1. What is the Control Plane Policing (CoPP) feature designed to accomplish?
- manage services provided by the control plane
- prevent unnecessary traffic from overwhelming the route processor
- disable control plane services to reduce overall traffic
- direct all excess traffic away from the route processor
2. A network administrator wants to configure a user-defined method list on a Cisco router that uses the database on this device when the external server is not available for authentication. Which command does accomplish this goal?
- aaa authentication login default local group radius
- aaa authentication login default group radius local
- aaa authentication login REMOTE_ACCESS local group radius
- aaa authentication login MANAGEMENT_ACCESS group radius local
3. Which operation order should the network administrator follow in order to troubleshoot policy maps?
- The default class is evaluated first, then the other class maps are evaluated in the order they are listed.
- The class maps are evaluated from the top down.
- The class maps are evaluated from the bottom up.
- The class map with more “match” commands is evaluated first, then the next class map with more “match” commands, and so on.
4. Which IPv6 First-Hop security feature learns and populates the binding table for stateless autoconfiguration addresses?
- DHCPv6 Guard
- Source Guard
- RA Guard
- IPv6 neighbor discovery inspection
5. A user complains about not being able to gain access to the network. What command would be used by the network administrator to determine which AAA method list is being used for this particular user as the user logs on?
- debug aaa accounting
- debug aaa authorization
- debug aaa authentication
- debug aaa protocol
6. A network administrator wants to verify the number of packets that have conformed to a specific class map used for CoPP. Which command should the administrator use?
- show access-list
- show class-map
- show policy-map
- show policy-map control-plane
7. A junior network engineer needs to configure uRPF on a Cisco router interface to eliminate spoofed IP packets on a network. Which command should be used to configure uRPF mode when using asymmetric routing?
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx allow-default
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via any
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx allow-self-ping
8. What is one function of the binding table for IPv6 First-Hop security?
- It keeps any router rogue IP addresses filtered by RA Guard.
- It keeps rogue DHCPv6 servers filtered by DHCPv6 Guard.
- It keeps IPv6 neighbors that are connected to a device.
- It keeps Layer 2 addresses filtered by Source Guard.
9. A junior engineer is learning about uRPF configuration. Which instruction should be followed when a Cisco router is configured with uRPF?
- Use the show ip interface command to verify that uRPF is enabled on an interface.
- Configure URPF with loose mode on router interfaces that connect to subnets with end stations.
- Configure uRPF with strict mode when asymmetric routing occurs.
- Configure URPF with loose mode on uplinks.
10. Which IPv6 First-Hop Security feature is used to block unwanted advertisement messages from unauthorized routers?
- RA Guard
- DHCPv6 Guard
- IPv6 ND inspection
- Source Guard
11. What is the first step to check when troubleshooting server-based AAA authentication on a Cisco router?
- Check to verify that AAA is enabled.
- Check to verify the server IP address is configured.
- Check to verify a username and password are configured for console access.
- Check to verify there is connectivity between the router and the server.
12. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator configures AAA authentication on R1. When the administrator tests the configuration by telnetting to R1 and no ACS servers can be contacted, which password should the administrator use in order to login successfully?
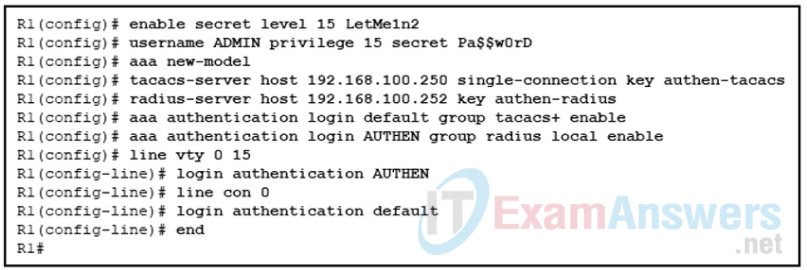
- LetMe1n2
- Pa$$w0rD
- authen-radius
- authen-tacacs
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. Which command successfully configures a user-defined method list on a Cisco IOS device that uses the database on the device if the external server is not available for authentication?
- aaa authentication login default local group radius
- aaa authentication login default group radius local
- aaa authentication login REMOTE_ACCESS local group radius
- aaa authentication login MANAGEMENT_ACCESS group radius local
2. Your Cisco router is configured with the following command:
aaa authentication login default group radius local
What will occur during login if the local database does not contain any username and password when it is checked?
- The RADIUS server will be used for authentication.
- Authentication will fail.
- The user will be granted access.
- The line password will be used.
3. Your router is configured as follows:
R1# show run | i aaa|username aaa new-model username ENARSI password 0 EXAM R1# show run | s vty line vty 0 4 password cisco transport input all R1#
Based on the configuration, what will occur when someone uses Telnet to reach the router?
- Authentication will fail because there is no AAA method list.
- The user will be required to use the line password cisco.
- The user will be required to use the username ENARSI with the password EXAM.
- The user will be granted access either with the username ENARSI with the password EXAM or with the line password cisco.
4. Which of the following commands would you use if you needed uRPF to match the return interface with the incoming interface and a default route?
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx allow-default
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via any allow-default
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via any allow-default 111
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx allow-self-ping
5. Which of the following commands would you use for uRPF if the traffic flow were asynchronous?
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx allow-default
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via any
- ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx allow-self-ping
6. Which of the following commands would you use to verify the number of packets that have conformed to a specific class map that you are using for CoPP?
- show access-list
- show class-map
- show policy-map
- show policy-map control-plane
7. How is a policy map processed?
- All at once, matching the best class map.
- From top down, matching the first class map that applies.
- From bottom up, matching the first class map that applies.
- They are not processed; the class map is processed.
8. What happens when traffic does not match any of the user-defined class maps specified in the policy map?
- It is ignored.
- It is dropped.
- It is transmitted.
- It is subject to the policy defined in the default class.
9. Which IPv6 First-Hop Security feature is used to block unwanted RA messages?
- RA Guard
- DHCPv6 Guard
- IPv6 ND inspection/snooping
- Source Guard
10. Which IPv6 First-Hop Security feature is able to validate the source of IPv6 traffic and, if the source is not valid, block it?
- RA Guard
- DHCPv6 Guard
- IPv6 ND inspection/snooping
- Source Guard
