1. What is the first attribute to be used in determining the best path when a BGP router has multiple paths for the same network prefix length?
- weight
- lowest MED
- local originated
- local preference
Explanation: The BGP best-path algorithm uses the attributes, in the following order, for the best-path selection:
- Weight.
- Local preference.
- Local originated (network statement, redistribution, or aggregation).
- AIGP.
- Shortest AS_Path.
- Origin type.
- Lowest MED.
- EBGP over IBGP.
- Lowest IGP next hop.
- If both paths are external (EBGP), prefer the first (oldest).
- Prefer the route that comes from the BGP peer with the lower RID.
- Prefer the route with the minimum cluster list length.
- Prefer the path that comes from the lowest neighbor address.
2. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator in autonomous system 65100 has set up a dual-homed BGP connection with an ISP. The administrator would like to ensure that all traffic from the ISP enters the autonomous system through the router R1. Which BGP attribute can the administrator configure on routers R1 and R2 to accomplish this?
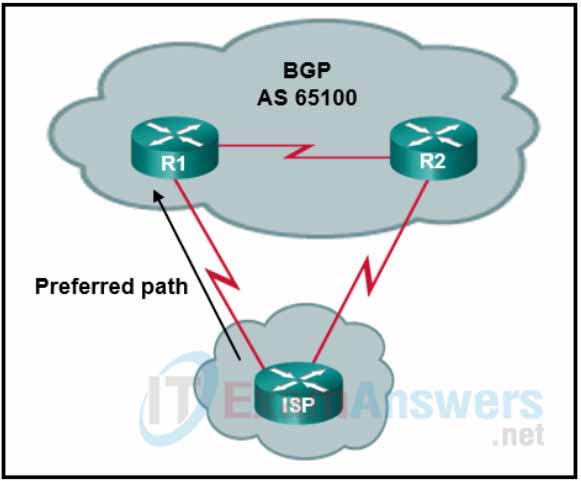
- multiple-exit discriminator
- local preference
- aggregate
- next-hop
- weight
Explanation: The multiple-exit discriminator (MED) is a nontransitive BGP attribute for best-path determination. MED uses a 32-bit value (0 to 4,294,967,295) called a metric. The purpose of MED is to influence traffic flows inbound from a different AS. A lower MED is preferred over a higher MED.
3. Which statement describes a feature of BGP transitive path attributes?
- They are carried from one AS to another.
- They are effective when the enterprise AS carries transitive data traffic.
- They are imported to an IGP when both IBGP and IGP are used within an AS.
- Their changes only influence the local BGP routing policy and provide information to neighboring BGP routers.
Explanation: BGP path attributes (PAs) can be either transitive or nontransitive. Transitive PAs are carried from one AS to another AS and those changes could affect downstream routing for other SPs too. Nontransitive PAs influence the routing policy only within the organization. All the BGP path attributes cannot be maintained within IGP protocols. Only BGP is capable of maintaining the path attribute as the prefix is advertised from one edge of the AS to the other edge.
4. What is the default local preference value assigned to a prefix received from a BGP peer?
Explanation: Local preference (LOCAL_PREF) is a well-known discretionary path attribute and is included with path advertisements throughout an AS. If an edge BGP router does not define the local preference upon receipt of a prefix, the default local preference value of 100 is used during best-path calculation and is included in advertisements to other iBGP peers.
5. When a BGP router needs to make the best-path decision based on the routing protocol used to advertise the route, which source is the most preferred by BGP?
- IBGP peer
- EBGP peer
- a peer that is a member of the peer group
- confederation member AS peer
Explanation: The eighth BGP best-path decision factor is whether the route comes from an IBGP, EBGP, or confederation member AS (Sub-AS) peering. The best-path selection order is as follows:
- EBGP peers (most desirable)
- Confederation member AS peers
- IBGP peers (least desirable)
6. Which BGP path attribute correlates to the AS hop count?
- AIGP
- AS_Path
- origin code
- multi-exit discriminator
Explanation: The fifth decision point in the BGP best-path algorithm is the AS_Path length, which typically correlates to the AS hop count. A shorter AS_Path is preferred over a longer AS_Path.
7. Which class of BGP path attributes is supported by all BGP implementations and is not advertised between autonomous systems?
- optional transitive
- optional nontransitive
- well-known mandatory
- well-known discretionary
Explanation: The BGP prefix path attributes are classified as follows:
- Well-known mandatory – supported by all BGP implementations and advertised between autonomous systems
- Well-known discretionary – supported by all BGP implementations and not advertised between autonomous systems
- Optional transitive – supported by some BGP implementations and advertised between autonomous systems
- Optional nontransitive – supported by some BGP implementations and not advertised between autonomous systems
8. What is the term used to refer to the value of the BGP multi-exit discriminator (MED) attribute?
- cost
- metric
- priority
- selection
Explanation: The BGP multi-exit discriminator (MED) attribute is nontransitive. The MED uses a 32-bit value (0 to 4,294,967,295) called a metric.
9. A network administrator is configuring BGP multipathing. In order for additional paths to be placed in the RIB, which three BGP path attributes must match the best-path? (Choose three.)
- AIGP
- weight
- originated
- local preference
- AS_Path length
- neighbor IP address
Explanation: BGP selects only one best path, but it allows for the installation of multiple routes into the RIB. When BGP multipathing is configured, the additional paths need to match the following best-path BGP path attributes:
- Weight
- Local preference
- AS_Path length
- AS_Path content
- Origin
- MED
- Advertisement method (IBGP or EBGP)
10. Which two conditions must be met before a BGP route is eligible as a best path? (Choose two.)
- It must have the lowest AD value.
- It must pass the route validity check.
- It must have at least one backup route.
- It must have the highest MED attribute.
- The next-hop IP address for the route must be resolvable.
Explanation: All BGP prefixes must pass the route validity check, and the next-hop IP address must be resolvable for the route to be eligible as a best path.
11. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a BGP router. Which two statements describe the result of the configuration? (Choose two.)
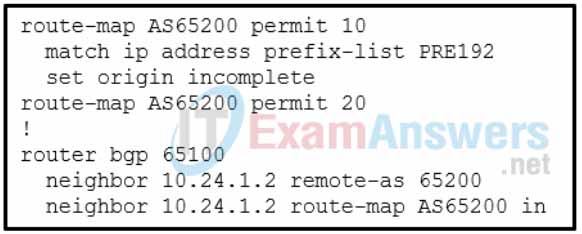
- The routes that match the prefix list PRE192 are least preferred for outbound traffic.
- Received routes that match the prefix list PRE192 are assigned an i in the BGP table.
- Received routes that match the prefix list PRE192 are assigned a ? in the BGP table.
- The routes that match the prefix list PRE192 are considered least desirable for inbound traffic.
- Received routes that do not match the prefix list PRE192 will not advertise the origin attribute to neighbor peers.
Explanation: The sixth decision point in the best-path algorithm is the well-known mandatory BGP attribute named origin. By default, networks that are advertised on Cisco routers using the network statement are set with the i (for IGP) origin, and redistributed networks are assigned the ? (incomplete) origin attribute. The origin preference order is as follows:
- IGP origin
- Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) origin
- Incomplete origin
The origin attribute of a prefix can be modified by using the command set origin {igp |incomplete} on a route map. Because the origin attribute is a well-known mandatory BGP attribute, it will be included in the advertisement to BGP peers.
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. True or false: BGP summarization provides a mechanism for load balancing traffic between service providers.
Explanation: Summarizing prefixes can shorten the prefix length, making a path less desirable compared to a longer prefix length.
2. True or false: A BGP router advertises every path for a prefix so that every neighbor can build its own topology table.
Explanation: BGP advertises only the path that the local router deems the best path.
3. Which of the following techniques is the second selection criterion for the BGP best path?
- Weight
- Local preference
- Origin
- MED
Explanation: Local preference is the second selection criterion for the BGP best path.
4. True or false: A router deletes a path from the Loc-RIB table after detecting that the current best path is inferior to a new superior path for a network prefix.
Explanation: A router deletes paths from the Loc-RIB table for a network prefix only after the route (path) has been withdrawn by the advertising neighbor. A router withdraws a path for a prefix if it is no longer available or if it needs to advertise a different best path for that network prefix.
5. In the BGP best-path algorithm, what attribute does BGP use after network origination (local, aggregation, received by peer) to select the best path?
- Local preference
- AS_Path
- Accumulated Interior Gateway Protocol (AIGP)
- MED
Explanation: BGP uses AIGP after network origination.
6. Which of the following attributes is locally significant to the BGP best-path algorithm?
- Weight
- Local preference
- AS_Path
- MED
Explanation: BGP weight is locally significant to the local router and does not impact other routers in an organization as it is not advertised to other routers.
7. True or false: MED can only be compared between three or more different Ass.
Explanation: By default, MED can only be compared between paths that are advertised from the same AS. Other configuration options, such as always-compare med, can change this behavior.
8. True or false: When BGP multipathing is enabled, a router can select multiple paths as the best path so that they can all be installed into the RIB.
Explanation: BGP selects only one best path, even with multipathing enabled. BGP can present multiple paths to the RIB for installation.


