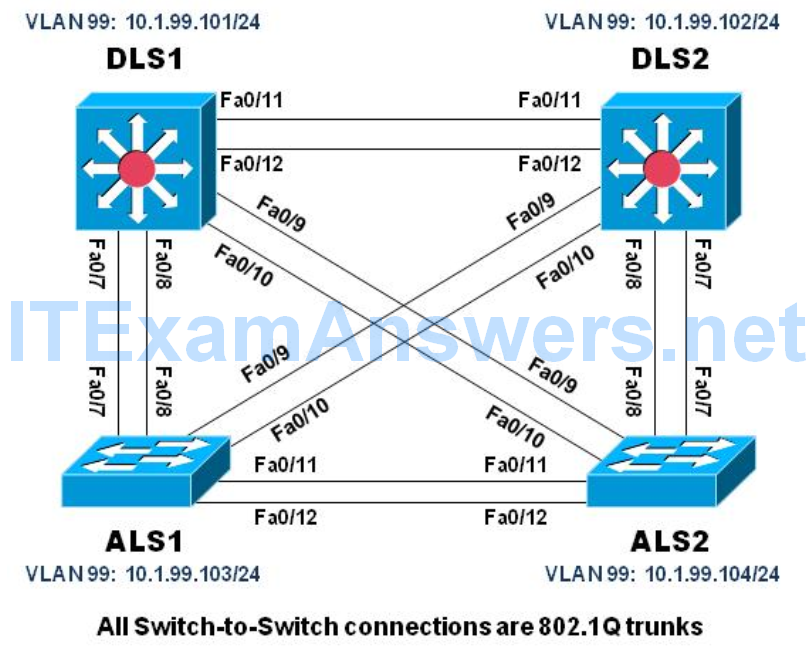
Topology
Objectives
- Setup a VTP v2 Domain.
- Create and maintain VLANs.
- Configure 802.1Q Trunking.
- Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
Background
VLANs logically segment a network by function, team, or application, regardless of the physical location of the users. End stations in a particular IP subnet are often associated with a specific VLAN. VLAN membership on a switch that is assigned manually for each interface is known as static VLAN membership.
Trunking, or connecting switches, and the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) are technologies that support VLANs. VTP manages the addition, deletion, and renaming of VLANs on the entire network from a single switch.
Note: This lab uses Cisco Catalyst 3560 and 2960 switches running Cisco IOS 15.0(2)SE6 IP Services and LAN Base images, respectively. The 3560 and 2960 switches are configured with the SDM templates “dual ipv4-andipv6 routing” and “lanbase-routing”, respectively. Depending on the switch model and Cisco IOS Software version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in this lab. Catalyst 3650 switches (running any Cisco IOS XE release) and Catalyst 2960-Plus switches (running any comparable Cisco IOS image) can be used in place of the Catalyst 3560 switches and the Catalyst 2960 switches.
Required Resources
- Cisco 2960 with the Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)SE6 C2960-LANBASEK9-M or comparable
- Cisco 3560v2 with the Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)SE6 C3560-IPSERVICESK9-M or comparable
- Computer with terminal emulation software
- Ethernet and console cables
Part 1: Prepare for the Lab
Step 1: Prepare the switches for the lab
Use the reset.tcl script you created in Lab 1 “Preparing the Switch” to set your switches up for this lab. Then load the file BASE.CFG into the running-config with the command copy flash:BASE.CFG running-config. An example from DLS1:
DLS1# tclsh reset.tcl Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files! Continue? [confirm] [OK] Erase of nvram: complete Reloading the switch in 1 minute, type reload cancel to halt Proceed with reload? [confirm] *Mar 7 18:41:40.403: %SYS-7-NV_BLOCK_INIT: Initialized the geometry of nvram *Mar 7 18:41:41.141: %SYS-5-RELOAD: Reload requested by console. Reload Reason: Reload command. <switch reloads - output omitted> Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: n Switch> en *Mar 1 00:01:30.915: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Vlan1, changed state to administratively down Switch# copy BASE.CFG running-config Destination filename [running-config]? 184 bytes copied in 0.310 secs (594 bytes/sec) DLS1#
Step 2: Configure basic switch parameters.
Configure an IP address on the management VLAN according to the diagram. VLAN 1 is the default management VLAN, but following best practice, we will use a different VLAN. In this case, VLAN 99.
Enter basic configuration commands on each switch according to the diagram.
DLS1 example:
DLS1# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. DLS1(config)# interface vlan 99 DLS1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.99.101 255.255.255.0 DLS1(config-if)# no shutdown
The interface VLAN 99 will not come up immediately, because the broadcast domain it is associated with (VLAN 99) doesn’t exist on the switch. We will fix that in a few moments.
(Optional) On each switch, create an enable secret password and configure the VTY lines to allow remote access from other network devices.
DLS1 example:
DLS1(config)# enable secret class DLS1(config)# line vty 0 15 DLS1(config-line)# password cisco DLS1(config-line)# login
Note: The passwords configured here are required for NETLAB compatibility only and are NOT
recommended for use in a live environment.
Note(2): For purely lab environment purposes, it is possible to configure the VTY lines so that they accept any Telnet connection immediately, without asking for a password, and place the user into the privileged EXEC mode directly. The configuration would be similar to the following example for DLS1:
DLS1(config)# enable secret class DLS1(config)# line vty 0 15 DLS1(config-line)# no login DLS1(config-line)# privilege level 15
Part 2: Configure VTP Version 2, VLANs, and Trunking.
A VTP domain, also called a VLAN management domain, consists of trunked switches that are under the same administrative responsibility sharing the same VTP domain name. A switch can be in only one VTP domain, and VLAN database contents in the domain are globally synchronized. VLAN information is not propagated until a domain name is specified and trunks are set up between the devices.
There are three versions of VTP available; Version 1 and 2 are able to support normal-range VLANs only, while version 3 can support normal- and extended-range VLANs, as well as the synchronization of other databases. Support for version 3 on the Catalyst platforms used in this lab was added in IOS version 12.2(52)SE. Older IOS versions do not generally support VTP version 3.
Switches operate in one of four VTP modes. The default VTP mode for the 2960 and 3560 switches is server mode, however, our Lab 1 configuration changes this to transparent.
| VTP Mode | Description |
| VTP Server | You can create, modify, and delete VLANs and specify other configuration parameters, such as VTP version and VTP pruning, for the entire VTP domain. VTP servers advertise their VLAN configuration to other switches in the same VTP domain and synchronize their VLAN configuration with other switches based on advertisements received over trunk links. VTP server is the default mode. In VTP Server mode, VLAN configurations are only stored in the flash:vlan.dat file. While VLANs are manipulated in the configuration mode, the configuration commands do not appear in the running-config. |
| VTP Client | A VTP client behaves like a VTP server and transmits and receives VTP updates on its trunks, but you cannot create, change, or delete VLANs on a VTP client. VLANs are configured on another switch in the domain that is in server mode. In VTP Client mode, VLAN configurations are only stored in the flash:vlan.dat file. The configuration of VLANs does not appear in the running-config. |
| VTP Transparent | VTP transparent switches do not participate in VTP. A VTP transparent switch does not advertise its VLAN database nor synchronize its VLAN database based on received advertisements. However, transparent switches forward received VTP messages under two circumstances: either the VTP domain name of the transparent switch is empty (not yet configured), or it matches the domain name in the received VTP messages. In VTP Transparent mode, VLAN configurations are stored both in flash:vlan.dat file and also are present in the running-config. If extended range VLANs are used, however, they are stored in the flash:vlan.dat only if the switch is running VTP version 3. |
| VTP Off0 | A switch in VTP Off mode functions in the same manner as a VTP transparent switch, except that it does not forward VTP advertisements on trunks. VTP off is only available on switches that support VTP version 3 although it is not necessary to run VTP version 3 on the switch to be able to put it into the Off mode. In VTP Off mode, VLAN configurations are stored both in flash:vlan.dat file and also are present in the running-config. If extended range VLANs are used, however, they are stored in the flash:vlan.dat only if the switch is running VTP version 3. |
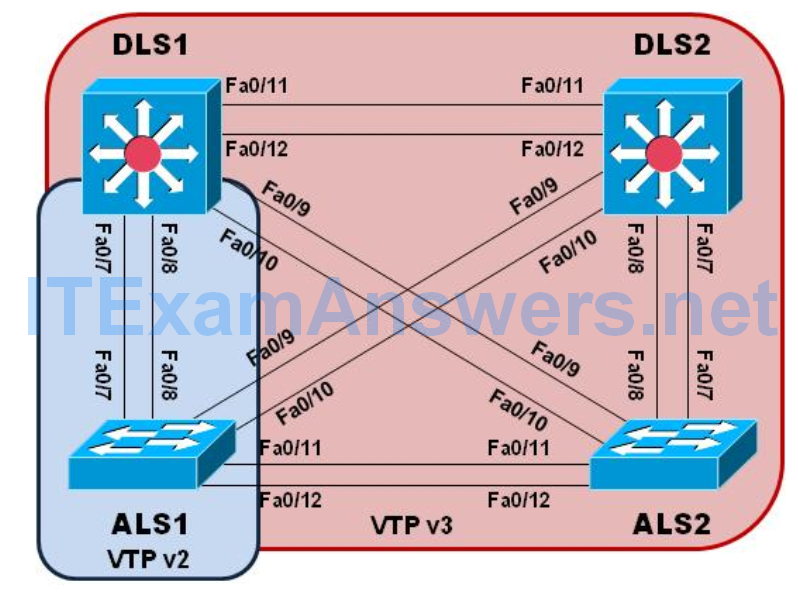
In this lab we will demonstrate the configuration and operation of both VTP versions 2 and 3. We will do this by first configuring VTP version 2 between DLS1 and ALS1, and then configuring DLS1, DLS2 and ALS2 with VTP version 3.
Topology
Step 1: Verify VTP status
Issue the show vtp status command on DLS1
DLS1# show vtp status
VTP Version capable : 1 to 3
VTP version running : 1
VTP Domain Name :
VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
Device ID : 64a0.e72a.2200
Configuration last modified by 0.0.0.0 at 0-0-00 00:00:00
Feature VLAN:
--------------
VTP Operating Mode : Transparent
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005
Number of existing VLANs : 5
Configuration Revision : 0
MD5 digest : 0x57 0xCD 0x40 0x65 0x63 0x59 0x47 0xBD
0x56 0x9D 0x4A 0x3E 0xA5 0x69 0x35 0xBC
Because no VLAN configurations were made, all settings except the VTP mode that was changed in Lab 1 are the defaults. This switch is capable of running version 1, 2 or 3 of VTP and runs version 1 by default. All switches in the VTP domain must run the same VTP version. The VTP mode is set to Transparent as a result of steps performed in Lab 1. The number of existing VLANs is the five built-in VLANs. Different switches in the Catalyst family support different numbers of local VLANs. The 3560 switch used in this lab supports a maximum of 1,005 VLANs locally, while the 2960 switch used in this lab supports at most 255 VLANs. Lastly, note that the configuration revision is 0.
As you should recall from CCNA, the configuration revision number is compared amongst VTPv1 or VTPv2 switches and the VLAN database from the switch with the highest revision number is adopted by all the other switches in the VLAN management domain. Every time VLAN information is modified and saved in the VLAN database (vlan.dat), the revision number is increased by one when the user exits from VLAN configuration mode.
In VTPv3, revision numbers are still used but they no longer determine the switch whose database is going to apply to the entire domain. Instead, a single designated switch in a VTP domain called the primary server is allowed to assert its database in the entire VTP domain, even if its own revision number is lower. Other switches that are not primary servers are not allowed to assert their databases even if their revision numbers are higher.
Multiple switches in the VTP domain can be in VTP server mode. In VTPv1 and VTPv2, any of these server switches can be used to manage all other switches in the VTP domain. In VTPv3, a single primary server for a particular VTP domain is designated to control where changes originate from in the switched network. This enables careful management and protection of the VLAN database.
Step 2: Configure VTP on DLS1.
We will start off this lab by configuring DLS1 for VTP Server mode and setting the VTP domain name and VTP version 2. We will also set a VTP password, which provides some rudimentary protection against automatic VLAN database propagation. Because this password is set, VTPv2 will not allow ALS1 to automatically learn the domain name once trunks are installed.
DLS1# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. DLS1(config)# vtp domain SWLAB Changing VTP domain name from NULL to SWLAB DLS1(config)# vtp version 2 DLS1(config)# vtp mode server Setting device to VTP Server mode for VLANS. DLS1(config)# vtp password cisco123 Setting device VTP password to cisco123 DLS1(config)# *Mar 1 00:29:10.895: %SW_VLAN-6-VTP_DOMAIN_NAME_CHG: VTP domain name changed to SWLAB.
Verify these settings by using the show vtp status command again.
DLS1# show vtp status
VTP Version capable : 1 to 3
VTP version running : 2
VTP Domain Name : SWLAB
VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
Device ID : 64a0.e72a.2200
Configuration last modified by 0.0.0.0 at 0-0-00 00:00:00
Local updater ID is 0.0.0.0 (no valid interface found)
Feature VLAN:
--------------
VTP Operating Mode : Server
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005
Number of existing VLANs : 5
Configuration Revision : 0
MD5 digest : 0xA7 0xE6 0xAF 0xF9 0xFE 0xA0 0x88 0x6B
0x21 0x6D 0x70 0xEE 0x04 0x6D 0x90 0xF3
Step 3: Configure VLANs on DLS1
Next configure the VLANs that will be required to support the network. There are two ways to create VLANs, either directly via the vlan command or by assigning an interface to a non-existent VLAN. For now, you will create the VLANs directly on the switch. Create:
- VLAN 99 to enable the management interface.
- VLAN 999 as a “parking lot” VLAN for unused access ports
– Suspend this VLAN to prevent ports in the VLAN from every communicating with each other. - The VLANs required for network operations, which are VLANs 100, 110, and 120.
Suspending a VLAN deserves a special mention. Each VLAN has an operational state associated with it: it can be either active (the default state) or suspended. A suspended VLAN exists but it does not operate.
Access ports assigned to a suspended VLAN drop all frames and are unable to communicate, similar to ports put into a nonexistent VLAN. Putting a suspended VLAN back into the active state reinstates normal communication on ports in that VLAN.
To globally suspend a VLAN, use the state suspend command in the VLAN configuration mode. This state is propagated by VTP to all other switches in the VTP domain if VTP is in use.
To locally shut down a VLAN, use the shutdown command in the VLAN configuration mode. This setting is not propagated through VTP.
Do not confuse the shutdown command in the VLAN configuration mode with the same command available under interface Vlan mode, which has a different and unrelated meaning. Further discussion on suspending and reactivating VLANs can be found in Part 3, Step 7 of this lab.
DLS1(config)# vlan 99 DLS1(config-vlan)# name MANAGEMENT DLS1(config-vlan)# vlan 100 DLS1(config-vlan)# name SERVERS DLS1(config-vlan)# vlan 110 DLS1(config-vlan)# name GUEST DLS1(config-vlan)# vlan 120 DLS1(config-vlan)# name OFFICE DLS1(config-vlan)# vlan 999 DLS1(config-vlan)# name PARKING_LOT DLS1(config-vlan)# state suspend DLS1(config-vlan)# vlan 666 DLS1(config-vlan)# name NATIVE_DO_NOT_USE DLS1(config-vlan)# exit
The VLANs will not appear in the VLAN database until the exit command is issued.
After configuring the VLANs, issue the show vtp status command and you will see that the all-important configuration revision number has increased based on these changes to the VLAN database. Note that the revision number you have when performing this lab may be different.
DLS1#show vtp status | include Configuration Revision Configuration Revision : 6
Step 4: Configure trunking on DLS1
VTP will only propagate information over trunks. Cisco switches support Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP), which allows automatic negotiation of trunks. The partial output here from ALS1 shows you the default trunking mode:
ALS1#show interface f0/7 switchport Name: Fa0/7 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: dynamic auto Operational Mode: down Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Negotiation of Trunking: On Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled
Switches that are interconnected and have DTP enabled can form a trunk automatically if either end is in the dynamic desirable mode or static trunk mode on the condition that either both switches use the same VTP domain name or at least one of the switches does not yet have the VTP domain name configured.
The dynamic auto mode on both ends will prevent a trunk from automatically forming; however, this is not really a valid safeguard against unintentional trunk connections as the port can become a trunk if the other side changes to dynamic desirable or static trunk mode.
As a best practice you should configure each interface into either access or trunk mode and use the switchport nonegotiate interface configuration command to disable the propagation of DTP messages. Never leave ports to operate in the dynamic mode.
Configure the appropriate interfaces on DLS1 to be trunks.
- Because DLS1 is a 3560, you must first specify the encapsulation protocol for the interface. Catalyst
3560 switches support ISL (Inter-Switch Link) and 802.1Q encapsulations for trunk interfaces. In the
topology, all the trunks are 802.1Q trunks. - Change the native VLAN from the default of VLAN 1 to VLAN 666.
- Set the interfaces to be in trunking mode only, and include the switchport nonegotiate
command. - The no shutdown command is needed because the Lab 1 configuration has all interfaces
shutdown.
DLS1(config)# interface range f0/7-12 DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk native vlan 666 DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport nonegotiate DLS1(config-if-range)# no shutdown DLS1(config-if-range)#
By default, all VLANs are allowed on all trunks. You can explicitly control which VLANs are allowed on a trunk by using the switchport trunk allowed vlan vlan-id command on the interface at each end of the trunk.
There are several approaches to deciding what VLANs to allow or disallow to cross the trunk. Common practice is to disallow VLAN 1 and the PARKING_LOT vlan. You could go a step further and disallow any unused VLAN numbers, but you would then have to modify all the trunks should you later add a new VLAN to the network.
In this lab, disallowing the PARKING_LOT VLAN from all trunks is not really necessary since the VLAN has been suspended. Disallowing the VLAN can serve as an additional protection against inadvertent reactivation of this VLAN.
Disallowing VLAN 1, also referred to as VLAN 1 Minimization, excludes VLAN 1 from the trunk but does not restrict layer 2 management traffic (such as CDP, LLDP, VTP, STP, etc) from passing.
Since only these 2 VLANs are being disallowed, the except option of the command can be used:
DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk allowed vlan ? WORD VLAN IDs of the allowed VLANs when this port is in trunking mode add add VLANs to the current list all all VLANs except all VLANs except the following none no VLANs remove remove VLANs from the current list DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk allowed vlan except 1,999 DLS1(config-if-range)#
Validate these settings by examining the switchport configuration for one of the trunk interfaces:
DLS1#show interface f0/7 switchport Name: Fa0/7 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Negotiation of Trunking: Off Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 666 (NATIVE_DO_NOT_USE) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled <output omitted> Trunking VLANs Enabled: 2-998,1000-4094 <output omitted>
Step 5: Configure VTP and trunking on ALS1
Next configure VTP and trunking on ALS1. Configure ALS1 to be in VTP Client mode and then configure all of the appropriate trunk interfaces to use a native VLAN of 666 and to be in trunking mode only. The native VLAN number does not have to be the same across your network, but it must match between switches on a given connected trunk. Also, disallow VLANs 1 and 999.
ALS1(config)# vtp mode client Setting device to VTP Client mode for VLANS. ALS1(config)# interface range f0/7-12 ALS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk native vlan 666 ALS1(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk ALS1(config-if-range)# switchport nonegotiate ALS1(config-if-range)# switchport trunk allowed vlan except 1,999 ALS1(config-if-range)# no shutdown ALS1(config-if-range)# exit ALS1(config)#
After activating the interfaces, use the show interface trunk command to see the status of the trunks.
You should see interfaces Fa0/7 and Fa0/8 in trunking mode.
ALS1# show interface trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/7 on 802.1q trunking 666 Fa0/8 on 802.1q trunking 666 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/7 2-998,1000-4094 Fa0/8 2-998,1000-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/7 none Fa0/8 none Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/7 none Fa0/8 none ALS1#
Now if you look at the VTP status on ALS1, you will see the values are at their defaults even though the trunk is operational. This is because of the VTP password.
ALS1# show vtp status
VTP Version capable : 1 to 3
VTP version running : 1
VTP Domain Name :
VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
Device ID : 64a0.e72a.2200
Configuration last modified by 0.0.0.0 at 0-0-00 00:00:00
Feature VLAN:
--------------
VTP Operating Mode : Client
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 255
Number of existing VLANs : 5
Configuration Revision : 0
MD5 digest : 0x57 0xCD 0x40 0x65 0x63 0x59 0x47 0xBD
0x56 0x9D 0x4A 0x3E 0xA5 0x69 0x35 0xBC
Set the VTP password on ALS1 and the VLAN database will be synchronized. However before you can set the password, the VTP domain name must be manually configured.
ALS1# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. ALS1(config)# vtp domain SWLAB Changing VTP domain name from NULL to SWLAB ALS1(config)# vtp password cisco123 Setting device VTP password to cisco123 ALS1(config)# end *Mar 1 00:27:21.902: %SW_VLAN-6-VTP_DOMAIN_NAME_CHG: VTP domain name changed to SWLAB.
Now check the VTP status and you will see a revision number matching that of DLS1, and that VLANs 99, 100, 110, 120, 666 and 999 are all in the local VLAN database.
ALS1# show vtp status
VTP Version capable : 1 to 3
VTP version running : 2
VTP Domain Name : SWLAB
VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
Device ID : 64a0.e72a.2200
Configuration last modified by 0.0.0.0 at 3-1-93 00:04:37
Feature VLAN:
--------------
VTP Operating Mode : Client
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 255
Number of existing VLANs : 11
Configuration Revision : 6
MD5 digest : 0xF3 0x8A 0xEA 0xFA 0x9B 0x39 0x6D 0xF5
0xA6 0x03 0x2F 0xB8 0x16 0xC1 0xE6 0x8C
ALS1# show vlan brief | incl active
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
99 MANAGEMENT active
100 SERVERS active
110 GUEST active
120 OFFICE active
666 NATIVE_DO_NOT_USE active
ALS1#
VLAN 999 will be missing from the filtered output above because it only includes VLANs in active state and VLAN 999 is suspended. Using the show vlan brief without filtering would show the VLAN 999.
You will also see that the configured VLANs except VLANs 1 and 999 are allowed over the trunks
ALS1#show interface trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/7 on 802.1q trunking 666 Fa0/8 on 802.1q trunking 666 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/7 2-998,1000-4094 Fa0/8 2-998,1000-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/7 99-100,110,120,666,999 Fa0/8 99-100,110,120,666,999 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/7 99-100,110,120,666 Fa0/8 99-100,110,120,666 ALS1#
You will also see that the state of interface VLAN 99 has changed to ‘up’
*Mar 1 00:27:52.336: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan99, changed state to up
Because ALS1 is in VTP Client mode, local changes to the VLAN database cannot be made:
ALS1(config)# vlan 199 VTP VLAN configuration not allowed when device is in CLIENT mode. ALS1(config)#
At this point, VTP version 2 is working and secured between DLS1 and ALS1. You should now be able to ping DLS1 from ALS1 and vice versa.
Step 6: Park unused interfaces
On DLS1 and ALS1, place all of interfaces that will not be used into the PARKING_LOT VLAN and shut them down. For this lab, the interfaces being used on all switches are F0/6 through F0/12.
An example from DLS1:
DLS1(config)# interface range f0/1-5,f0/13-24,g0/1-2 DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport mode access DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport nonegotiate DLS1(config-if-range)# switchport access vlan 999 DLS1(config-if-range)# shutdown DLS1(config-if-range)# exit
Part 3: Configure VTP version 3, VLANs, and Trunking
In this part of the lab you will configure VTP version 3 to operate across the rest of the switched network. VTP version 3 provides some significant benefits to the network administrator.
1. The concept of a primary server was added. In VTP versions 1 and 2, all VTP server switches are equal; any one of them may add/remove/rename VLANs and change their state. In VTP version 3, only the primary server can do this. There can be at most one primary server present in a VTP domain. The role of a primary server is a runtime state. It is not a part of the configuration; rather, this state is requested in privileged EXEC mode and is relinquished whenever another switch attempts to become the primary server or when the switch is reloaded.
2. VTP version 3 has the ability to hide the VTP password. On a VTP version 1 or 2 switch, issuing the command show vtp password will show the password to you in plain text. VTP version 3 allows you to specify that the password be hidden in the output, preventing the password from being inadvertently or maliciously divulged.
3. VTP version 3 can propagate information about extended-range VLANs; VLANs numbered between 1006 and 4094. To support these VLANs with VTP version 2, all switches had to be in transparent mode and the VLANs had to be configured manually on a switch-by-switch basis.
4. VTP version 3 only supports pruning for normal-range VLANs.
5. VTP version 3 supports propagating Private VLAN information. As with extended-range VLANs, the lack of PVLAN support in VTP version 2 required all switches to be transparent mode and manual configuration at each switch.
6. VTP version 3 added support for opaque databases. In other words, VTP version 3 can transport more than just the VLAN database between switches. The only option at this time is to share the Multiple Spanning Tree (MSTP) database, but room was left for expansion. We will cover MSTP in a later lab.
VTP version 3 is backwards compatible with VTP version 2; at the boundary of the two protocols, a VTP version 3 switch will send out both version 3 and version 2-compatible messages. Version 2 messages received by a version 3 switch are discarded.
Step 1: Configure VTP on DLS1, DLS2, and ALS2
VTP version 3 cannot be configured unless a VTP domain name has been set, so for this step, setting the domain name is not needed on DLS1. Configure VTP version 3 on DLS1, DLS2, and ALS2 using the following parameters
- VTP domain SWLAB (DLS2 and ALS2 only)
- VTP version 3
- VTP mode server (DLS2 and ALS2 only)
- VTP password cisco123 (DLS2 and ALS2 only)
DLS1 Configuration:
DLS1(config)# vtp version 3
DLS1(config)#
*Mar 1 00:08:17.637: %SW_VLAN-6-OLD_CONFIG_FILE_READ: Old version 2 VLAN
configuration file detected and read OK. Version 3
files will be written in the future.
DLS1(config)# end
DLS1#
Example configuration on ALS2:
ALS2(config)# vtp domain SWLAB Changing VTP domain name from NULL to SWLAB ALS2(config)# vtp version 3 ALS2(config)# vtp mode server Setting device to VTP Server mode for VLANS. ALS2(config)# vtp password cisco123 Setting device VTP password to cisco123 ALS2(config)# end *Mar 1 18:46:38.236: %SW_VLAN-6-VTP_DOMAIN_NAME_CHG: VTP domain name changed to SWLAB. *Mar 1 18:46:38.345: %SW_VLAN-6-OLD_CONFIG_FILE_READ: Old version 2 VLAN configuration file detected and read OK. Version 3 files will be written in the future. ALS2#
Step 2: Configure trunking on DLS2 and ALS2
In steps 4 and 5 of part 1, we configured and activated all the trunk interfaces on DLS1 and ALS1. Now configure and activate all the trunk interfaces on DLS2 and ALS2.
Example from DLS2:
DLS2(config)# interface range f0/7-12 DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport trunk native vlan 666 DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport mode trunk DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport nonegotiate DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport trunk allowed vlan except 1,999 DLS2(config-if-range)# no shutdown DLS2(config-if-range)# exit DLS2(config)#
Step 3: Verify trunking and VTP on DLS2 and ALS2
Next verify that DLS2 and ALS2 trunking is operational. Here is an example from DLS2
DLS2# show interface trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/7 on 802.1q trunking 666 Fa0/8 on 802.1q trunking 666 Fa0/9 on 802.1q trunking 666 Fa0/10 on 802.1q trunking 666 Fa0/11 on 802.1q trunking 666 Fa0/12 on 802.1q trunking 666 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/7 2-998,1000-4094 Fa0/8 2-998,1000-4094 Fa0/9 2-998,1000-4094 Fa0/10 2-998,1000-4094 Fa0/11 2-998,1000-4094 Fa0/12 2-998,1000-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/7 none Fa0/8 none Fa0/9 none Fa0/10 none Fa0/11 none Fa0/12 none Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/7 none Fa0/8 none Fa0/9 none Fa0/10 none Fa0/11 none Fa0/12 none
Next, validate VTP is operational. Here is an example from DLS2:
DLS2# show vtp status VTP Version capable : 1 to 3 VTP version running : 3 VTP Domain Name : SWLAB VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled Device ID : e840.406f.7380 Feature VLAN: -------------- VTP Operating Mode : Server Number of existing VLANs : 5 Number of existing extended VLANs : 0 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Configuration Revision : 0 Primary ID : 0000.0000.0000 Primary Description : MD5 digest : Feature MST: -------------- VTP Operating Mode : Transparent Feature UNKNOWN: -------------- VTP Operating Mode : Transparent DLS2#
Notice that the configuration revision number is zero and the number of local VLANs is the default of 5. There has been no update because DLS1’s configuration revision number was reset to zero when the VTP version was changed, so at this point DLS2 and ALS2 will not learn about the configured VLANs because as far as they are concerned, they have the same database as DLS1.
DLS1# show vtp status | inc Configuration Revision Configuration Revision : 0
If we attempt to add VLANs at DLS1, or any of the other VTP version 3 switches, our attempt will not work and we will be told that we cannot add VLANs.
DLS1(config)# vlan 111 VTP VLAN configuration not allowed when device is not the primary server for vlan database. DLS1(config)#
Step 4: Configure the Primary VTP Server
In a VTP version 3 domain, only the “Primary Server” can make changes to the VLAN database. Becoming the primary server requires the vtp primary privileged EXEC command be executed. When you issue that command, the switch checks to see if there is another switch acting as primary server already, and asks you to confirm that you want to continue.
In the output from DLS2 above, note that the Primary ID field equals 0000.0000.0000. That field will display the base MAC address of the primary server once a device is promoted into that role.
Also note that a separate primary server can be configured independently for each feature supported; VLAN or MST. If no feature is specified, the vlan feature is assumed.
Lastly, there is a force option which causes the switch not to check for conflicts in the identity of the primary server. If different switches in the VTP domain identify different switches as the primary server, there is a good chance there are inconsistencies in the VLAN database.
DLS1# vtp primary ? force Do not check for conflicting devices mst MST feature vlan Vlan feature <cr> DLS1# vtp primary vlan This system is becoming primary server for feature vlan No conflicting VTP3 devices found. Do you want to continue? [confirm] DLS1# *Mar 1 00:42:54.983: %SW_VLAN-4-VTP_PRIMARY_SERVER_CHG: e840.406f.7280 has become the primary server for the VLAN VTP feature
Now verify the primary on DLS2 or ALS2: DLS2# show vtp status | i Primary Primary ID : e840.406f.7280 Primary Description : DLS1 DLS2#
The promotion of DLS1 to primary increments its configuration revision number to 1, so the VLANs that were previously created on DLS1 are propagated to DLS2 and ALS2 automatically.
ALS2# sho vlan brief | inc active 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4 99 MANAGEMENT active 100 SERVERS active 110 GUEST active 120 OFFICE active 666 NATIVE_DO_NOT_USE active
VLAN 999 will be missing from the filtered output above because it only includes VLANs in active state and VLAN 999 is suspended. Using the show vlan brief without filtering would show the VLAN 999.
Step 5: Park unused interfaces.
On DLS2 and ALS2, place all of interfaces that will not be used into the PARKING_LOT VLAN and shut them down. For this lab, the interfaces being used on all switches are F0/6 through F0/12.
An example from DLS2:
DLS2(config)# interface range f0/1-5,f0/13-24,g0/1-2 DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport mode access DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport nonegotiate DLS2(config-if-range)# switchport access vlan 999 DLS2(config-if-range)# shutdown DLS2(config-if-range)# exit
Step 6: Verify VLAN management capability
DLS1 is able to create VLANs, including extended-range VLANs. Note that because ALS1 is running VTP version 2 and its revision number is 6, it will ignore any of the VTPv2 messages sent to it because they have a lower revision number. When a VTP message with an equal revision number but different MD5 checksum is received, ALS1 will report an error. Here we added seven VLANs and then remove 6 of them to push the revision number on DLS1 to 9.
DLS1# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. DLS1(config)# vlan 510 DLS1(config-vlan)# name TEST510 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# vlan 511 DLS1(config-vlan)# name TEST511 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# vlan 512 DLS1(config-vlan)# name TEST512 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# vlan 513 DLS1(config-vlan)# name TEST513 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# vlan 514 DLS1(config-vlan)# name TEST514 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# vlan 515 DLS1(config-vlan)# name TEST515 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# vlan 1500 DLS1(config-vlan)# name TEST-EXT-1500 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# no vlan 510-514 DLS1(config)# end DLS1# ALS1# show vlan brief | i active 1 default active Fa0/6 99 MANAGEMENT active 100 SERVERS active 110 GUEST active 120 OFFICE active 515 TEST515 active 666 NATIVE_DO_NOT_USE active ALS1# ALS2#show vlan brief | inc active 1 default active Fa0/6 99 MANAGEMENT active 100 SERVERS active 110 GUEST active 120 OFFICE active 515 TEST515 active 666 NATIVE_DO_NOT_USE active 1002 fddi-default act/unsup 1003 trcrf-default act/unsup 1004 fddinet-default act/unsup 1005 trbrf-default act/unsup 1500 TEST-EXT-1500 active ALS2#
At this point, you should be able to ping each switch from every other switch.
Step 7: Change the VLAN status to deactivate ports.
As already briefly discussed in Part 2, Step 3 of this lab, the default status of VLAN 1 and user-created
VLANs is “active”. A VLAN can be made locally inactive by entering the global configuration command
shutdown vlan vlan-id, where vlan-id is the number of the VLAN to be shut down.
Alternatively, the VLAN can be shut down by issuing the shutdown command while in VLAN configuration mode and then exiting.
Both these options are equivalent, however only the shutdown vlan command works in while in VTP
Client mode.
Shutdown the Guest VLAN 110 on ALS1, wait a few moments, exit the configuration mode and then issue the show vlan brief command. The status should change to “act/lshut”.
ALS1(config)# shutdown vlan 110
ALS1# show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/6
99 MANAGEMENT active
100 SERVERS active
110 GUEST act/lshut
515 TEST515 active
120 OFFICE active
666 NATIVE_DO_NOT_USE active
999 PARKING_LOT suspended Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15
Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19
Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23
Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 trcrf-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trbrf-default act/unsup
ALS1#
Reactivate all ports in ALS1 Guest VLAN 110 using the no shutdown command in VLAN configuration
mode.
ALS1(config)# no shutdown vlan 110
As discussed and demonstrated in Part 2, Step 3 of this lab, you can put a VLAN into suspended status by using the state suspend command while in VLAN configuration mode on a VTPv2 server switch or on the VTPv3 primary server switch. In a mixed VTP version network, the suspension only works network-wide if it originates from the VTPv3 primary server. Suspending a VLAN causes all ports in that VLAN throughout the VTP domain to stop transferring data.
Suspend Guest VLAN 110 on DLS1, wait a few moments, exit VLAN configuration mode and then issue the show vlan brief | include suspended command. The status should change show the VLAN as suspended.
DLS1(config)# vlan 110 DLS1(config-vlan)# state ? active VLAN Active State suspend VLAN Suspended State DLS1(config-vlan)# state suspend DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)#end DLS1# DLS1# sho vlan brief | include suspended 110 GUEST suspended 999 PARKING_LOT suspended Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4 DLS1#
Issue the show vlan brief | include suspended command on another switch in the network, and you
will see that the VLAN status is suspended as well.
DLS2# show vlan brief | include suspended 110 GUEST suspended 999 PARKING_LOT suspended Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4 DLS2#
Reactivate VLAN 110 using the state active command in VLAN configuration mode.
DLS1(config)# vlan 110 DLS1(config-vlan)# state active DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)#
Issue the show vlan brief | include suspended command on another switch in the network, and you will see that the VLAN status is no longer listed.
DLS2# show vlan brief | include suspended 999 PARKING_LOT suspended Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4 DLS2#
Step 8: End of Lab
Save your configurations. The equipment should be in the correct end state from this lab for Lab 3-2, EtherChannel.
Device Configurations:
Below are the final configurations for each switch.
DLS1
DLS1# show run | exclude ! Building configuration... Current configuration : 4121 bytes version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname DLS1 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 no ip domain-lookup ip domain-name CCNP.NET spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id vlan internal allocation policy ascending interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/5 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/8 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/13 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/14 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/15 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/16 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/17 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/19 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/20 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/21 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/22 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/23 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/24 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface Vlan1 no ip address interface Vlan99 ip address 10.1.99.101 255.255.255.0 ip http server ip http secure-server line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous line vty 0 4 login line vty 5 15 login end
DLS2
DLS2# show run | exclude ! Building configuration... Current configuration : 3979 bytes version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname DLS2 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 no ip domain-lookup ip domain-name CCNP.NET spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id vlan internal allocation policy ascending interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/5 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/8 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/13 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/14 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/15 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/16 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/17 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/19 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/20 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/21 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/22 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/23 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/24 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown interface Vlan99 ip address 10.1.99.102 255.255.255.0 ip http server ip http secure-server line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous line vty 0 4 login line vty 5 15 login end
ALS1
ALS1# show run | exclude ! Building configuration... Current configuration : 3872 bytes version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname ALS1 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 no ip domain-lookup ip domain-name CCNP.NET spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id vlan internal allocation policy ascending interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/5 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/8 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/13 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/14 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/15 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/16 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/17 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/19 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/20 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/21 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/22 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/23 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/24 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown interface Vlan99 ip address 10.1.99.103 255.255.255.0 ip http server ip http secure-server line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous line vty 0 4 login line vty 5 15 login end
ALS2
ALS2# show run | exclude ! Building configuration... Current configuration : 3872 bytes version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname ALS2 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 no ip domain-lookup ip domain-name CCNP.NET spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id vlan internal allocation policy ascending interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/5 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/8 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport trunk native vlan 666 switchport trunk allowed vlan 2-998,1000-4094 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate interface FastEthernet0/13 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/14 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/15 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/16 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/17 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/19 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/20 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/21 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/22 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/23 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface FastEthernet0/24 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate shutdown interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown interface Vlan99 ip address 10.1.99.104 255.255.255.0 ip http server ip http secure-server line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous line vty 0 4 login line vty 5 15 login end
