1. What is the correct BGP command to summarize the addresses from 172.16.0.0 through 172.16.15.0 into a single address that will be advertised by BGP?
- summary-address 172.16.0.0 0.15.255.255 summary-only
- summary-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.240.0 summary-only
- aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 0.15.255.255 summary-only
- aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.240.0 summary-only
2. A network administrator is configuring a prefix list to match networks for BGP route filtering. Which two networks match the prefix match specification 10.224.0.0/12 ge 24 le 28? (Choose two.)
- 10.224.10.0/12
- 10.240.10.0/24
- 10.230.15.0/24
- 10.192.20.0/26
- 10.239.255.240/28
3. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting BGP configuration and wants to verify routes that carry the 100 AS in the AS_Path value. Which regular expression should the administrator use in the command show bgp ipv4 unicast regex regex-pattern?
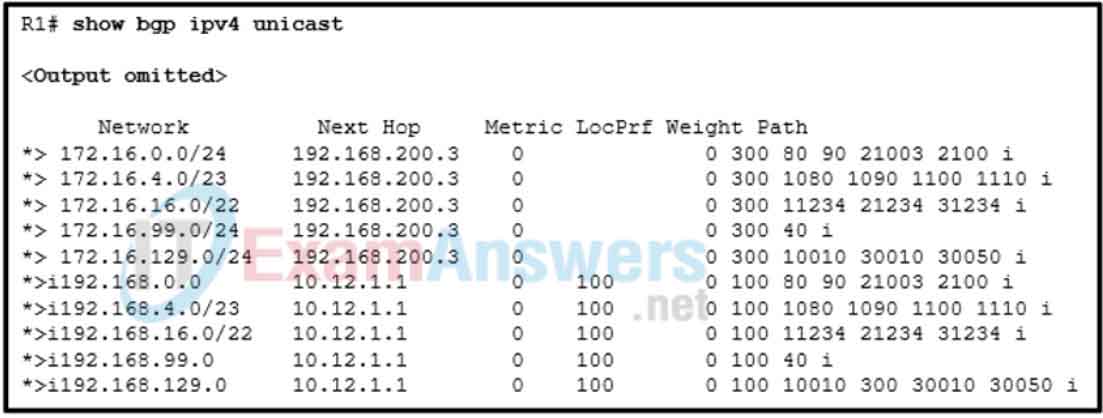
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regex .100.
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regex $100
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regex 100_
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regex ^100^
4. What is the purpose of the BGP maximum prefix feature?
- to restrict the number of routes received from a peer
- to restrict the bandwidth used for a specific set of routes
- to restrict the number of peers that will advertise the same route
- to restrict the number of routes sent to a peer with low bandwidth
5. A network administrator is configuring an ACL to match networks for BGP route filtering. The administrator creates an ACE permit ip 10.0.128.0 0.0.63.0 255.255.255.0 0.0.0.0. Which network matches the ACE?
- 10.0.63.0/24
- 10.0.130.0/24
- 10.0.192.0/24
- 10.0.128.0/25
6. A network administrator is configuring a BGP router with the neighbor 10.12.1.2 maximum-prefix 12 command. Which three actions will the router take when the peer at 10.12.1.2 advertises more than 12 routes?(Choose three.)
- closes the BGP session
- sends a syslog message
- moves the peer to the ldle state
- sends a warning message to the peer
- closes the BGP session for 60 seconds and then restarting the BGP peering process
- transitions the BGP session to listening mode but does not install any new routes into the BGP table
7. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring BGP route filtering on R1. The router ID for R1 is configured with lookback address 192.168.1.1. Which three routes are allowed from the BGP neighbor router 10.12.1.2 to inject into the BGP table of R1? (Choose three.)
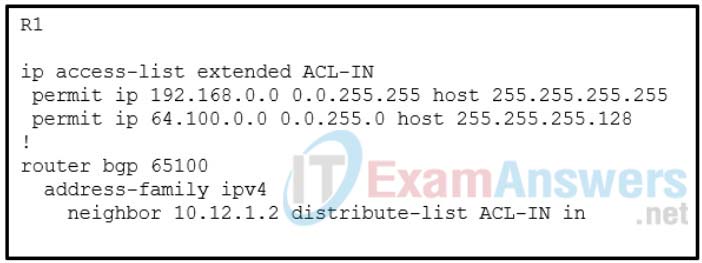
- 192.168.1.1/32
- 192.168.2.2/32
- 192.168.3.3/32
- 10.12.1.0/24
- 64.100.3.0/25
- 64.100.2.192/26
8. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast 172.16.0.0 command to check the route information in the BGP table. Which statement describes the characteristic of the advertisement of this route?
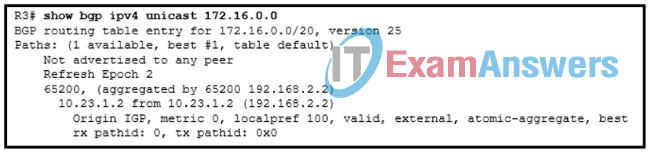
R3# show bgp ipv4 unicast 172.16.0.0
BGP routing table entry for 172.16.0.0/20, version 25
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table default)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 2
65200, (aggregated by 65200 192.168.2.2)
10.23.1.2 from 10.23.1.2 (192.168.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, atomic-aggregate, best
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
- The route is advertised through IGP.
- The route is advertised through a static route.
- The route is advertised without including path attributes before the aggregation.
- The route is advertised with the aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.240.0 command.
9. A network administrator is configuring a BGP router with the neighbor 10.12.1.2 maximum-prefix 20 75 command. What will happen when the peer at 10.12.1.2 advertises 15 routes?
- The router sends a warning message to the peer.
- The router drops any further advertisements from the peer.
- The router moves the peer to the Idle state and closes the BGP session.
- The router transitions to listening mode and does not install any new routes into the BGP table.
10. Which statement describes a characteristic of a BGP peer group?
- Member routers are of the same model.
- Member routers form a fully meshed connection.
- Member routers share the same outbound routing policy.
- Member routers share the same outbound and inbound routing policy.
11. Which three options are well-known BGP community sets? (Choose three.)
- Internet
- Test_Only
- No_Export
- No Transit
- Transit_Only
- No Advertise
12. Refer to the exhibit. When considering the route map configuration for BGP, what is the result when inbound traffic is received with a source IP that matches ACL1?
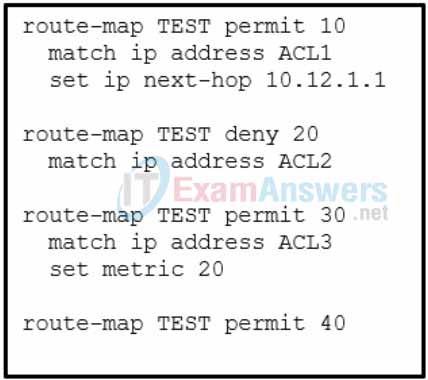
- The incoming network traffic will go through the whole route map.
- The optional action is processed, and the route map completes.
- If the incoming network traffic does not match ACL2 and ACL3, it will be dropped.
- The optional action is processed, and route map continues to test with ACL2.
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. Which BGP command advertises a summary route to prevent link-flap processing by downstream BGP routers?
- aggregate-address network subnet-mask as-set
- aggregate-address network subnet-mask summary-only
- summary-address network subnet-mask
- summary-address network mask subnet-mask
2. What is the BGP atomic aggregate?
- A BGP path attribute used to indicate that a prefix should not be advertised to a peer
- A BGP path attribute that indicates a loss of path attributes
- The amount of time that a peer’s routes should not be installed due to a flapping link
- The BGP routes that are suppressed during summarization
3. Which extended ACL entry allows any network in the 172.16.x.x network with a /24 to /32 prefix length?
- permit ip 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 255.255.255.0 0.0.0.255
- permit ip 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 0.0.255.255 0.0.0.0
- permit ip 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 255.255.255.0 0.0.0.255
- permit ip 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 0.0.255.255 0.0.0.0
4. Which command displays only the network prefixes that originate from AS 40 or AS 45?
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regexp _40|45$
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regexp ^40|45
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regexp _4(0|5)$
- show bgp ipv4 unicast regexp _[40,45]$
5. True or false: A BGP AS_Path ACL and a prefix list can be applied to a neighbor at the same time.
- True
- False
6. Which of the following is not a well-known BGP community?
- No_Advertise
- Internet
- No_Export
- Private_Route
7. A router has been configured with the command neighbor 10.12.1.2 maximum-prefix 100. What happens when the BGP peer advertises 101 prefixes to it?
- The 101st prefix overwrites the 1st prefix in the Loc-RIB table.
- The 101st prefix is discarded.
- The BGP session is shut down.
- The 101st prefix is received and installed in the Loc-RIB table, and a warning message is generated.
8. What is the primary difference between a BGP peer group and a peer template?
- They can have different inbound routing policies.
- They can have different outbound routing policies.
- They can have different BGP authentication settings.
- They can have different BGP timers.
