1. What effect does the global configuration command spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default have when enabled on an access switch?
- All PortFast enabled ports become designated ports.
- All PortFast enabled ports stop sending BPDUs, but if a BPDU is received on the port, the port gets out of the PortFast state, thereby disabling the BPDU filtering.*
- All PortFast enabled ports start participating in the spanning-tree calculations.
- All switch ports start filtering the superior BPDUs coming from other switches and the
access switch becomes a root bridge.
2. What are three important steps in troubleshooting STP problems? (Choose three.)
- Capture traffic on a saturated link and check whether identical frames are traversing multiple links.*
- Check each side of a point-to-point link for duplex mismatch.*
- Adjust BPDU timers so that there is less overhead traffic on the switching fabric.
- Administratively disable ports that should be blocking and check to see if connectivity is restored.*
- Administratively disable multicasting and check to see if connectivity is restored.
- Administratively create bridge loops and see what path the traffic takes.
3. Which STP timer defines the length of time spent in the listening and learning states?
- hello time
- forward aging
- forward delay*
- max age
- max delay
4. What priority value should be entered on a switch, via the spanning-tree vlan 20 priority priority command, if the desired priority for VLAN 20 is 4116?
- 4116
- 4106*
- 4096
- 32788
5. Refer to the exhibit. Switch SW1 is receiving traffic from SW2. However, SW2 is not receiving traffic from SW1. Which STP feature should be implemented to prevent inadvertent loops in the network?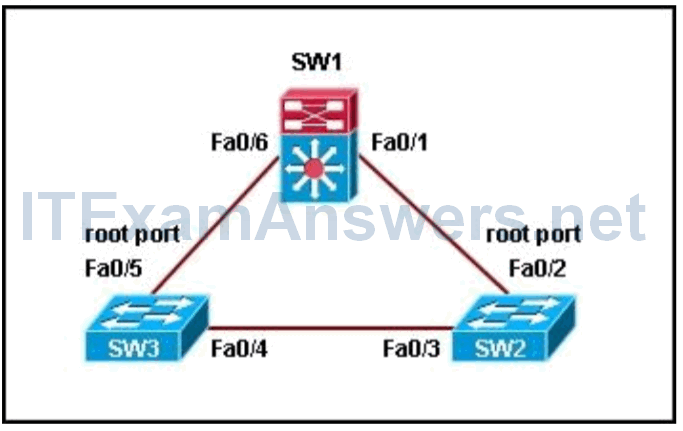
- PortFast
- BPDU filtering
- UDLD*
- BPDU guard
6. Which statement is true about the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
- With each network change, the STP algorithm is run on all switches that have a root port.
- Each switch determines a designated port that provides the best path to the root switch.
- The designated port will be on the switch with the best path to the root switch.*
- A topology change will cause the switch where the change occurred to send messages
about the change throughout the tree.
7. Which protocol should an administrator recommend to manage bridged links when the customer requires a fully redundant network that can utilize load balancing technologies and reconverge on link failures in less than a second?
- IEEE 802.1D(STP)
- IEEE 802.1Q (CST)
- Cisco PVST+
- IEEE 802.1s (MST)*
8. Which three parameters should match all switches within an MST region? (Choose three.)
- configuration name*
- VLAN-to-instance mappings*
- revision number*
- bridge priority
- port costs on trunk ports
- trunk encapsulation method
9. Assuming that all switches in a network have the default bridge priority for each MST instance, what effect does the command spanning-tree mst 10 root primary have when entered on a single switch?
- sets the bridge priority on the switch to 24582 for MST instance 10
- sets the bridge priority on the switch to 24576 for MST instance 10*
- sets the bridge priority on the switch to 28672 for MST instance 10
- sets the bridge priority on the switch to 24586 for MST instance 10
10. Which protocol extends the IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree (RST) algorithm to multiple spanning trees?
- CST
- STP
- RSTP+
- MST*
11. Refer to the exhibit. What conclusion does the output support?
- Standard IEEE 802.1D behavior is shown.*
- IEEE 802.1w is enabled on VLAN 1.
- PortFast is enabled on interface Fa0/6.
- The forward delay timer has been changed from the default value.
12. Refer to the exhibit. After the sequence of commands is entered, how many VLANs will be assigned to the default instance?
- 4064
- 4094
- 4062
- 4061*
13. Which interfaces should loop guard be enabled on?
- designated ports
- root port and alternate ports*
- root port and ports configured with PortFast
- root ports
- ports configured with PortFast
14. One switch in a Layer 2 switched spanning-tree domain is converted to PVRST+ using the spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst global configuration mode command. The remaining switches are running PVST+. What is the effect on the spanning-tree operation?
- Spanning tree is effectively disabled in the network.
- All switches default to one 802.1D spanning tree for all VLANs.
- The PVRST+ switch forwards 802.1D BPDUs, but do but does not participate as a node in any
spanning tree. - The PVSRT+ reverts to PVST+ to interoperate with the PVST+ switches.*
15. Refer to the exhibit. What implementation of spanning tree best describes the spanning-tree operational mode of the switch?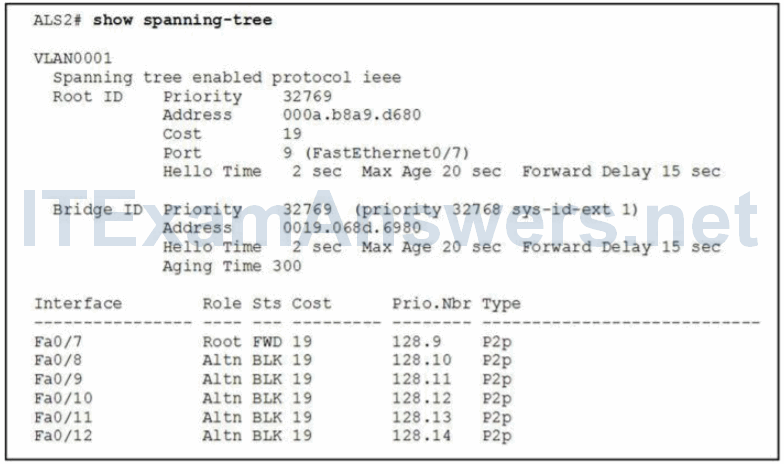
- PVRST+
- IEEE 802.1D*
- IEEE 802.1s
- IEEE 802.w
16. Refer to the exhibit. What two conclusions does the output show to be true? (Choose two.)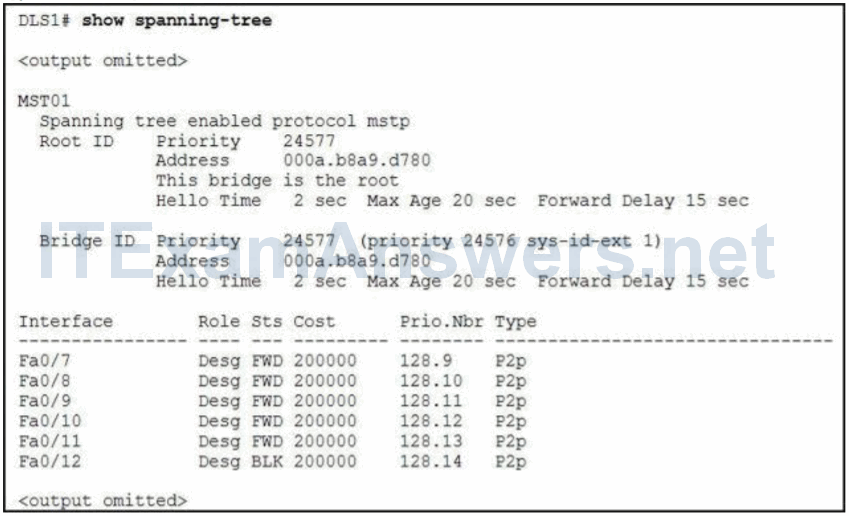
- DLS1 is running IEEE 802.1s on instance 1.*
- Interface Fa0/12 will move into the errdisable state if a BPDU is received.
- DLS1 is running IEEE 802.1D on instance 1.
- DLS1 is the root bridge for instance 1.*
- Interfaces Fa0/1 through Fa0/6 are trunk ports.
17. Refer to the exhibit.
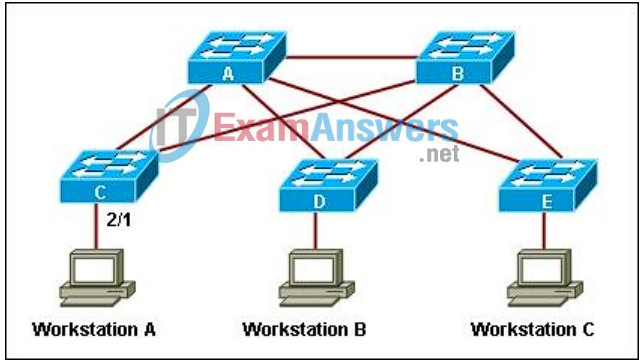
STP is configured on all switches in the network. Recently, the user on workstation A lost connectivity to the rest of the network. At the same time, the administrator received the console message:
%SPANTREE-2-RX_PORTFAST:Received BPDU on PortFast enable port.Disabling 2/1
What is the cause of the problem?
- The STP PortFast BPDU Guard feature has disabled port 2/1 on the switch.*
- PAgP has removed port 2/1 from the EtherChannel bundle.
- STP PortFast feature has been enabled on port 2/1.
- STP PortFast feature has been disabled on port 2/1.
18. Which two statements are true about STP root guard? (Choose two.)
- Root guard is enabled on a per-port basis.*
- If a root guard enabled port receives a inferior BPDU from a nonroot switch, the port transitions to the blocking state to prevent a root bridge election.
- Root guard requires that PortFast be enabled on a switch port.
- Root guard re-enables a switch port once it stops receiving superior BPDUs.*
- Root guard should be configured on all ports on the desired root bridge to prevent another bridge from becoming the root.
19. Refer to the exhibit. STP is enabled on all switches in the network. The port on switch A that connects to switch B is half duplex. The port on switch B that connects to switch A is full duplex. What are three problems that this scenario could create? (Choose three.)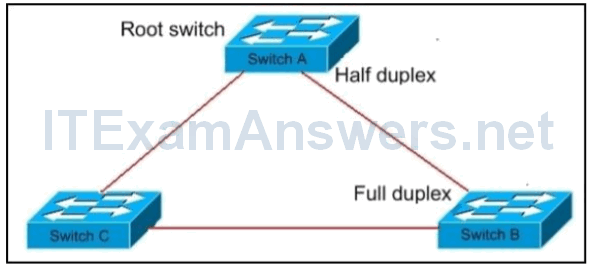
- Switch B may unblock its port to switch C, thereby creating a loop.*
- Switch A is performing carrier sense and collision detection, and switch B is not.*
- Autonegotiation results in both switch A and switch B failing to perform carrier sense.
- Spanning tree will keep re-calculating, thereby consuming all the CPU normally used for traffic.
- BPDUs may not successfully negotiate port states on the link between switch A and switch B.*
- Switch B will become the root switch.
20. Users complain that they lost connectivity to all resources in the network. A network administrator suspects the presence of a bridging loop as a root cause of the problem. Which two actions will determine the existence of the bridging loop? (Choose two.)
- Capture the traffic on the saturated link and verify if duplicate packets are seen.*
- Verify that the management VLAN is properly configured on all root bridges.
- Check the port utilization on devices and look for abnormal values.*
- Confirm MAC port security is enabled on all access switches.
- Ensure that the root guard and loop guard are properly configured on all distribution links.
21. What happens when a switch running IEEE 802.1D receives a topology change message from the root bridge?
- The switch uses the forward delay timer to age out entries in the MAC address table.*
- The switch uses the hello to age out entries in the MAC address table.
- The switch uses the forward delay and the max-age timer to age out entries in the MAC address table.
- The switch uses the max-age timer to age out entries in the MAC address table.
22. What three fields are included in a BPDU? (Choose three.)
- cost of path
- link-state ID
- port ID
- bridge ID (Priority + MAC address)
- STP ID
23. What will happen when a BPDU is received on a loop guard port that is in a loop-inconsistent state?
- The port will transition to blocking state.
- The port will transition to forwarding state automatically.
- The port will transition to the appropriate state as determined by the normal function of the spanning tree.*
- The port will be disabled and the administrator must re-enable it manually.
24. Which two statements are true about the RSTP negotiations between switches? (Choose two.)
- All ports that are directly connected to end stations must be enabled as designated ports.
- UplinkFast must be configured on all designated switches.
- BackboneFast must be configured on all root switches.
- It greatly improves the restoration times for any VLAN that requires a topology convergence due to link up.*
- Switches must be connected by a point-to-point link.*
25. Refer to the exhibit. The configuration on the switch was changed between Output #1 and Output #2. What was done on the switch?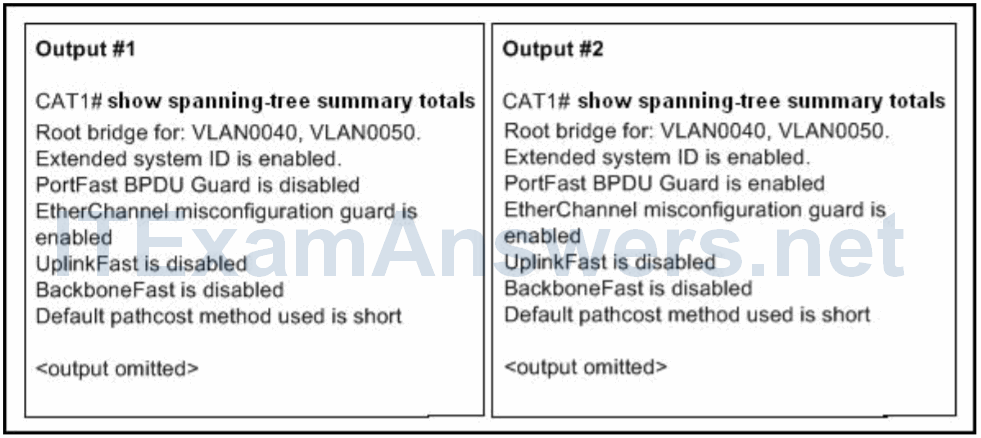
- The command spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default was issued in interface configuration mode.
- The command spanning-tree etherchannel guard misconfig was issued in global configuration mode.
- The command no spanning-tree uplinkfast was issued in global configuration mode.
- The command spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default was issued in global configuration mode.*
- The command no spanning-tree backbonefast was issued in global configuration mode.
- The command spanning-tree etherchannel guard misconfig was issued in interface configuration mode.
Download PDF File below:

What will happen when a BPDU is received on a loop guard port that is in a loop-inconsistent state?Correct answer: The port will transition to the appropriate state as determined by the normal function of the spanning tree.
What priority value should be entered on a switch, via the spanning-tree vlan 20 priority priority command, if the desired priority for VLAN 20 is 4116?
Correct Answer : 4096