1. Which two protocols are allowed to be routed by EIGRP as a consequence of the PDM feature? (Choose two.)
- IPv4
- TCP
- IPv6
- UDP
- RTP
2. Which bandwidth value is used when calculating the EIGRP metric of a route?
- the fastest bandwidth of all interfaces on the router
- the slowest bandwidth of all interfaces on the router
- the fastest bandwidth of all outgoing interfaces between the source and destination
- the slowest bandwidth of all outgoing interfaces between the source and destination
3. Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes the result of the last entry in the exhibited configuration?

- The routing table will include up to four unequal-cost routes learned via EIGRP.
- The routing table will include any route learned via EIGRP with a metric less than four times the successor metric.
- The routing table will include up to two equal-cost routes learned via EIGRP for the two advertised networks.
- The routing table will include all routes learned via EIGRP with a metric less than four times the feasible distance of the advertised networks.
4. What is the administrative distance of externally learned EIGRP routes?
- 170
- 90
- 110
- 120
5. Which protocol is used by EIGRP for delivering and receiving EIGRP packets?
- RTP
- TCP
- UDP
- ICMP
6. Which destination MAC address is used when a multicast EIGRP packet is encapsulated into an Ethernet frame?
- 01-00-5E-00-00-09
- 01-00-5E-00-00-10
- 01-00-5E-00-00-0A
- 01-00-5E-00-00-0B
7. Which two parameters are used by EIGRP as metrics to select the best path to reach a network? (Choose two.)
- hop count
- bandwidth
- jitter
- resiliency
- delay
- confidentiality
8. What are three features of EIGRP? (Choose three.)
- uses the Shortest Path First algorithm
- establishes neighbor adjacencies
- uses the Reliable Transport Protocol
- sends full routing table updates periodically
- broadcasts updates to all EIGRP routers
- supports equal and unequal cost load balancing
9. Which three metric weights are set to zero by default when costs are being calculated using the EIGRP classic metric? (Choose three.)
- K1
- K2
- K3
- K4
- K5
- K6
10. Refer to the exhibit. Which command was used to generate this output?
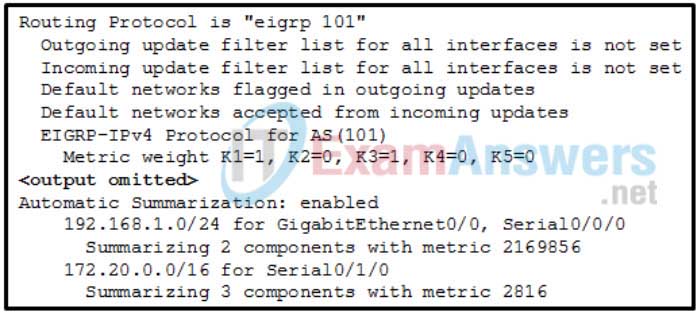
- show ip eigrp neighbors
- show ip eigrp topology all-links
- show ip eigrp traffic
- show ip protocols
11. What two conditions will result in an EIGRP route going into the active state? (Choose two.)
- One neighbor has not met the feasibility condition.
- The router is not sending queries.
- The successor is down.
- There is no feasible successor.
- The network has been recalculated.
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. EIGRP uses protocol number ____ for inter-router communication.
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
2. How many packet types does EIGRP use for inter-router communication?
- Three
- Four
- Five
- Six
- Seven
3. Which of the following is not required to match to form an EIGRP adjacency?
- Metric K values
- Primary subnet
- Hello and hold timers
- Authentication parameters
4. What is an EIGRP successor?
- The next-hop router for the path with the lowest path metric for a destination prefix
- The path with the lowest metric for a destination prefix
- The router selected to maintain the EIGRP adjacencies for a broadcast network
- A route that satisfies the feasibility condition where the reported distance is less than the feasible distance
5. What attributes does the EIGRP topology table contain? (Choose all that apply.)
- Destination network prefix
- Hop Count
- Total path delay
- Maximum path bandwidth
- List of EIGRP neighbors
6. What destination addresses does EIGRP use when feasible? (Choose two.)
- IP address 224.0.0.9
- IP address 224.0.0.10
- IP address 224.0.0.8
- MAC address 01:00:5E:00:00:0A
- MAC address 0C:15:C0:00:00:01
7. The EIGRP process is initialized by which of the following technique? (Choose two.)
- Using the interface command ip eigrp as-number ipv4 unicast
- Using the global configuration command router eigrp as-number
- Using the global configuration command router eigrp process-name
- Using the interface command router eigrp as-number
8. True or false: The EIGRP router ID (RID) must be configured for EIGRP to be able to establish neighborship.
- True
- False
9. True or false: When using MD5 authentication between EIGRP routers, the key-chain sequence number can be different, as long as the password is the same.
- True
- False
10. Which value can be modified on a router to manipulate the path taken by EIGRP but does not have impacts on other routing protocols, like OSPF?
- Interface bandwidth
- Interface MTU
- Interface delay
- Interface priority
