1. Refer to the exhibit. Which two conclusions can be derived from the output? (Choose two.)
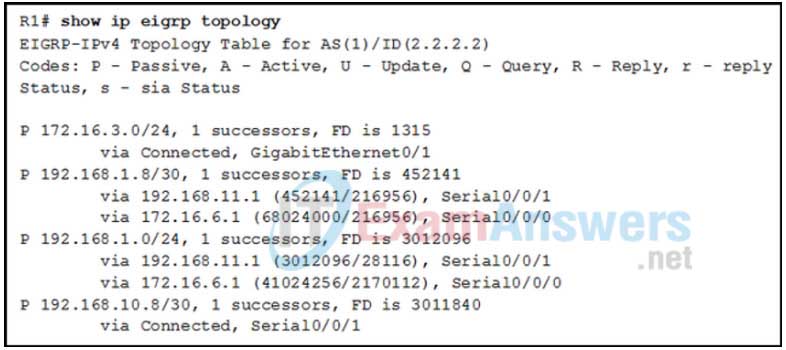
- There is one feasible successor to network 192.168.1.8/30.
- The network 192.168.10.8/30 can be reached through 192.168.11.1.
- The reported distance to network 192.168.1.0/24 is 41024256.
- The neighbor 172.16.6.1 meets the feasibility condition to reach the 192.168.1.0/24 network.
- Router R1 has two successors to the 172.16.3.0/24 network.
2. Refer to the exhibit. After the configuration shown is applied on router R1, the exhibited status message is displayed. Router R1 is unable to form a neighbor relationship with R2 on the serial 0/1/0 interface. What is the most likely cause of this problem?

- The passive-interface command should have been issued on serial 0/1/0.
- The hello interval has been altered on serial 0/1/0 and is preventing a neighbor relationship from forming.
- The network statement used for EIGRP 55 does not enable EIGRP on interface serial 0/1/0.
- The IPv4 address configured on the neighbor that is connected to R1 serial 0/1/0 is incorrect.
- The networks that are configured on serial 0/0/0 and serial 0/1/0 of router R1 are overlapping.
3. Refer to the exhibit. The routing table on R2 does not include all networks that are attached to R1. The network administrator verifies that the network statement is configured to include these two networks. What is a possible cause of the issue?
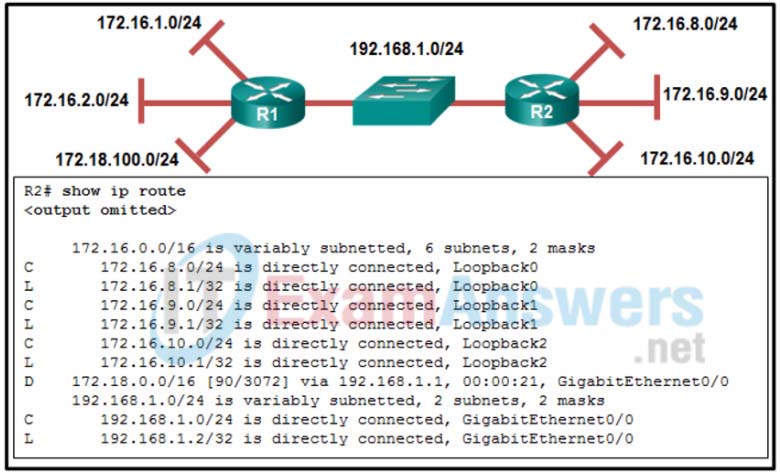
- The AS number does not match between R1 and R2.
- The network statements should include the wild card mask.
- The no auto-summary command is missing in the R1 configuration.
- The interfaces that are connected to these two networks are configured as passive interfaces.
4. Refer to the exhibit. Two routers have been configured to use EIGRP. Packets are not being forwarded between the two routers. What could be the problem?
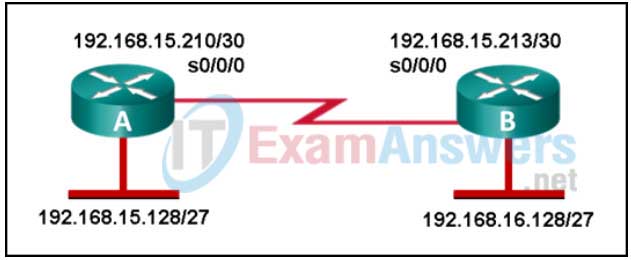
- EIGRP does not support VLSM.
- The routers were not configured to monitor neighbor adjacency changes.
- The default bandwidth was used on the routers.
- An incorrect IP address was configured on a router interface.
5. Refer to the exhibit. Router CiscoVille has been partially configured for EIGRP authentication. What is missing that would allow successful authentication between EIGRP neighbors?

- The interfaces that will use EIGRP authentication must be specified.
- The same key number must be used on any EIGRP neighbor routers.
- The keychain for EIGRP authentication must be configured on the interfaces.
- The CiscoVille router requires a second keychain to function correctly when using two interfaces for EIGRP authentication.
6. Refer to the exhibit. How did the router obtain the last route that is shown?

- The ip route command was used.
- The ipv6 route command was used.
- Another router in the same organization provided the default route by using a dynamic routing protocol.
- The ip address interface configuration mode command was used in addition to the network routing protocol configuration mode command.
7. A network administrator is troubleshooting the EIGRP routing between two routers, R1 and R2. The problem is found to be that only some, but not all networks attached to R1 are listed in the routing table of router R2. What should the administrator investigate on router R1 to determine the cause of the problem?
- Does the AS number match the AS number on R2?
- Does the hello interval setting match the hello interval on R2?
- Do the network commands include all the networks to be advertised?
- Is the interface connected to R2 configured as a passive interface?
8. Refer to the exhibit. R3 has two possible paths to the 172.16.99.0 network. What is the missing value of this output?
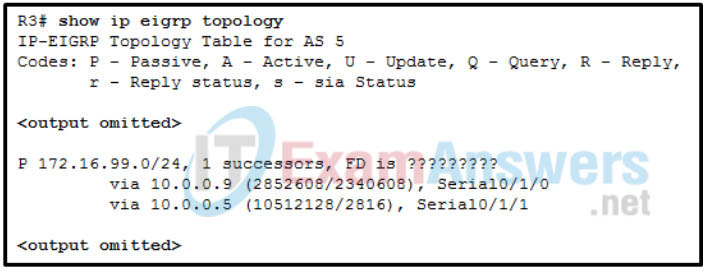
- 2340608
- 2816
- 10512128
- 2852608
9. A network administrator wants to verify the default delay values for the interfaces on an EIGRP-enabled router. Which command will display these values?
- show ip protocols
- show running-config
- show interfaces
- show ip route
10. Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 are directly connected via their serial interfaces and are both running the EIGRP routing protocol. R1 and R2 can ping the directly connected serial interface of their neighbor, but they cannot form an EIGRP neighbor adjacency.
What action should be taken to solve this problem?
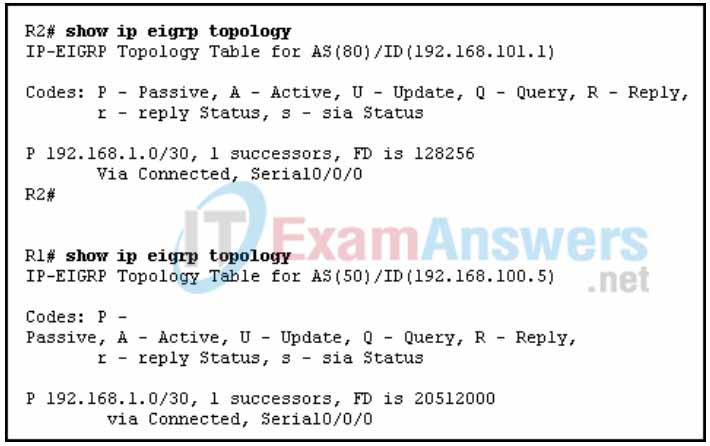
- Enable the serial interfaces of both routers.
- Configure EIGRP to send periodic updates.
- Configure the same hello interval between the routers.
- Configure both routers with the same EIGRP process ID.
11. While troubleshooting an EIGRP problem on a router, a network engineer needs to verify the IPv4 EIGRP implementation. To check the IP addressing, queue counts, and hold times for the adjacent routers, which command should be used?
- show ip eigrp topology
- show ip eigrp neighbors
- show ip protocols
- show ip eigrp interfaces
12. Refer to the exhibit. Why did R1 and R2 not establish an adjacency?
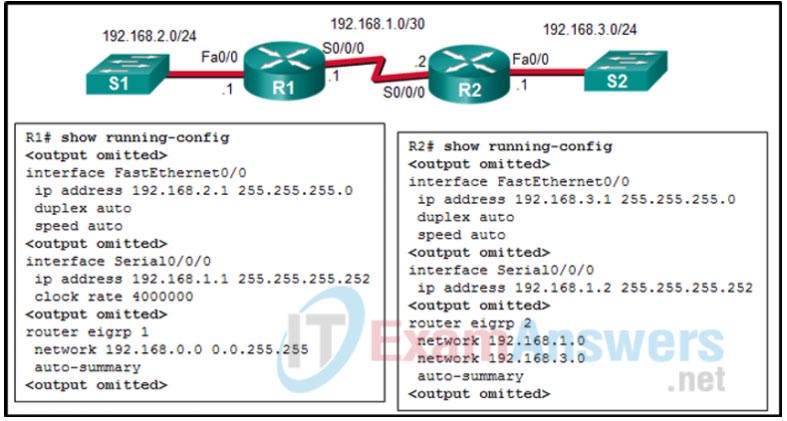
- The AS number does not match on R1 and R2.
- The automatic summarization is enabled on R1 and R2.
- The IPv4 address of Fa0/0 interface of R1 has a wrong IP address.
- There is no network command for the network 192.168.1.0/24 on R1.
13. For troubleshooting missing EIGRP routes on a router, what three types of information can be collected using the show ip protocols command? (Choose three.)
- any interfaces that are enabled for EIGRP authentication
- any interfaces on the router that are configured as passive
- the IP addresses that are configured on adjacent routers
- any ACLs that are affecting the EIGRP routing process
- networks that are unadvertised by the ElIGRP routing protocol
- the local interface that is used to establish an adjacency with EIGRP neighbors
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. Which command enables you to verify the routers that have formed EIGRP adjacencies with the local router, how long they have been neighbors, and the current sequence numbers of EIGRP packets?
- show ip eigrp interfaces
- show ip eigrp neighbors
- show ip route eigrp
- show ip protocols
2. Which of the following are reasons EIGRP neighbor relationships might not form? (Choose three.)
- Different autonomous system numbers
- Different K values
- Different timers
- Different authentication parameters
3. Which command enables you to verify the configured EIGRP K values?
- show ip protocols
- show ip eigrp interfaces
- show ip eigrp neighbor
- show ip eigrp topology
4. Which command enables you to verify EIGRP authentication, split horizon, and configured EIGRP timers?
- show ip interfaces
- show ip protocols
- show ip eigrp interfaces detail
- show ip eigrp neighbor
5. Besides a neighbor relationship not being formed, which three of the following are reasons routes might be missing in an EIGRP autonomous system? (Choose three.)
- Interface not participating in the EIGRP process
- Filters
- Incorrect stub configuration
- Passive interface feature
6. Which command enables you to verify whether any route filters have been applied to an EIGRP-enabled interface?
- show ip interface brief
- show ip interface
- show ip protocols
- show ip eigrp interface
7. Which command enables you to verify the maximum paths configured for load balancing and whether unequal-path load balancing has been enabled?
- show ip protocols
- show ip eigrp interfaces
- show ip eigrp neighbors
- show ip interfaces
8. You have a DMVPN network that has a hub and three spokes. The spokes are not learning the routes of the other spokes. Of the following options, which is most likely the reason for this?
- Split horizon is enabled on the GRE interfaces of the spokes
- Split horizon is enabled on the hub’s mGRE interface
- Split horizon is disabled on the hub’s mGRE interface
- Split horizon is disabled on the GRE interfaces of the spokes
9. An EIGRP summary route is not showing up on the expected routes in the AS. Which of the following questions should you answer while troubleshooting? (Choose three.)
- Did you enable route summarization on the correct interface?
- Did you associate the summary route with the correct EIGRP autonomous system?
- Did you create the appropriate summary route?
- Did you create a route to NULL0?
10. The IP addressing scheme for your routing domain is discontiguous. What command should you use in EIGRP configuration mode to make sure that you do not have any routing issues in your EIGRP autonomous system?
- no auto-summary
- auto-summary
- passive-interface
- network ip_address wildcard_mask
