1. What is the default maximum amount of bandwidth that can be used for exchanging EIGRP messages on an EIGRP-configured interface?
- 50%
- 10%
- 100%
- 75%
2. If replies are not received from all outstanding queries, how long will an EIGRP router wait before placing a route into the SIA state?
- 3 seconds
- 60 seconds
- 120 seconds
- 180 seconds
3. What is the purpose of the EIGRP Null0 summary route?
- to enhance security by hiding all internal networks that are included in a summary route
- to prevent routing loops for destination networks which do not actually exist but are included in a summary route
- to reduce bandwidth consumption for traffic that is leaving the network
- to ensure that all traffic destined for individual subnets uses one single best path
4. A network student has to prepare a paper about EIGRP network summarization, but the student does not know much about summarization metrics. What piece of information is accurate about EIGRP summarization?
- The summarizing router uses the highest metric of the component routes in the summary aggregate prefix.
- The path metric for the summary aggregate is based on an average of the path attributes of the component routers.
- Every time a matching component route for the summary aggregate is added or removed, downstream routes must run the DUAL again.
- EIGRP path attributes are inserted into the summary route so that downstream routers can calculate the correct path metric for the summarized prefix.
5. Refer to the exibit. Both routers are configured to use the EIGRP routing protocol. The network administrator wants to enable manual summarization by issuing the displayed command. Where should the administrator apply this command?
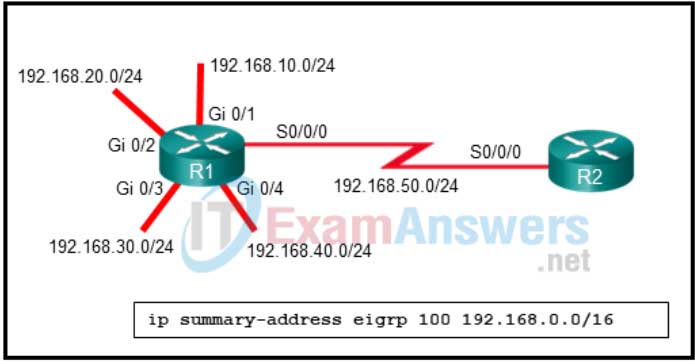
- in router configuration mode after entering the router eigrp 100 command
- in interface mode on the Gi0/1 interface of R1
- in interface mode on the S0/0/0 interface of R1
- in interface mode on the S0/0/0 interface of R2
6. Which time interval is used by default to send EIGRP hello packets on low bandwidth interfaces?
- 1 second
- 5 seconds
- 60 seconds
- 30 seconds
7. How can an EIGRP route be manipulated using offset lists?
- Completely remove a specific set of component routes.
- Reduce the total path metric to a more preferred value.
- Add the total path metric to a specific set of routes.
- Add delay to the path metric for a specific set of routes.
8. A network administrator is configuring the hello timer and the hold timer on an EIGRP router. What is a factor that the administrator needs to consider?
- EIGRP hello intervals should be less than the EIGRP hold timers.
- EIGRP hello intervals and hold timers must match between EIGRP neighbors to form an EIGRP adjacency.
- EIGRP hold timers specify the minimum time that the router should wait to send the next hello.
- EIGRP hello intervals specify the maximum time that the router should wait to receive the next hello.
9. A junior network engineer is learning about mechanisms to prevent routing loops on EIGRP. Which valuable piece of information can the network engineer learn about split horizon on an EIGRP network?
- Split horizon is disabled by default on all interfaces.
- Split horizon needs to be enabled on a Layer 2 Virtual Private Network.
- Split horizon needs to be disabled on hub-and-spoke topologies.
- Split horizon can only be disabled in global configuration mode.
10. When the distribute-list 1 in serial 0/0 command is used, which EIGRP routing updates would be permitted?
- Routing updates that are received on the serial 0/0 interface and permitted by ACL 1.
- Routing updates that are received on the serial 0/0 interface and permitted by prefix-list 1.
- Routing updates that are received on the serial 0/0 interface and permitted by route-map 1.
- Routing updates that are received on the serial 0/0 interface and permitted by offset-list 1.
11. The show ip eigrp topology command output on a router displays a successor route and a feasible successor route to network 192.168.1.0/24. In order to improve network convergence, what does EIGRP do when the primary route to this network fails?
- The router sends query packets to all EIGRP neighbors for a better route to network 192.168.1.0/24.
- DUAL immediately recomputes the algorithm to calculate the next backup route.
- Packets that are destined for network 192.168.1.0/24 are sent out the default gateway instead.
- The backup route to network 192.168.1.0/24 is installed in the routing table.
12. Which time interval is used by default to send EIGRP hello packets on high bandwidth interfaces?
- 1 second
- 5 seconds
- 10 seconds
- 20 seconds
- 30 seconds
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. What is the default EIGRP hello timer for a high-speed interface?
- 1 second
- 5 seconds
- 10 seconds
- 20 seconds
- 30 seconds
- 60 seconds
2. What is the default EIGRP hello timer for a low-speed interface?
- 1 second
- 5 seconds
- 10 seconds
- 20 seconds
- 30 seconds
- 60 seconds
3. When a path is identified using EIGRP and in a stable fashion, the route is considered _____.
- passive
- dead
- active
- alive
4. How does an EIGRP router indicate that a path computation is required for a specific route?
- EIGRP sends out an EIGRP update packet with the topology change notification flag set.
- EIGRP sends out an EIGRP update packet with a metric value of zero.
- EIGRP sends out an EIGRP query with the delay set to infinity.
- EIGRP sends a route withdrawal, notifying other neighbors to remove the route from the topology table.
5. True or false: EIGRP summarization is performed with the command summary-aggregate network subnet-mask under the EIGRP process for classic mode configuration.
- True
- False
6. True or false: EIGRP automatic summarization is enabled by default and must be disabled to prevent issues with networks that cross classful network boundaries.
- True
- False
7. True or false: EIGRP stub site functions can be deployed at all branch sites, regardless of whether downstream EIGRP routers are present.
- True
- False
8. How do EIGRP offset lists manipulate a route?
- Completely removing a set of specific routes
- Reducing the total path metric to a more preferred value
- Adding the total path metric to a specific set of routes
- Adding delay to the path metric for a specific set of routes
