1. What do devices on the same IPv4 subnet have in common?
- They all use the same default gateway.
- They all have a subnet mask of /8, /16, or /24.
- They all have the same last octet in their IPv4 addresses.
- They all have the same number in the first three octets of their IPv4 address.
2. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has added a new subnet to the network and needs hosts on that subnet to receive IPv4 addresses from the DHCPv4 server.
What two commands will allow hosts on the new subnet to receive addresses from the DHCP4 server? (Choose two.)
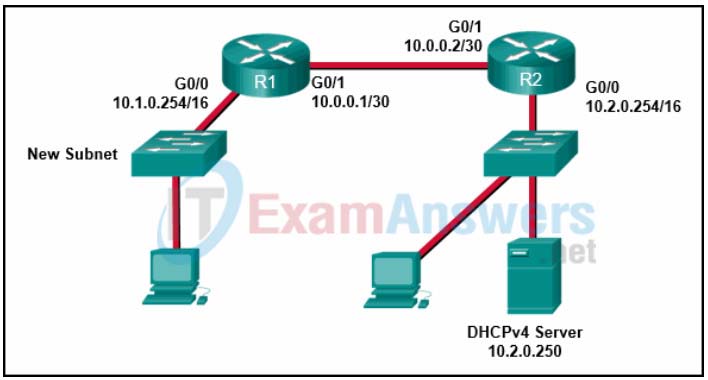
- R1(config)# interface G0/0
- R1(config-if)# ip helper-address 10.2.0.250
- R2(config)# interface G0/0
- R2(config-if)# ip helper-address 10.2.0.250
- R1(config-if)# ip helper-address 10.1.0.254
- R1(config)# interface G0/1
3. Refer to the exhibit. How will R1 generate the interface ID portion of the IPv6 address on interface FastEthernet 0/0?

- by using stateful DHCP
- by using a manually set value of 64
- by using a randomly generated 64-bit number
- by using the interface MAC address with a 16-bit filler
4. What is the function of ARP?
- resolves domain names to IP addresses
- provides automatic IP address assignments to hosts
- sends error and operational information messages to hosts
- maps IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses
5. Which command will create a static route on R2 in order to reach PC B?
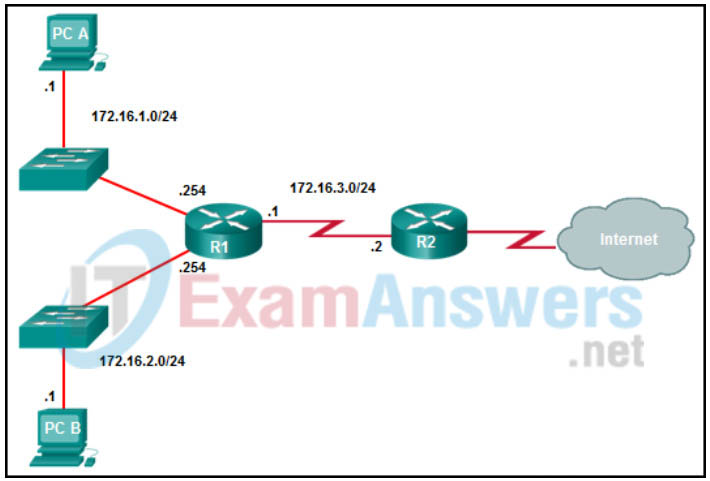
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 172.16.3.1
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.254
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.3.1
- R2(config)# ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.254
6. Which statement describes one purpose of the subnet mask setting for a host?
- It is used to describe the type of the subnet.
- It is used to identify the default gateway.
- It is used to determine to which network the host is connected.
- It is used to determine the maximum number of bits within one packet that can be placed on a particular network.
7. Refer to the exhibit. Host A is unable to obtain an IP address from the DHCP server. Which procedure would solve this problem?
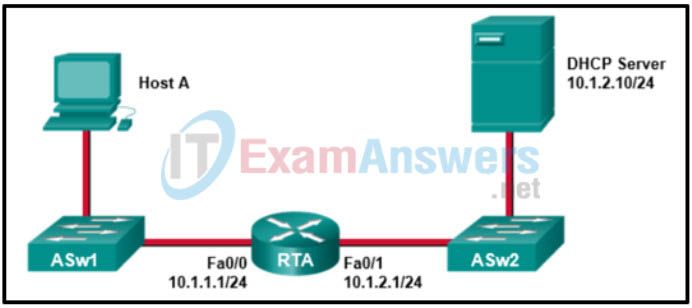
- Configure interface Fa0/0 of router RTA with the ip helper-address 10.1.2.1 command.
- Configure interface Fa0/0 of router RTA with the ip helper-address 10.1.2.10 command.
- Configure interface Fa0/1 of router RTA with the ip helper-address 10.1.2.10 command.
- Configure interface Fa0/0 of router RTA with the ip forward-protocol 67 command.
8. What two methods can be used to generate an interface ID by an IPv6 host that is using SLAAC? (Choose two.)
- EUI-64
- random generation
- stateful DHCPv6
- DAD
- ARP
9. Which routing protocol uses an administrative distance of 110?
- RIP
- OSPF
- EIGRP
- BGP
10. Which type of packet is sent by a DHCP server after receiving a DHCP Discover message?
- DHCP ACK
- DHCP Discover
- DHCP Offer
- DHCP Request
11. What are the two main components of Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)? (Choose two.)
- adjacency tables
- MAC-address tables
- routing tables
- ARP tables
- forwarding information base (FIB)
12. Which destination IP address is used when an IPv6 host sends a DHCPv6 SOLICIT message to locate a DHCPv6 server?
- FF02::1:2
- FF02::1
- FE80::1
- FF02::2
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. What occurs when a PC with the IP address 10.1.1.27/28 needs to communicate with a PC that has IP address 10.1.1.18? (Choose two.)
- a. It sends the frame to its default gateway.
- b. It sends the frame directly to the destination PC.
- c. It uses ARP to get the MAC address of the default gateway.
- d. It uses ARP to get the MAC address of the destination PC.
2. What occurs when a PC with the IP address 10.1.1.27/29 needs to communicate with a PC that has IP address 10.1.1.18? (Choose two.)
- a. It sends the frame to its default gateway.
- b. It sends the frame directly to the destination PC.
- c. It uses ARP to get the MAC address of the default gateway.
- d. It uses ARP to get the MAC address of the destination PC.
3. Which command enables you to verify the IP address configured on a router’s interface?
- a. ipconfig
- b. show ip interface
- c. arp -a
- d. show ip arp
4. What is the correct order of operations for the DHCP for IPv4 process?
- a. Offer, Request, Ack, Discover
- b. Discover, Request, Ack, Offer
- c. Request, Offer, Discover, Ack
- d. Discover, Offer, Request, Ack
5. Which command is needed on a router interface to forward DHCP Discover messages to a DHCP server on a different subnet?
- a. ip address dhcp
- b. ip helper-address
- c. ip dhcp-forwarder
- d. ip dhcp server
6. Which command enables a router interface to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server?
- a. ip dhcp client
- b. ip dhcp server
- c. ip address dhcp
- d. ip helper-address
7. What protocol is used with IPv6 to determine the MAC address of a device in the same local area network?
- a. Address Resolution Protocol
- b. Inverse Address Resolution Protocol
- c. Neighbor Discovery Protocol
- d. Neighbor Solicitation
8. Which of the following are true when using EUI-64? (Choose two.)
- a. The interface MAC address is used unmodified.
- b. The interface MAC address is used with FFFE added to the middle.
- c. The seventh bit from the left in the MAC address is flipped.
- d. The seventh bit from the right in the MAC address is flipped.
9. What command is used on a Cisco IOS router to enable SLAAC on an interface?
- a. ipv6 address autoconfig
- b. ipv6 address dhcp
- c. ipv6 address prefix eui-64
- d. ipv6 nd ra suppress
10. Which of the following are requirements for stateless address autoconfiguration to function? (Choose three.)
- a. The prefix must be /64.
- b. The router must be sending and not suppressing RA messages.
- c. The router must be enabled for IPv6 unicast routing.
- d. The router must be sending RS messages.
11. Which command is used to enable a router to inform clients that they need to get additional configuration information from a DHCPv6 server?
- a. ipv6 nd ra suppress
- b. ipv6 dhcp relay destination
- c. ipv6 address autoconfig
- d. ipv6 nd other-config-flag
12. What command enables you to configure a router interface as a DHCPv6 relay agent?
- a. ipv6 forwarder
- b. ipv6 helper-address
- c. ipv6 dhcp relay destination
- d. ipv6 dhcp client
13. Which two data structures reside at the router’s data plane?
- a. IP routing table
- b. ARP cache
- c. Forwarding Information Base
- d. Adjacency table
14. Which command enables you to verify routes in the FIB?
- a. show ip route
- b. show ip arp
- c. show ip cef
- d. show adjacency detail
15. Which of the following populate a routing protocol’s data structure, such as the EIGRP topology table? (Choose three.)
- a. Updates from a neighbor
- b. Redistributed routes
- c. Interfaces enabled for the routing process
- d. Static routes
16. Which of the following has the lowest default administrative distance?
- a. OSPF
- b. EIGRP (internal)
- c. RIP
- d. eBGP
17. What is the default administrative distance of an OSPF intra-area route?
- a. 90
- b. 110
- c. 115
- d. 120
18. How can you create a floating static route?
- a. Provide the static route with a metric higher than the preferred source of the route.
- b. Provide the static route with a metric lower than the preferred source of the route.
- c. Provide the static route with an AD higher than the preferred source of the route.
- d. Provide the static route with an AD lower than the preferred source of the route.
19. What occurs when you create an IPv4 static route with an Ethernet interface designated instead of a next-hop IP address?
- a. The router uses ARP to get the MAC address of the directly connected router’s IP address.
- b. The router forwards the packet with the destination MAC address FFFF:FFFF:FFFF.
- c. The router uses ARP to get the MAC address of the IP address in the source of the packet.
- d. The router uses ARP to get the MAC address of the IP address in the destination of the packet.
