Assessment – ROUTE Chapter 6 – CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0) Exam Answers
1. Which BGP routers will become peers and share routing information?
- BGP routers that are configured with the same network command
- BGP routers share routing information with all routers in the same AS by default.
- BGP routers that are configured with the neighbor command
- BGP routers that are configured with the same peer command
2. Refer to the exhibit. BGP sessions are established between all routers. RTC receives route updates for network 209.165.200.224/27 from autonomous system 300 with the weight attribute set to 3000. RTB also learns about network 209.165.200.224/27 from autonomous system 200 with a weight of 2000. Which router will be used by RTA as a next hop reach this network?
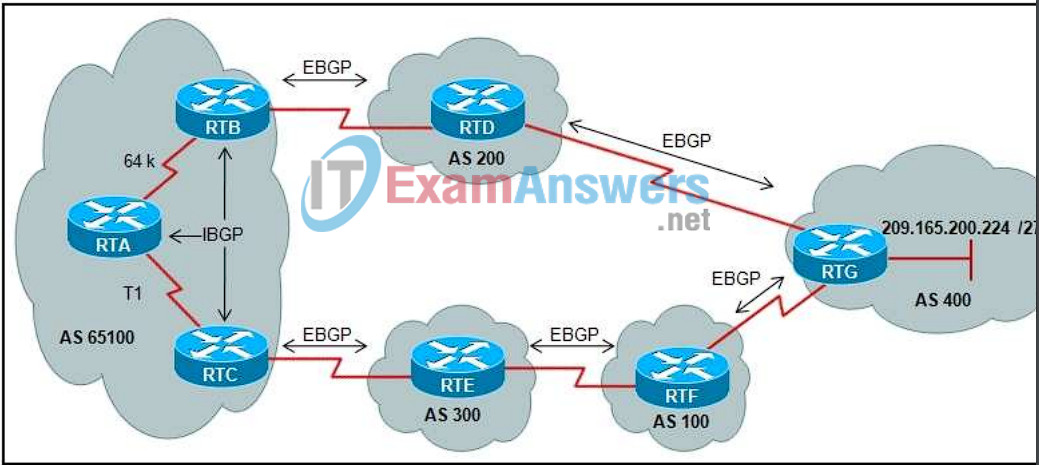
- RTB because of the lowest weight
- RTB because of the slow 64 kb/s link
- RTB because of the shortest AS_Path
- RTC because of the highest weight
- RTC because of the longest AS_Path
- RTC because of the T1 link
3. Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true?
RTA(config)# router bgp 100 RTA(config-router)# neighbor 190.10.50.1 remote-as 100 RTA(config-router)# neighbor 170.10.20.2 remote-as 300 RTA(config-router)# network 150.10.0.0
- The neighbor at 190.10.50.1 is an external peer.
- The neighbor at 170.10.20.2 is an internal peer.
- RTA is going to advertise that it is part of AS 300.
- RTA is going to advertise network 150.10.0.0 to its neighbors if 150.10.0.0 or its subnets are in the IP routing table.
4. Refer to the exhibit. Router R2 is currently unable to access network 172.16.10.0/24. Based on the information in the exhibit, which configuration would fix the problem?
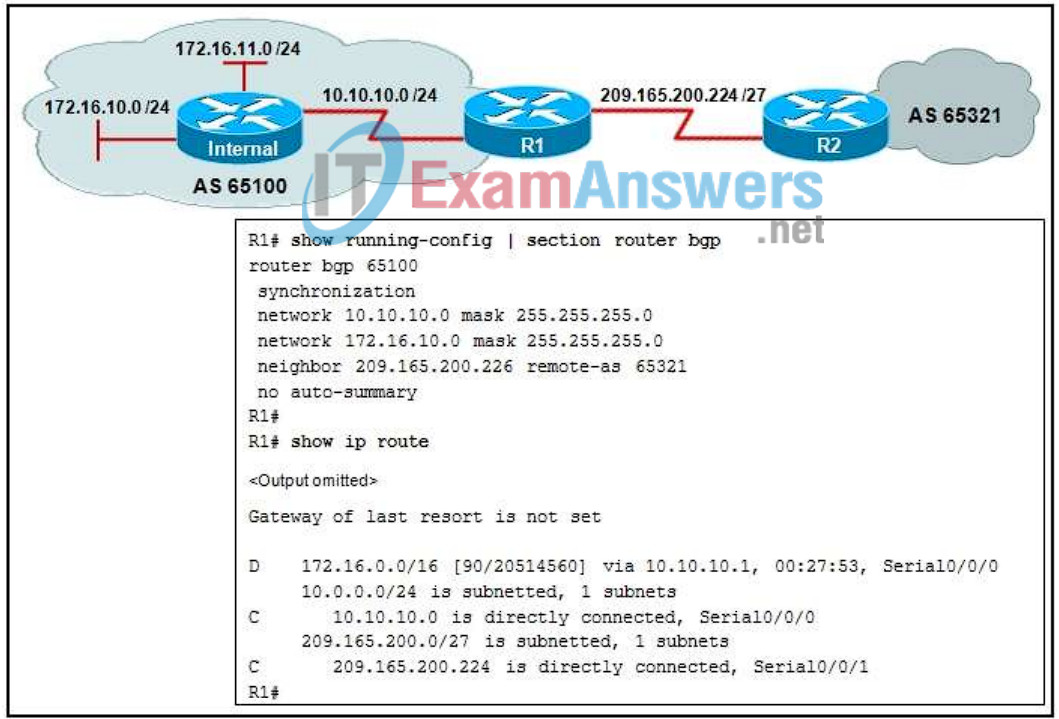
- R1(config)# router bgp 65100
R1(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 mask 255.0.0.0 - R1(config)# router bgp 65100
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 - R1(config)# router bgp 65100
R1(config-router)# no synchronization - R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# no auto-summary
5. Which two statements are key characteristics of BGP? (Choose two.)
- It uses cost as its metric.
- It is a link-state routing protocol.
- It is a policy-based routing protocol.
- It uses bandwidth and delay as its metric.
- It is an advanced distance vector routing protocol.
- It provides interdomain routing between autonomous systems.
6. Refer to the exhibit. Which two configurations will allow router R1 to establish a neighbor relationship with router R2? (Choose two.)
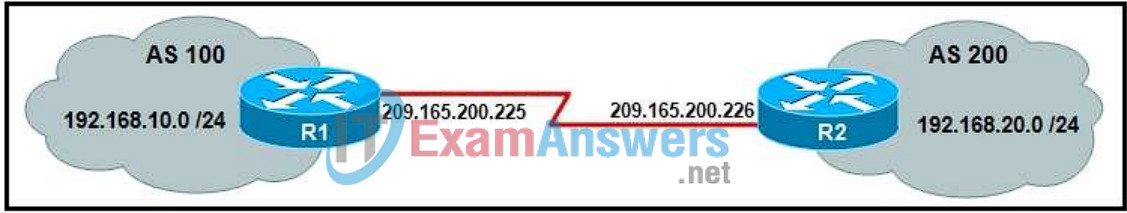
- R1(config)# router bgp 100
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.20.0 - R1(config)# router bgp 100
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0
R1(config-router)# neighbor 209.165.200.226 remote-as 200 - R1(config)# router bgp 200
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.20.0
R1(config-router)# neighbor 209.165.200.225 remote-as 100 - R2(config)# router bgp 200
R2(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0 - R2(config)# router bgp 200
R2(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0
R2(config-router)# neighbor 209.165.200.226 remote-as 200 - R2(config)# router bgp 200
R2(config-router)# network 192.168.20.0
R2(config-router)# neighbor 209.165.200.225 remote-as 100
7. An enterprise must interconnect multiple sites. Which technology would provide secure and manageable connections over the Layer 3 ISP network without the additional expense of leased lines?
- IBGP
- IP SLA
- MPLS VPN
- BGP dual-homed
- BGP dual-multihomed
8. An enterprise has routers with limited resources but requires the best path to selected external networks. Which multihoming option would provide the best solution?
- multihoming with default routes from all providers
- multihoming with full Internet routes from all providers
- multihoming with default routes and partial Internet routes from all providers
- multihoming with partial Internet routes from one provider and default routes from all other providers
9. Refer to the exhibit. An organization has configured a multihomed solution using EBGP between two edge routers and two ISPs. The edge routers are receiving only default routes from each ISP EBGP peer. Which two statements are true of this solution? (Choose two.)
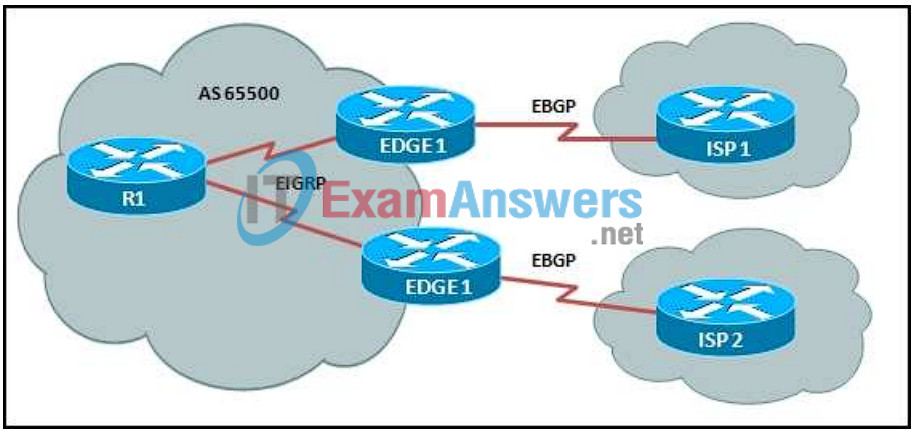
- EIGRP will choose the best route to exit the autonomous system.
- Traffic between the ISPs will be routed through autonomous system 65500.
- All routers in autonomous system 65500 must have complete knowledge of external routes.
- A TCP session must be established between the edge routers and the ISP routers.
- Full-mesh IBGP must be configured in autonomous system 65500 for internal hosts to reach the ISPs.
10. Refer to the exhibit. Autonomous system 65500 is routing traffic between two external BGP autonomous systems, autonomous system 65200 and autonomous system 65100. Synchronization is disabled on BGP in autonomous system 65500. Which routers should have IBGP peer relationships for routing between autonomous system 65200 and autonomous system 65100 to work properly?
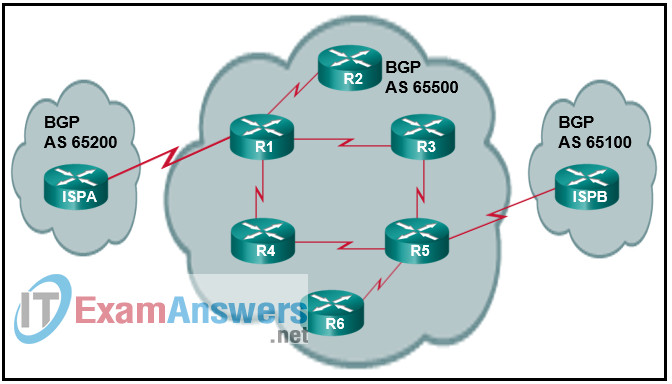
- R1 and R5
- R1, R3, and R4
- R1, R3, R4, and R5
- ISP A, R1, R5, and ISP B
11. What is the range of autonomous system numbers reserved for private use?
- 1 to 32768
- 1 to 65535
- 32768 to 65535
- 64512 to 65535
- 65512 to 65535
12. Refer to the exhibit. BGP sessions are established between all routers. Router RTC has the local preference for network 209.165.200.224/27 set to 200 and router RTB has a local preference set to 150 for the same network. Which router will by RTA as a next hop to reach network 209.165.299.224/27?
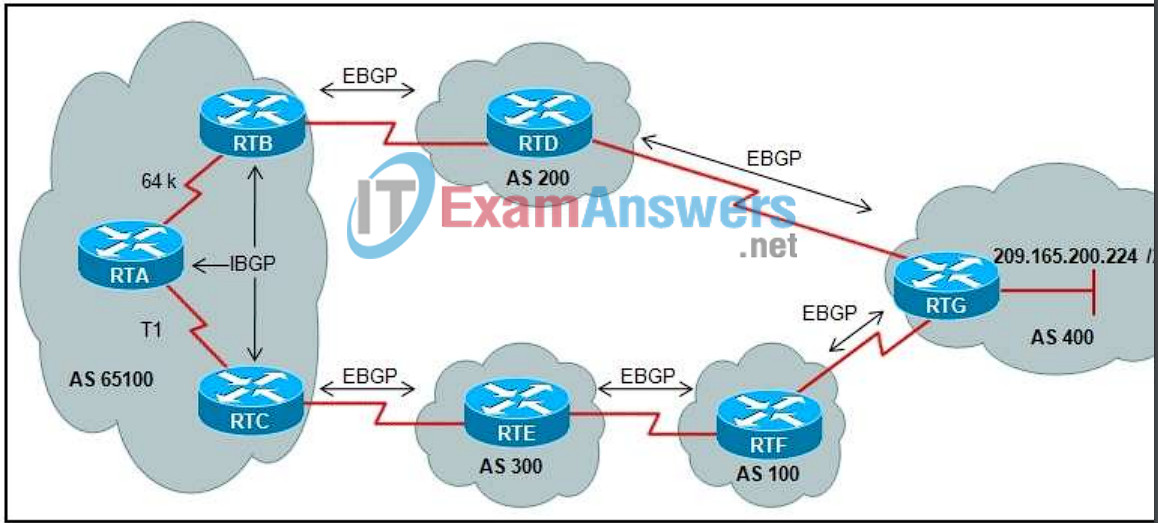
- RTB because of the lowest local preference
- RTB because of the slow 64 kb/s link
- RTB because of the shortest AS_Path
- RTC because of the highest local preference
- RTC because of the longest AS_Path
- RTC because of the T1 link
13. Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 is receiving the prefix 10.22.0.0/16 from an IBGP peer. The prefix appears in the BGP table of R1, but not in the IP routing table. What could be preventing R1 from installing 10.22.0.0/16 in the routing table?
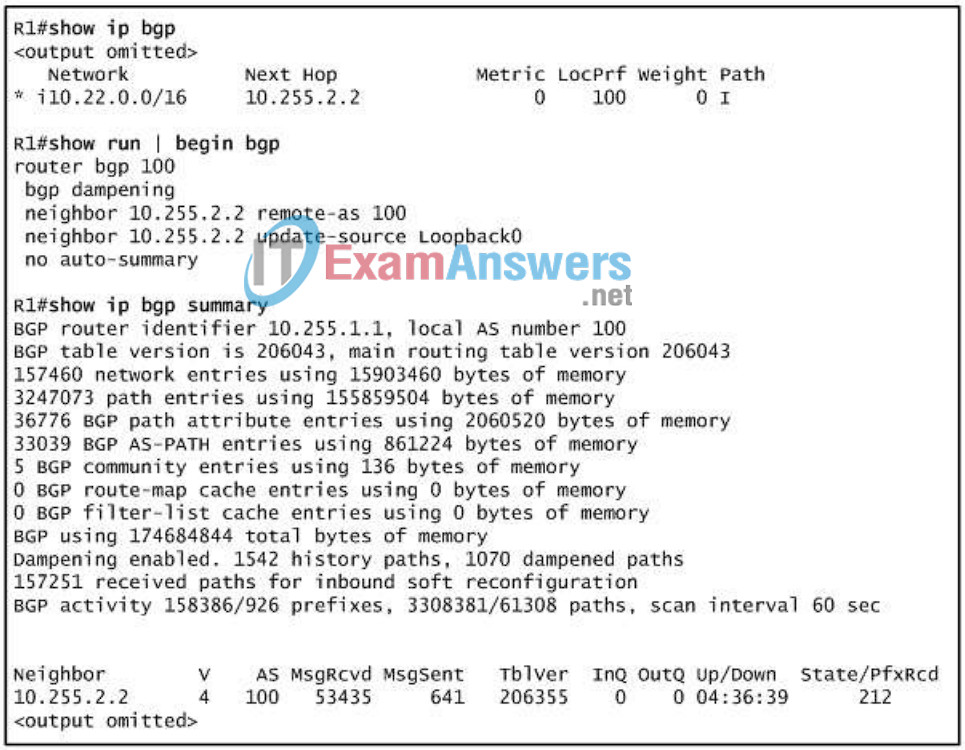
- automatic summarization disabled
- EBGP multihop misconfiguration
- incorrect use of the update-source command
- route dampening
- synchronization
14. How can static routes be dynamically injected into BGP?
- Create the static routes with an administrative distance equal to BGP.
- Apply the redistribute static command to the BGP configuration.
- Create a prefix list that covers the scope of the networks that are specified by the static routes.
- Use route maps instead of static routes to dynamically update the convergence.
15. Which two options best describe an exterior routing protocol (EGP)? (Choose two.)
- an interdomain routing protocol
- an intradomain routing protocol
- a routing protocol that is used for intradomain routing such as IS-IS and OSPFv3
- a routing protocol that exchanges routing information within an autonomous system
- a routing protocol that exchanges routing information between different autonomous systems
16. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the show ip bgp summary and debug ip bgp output, which two statements must be true? (Choose two.)
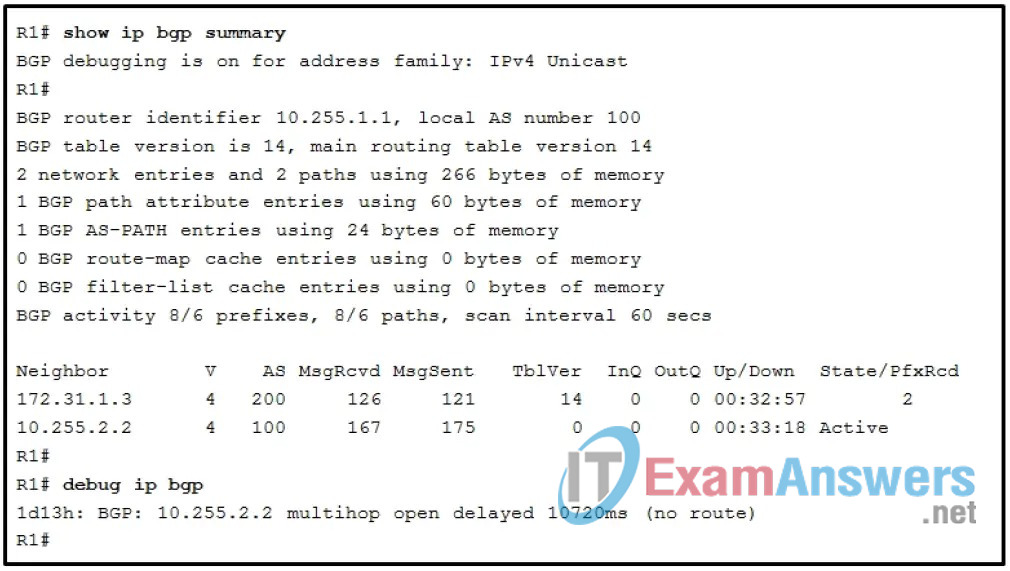
- The router at 10.255.2.2 is an EBGP peer.
- The ebgp multi-hop command is missing from the BGP configuration.
- R1 has established an EBGP peering relationship.
- R1 is directly connected to an IBGP peer.
- R1 cannot route BGP packets to 10.255.2.2.
17. Which BGP attribute is used by BGP to ensure a loop-free topology on the Internet?
- Next_hop
- As_path
- local preference
- Atomic aggregate
- Origin
18. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator in autonomous system 65100 has set up a dual-homed BGP connection with an ISP. The administrator would like to ensure that all traffic from the ISP enters the autonomous system through router R1. Which BGP attribute can the administrator configure on routers R1 and R2 to accomplish this?
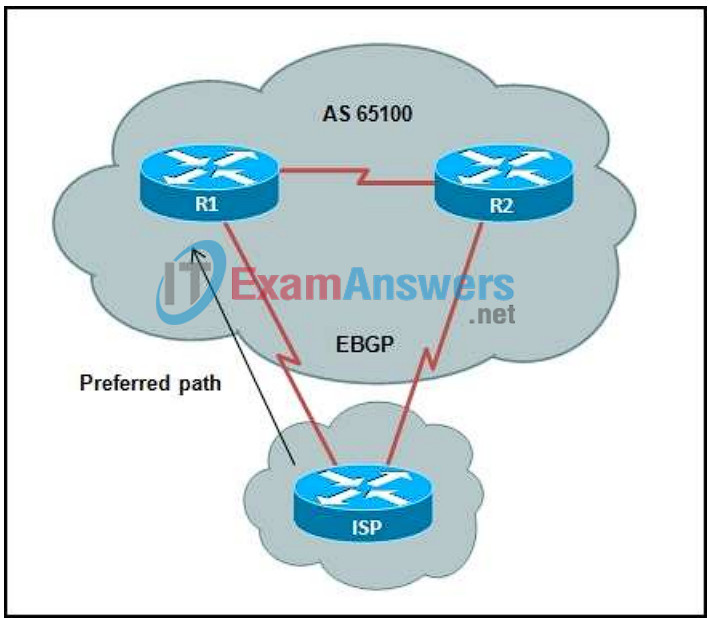
- multi_exit_discriminator
- local preference
- aggregate
- next-hop
- weight
19. Which routes are available to a BGP speaker to advertise to peers once an adjacency is formed?
- only routes in the IP routing table
- only routes in the BGP forwarding database
- only routes that are learned from IBGP peers in the same autonomous system
- any route in either the IP routing table or BGP forwarding database
20. What is a disadvantage to multihoming and accepting only a default route from each ISP?
- Because of load balancing between ISPs, suboptimal routing may occur.
- Because routers will select the edge router based on the IGP metric, suboptimal routing may occur.
- Because routing loops within the IGP routing domain may occur, only a single ISP connection can be used.
- Because no more than one default route can be advertised into the IGP routing domain, only a single ISP connection can be used.
