can be configured only to receive routes.
103. Which is the correct order of the four steps to configure CoPP on a Cisco router?
1) Configure extended ACLs to identify specific granular traffic.
2) Configure the class map to define interesting traffic.
3) Configure a policy map to apply actions to the identified traffic.
4) Configure a service policy to identify which interface should be activated for the service.
1) Configure a service policy to identify which interface should be activated for the service.
2) Configure extended ACLs to identify specific granular traffic.
3) Configure the class map to define interesting traffic.
4) Configure a policy map to apply actions to the identified traffic.
1) Configure extended ACLs to identify specific granular traffic.
2) Configure the class map to define interesting traffic.
3) Configure a service policy to identify which interface should be activated for the service.
4) Configure a policy map to apply actions to the identified traffic.
1) Configure a policy map to apply actions to the identified traffic.
2) Configure a service policy to identify which interface should be activated for the service.
3) Configure extended ACLs to identify specific granular traffic.
4) Configure the class map to define interesting traffic.
104. Which are two characteristics of the stub feature in EIGRP ? (Choose two.)
- It stops the hub router from propagating dynamically learned EIGRP prefixes to the stub routers.
- It stops the hub router from sending queries to the stub router.
- It prevents routing loops by using the split-horizon rule.
- It stops the stub router from sending queries to IPv6 peers.
- It stops the stub router from propagating dynamically learned EIGRP prefixes to the hub routers.
105. Which three requirements are necessary for two OSPFv2 routers to form an adjacency? (Choose three.)
- The OSPF hello or dead timers on each router must match.
- The link interface subnet masks must match.
- The OSPFv2 process ID must be the same on each router.
- The two routers must include the inter-router link network in an OSPFv2 network command.
- The OSPFv2 process is enabled on the interface by entering the ospf process area-id command.
- The link interface on each router must be configured with a link-local address.
106. When creating an IPv6 static route, when must a next-hop IPv6 address and an exit interface both be specified?
- when the static route is a default route
- when the next hop is a link-local address
- when the exit interface is a point-to-point interface
- when CEF is enabled
107. Refer to the exhibit. Which two conclusions can be derived from the output? (Choose two.)

- There is one feasible successor to network 192.168.1.8/30.
- The network 192.168.10.8/30 can be reached through 192.168.11.1.
- The reported distance to network 192.168.1.0/24 is 41024256.
- The neighbor 172.16.6.1 meets the feasibility condition to reach the 192.168.1.0/24 network.
- Router R1 has two successors to the 172.16.3.0/24 network.
108. A network engineer has manually configured the Hello interval to 15 seconds on an interface of a router that is running OSPFv2. By default, how will the Dead interval on the interface be affected?
- The Dead interval will not change from the default value.
- The Dead interval will now be 15 seconds.
- The Dead interval will now be 30 seconds.
- The Dead interval will now be 60 seconds.
109. What command specifies a BGP neighbor that has an IP address of 5.5.5.5/24 and that is in AS 500?
- (config-router)# neighbor 5.5.5.5 remote-as 500
- (config-router)# network 5.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
- (config-router)# router bgp 500
- (config-router)# neighbor 500 remote-as 5.5.5.5
110. In a mulitarea OSPF internetwork, which route source descriptor is used to denote the best paths within the internetwork that are as a result of processing type 3 and type 4 LSAs?
- O E1
- O IA
- O
- O E2
111. Refer to the exhibit. Which two networks contain feasible successors? (Choose two.)
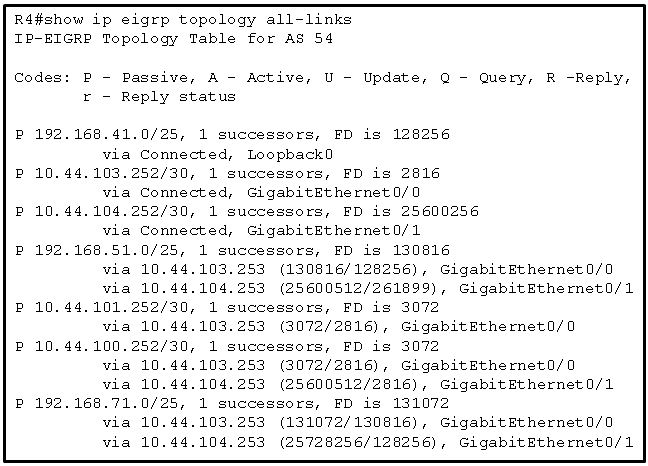
- 192.168.71.0
- 192.168.51.0
- 10.44.100.252
- 10.44.104.253
- 10.44.101.252
112. Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has issued the verification command while troubleshooting a routing loop on the network. What is the error in the configuration?

- The redistribute command is issued to filter routes using the route map instead of the prefix list.
- The route map is dropping all other routes that do not match the prefix list TAG_172.16.0.0.
- The match ip address command refers to the incorrect network prefix.
- The prefix list of TAG_172.16.0.0 is configured with an invalid sequence number.
113. How is a DHCPDISCOVER transmitted on a network to reach a DHCP server?
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the broadcast IP address as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with a multicast IP address that all DHCP servers listen to as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the IP address of the default gateway as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the IP address of the DHCP server as the destination address.
114. Refer to the exhibit. What can the field engineer conclude about the EIGRP authentication between RouterA and RouterB?
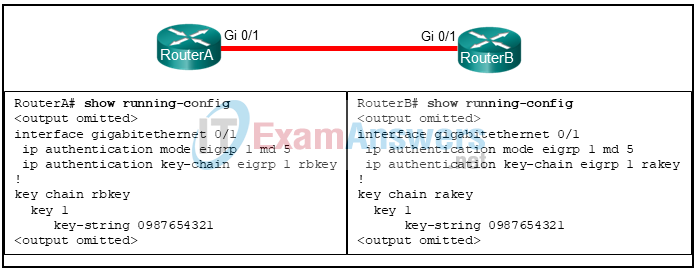
- Authentication will succeed and EIGRP updates can be exchanged.
- Authentication will fail because the key chain names do not match.
- Authentication will fail because the key chain names must match the router names.
- Authentication will fail because only one key is configured.
115. What are two features of OSPF interarea route summarization? (Choose two.)
- Route summarization results in high network traffic and router overhead.
- Routes within an area are summarized by the ABR.
- Type 3 and type 5 LSAs are used to propagate summarized routes by default.
- ASBRs perform all OSPF summarization.
- ABRs advertise the summarized routes into the backbone.
116. Refer to the exhibit. What kind of OSPF authentication has been configured on this interface?
- simple
- null
- plain text
- MD5
117. A network administrator needs to learn information about EIGRP load balancing to configure an EIGRP network. Which piece of information is accurate about this subject?
- The variance multiplier is obtained by dividing the successor route metric by the feasible successor metric.
- Any feasible distance of a feasible successor with a metric above the EIGRP variance value is installed into the RIB.
- The maximum equal-cost multipathing routing for EIGRP is four routes.
- The EIGRP variance value is the feasible distance for a route multiplied by the EIGRP variance multiplier.

Still valid?
is this still valid mate. How was your exam?
Is it still valid?
Yes, still valid, you will get high score
is this still valid plz reply me
Yes, still valid
Are the specific questions also valid for the exam?
Yes, still valid.
This is the correct option for Q25
“IPsec: An IKE session is established but …”
the literal explanation proves the answer is wrong for Question 9
New questions are very available, when can you put in the effort and upload them?
Surely new questions can be uploaded???
There are new questions, when will it be updated?
are these still valid? which file do you guys study to prepare for the enarsi test? please guide
25
*40$ – originated in AS 40 / was born in
^40* – directly connected AS / received from
…bad question.
plz post all quiz
When are more questions coming?
Where are The rest of The questions. There should be like 200?
24
10.0.32.0-10.0.63.0
/24-/26
10.0.62.0/25
Is this right?
Is there a valid dump for the ENARSI exam?
can’t wait! :-)
Sorry, hope you can share :(
A friend sent me something…give me mail….I’ll sent you and u publish?
[email protected]
Thank you!
PDFs sent.
This link goes to an unavailable page. Can you please double check?
Please can you share here