1. The help desk receives several calls on Monday morning stating that users cannot connect to a local print server that was working on Friday. Which statement about the problem would be correct?
- The inability to connect to the print server is a symptom of a problem.
- The inability to connect to the print server caused the problem.
- The connectivity problem occurred Monday morning.
- The inability to connect to the print server is the problem.
2. Which condition is a symptom of a connectivity issue on a router that provides access to the Internet?
- An interface status is down.
- A static route is misconfigured.
- An incorrect network statement exists.
- A cable is unplugged.
3. What is a symptom of an incorrectly applied network command when issued under the routing process?
- a down status on an interface
- a user who is unable to connect to machines that are located on the same subnet
- a routing protocol that is not running
- a timeout message when attempting to ping a device on another network
4. What is an important element of troubleshooting, regardless of the method used?
- spending a significant amount of time analyzing the information
- using a single troubleshooting process
- following a structured and systematic process
- executing the steps in the same order every time
5. A user creates a trouble ticket indicating that the Internet is inaccessible. The network administrator receives the ticket and determines that this user is the only one having problems. A ping command issued from the administrative PC to the user PC is successful. What should the administrator do next?
- Escalate the issue to the desktop support group.
- Contact the ISP to determine if there is an issue on the ISP side.
- Swap out the patch cable between the user PC and the switch to determine if that solves the problem.
- View the route table on the core router to determine if there is a routing issue.
6. What is a benefit of change control during the processes of regular network maintenance?
- elimination of the need to perform a regular network backup
- reduction in the frequency and duration of unplanned outages
- simplification of the process for creating a network baseline
- elimination of the need to troubleshoot planned outages
7. What is the first step of a structured troubleshooting process?
- Analyze information and eliminate possibilities.
- Solve the problem.
- Gather facts.
- Propose and test a hypothesis.
- Define the problem.
8. Refer to the exhibit. What principles are depicted in the exhibit?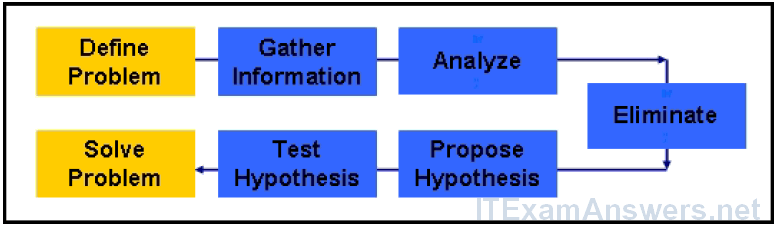
- the main path traffic follows in the network
- the main subprocesses of structured troubleshooting
- the main phases of the divide and conquer troubleshooting process
- the main phases of communication and change control
9. Which element forms the basis of a good problem description?
- description of observed symptoms
- impact of observed symptoms on productivity
- conclusions about observed symptoms
- interpretation of observed symptoms
10. What is a situation where escalation of an issue is inadvisable?
- Management has not been consulted.
- Escalation will slow the procedure.
- The problem has an impact on the performance of the entire network.
- Solving the problem would showcase the skills and knowledge of the troubleshooter.
- The problem is actually a set of problems.
11. During the troubleshooting of an issue, it is determined that the most probable cause of the issue is not within the administrator’s area of responsibility. What is the next step in the problem solving process?
- Test a hypothesis.
- Propose a solution.
- Escalate.
- Gather information.
12. After a proposed solution has been implemented, the network administrator realizes that new problems have been introduced by the changes. What is the next step in the troubleshooting process?
- Determine an appropriate workaround.
- Escalate the problem to another department.
- Execute the rollback plan.
- Propose a hypothesis.
13. To correct an issue that was discovered a few days earlier, an administrator makes a change during a regularly scheduled maintenance window. After making the change, the administrator discovers that a new problem has occurred. What should the administrator do next?
- Gather information about the new problem and form a new hypothesis.
- Rollback the change and resume the troubleshooting process.
- Continue making changes until the symptoms disappear.
- Leave the change in place and troubleshoot the new problems at a later time.
14. What are two situations where escalation of a case is recommended? (Choose two.)
- when shift work requires handing off the problem
- when the end-user reporting the problem is a manager
- when there is an inability to clearly communicate the problem
- when there is a lack of desire to solve the issue
- when the cause of the problem is within the area of responsibility of the troubleshooter
- when insufficient knowledge and skills exist
15. In which structured troubleshooting process phase would a network engineer ask questions such as “When did it last work?” or “Has it ever worked?”
- propose a hypothesis phase
- gather facts phase
- solve the problem phase
- define the problem phase
- analyze information phase
- eliminate possibilities phase
16. In which phase of the structured troubleshooting process should a network administrator clearly communicate to the affected network users what is going to be done and why it is being done?
- the proposal and testing of a hypothesis
- the gathering of facts
- the analysis of information
- the definition of the problem
- the elimination of possibilities
