CCNP Enterprise: Advanced Routing (Version 8.0) – Routing Concepts and EIGRP Exam
1. Refer to the exhibit. What address should be configured on PC1 as its default gateway so that PC1 can communicate with File_server1?
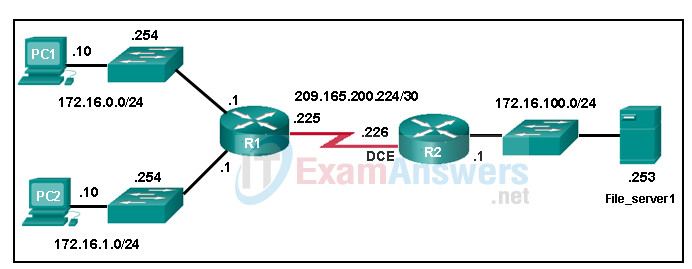
- 172.16.100.1
- 209.165.200.225
- 209.165.200.226
- 172.16.0.254
- 172.16.0.1
2. What would be the interface ID of an IPv6 enabled interface with a MAC address of 1C-6F-65-C2-BD-F8 when the interface ID is generated by using the EUI-64 process?
- 106F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- C16F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 0C6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 1E6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
3. A company uses the method SLAAC to configure IPv6 addresses for the workstations of the employees. A network administrator configured the IPv6 address on the LAN interface of the router. The interface status is UP. However, the workstations on the LAN segment did not obtain the correct prefix and prefix length. What else should be configured on the router that is attached to the LAN segment for the workstations to obtain the information?
- R1(config-if)# ipv6 nd other-config-flag
- R1(config-if)# ipv6 enable
- R1(config)# ipv6 dhcp pool < name of the pool >
- R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
4. What does a router use to determine which route from those installed in the routing table is chosen to forward packets?
- shortest prefix length
- lowest metric
- longest prefix length
- lowest administrative distance
5. A computer has to send a packet to a destination host in the same LAN. How will the packet be sent?
- The packet will be sent to the default gateway first, and then, depending on the response from the gateway, it may be sent to the destination host.
- The packet will be sent only to the default gateway.
- The packet will first be sent to the default gateway, and then from the default gateway it will be sent directly to the destination host.
- The packet will be sent directly to the destination host.
6. Match the types of EIGRP routes to the correct default administrative distances. (Not all options are used.)
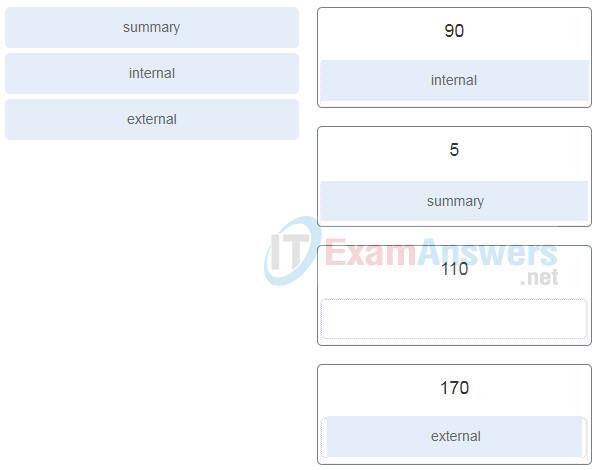
7. Which two statements accurately describe EIGRP tables? (Choose two.)
- Administrative distance is shown as a column in the neighbor table.
- A feasible successor route can be found in the topology table.
- The topology table shows whether a route is in the passive or active state.
- A successor route can only be found in the routing table.
- The routing table shows the amount of time elapsed since a router adjacency was formed.
- The neighbor table shows all adjacent Cisco devices.
8. Refer to the exhibit. R3 has two possible paths to the 172.16.99.0 network. What is the reported distance of the feasible successor route?
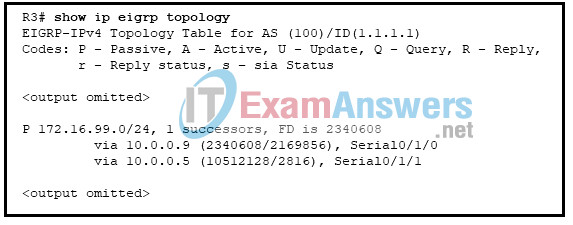
- 2340608
- 2816
- 10512128
- 2169856
9. Which two statements accurately describe an EIGRP successor route? (Choose two.)
- It is flagged as active in the routing table.
- It is the route with the highest path metric to reach a destination.
- It is saved in the topology table for use if the primary route fails.
- It may be backed up by a feasible successor route.
- It is used by EIGRP to forward traffic to the destination.
10. What two statements describe EIGRP authentication? (Choose two.)
- EIGRP authentication uses a pre-shared key.
- EIGRP authentication requires that both routers have the same key chain name.
- EIGRP authentication can protect updates from from a protected router to an unprotected one.
- EIGRP authentication uses the MD5 algorithm.
- EIGRP authentication uses varying levels of WEP to encrypt data exchanged between routers.
11. What is an EIGRP successor for a destination network?
- the next hop on the primary route with the smallest feasible distance to the destination
- the next hop on a backup route with the largest feasible distance to the destination
- the next hop on a backup route with the smallest feasible distance to the destination
- the next hop on the primary route with the largest feasible distance to the destination
12. What two values must match between two EIGRP directly connected neighbors to establish and maintain an adjacency? (Choose two.)
- router ID
- Area ID
- metric parameters
- hello timers
- autonomous system number
13. When would the network administrator use the ip bandwidth-percent eigrp as-number percent command?
- when the connection is serial instead of Ethernet
- when there is a low bandwidth connection
- when the connection is on a shared medium
- when the link is always busy
14. When an EIGRP router detects a topology change, how does the router notify neighbor routers that a new route calculation is required for a specific route?
- An EIGRP query packet is sent out with the delay set to infinity.
- An EIGRP update packet is sent out with a metric value of zero.
- A route withdrawal is sent out, notifying other neighbors to remove the route from the topology table.
15. Which command would limit the amount of bandwidth used by EIGRP for protocol control traffic to approximately 128 kbps on a 1.544 Mbps link?
- ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 100 25
- ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 100 8
- ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 100 40
- ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 100 30
16. Which action does split horizon use to reduce incorrect routing information?
- It limits the number of hops a packet can traverse through the network before the packet should be discarded.
- It marks routes as unreachable in routing updates sent to other routers.
- It prevents routers from accepting higher cost routes to networks previously marked as inaccessible before the timer expires.
- It prevents routers from advertising a network through the interface from which the update came.
17. Refer to the exhibit. The routing table on R2 does not include all networks that are attached to R1. The network administrator verifies that the network statement is configured to include these two networks. What is a possible cause of the issue?
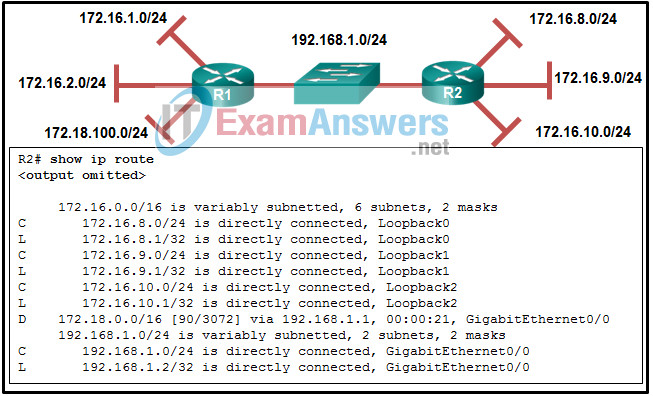
- The AS number does not match between R1 and R2.
- The no auto-summary command is missing in the R1 configuration.
- The interfaces that are connected to these two networks are configured as passive interfaces.
- The network statements should include the wild card mask.
18. What two actions will the EIGRP DUAL take if a link to a network goes down? (Choose two.)
- query neighbors for a new route
- search topology table for a feasible successor
- search routing table for a feasible successor
- put the route into passive mode
- run the SPF algorithm to find a new successor
19. Refer to the exhibit. Which two routes will be advertised to the router ISP if autosummarization is disabled? (Choose two.)
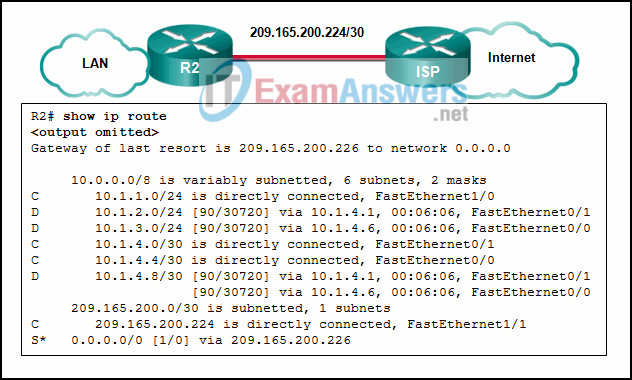
- 10.1.4.0/24
- 10.1.4.0/30
- 10.1.0.0/16
- 10.1.2.0/24
- 10.1.4.0/28
20. Two routers, R1 and R2, have established an EIGRP neighbor relationship, but there is still a connectivity problem. Which issue could be causing this problem?
- an access list that is blocking advertisements from other networks
- an authentication mismatch
- automatic summarization that is disabled on both routers
- a process ID mismatch
21. Refer to the exhibit. Remote users are experiencing connectivity problems when attempting to reach hosts in the 172.21.100.0 /24 network. Using the output in the exhibit, what is the most likely cause of the connectivity problem?
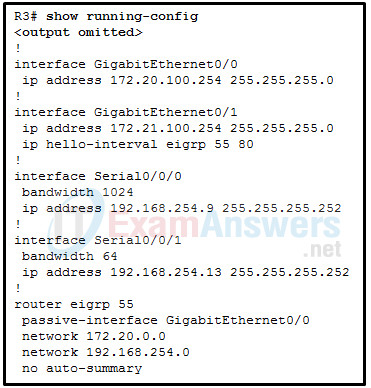
- The hello timer has been modified on interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 of R3 and not on the neighbor, causing a neighbor adjacency not to form.
- The GigabitEthernet interfaces are not limiting the flow of EIGRP message information and are being flooded with EIGRP traffic.
- The passive-interface command is preventing neighbor relationships on interface GigabitEthernet 0/0.
- The GigabitEthernet 0/1 interface is not participating in the EIGRP process.
22. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has issued the displayed commands. The EIGRP routing domain has completely converged and a network administrator is planning to configure EIGRP authentication throughout the complete network. On which two interfaces should EIGRP authentication be configured between R2 and R3? (Choose two.)
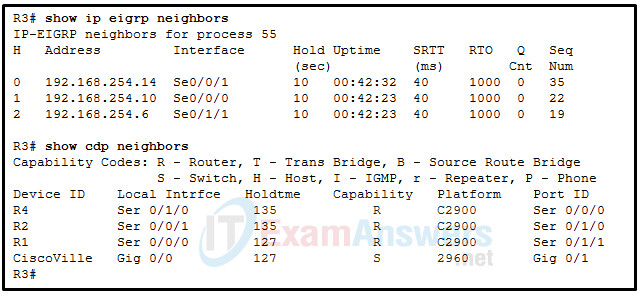
- serial 0/1/0 of R2
- serial 0/1/0 of R4
- serial 0/0/1 of R2
- gig 0/0 of R3
- serial 0/0/1 of R3
23. Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 are directly connected via their serial interfaces and are both running the EIGRP routing protocol. R1 and R2 can ping the directly connected serial interface of their neighbor, but they cannot form an EIGRP neighbor adjacency. What action should be taken to solve this problem?
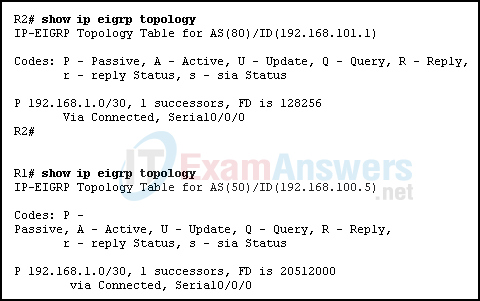
- Configure EIGRP to send periodic updates.
- Configure both routers with the same EIGRP autonomous system number.
- Configure the same hello interval between the routers.
- Enable the serial interfaces of both routers.
24. Refer to the exhibit. Considering that R2, R3, and R4 are correctly configured, why did R1 not establish an adjacency with R2, R3, and R4?
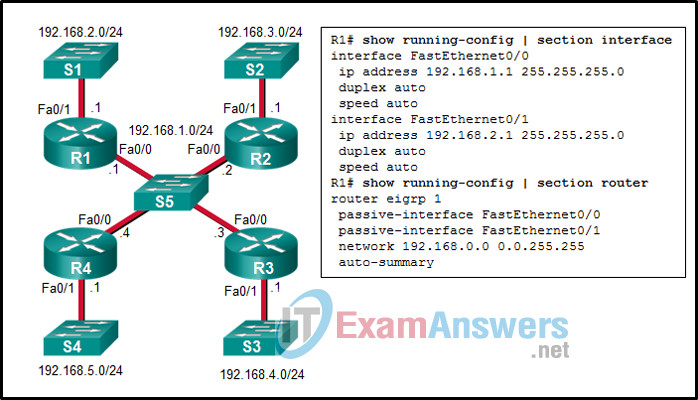
- because the Fa0/0 interface of R1 is declared as passive for EIGRP
- because the automatic summarization is enabled on R1
- because the IPv4 address on Fa0/0 interface of R1 is incorrect
- because there is no network command for the network 192.168.1.0/24 on R1
25. Which two protocols are allowed to be routed by EIGRP as a consequence of the PDM feature? (Choose two.)
- RTP
- UDP
- IPv6
- IPv4
- TCP
26. An administrator needs to verify if EIGRP has been configured correctly on a router. Which command can be used to display specific routes to verify if they were learned using EIGRPv6?
- show ipv6 route ipv6-address/prefix-length
- show ipv6 route
- show ipv6 eigrp neighbors
- show ipv6 route eigrp
27. Which multicast address is used by the EIGRPv6 process to form neighbor adjacencies?
- FF02::FA00:100
- FF02::2
- FF02::A
- FF02::1
28. An administrator is troubleshooting connectivity between two routers configured with EIGRPv6. The routing table, for both the respective routers, displays all the advertised networks and the authentication parameters for key ID and the key string match. Unfortunately, authentication fails between the two routers. What is a possible cause?
- a passive interface present on one of the routers
- mismatched valid times
- improperly configured timers.
- IPv6 not enabled on one connected interface
29. An administrator is troubleshooting a router in a mixed EIGRPv4 and EIGRPv6 network. Which command can be used to see if the split horizon rule has been applied to an interface for the IPv6 address family?
- show ipv6 eigrp interfaces
- show eigrp address-family ipv6 interfaces detail
- show eigrp address-family ipv6 interfaces
- show ipv6 protocols
30. What operational feature is different for EIGRP for IPv6 compared to EIGRP for IPv4?
- the source and destination addresses used within the EIGRP messages
- neighbor discovery mechanisms
- router ID configuration
- DUAL algorithm calculations
31. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a router for DHCPv6 operation. Which conclusion can be drawn based on the commands?
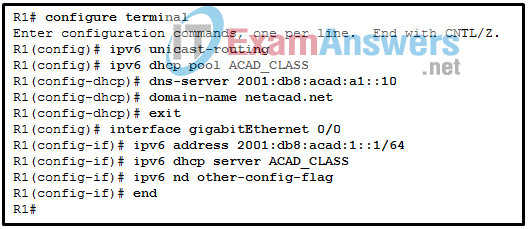
CCNP Enterprise: Advanced Routing ( Version 8.0) – Routing Concepts and EIGRP Exam 31
- The router is configured for stateless DHCPv6 operation.
- The DHCPv6 server name is ACAD_CLASS.
- The router is configured for stateful DHCPv6 operation, but the DHCP pool configuration is incomplete.
- Clients would configure the interface IDs above 0010.
32. Which ICMPv6 message type contains network configuration information for clients that are performing SLAAC?
- neighbor advertisement
- router advertisement
- neighbor solicitation
- router solicitation
33. Refer to the exhibit. Which set of commands will configure static routes that will allow the Park and the Alta routers to a) forward packets to each LAN and b) direct all other traffic to the Internet?
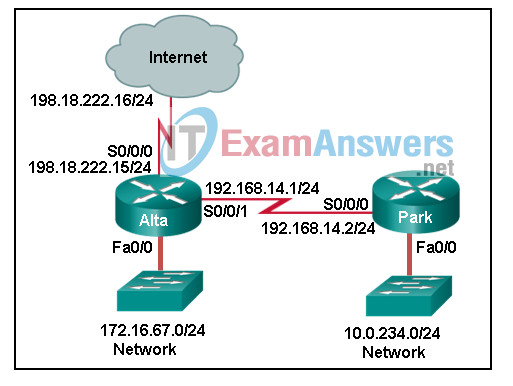
CCNP Enterprise: Advanced Routing ( Version 8.0) – Routing Concepts and EIGRP Exam 33
Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Alta(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
Park(config)# ip route 172.16.67.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Alta(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1
Park(config)# ip route 172.16.67.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.1
Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Park(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.14.1
Alta(config)# ip route 10.0.234.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.14.2
Alta(config)# ip route 198.18.222.0 255.255.255.255 s0/0/0
34. A network administrator wants to verify the default delay values for the interfaces on an EIGRP-enabled router. Which command will display these values?
- show running-config
- show ip protocols
- show interfaces
- show ip route
35. Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 has recently been configured to operate in an IPv6 only network and is connected via interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 to router R2. R2 is configured correctly, but will not form a neighbor relationship with R1 What is the problem?

CCNP Enterprise: Advanced Routing ( Version 8.0) – Routing Concepts and EIGRP Exam 35
- The IP address is missing on interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/0.
- The router ID has not been created on router R1.
- The EIGRPv6 process has not been activated on interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/0.
- The command ipv6 unicast-routing has not been implemented.
36. Which address will EIGRP for IPv6 use as the router ID?
- the highest IPv4 address that is configured on any enabled interface
- the highest link-local address that is configured on any enabled interface
- the highest interface MAC address
- the highest IPv6 address that is configured on any enabled interface
37. An administrator is troubleshooting two routers in an EIGRPv6 network. A route filter was applied on one of the routers and since then, routes are no longer being populated as expected. What two commands can be used to verify that the filter was applied correctly and to display the IPv6 prefix list? (Choose two.)
- show ipv6 protocols
- show access-lists ipv6
- show run | section ipv6 router eigrp
- show ipv6 prefix-list
- show ipv6 eigrp interfaces detail
38. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is attempting to install an IPv6 static route on router R1 to reach the network attached to router R2. After the static route command is entered, connectivity to the network is still failing. What error has been made in the static route configuration?
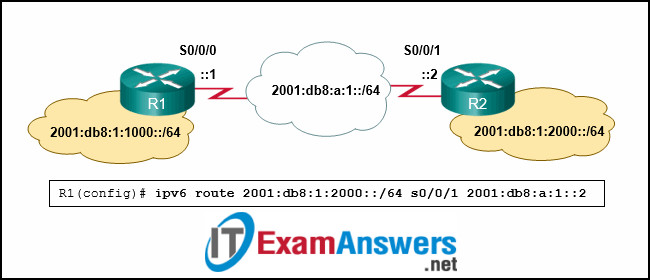
- The interface is incorrect.
- The next hop address is incorrect.
- The destination network is incorrect.
- The network prefix is incorrect.
39. Refer to the exhibit. Router CiscoVille has been partially configured for EIGRP authentication. What is missing that would allow successful authentication between EIGRP neighbors?

- The CiscoVille router requires a second keychain to function correctly when using two interfaces for EIGRP authentication.
- The keychain for EIGRP authentication must be configured on the interfaces.
- The interfaces that will use EIGRP authentication must be specified.
- A username and password must be configured.
40. Which configuration is necessary to ensure successful operation of EIGRP for IPv6?
- The router eigrp autonomous-system command is required within the router configuration mode.
- The eigrp router-id command requires an IPv6 address within the router configuration mode.
- The network command is required within the router configuration mode.
- The no shutdown command is required within the router configuration mode.
41. Which destination address is used by EIGRP for IPv6 messages?
- the 32-bit router ID of the neighbor
- the unique local IPv6 address of the neighbor
- the IPv6 global unicast address of the neighbor
- the all-EIGRP-routers link-local multicast address
42. Which two statements describe characteristics of EIGRPV6? (Choose two.)
- Route advertisement is configured under the interface configuration.
- Neighbor relationships are formed using the link-local address.
- EIGRPv6 supports only 64 bit addresses.
- Mismatched timers are not supported.
- Route advertisement is configured under the IPv6 router EIGRPv6 configuration.
- Neighbor relationships can be formed only on the configured IPv6 address.
43. Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP has been configured on all routers in the network. An EIGRP summary route is configured on the HQ router. How will packets destined for the 192.168.0.10/24 network be handled by router HQ?
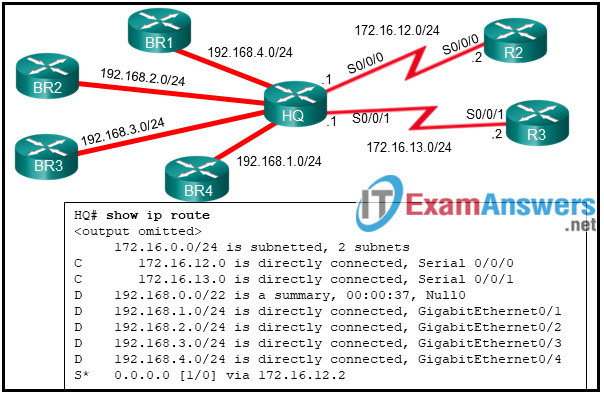
- The traffic will be forwarded to the BR1 and BR2 branch routers.
- The traffic will be forwarded to routers BR1, BR2, BR3, and BR4.
- The traffic will be forwarded to the BR3 and BR4 branch routers.
- The traffic will be forwarded to the Null0 interface and will be discarded.
- The traffic will be forwarded to router R2 using the default route.
44. When multiple routing protocols have a route to the same destination network, what determines which route is installed in the routing table?
- lowest hop count
- best metric
- lowest cost
- lowest administrative distance
- greatest available bandwidth

The correct answers of the question bellow are:
42. Which two statements describe characteristics of EIGRPV6? (Choose two.)
I fixed it, thank you very much!
The correct answers of the question bellow are:
42. Which two statements describe characteristics of EIGRPV6? (Choose two.)
42) – Which two statements describe characteristics of EIGRPv6? (Choose two.)The correct answers are
are these dumps still valid ?
At question 43 is this Valid
The traffic will be forwarded to the Nullo interface and will be discarded.
not
The traffic will be forwarded to the BR1 and BR2 branch routers
Added all, thanks for your sharing!
14 When multiple routing protocols have a route to the same destination network, what determines which route is installed in the routing table?
Hi Admin,
Is this a latest dump?
is that valid for you
Is this the latest dump?
Yes, it’s latest questions, if you have new question, please comment in here
Many thanks!!
are these valid dumps ? has anyone taken the exam yet? Please share your thoughts
Hi can you update anwser of examn, pleaseChapters 6 – 10: OSPF Exam … examn`s 11 14? 15-17? 18 – 20? 21 – 23? and final exman?
Updated: https://itexamanswers.net/ccnp-enterprise-enarsi-v8-exam-answers-advanced-routing.html
THX for information, you have other examns?
Updated: https://itexamanswers.net/ccnp-enterprise-enarsi-v8-exam-answers-advanced-routing.html