19.2.1 Packet Tracer – Configure GRE (Answers)
Topology
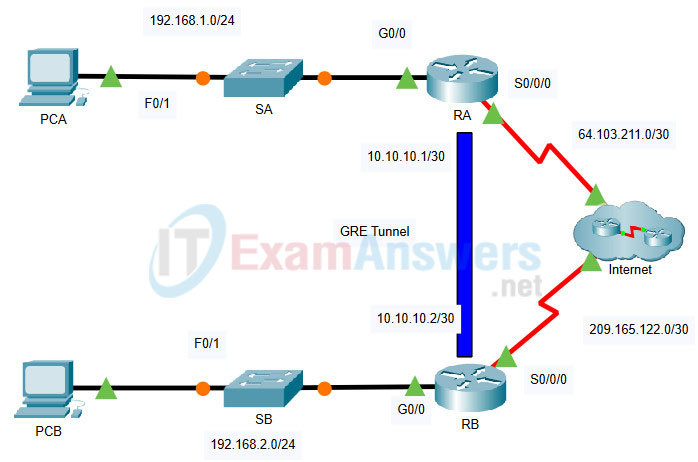
19.2.1 Packet Tracer – Configure GRE
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA | G0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 64.103.211.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| Tunnel 0 | 10.10.10.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| RB | G0/0 | 192.168.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 209.165.122.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| Tunnel 0 | 10.10.10.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| PCA | NIC | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PCB | NIC | 192.168.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.2.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Verify Router Connectivity
- Part 2: Configure GRE Tunnels
- Part 3: Verify PC Connectivity
Scenario
You are the network administrator for a company which wants to set up a GRE tunnel to a remote office. Both networks are locally configured. You need configure the tunnel and static routes.
Instructions
Part 1: Verify Router Connectivity
Step 1: Ping RA from RB.
Use the show ip interface brief command on RA to determine the IP address of the S0/0/0 port.
From RB ping the IP S0/0/0 address of RA.
Step 2: Ping PCA from PCB.
Attempt to ping the IP address of PCA from PCB. We will repeat this test after configuring the GRE tunnel. What were the ping results? Explain.
The pings failed because there is no route to the destination.
Part 2: Configure GRE Tunnels
Step 1: Configure the Tunnel 0 interface of RA.
a. Enter into the configuration mode for RA Tunnel 0.
RA(config)# interface tunnel 0
b. Set the IP address as indicated in the Addressing Table.
RA(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252
c. Set the source and destination for the endpoints of Tunnel 0.
RA(config-if)# tunnel source s0/0/0 RA(config-if)# tunnel destination 209.165.122.2
d. Configure Tunnel 0 to convey IP traffic over GRE.
RA(config-if)# tunnel mode gre ip
e. The Tunnel 0 interface should already be active. In the event that it is not, treat it like any other interface.
RA(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 2: Configure the Tunnel 0 interface of RB.
Repeat Steps 1a – e with RB. Be sure to change the IP addressing as appropriate.
RB(config)# interface tunnel 0 RB(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252 RB(config-if)# tunnel source s0/0/0 RB(config-if)# tunnel destination 64.103.211.2 RB(config-if)# tunnel mode gre ip RB(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 3: Configure a route for private IP traffic.
Establish a route between the 192.168.X.X networks using the 10.10.10.0/30 network as the destination.
RA(config)# ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2 RB(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.1
Part 3: Verify Router Connectivity
Step 1: Ping PCA from PCB.
Attempt to ping the IP address of PCA from PCB. The ping should be successful.
Step 2: Trace the path from PCA to PCB.
Attempt to trace the path from PCA to PCB. Note the lack of public IP addresses in the output.
Device Configs
Router RA
enable configure terminal interface Tunnel0 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 tunnel source Serial0/0/0 tunnel destination 209.165.122.2 tunnel mode gre ip ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2 end
Router RB
enable configure terminal interface Tunnel0 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.252 tunnel source Serial0/0/0 tunnel destination 64.103.211.2 tunnel mode gre ip ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.1 end

Nice, keep the great work!