1. Which transport layer port is used in BGP peering?
- UDP port 289
- TCP port 289
- UDP port 179
- TCP port 179
2. Which routing protocol is used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems on the Internet?
- IS-IS
- EIGRP
- OSPF
- BGP
3. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring BGP on the router RT1. Which command set will allow RT1 to establish a neighbor relationship with RT2?
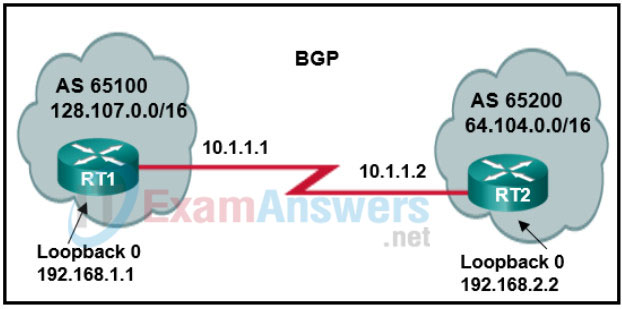
- RT1(config)# router bgp 65100
RT1(config-router)# network 128.107.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
RT1(config-router)# neighbor 10.1.1.2 remote-as 65200 - RT1(config)# router bgp 65100
RT1(config-router)# network 128.107.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
RT1(config-router)# neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 65200 - RT1(config)# router bgp 65100
RT1(config-router)# network 128.107.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
RT1(config-router)# neighbor 192.168.2.2 remote-as 65200 - RT1(config)# router bgp 65200
RT1(config-router)# network 64.104.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
RT1(config-router)# neighbor 10.1.1.2 remote-as 65100
4. Which two characteristics are associated with IBGP? (Choose two.)
- AS numbers reserved for IBGP sessions are from 65000 to 65400.
- The IBGP sessions are established among IBGP routers in the same AS.
- An IBGP session is established between an edge router and an ISP router.
- When IBGP prefixes are installed into the RIB, they are assigned an AD of 200.
- The AD value assigned to an IBGP prefix is dependent upon whether the connected router is in the same AS.
5. What is used by BGP to determine the best path to a destination?
- cost
- hop count
- attributes
- administrative distance
6. What is the first BGP message type that is sent after a TCP session is established between BGP peers?
- hello
- keepalive
- notification
- open
- update
7. What is a characteristic of an IBGP session type?
- Neighbors may be located anywhere within multiple autonomous systems, even several hops away from each other.
- A session typically occurs between routers in different autonomous systems with multiple ISPs.
- It can be established between routers in the same AS or that participate in the same BGP confederation.
- It occurs between routers in two different autonomous systems.
8. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast summary command to verify the BGP session after basic BGP configuration is completed. Which three pieces of information are found in the BGP session summary? (Choose three.)
- the AS number of the peer
- the BGP router ID of the peers
- the peer synchronization configuration
- the routes that are redistributed into BGP
- the IGP that is configured on the BGP peer
- the number of exchanged prefixes with a neighbor
9. Which method is used to provide a loop-free routing BGP table for IBGP routers in a single AS?
- AS_Path attribute
- full mesh connection requirement
- identical weight attribute on all IBGP routers
- static route establishment between each connected pair of IBGP routers
10. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast | begin Network command to check the routes in the BGP table. What does the symbol ? at the end of a route indicate?
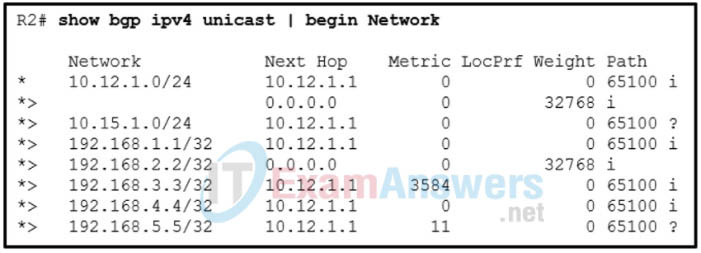
- The route is redistributed into BGP.
- The route is learned through a static route.
- The route is the best route for the network prefix.
- The route is originated from a connected network to the router.
11. What change was made to BGP to address the expected depletion of autonomous system numbers?
- the ability to incorporate hierarchical network design
- the use of a 2-octet autonomous system number
- the use of a 4-octet autonomous system number
- the ability to use RFC 1918 address space
12. Which two statements describe the configuration differences when MP-BGP is applied using the IPv6 protocol compared to IPv4 protocol? (Choose two.)
- IPv6 uses multicast to establish neighbor sessions.
- IPv4 addresses cannot be used to define a BGP RID.
- Routers with only IPv6 addressing must have the BGP RID statically defined.
- Routers with only IPV6 addressing must use AS numbers beyond 65535.
- The IPv6 address family must be initialized and the neighbor activated.
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. Which of the following autonomous system(s) are private? (Choose two.)
- 64,512 through 65,535
- 65,000 through 65,535
- 4,200,000,000 through 4,294,967,294
- 4,265,000 through 4,265,535,016
2. Which BGP attribute must be recognized by all BGP implementations and advertised to other autonomous systems?
- Well-known mandatory
- Well-known discretionary
- Optional transitive
- Optional non-transitive
3. True or false: BGP supports dynamic neighbor discovery by both routers.
- True
- False
4. True or false: BGP sessions are always one hop away from a neighbor.
- True
- False
5. True or false: The IPv4 address family must be initialized to establish a BGP session with a peer using IPv4 addressing.
- True
- False
6. Which command is used to view the BGP neighbors and their hello interval?
- show bgp neighbors
- show bgp afi safi neighbors
- show bgp afi safi summary
- show afi bgp interface brief
7. How many tables does BGP use for storing prefixes?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
8. True or false: A route learned from an eBGP peer is advertised to an iBGP neighbor.
- True
- False
9. True or false: A route learned from an iBGP peer is advertised to an iBGP neighbor.
- True
- False
10. Which of the following are considering iBGP scalability enhancements? (Choose two.)
- Route reflectors
- BGP route aggregation
- BGP confederations
- BGP alliances
11. True or false: The IPv6 address family must be initialized to establish a BGP session with a peer using IPv6 addressing.
- True
- False
12. True or false: IPv6 prefixes can be advertised only across a BGP session established with IPv6 addresses.
- True
- False
