3.1.2 Lab – Implement Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features (Answers)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
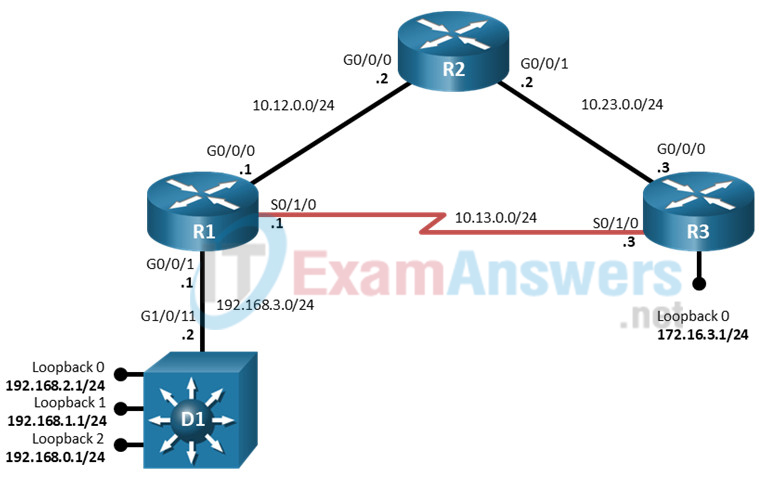
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0/0 | 10.12.0.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| G0/0/1 | 192.168.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| S0/1/0 | 10.13.0.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| R2 | G0/0/0 | 10.12.0.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
| G0/0/1 | 10.23.0.2 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| R3 | G0/0/0 | 10.23.0.3 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S0/1/0 | 10.13.0.3 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Loopback0 | 172.16.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| D1 | G1/0/11 | 192.168.3.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
| Loopback0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Loopback1 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Loopback2 | 192.168.0.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 2: Implement EIGRP for IPv4
- Part 3: Implement Advanced Features
Background / Scenario
Customizing the operation of EIGRP can yield many benefits, most notably speeding convergence and stabilizing network operations during outages. In this lab you will explore some advanced techniques that can be used to customize and improve EIGRP performance on an enterprise network.
Note: The routers used with CCNP hands-on labs are Cisco 4221s with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 3650s with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs.
Note: Make sure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
• 3 Routers (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
• 1 Switch (Cisco 3650 with Cisco IOS XE release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
• 1 PC (Choice of operating system with a terminal emulation program installed)
• Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
• Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings and interface addressing.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Configure basic settings for each device.
a. Console into each device, enter global configuration mode, and apply the basic settings. The startup configurations for each device are provided below.
Router R1
hostname R1 no ip domain lookup banner motd # R1, Implement Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features # line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco123 login exit ! interface g0/0/0 ip address 10.12.0.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit interface s0/1/0 ip address 10.13.0.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit interface g0/0/1 ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit end
Router R2
hostname R2 no ip domain lookup banner motd # R2, Implement Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features # line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco123 login exit ! interface g0/0/0 ip address 10.12.0.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit interface g0/0/1 ip address 10.23.0.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit end
Router R3
hostname R3 no ip domain lookup banner motd # R3, Implement Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features # line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco123 login transport input telnet exit interface g0/0/0 ip address 10.23.0.3 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit interface s0/1/0 ip address 10.13.0.3 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit interface loopback 0 ip address 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit end
Switch D1
hostname D1 no ip domain lookup ip routing banner motd # D1, Implement Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features # line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco123 login exit interface range g1/0/1-24 shutdown exit interface g1/0/11 no switchport ip address 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit interface loopback 0 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit interface loopback 1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit interface loopback 2 ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown exit end
b. Set the clock on all devices to UTC time.
c. Save the running configuration to startup-config on all devices.
Part 2: Implement EIGRP for IPv4
In this part, you will configure classic EIGRP for IPv4 and verify that all routing tables are converged.
Step 1: Configure classic EIGRP for IPv4.
Configure classic EIGRP for IPv4 on all devices. Use Autonomous System number 98, and advertise only the connected interfaces on each device.
R1# config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)# router eigrp 98 R1(config-router)# network 10.12.0.0 0.0.0.255 R1(config-router)# network 10.13.0.0 0.0.0.255 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 R1(config-router)# exit R1(config)# end R2# config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R2(config)# router eigrp 98 R2(config-router)# network 10.12.0.0 0.0.0.255 R2(config-router)# network 10.23.0.0 0.0.0.255 R2(config-router)# exit R2(config)# end R3# config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R3(config)# router eigrp 98 R3(config-router)# network 10.23.0.0 0.0.0.255 R3(config-router)# network 10.13.0.0 0.0.0.255 R3(config-router)# network 172.16.3.0 0.0.0.255 R3(config-router)# exit R3(config)# end D1# config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. D1(config)# router eigrp 98 D1(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 D1(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 D1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 D1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 D1(config-router)# exit D1(config)# end
Step 2: Verify EIGRP for IPv4 routing.
Verify that each device has a complete routing table for all the networks shown in the topology and Addressing Table.
R1# show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
D 10.23.0.0/24 [90/3072] via 10.12.0.2, 00:06:05, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 172.16.3.0 [90/131072] via 10.12.0.2, 00:06:04, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.0.0/24
[90/130816] via 192.168.3.2, 00:05:37, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
D 192.168.1.0/24
[90/130816] via 192.168.3.2, 00:05:37, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
D 192.168.2.0/24
[90/130816] via 192.168.3.2, 00:05:37, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
R2# show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
D 10.13.0.0/24
[90/1782016] via 10.12.0.1, 00:06:47, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 172.16.3.0 [90/130816] via 10.23.0.3, 00:06:47, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
D 192.168.0.0/24 [90/131072] via 10.12.0.1, 00:06:20, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/131072] via 10.12.0.1, 00:06:20, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.2.0/24 [90/131072] via 10.12.0.1, 00:06:20, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/3072] via 10.12.0.1, 00:06:44, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
R3# show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
D 10.12.0.0/24 [90/3072] via 10.23.0.2, 00:07:25, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.0.0/24 [90/131328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:07:01, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/131328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:07:01, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.2.0/24 [90/131328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:07:01, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/3328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:07:25, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D1# show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 10.12.0.0 [90/3072] via 192.168.3.1, 00:07:37, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
D 10.13.0.0
[90/1782016] via 192.168.3.1, 00:07:37, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
D 10.23.0.0 [90/3328] via 192.168.3.1, 00:07:37, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 172.16.3.0
[90/131328] via 192.168.3.1, 00:07:37, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
Part 3: Implement Advanced Features
In this part of the lab you will customize several different settings within EIGRP and see the impact of those changes on the network.
Step 1: Modify timers.
EIGRP uses standard hello-interval and hold-time timers based on the speed of the interface. If the interface speed is a T1 or less, hellos are sent every 60 seconds and the hold-time is set to 180 seconds. If the interface speed is greater than a T1, hellos are sent every 5 seconds and the hold-time is set to 15 seconds. These default times might not be appropriate for some network scenarios.
a. To see what the timers are set to, issue the show ip eigrp interfaces detail command.
R1# show ip eigrp interfaces detail
EIGRP-IPv4 Interfaces for AS(98)
Xmit Queue PeerQ Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
Gi0/0/0 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/050 0
Hello-interval is 5, Hold-time is 15
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 5/1
Hello's sent/expedited: 29/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/5 Un/reliable ucasts: 7/3
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 2 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
Topologies advertised on this interface: base
Topologies not advertised on this interface:
Se0/1/0 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/1250 0
Hello-interval is 5, Hold-time is 15
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 4/0
Hello's sent/expedited: 32/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 6/5
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
Topologies advertised on this interface: base
Topologies not advertised on this interface:
Gi0/0/1 1 0/0 0/0 4 0/050 0
Hello-interval is 5, Hold-time is 15
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial
Packetized sent/expedited: 2/1
Hello's sent/expedited: 31/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/2 Un/reliable ucasts: 4/3
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 2 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
Topologies advertised on this interface: base
Topologies not advertised on this interface:
b. For this lab, the timers on R1 interface G0/0/0 and S0/1/0 need to be adjusted to send hellos every 10 seconds and establish a hold time of 30 seconds. EIGRP is unique in that each interface can have a customized hello-interval and hold-time. The times are not needed to match between the ends of a link. Change the timers using the ip hello-interval eigrp ASN seconds and the ip hold-time eigrp ASN seconds interface configuration commands.
R1# config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)# interface g0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 98 10 R1(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 98 30 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface s0/1/0 R1(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 98 10 R1(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 98 30 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# end
c. To verify that the changes were made, check the output of the show ip eigrp interfaces detail command.
R1# show ip eigrp interfaces detail
EIGRP-IPv4 Interfaces for AS(98)
Xmit Queue PeerQ Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
Gi0/0/0 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/050 0
Hello-interval is 10, Hold-time is 30
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 5/1
Hello's sent/expedited: 84/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/5 Un/reliable ucasts: 7/3
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 2 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
Topologies advertised on this interface: base
Topologies not advertised on this interface:
Se0/1/0 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/1250 0
Hello-interval is 10, Hold-time is 30
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 4/0
Hello's sent/expedited: 87/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 6/5
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
Topologies advertised on this interface: base
Topologies not advertised on this interface:
Gi0/0/1 1 0/0 0/0 4 0/050 0
Hello-interval is 5, Hold-time is 15
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 2/1
Hello's sent/expedited: 92/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/2 Un/reliable ucasts: 4/3
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 2 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
Topologies advertised on this interface: base
Topologies not advertised on this interface:
Step 2: Create summarized routes in EIGRP.
Large routing tables take more memory and require more CPU time to process. Reducing the size of the routing table is advantageous in all network scenarios. EIGRP supports summarization of routes at any point in the network. There is no boundary router limitation like the limitations imposed in OSPF. However, in order for the summary route to be valid, EIGRP requires that some component of the summary route be in the routing table for the router doing the summarization.
a. Issue the show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway command on R3 and note the group of networks from the 192.168 range of addresses. R1 is advertising this contiguous block of networks individually, instead of sending a summary.
R3# show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
D 10.12.0.0/24 [90/3072] via 10.23.0.2, 00:06:35, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.0.0/24 [90/131328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:06:08, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/131328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:06:08, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.2.0/24 [90/131328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:06:08, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/3328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:06:35, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
b. On R1, configure a summary of the networks between R1 and D1, as well as the networks on D1 on the interfaces connecting to R3 and R2.
R1# conf t R1(config)# interface g0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip summary-address eigrp 98 192.168.0.0 255.255.252.0 *Mar 6 00:07:33.742: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 98: Neighbor 10.12.0.2 (GigabitEthernet0/0/0) is resync: summary configured R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface s0/1/0 R1(config-if)# ip summary-address eigrp 98 192.168.0.0 255.255.252.0 *Mar 6 00:07:35.220: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 98: Neighbor 10.13.0.3 (Serial0/1/0) is resync: summary configured R1(config-if)# end
c. Now examine the routing table on R3 again using the show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway command. In the output, you now see a single route taking the place of what had been four distinct routes.
R3# show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
D 10.12.0.0/24 [90/3072] via 10.23.0.2, 00:07:59, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.0.0/22 [90/3328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:00:25, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Step 3: Control EIGRP query propagation with EIGRP stub routers.
EIGRP uses query messages to find a path to networks in the autonomous system. The query messages always require an acknowledgement. But a router will only send a response if it has a potential route that satisfies the query. If it does not have a route, it sends its own queries to its neighbors. This process can lead to long delays in reconvergence after an outage.
Query scoping refers to using various techniques to control how far across a network queries have to be sent. Summarization is one way of controlling query propagation. Another way to control query propagation is to use EIGRP stub routers where appropriate. When a router is single-homed to the rest of the network, and no other networks exist beyond that router, there is no real point in sending it a query looking for lost networks. The stub router declares itself as a stub to the router connected to the rest of the network, which is considered a hub router. The hub router then forwards no queries to the stub router because it knows there are no other networks, beyond those reported, existing beyond the stub router. In the topology for this lab, switch D1 is a stub router and R1 is its hub router.
a. To verify that switch D1 is receiving EIGRP queries, issue the shutdown command on R2 interface G0/0/1. On switch D1, issue the show ip eigrp events command. This command outputs a timestamped list of actions that EIGRP is taking. In the output, you will find an entry that says switch D1 received a query trying to find the 10.23.0.0/24 network. Take note of the time stamp.
D1# show ip eigrp events Event information for AS 98: 1 00:10:46.753 NDB delete: 10.23.0.0/24 1 2 00:10:46.753 RDB delete: 10.23.0.0/24 192.168.3.1 3 00:10:46.737 Metric set: 10.23.0.0/24 metric(Infinity) 4 00:10:46.737 Poison squashed: 10.23.0.0/24 lost if 5 00:10:46.737 Poison squashed: 10.23.0.0/24 rt net gone 6 00:10:46.737 Route installing: 10.23.0.0/24 192.168.3.1 7 00:10:46.737 Send reply: 10.23.0.0/24 192.168.3.1 8 00:10:46.737 Not active net/1=SH: 10.23.0.0/24 1 9 00:10:46.737 FC not sat Dmin/met: metric(Infinity) metric(1782272) 10 00:10:46.737 Find FS: 10.23.0.0/24 metric(1782272) 11 00:10:46.737 Rcv query met/succ met: metric(Infinity) metric(Infinity) 12 00:10:46.737 Rcv query dest/nh: 10.23.0.0/24 192.168.3.1
b. Issue the no shutdown command on R2 interface G0/0/1.
c. Configure D1 as an EIGRP stub router.
D1# config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. D1(config)# router eigrp 98 D1(config-router)# eigrp stub D1(config)# end D1# Mar 6 00:11:40.624: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 98: Neighbor 192.168.3.1 (GigabitEthernet1/0/11) is down: peer info changed Mar 6 00:11:45.174: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 98: Neighbor 192.168.3.1 (GigabitEthernet1/0/11) is up: new adjacency
d. Verify that R1 sees switch D1 as a stub by examining the output of the show ip eigrp neighbor detail command.
R1# show ip eigrp neighbor detail
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(98)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO QSeq
(sec) (ms) CntNum
2 192.168.3.2 Gi0/0/1 14 00:00:39 3 100 010
Version 25.0/2.0, Retrans: 1, Retries: 0, Prefixes: 3
Topology-ids from peer - 0
Topologies advertised to peer: base
Stub Peer Advertising (CONNECTED SUMMARY ) Routes
Suppressing queries
1 10.13.0.3 Se0/1/0 11 00:11:44 1 100 028
Time since Restart 00:04:06
Version 25.0/2.0, Retrans: 0, Retries: 0, Prefixes: 3
Topology-ids from peer - 0
Topologies advertised to peer: base
0 10.12.0.2 Gi0/0/0 12 00:12:24 1 100 030
Time since Restart 00:04:07
Version 25.0/2.0, Retrans: 2, Retries: 0, Prefixes: 2
Topology-ids from peer - 0
Topologies advertised to peer: base
Max Nbrs: 0, Current Nbrs: 0
e. Issue the shutdown command on R2 interface G0/0/1. Take note of the timestamp on the syslog message reporting that the interface is down.
f. On switch D1, issue the show ip eigrp events command. You will see that no query was received looking for the 10.23.0.0/24 network. The query was stopped at R1, speeding up the convergence process.
D1# show ip eigrp events Event information for AS 98: 1 00:12:53.776 NDB delete: 10.23.0.0/24 1 2 00:12:53.776 Poison squashed: 10.23.0.0/24 rt net gone 3 00:12:53.776 RDB delete: 10.23.0.0/24 192.168.3.1 4 00:12:53.776 Not active net/1=SH: 10.23.0.0/24 1 5 00:12:53.776 FC not sat Dmin/met: metric(Infinity) metric(1782272) 6 00:12:53.776 Find FS: 10.23.0.0/24 metric(1782272) 7 00:12:53.776 Rcv update met/succmet: metric(Infinity) metric(Infinity) 8 00:12:53.776 Rcv update dest/nh: 10.23.0.0/24 192.168.3.1 9 00:12:53.776 Ignored route, hopcount: 10.23.0.0 255 10 00:12:50.077 Metric set: 172.16.3.0/24 metric(1910016) 11 00:12:50.077 Route installed: 172.16.3.0/24 192.168.3.1 12 00:12:50.077 Route installing: 172.16.3.0/24 192.168.3.1 13 00:12:50.077 Find FS: 172.16.3.0/24 metric(Infinity) 14 00:12:50.077 Free reply status: 172.16.3.0/24 15 00:12:50.077 Clr handle num/bits: 0 0x0 16 00:12:50.077 Clr handle dest/cnt: 172.16.3.0/24 0 17 00:12:50.077 Rcv reply met/succ met: metric(1910016) metric(1909760) 18 00:12:50.077 Rcv reply dest/nh: 172.16.3.0/24 192.168.3.1 19 00:12:50.077 Metric set: 10.23.0.0/24 metric(1782272) 20 00:12:50.076 Route installed: 10.23.0.0/24 192.168.3.1 21 00:12:50.076 Route installing: 10.23.0.0/24 192.168.3.1 22 00:12:50.076 Find FS: 10.23.0.0/24 metric(Infinity) 23 00:12:50.076 Free reply status: 10.23.0.0/24
g. Issue the no shutdown command on R2 interface G0/0/1.
Step 4: Filter EIGRP routes with a distribute list.
EIGRP supports several different filtering capabilities. The simplest and most direct is to use a distribute list. A distribute list refers to an access list which can be applied to all EIGRP updates being sent by a certain router, or it can be applied to a specific interface to modify updates as they exit. For this exercise, we will filter the 10.12.0.0/24 network from updates being sent out of R2 interface G0/0/1. This will cause a change in R3’s routing table.
a. Examine the routing table on R3 by issuing the show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway command. In the output, you can see that R3 has calculated the path via R2 at 10.23.0.2 to be the best path to reach the 10.12.0.0/24 network.
R3# show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
D 10.12.0.0/24 [90/3072] via 10.23.0.2, 00:00:17, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
D 192.168.0.0/22 [90/3328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:00:53, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
b. Our intent is to change the configuration at R2 so that R3 only learns about the 10.12.0.0/24 network from R1. Create an access list that denies the 10.12.0.0/24 network and permits all other networks.
R2# config t R2(config)# ip access-list standard EIGRP-FILTER R2(config-std-nacl)# deny 10.12.0.0 0.0.255.255 R2(config-std-nacl)# permit any R2(config-std-nacl)# exit
c. Enter EIGRP router configuration mode and configure the distribute list to reference the access list you just created, further specifying that the filter should be effective outbound on interface G0/0/1.
R2(config)# router eigrp 98 R2(config-router)# distribute-list EIGRP-FILTER out g0/0/1 R2(config-router)# end *Mar 6 00:19:56.379: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 98: Neighbor 10.23.0.3 (GigabitEthernet0/0/1) is resync: intf route configuration changed
d. On R3, issue the show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway command. As you can see, the successor for the 10.12.0.0/24 network has changed to R1 at 10.13.0.1.
R3# show ip route eigrp | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
D 10.12.0.0/24 [90/1792256] via 10.13.0.1, 00:01:30, Serial0/1/0
D 192.168.0.0/22 [90/3328] via 10.23.0.2, 00:03:00, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 4221 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 4300 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
Device Configs – Final
Router R1
R1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1619 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode none ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.12.0.1 255.255.255.0 ip hello-interval eigrp 98 10 ip hold-time eigrp 98 30 ip summary-address eigrp 98 192.168.0.0 255.255.252.0 negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! interface Serial0/1/0 ip address 10.13.0.1 255.255.255.0 ip hello-interval eigrp 98 10 ip hold-time eigrp 98 30 ip summary-address eigrp 98 192.168.0.0 255.255.252.0 ! interface Serial0/1/1 no ip address ! router eigrp 98 network 10.12.0.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.13.0.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.3.0 ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C R1, Implement Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 login ! end
Router R2
R2# show run Building configuration.. Current configuration : 1409 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! ! redundancy mode none ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.12.0.2 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 10.23.0.2 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! router eigrp 98 distribute-list EIGRP-FILTER out GigabitEthernet0/0/1 network 10.12.0.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.23.0.0 0.0.0.255 ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server ip http secure-server ! ip access-list standard EIGRP-FILTER deny 10.12.0.0 0.0.255.255 permit any ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C R2, Implement Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 login ! end
Router R3
R3# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1464 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R3 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode non ! interface Loopback0 ip address 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.23.0.3 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 no ip address negotiation auto ! interface Serial0/1/0 ip address 10.13.0.3 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial0/1/1 no ip address ! router eigrp 98 network 10.13.0.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.23.0.0 0.0.0.255 network 172.16.3.0 0.0.0.255 ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C R3, Implement Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 login transport input telnet ! end
Switch D1
D1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 6911 bytes ! version 16.9 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec ! Call-home is enabled by Smart-Licensing. service call-home no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname D1 ! vrf definition Mgmt-vrf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! no aaa new-model switch 1 provision ws-c3650-24ps ! ip routing ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! license boot level ipservicesk9 ! diagnostic bootup level minimal ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode sso ! transceiver type all monitoring ! class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control description Topology control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING class-map match-any system-cpp-default description Inter FED, EWLC control, EWLC data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFLSAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth description Punt Webauth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control description L2 LVX control packets class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station description MCAST END STATION class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control description L2 control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth description DOT1X Auth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control description Stackwise Virtual class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control description Routing control and Low Latency class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping description Protocol snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping description DHCP snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical description System Critical and Gold Pkt ! policy-map system-cpp-policy ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback2 ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf no ip address negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/9 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/11 no switchport ip address 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/12 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/17 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/18 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/19 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/20 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/21 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/1 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/3 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/4 ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! router eigrp 98 network 192.168.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 network 192.168.2.0 network 192.168.3.0 eigrp stub connected summary ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http secure-server ! control-plane service-policy input system-cpp-policy ! banner motd ^C D1, Implement Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 login line vty 5 15 login ! end

Could I got file as PKA.