1. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator in autonomous system 65100 has set up a dual-homed BGP connection with an ISP. The administrator would like to influence the ISP router so that all traffic from the ISP enters the autonomous system through router R1. Which BGP attribute can the administrator configure on routers R1 and R2 to accomplish this?
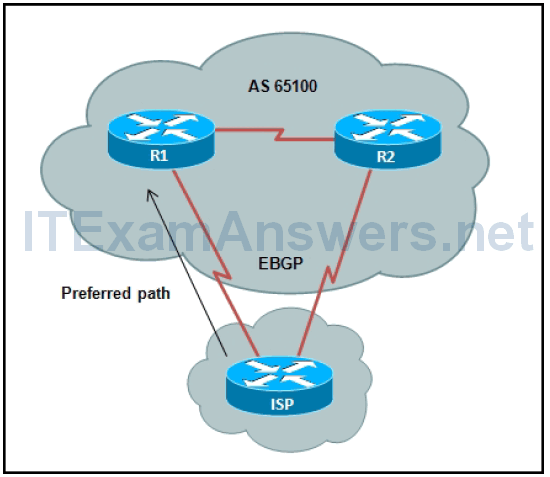
- multi_exit_discriminator
- next-hop
- aggregate
- weight
- local preference
2. Which two statements are key characteristics of BGP? (Choose two.)
- It uses bandwidth and delay as its metric.
- It is an advanced distance vector routing protocol.
- It is a policy-based routing protocol.
- It uses cost as its metric.
- It is a link-state routing protocol.
- It provides interdomain routing between autonomous systems.
3. Refer to the exhibit. Autonomous system 65500 is routing traffic between two external BGP autonomous systems, autonomous system 65200 and autonomous system 65100. Synchronization is disabled on BGP in autonomous system 65500. Which routers should have IBGP peer relationships for routing between autonomous system 65200 and autonomous system 65100 to work properly?
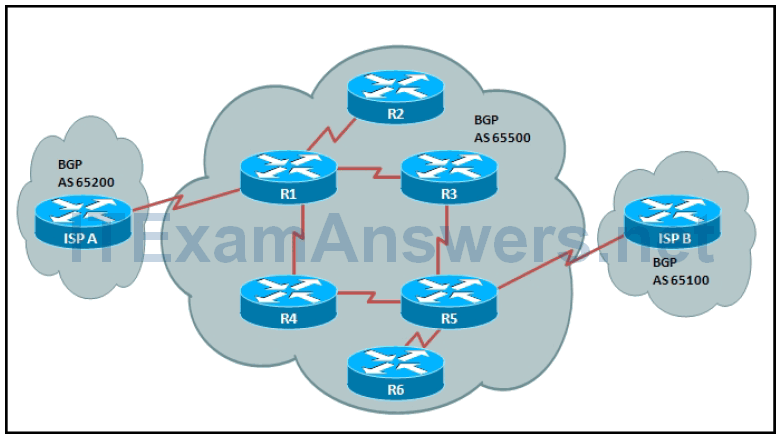
- ISP A, R1, R5, and ISP B
- R1, R3, R4, and R5
- R1 and R5
- R1, R3, and R4
4. Which BGP attribute is used by BGP to ensure a loop-free topology on the Internet?
- Origin
- Next_hop
- As_path
- local preference
- Atomic aggregate
5. Which BGP attribute can be configured on IBGP speakers so they will choose a desired path out of the autonomous system to an outside network?
- MED
- aggregate
- next hop
- local preference
6. Which routes are available to a BGP speaker to advertise to peers once an adjacency is formed?
- any route in either the IP routing table or BGP forwarding database
- only BGP routes in the IP routing table
- only routes that are learned from IBGP peers in the same autonomous system
- only routes in the BGP forwarding database
7. Which three statements are true of IBGP peers? (Choose three.)
- Once BGP peers exchange full BGP routing tables, only incremental updates are sent when routing tables change.
- Updates between peers are sent using Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP).
- IBGP peers must be directly connected.
- Routes learned from an IBGP peer are not propagated to other IBGP peers.
- A TCP session must be established before a peer adjacency is made.
8. Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true?
RTA(config)# router bgp 100 RTA(config-router)# neighbor 190.10.50.1 remote-as 100 RTA(config-router)# neighbor 170.10.20.2 remote-as 300 RTA(config-router)# network 150.10.0.0
- RTA is going to advertise that it is part of AS 300.
- The neighbor at 170.10.20.2 is an internal peer.
- RTA is going to advertise network 150.10.0.0 to its neighbors if 150.10.0.0 or its subnets are in the IP routing table.
- The neighbor at 190.10.50.1 is an external peer.
9. Which BGP routers will become peers and share routing information?
- BGP routers that are configured with the same peer command
- BGP routers that are configured with the same network command
- BGP routers that are configured with the neighbor command
- BGP routers share routing information with all routers in the same AS by default.
10. Refer to the exhibit. Which two configurations will allow router R1 to establish a neighbor relationship with router R2? (Choose two.)
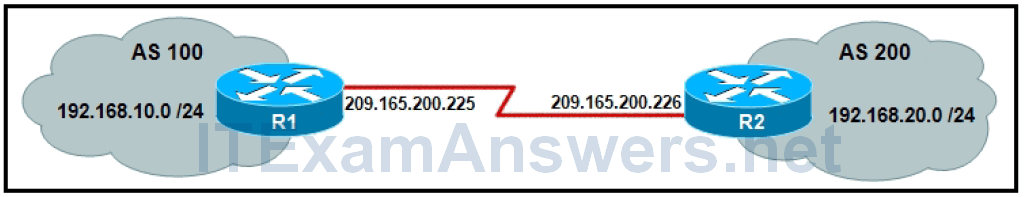
R1(config)# router bgp 200
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.20.0
R1(config-router)# neighbor 209.165.200.225 remote-as 100
R1(config)# router bgp 100
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.20.0
R2(config)# router bgp 200
R2(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0
R2(config-router)# neighbor 209.165.200.226 remote-as 200
R2(config)# router bgp 200
R2(config-router)# network 192.168.20.0
R2(config-router)# neighbor 209.165.200.225 remote-as 100
R1(config)# router bgp 100
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0
R1(config-router)# neighbor 209.165.200.226 remote-as 200
R2(config)# router bgp 200
R2(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0
11. Referto the exhibit. BGP sessions are established between all routers. RTC receives route updates for network 209.165.200.224/27 from autonomous system 300 with the weight attribute set to 3000. RTB also learns about network 209.165.200.224/27 from autonomous system 200 with a weight of 2000. Which router will be used by RTA as a next hop to reach this network?
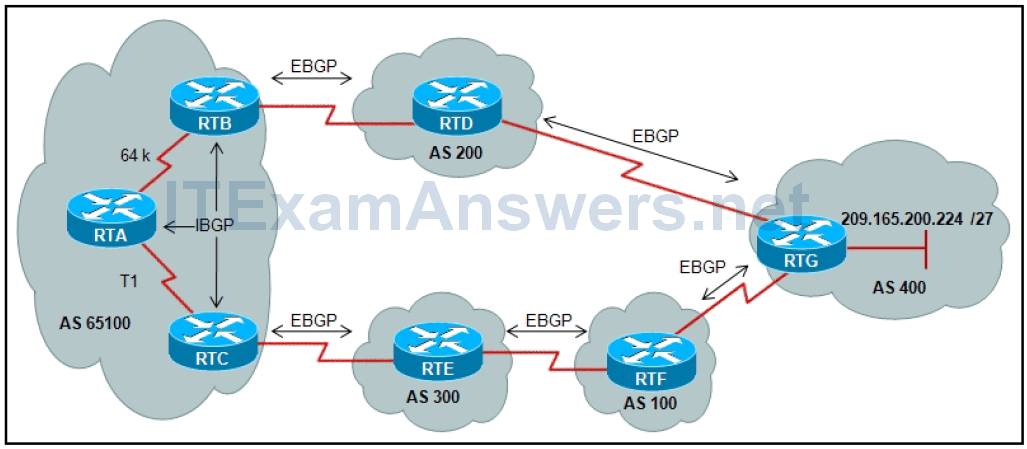
- RTC because of the highest weight
- RTC because of the T1 link
- RTB because of the slow 64 kb/s link
- RTB because of the shortest AS_Path
- RTC because of the longest AS_Path
- RTB because of the lowest weight
12. Which command would force a router to inject a route into BGP?
- summary
- route-inject
- network
- router bgp network
13. Refer to the exhibit. BGP sessions are established between all routers. Router RTC has the local preference for network 209.165.200.224/27 set to 200 and router RTB has a local preference set to 150 for the same network. Which router will be used by RTA as a next hop to reach network 209.165.200.224/27?
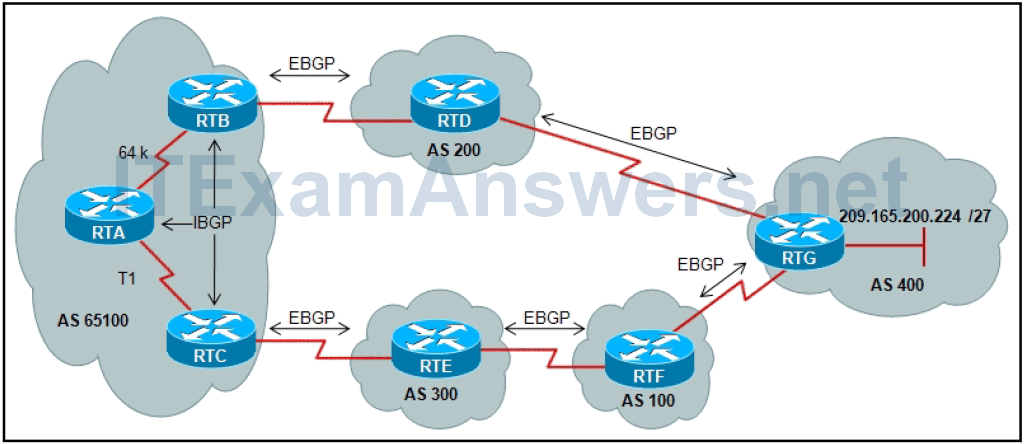
- RTC because of the T1 link
- RTC because of the highest local preference
- RTB because of the lowest local preference
- RTB because of the slow 64 kb/s link
- RTB because of the shortest AS_Path
- RTC because of the longest AS_Path
14. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the show ip bgp summary and debug ip bgp output, which two statements must be true? (Choose two.)
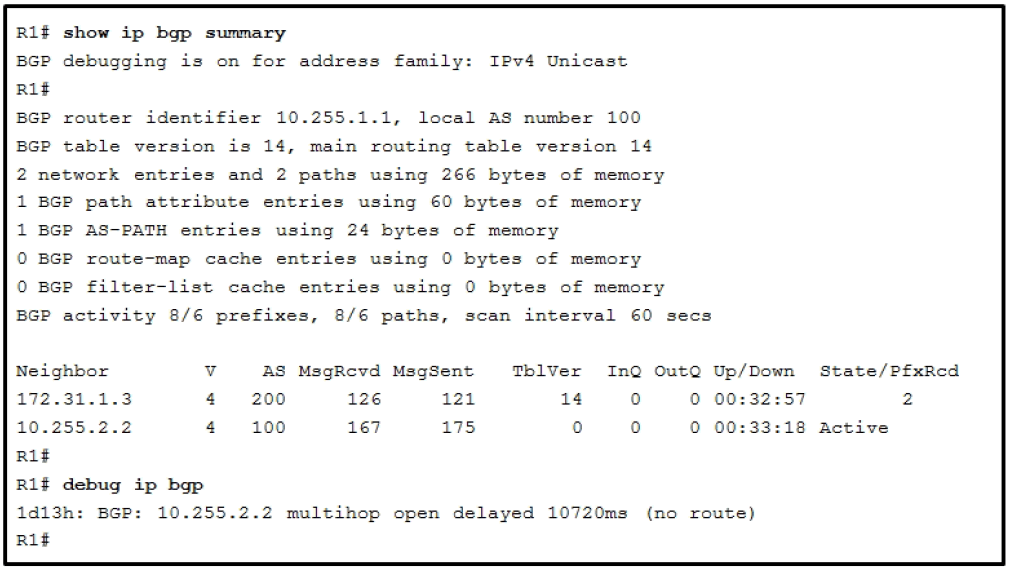
- R1 is directly connected to an IBGP peer.
- R1 cannot route BGP packets to 10.255.2.2.
- The router at 10.255.2.2 is an EBGP peer.
- The ebgp multi-hop command is missing from the BGP configuration.
- R1 has established an EBGP peering relationship.
15. Refer to the exhibit above. RTB receives an EBGP advertisement from RTD. When propagated into AS 65100 by IBGP, which router would be used as the next hop for RTC?
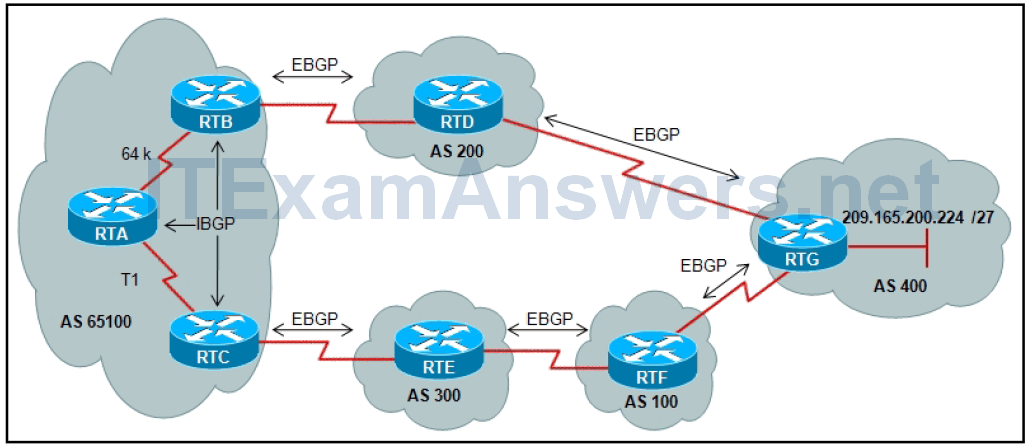
- RTD
- RTC
- RTA
- RTB
16. Which statements is not correct regarding MP-BGP?
- Neighbors must be activated with the address family using the neighbor activate command
- IPv4 can be used as the BGP transport for both IPv4 and IPv6 sessions
- A single BGP forwarding table is used for both IPv4 and IPv6 address families
- The show bgp all neighbors command can be used to show BGP neighbor adjacencies for IPv4 and IPv6
17. What are the characteristics of using the neighbor ip-address update-source command with a loopback address? (Choose two.)
- For IBGP, it allows the IGP to use the best path to the loopback address
- The neighbor command is configured using the neighbor’s loopback address
- It can only be used with IBGP
- The loopback address does not need to be reachable by TCP
