1. Refer to the exhibit. Which conclusion can be drawn from this OSPF multiaccess network?
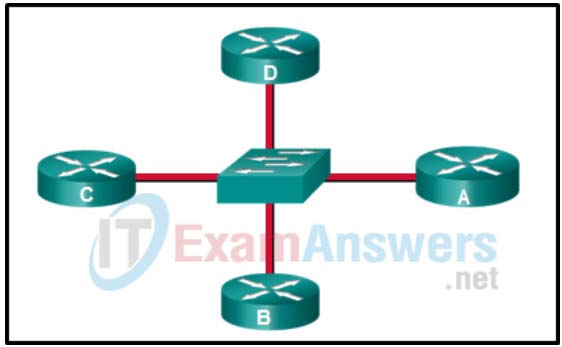
- When a DR is elected all other non-DR routers become DROTHER.
- All DROTHER routers will send LSAs to the DR and BDR to multicast 224.0.0.5.
- If the DR stops producing Hello packets, a BDR will be elected, and then it promotes itself to assume the role of DR.
- With an election of the DR, the number of adjacencies is reduced from 6 to 3.
Explanation: On OSPF multiaccess networks, a DR is elected to be the collection and distribution point for LSAs sent and received. A BDR is also elected in case the DR fails. All other non-DR or BDR routers become DROTHER. Instead of flooding LSAs to all routers in the network, DROTHERs only send their LSAs to the DR and BDR using the multicast address 224.0.0.6. If there is no DR/BDR election, the number of required adjacencies is n(n-1)/2 => 4(4-1)/2 = 6. With the election, this number is reduced to 3.
2. When OSPFv2 neighbors are establishing adjacencies, in which state do they elect a DR and BDR router?
- Exchange state
- Init state
- 2-Way state
- Loading state
Explanation: Down state: No hello packets are received.
Attempt: No recent information received by NBMA router, but still trying to communicate.
Init state: Hello packets received, but bidirectional communication not established.
2-way state: Bidirectional communication is established and if needed, a DR/BDR election occurs.
ExStart state: Negotiate master/slave role for LSDB synchronization.
Exchange state: Exchange of DBD packets occurs.
Loading state: Request for additional information is sent.
Full state: Routers converged and neighbors are fully adjacent.
3. Which OSPF router type is used in mutliarea OSPF to connect each area to the backbone?
Explanation: There are four OSPF router types:
- Internal routers, which have all interfaces in a single area
- Backbone routers, which have all interfaces in Area 0
- Area Border Routers (ABRs), which have interfaces in multiple areas
- Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs), which have an interface in the OSPF network and an interface in an external autonomous system
4. Which type of routing table entry would indicate that an external route was redistributed into the multiarea OSPF process?
Explanation: An O routing table entry indicates a route, from within the same area, that was learned through OSPF updates. An O IA route is a route from another OSPF area. An O E2 or O E1 route is an external route, such as one redistributed from RIP, EIGRP, or a static route, that was redistributed into the OSPF process. An S entry is for a static route. A C entry represents a directly connected network.
5. What is one reason to use the ip ospf priority command when the OSPF routing protocol is in use?
- to activate the OSPF neighboring process
- to influence the DR/BDR election process
- to provide a backdoor for connectivity during the convergence process
- to streamline and speed up the convergence process
Explanation: The OSPF priority can be set to a number between 0 and 255. The higher the number set, the more likely the router becomes the DR. A priority 0 stops a router from participating in the election process and the router does not become a DR or a BDR.
6. A network administrator is verifying a multi-area OSPF configuration by checking the routing table on a router in area 1. The administrator notices a route to a network that is connected to a router in area 2. Which code appears in front of this route in the routing table within area 1?
Explanation: In a routing table, a route with the code O IA indicates a network that is learned from another area and received by the ABR as an external LSA. The ABR has flooded the route into its area so that internal routers may add it to their databases. Label C would indicate a network that is directly connected to an interface on the router. Label O would indicate a network that is advertised by another router in the same area. Label O E2 would indicate an external network (non-OSPF network) that is advertised by an ASBR.
7. A network administrator has recently implemented OSPFv2 across the entire network topology. Which command can be implemented to prevent the forwarding of OSPF messages to Layer 2 switches and hosts on interface Fast Ethernet 0/1, while maintaining network connectivity?
- R1(config-if)# no ipv6 ospf 10
- R1(config-if)# no cdp enable
- R1(config-if)# no cdp run
- R1(config-router)# passive-interface FastEthernet 0/1
Explanation: To prevent OSPF from sending messages to a LAN interface that is activated for OSPF, in this case interface Fast Ethernet 0/1, the passive-interface FastEthernet 0/1command must be implemented in the R1(config-router)# mode.
8. Refer to the exhibit. Based on this configuration, which two OSPF router roles are assumed by R2? (Choose two.)
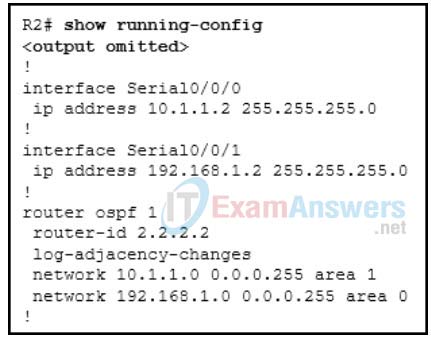
- backbone router
- internal router
- designated router
- area border router
- autonomous system boundary router
Explanation: R2 is a backbone router because one of its interfaces (S0/0/1) is in area 0. It is also an area border router (ABR) because it has one interface in area 0 and another interface in area 1.
9. A network engineer is testing OSPF routing and using loopback interfaces to represent future networks. The engineer enters the following commands on a router in OSPF Area 1:
RS29(config)# interface loopback 0
RS29(config-if)# ip address 10.5.54.1 255.255.255.0
RS29(config-if)# router ospf 1
RS29(config-router)# network 10.5.53.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
How will the route appear in each routing table of other area 1 routers?
- 10.5.54.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
L 10.5.54.1 [110/65] via 10.1.1.1, 00:37:15, Serial 0/0/1
- 10.5.54.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 10.5.54.1 [110/65] via 10.1.1.1, 00:37:15, Serial 0/0/1
- 10.5.54.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 10.5.54.1 [110/65] via 10.1.1.1, 00:37:15, Serial 0/0/1
- 10.5.54.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 10.5.54.1 [110/65] via 10.1.1.1, 00:37:15, Serial 0/0/1
Explanation: When a loopback interface is advertised through OSPF, it is always advertised with a /32 prefix length and shown in the routing table of other routers as an OSPF route with a /32 prefix. If the show ip ospf interface command is shown on the router with the loopback interface configured, the loopback interface shows as a loopback network type instead of a point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, broadcast, or nonbroadcast type.
10. Which command will a network engineer issue to verify the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a point-to-point WAN link between two routers that are running OSPFv2?
- show ip ospf neighbor
- show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0
- show ipv6 ospf interface serial 0/0/0
- show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/1
Explanation: The show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0 command will display the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a point-to-point serial WAN link between two OSPFv2 routers. The show ipv6 ospf interface serial 0/0/0 command will display the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a point-to-point serial link between two OSPFv3 routers. The show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/1 command will display the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a multiaccess link between two (or more) OSPFv2 routers. The show ip ospf neighbor command will display the dead interval elapsed time since the last hello message was received, but does not show the configured value of the timer.
11. In an OSPFv2 configuration, what is the effect of entering the command network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0?
- It changes the router ID of the router to 192.168.1.1.
- It enables OSPF on all interfaces on the router.
- It tells the router which interface to turn on for the OSPF routing process.
- It allows all 192.168.1.0 networks to be advertised.
Explanation: Entering the command network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 will turn on only the interface with that IP address for OSPF routing. It does not change the router ID. Instead, OSPF will use the network that is configured on that interface.
12. Why is MD5 authentication more secure than simple authentication for OSPF updates?
- MD5 does not send the password to the neighbor router.
- MD5 requires passwords that are at least 8 characters long.
- MD5 uses both a username and a password to authenticate the neighbor.
- MD5 employs IPsec to keep the updates from being intercepted.
Explanation: MD5 does not send the configured password across the network. MD5 generates a special hash, or signature, that is attached to the messages and sent to the neighbor. This signature is used to validate the neighbor instead of the password. MD5 does not use a username and does not enforce a minimum length on the password. While IPsec tunnels can be used to keep updates secure, they are not used specifically by MD5.
13. Refer to the exhibit. If no router ID was manually configured, what would router Branch1 use as its OSPF router ID?
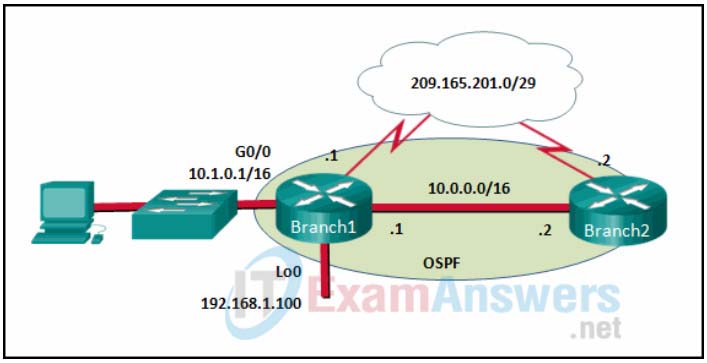
- 10.0.0.1
- 10.1.0.1
- 192.168.1.100
- 209.165.201.1
Explanation: In OSPFv2, a Cisco router uses a three-tier method to derive its router ID. The first choice is the manually configured router ID with the router-id command. If the router ID is not manually configured, the router will choose the highest IPv4 address of the configured loopback interfaces. Finally if no loopback interfaces are configured, the router chooses the highest active IPv4 address of its physical interfaces.
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. What protocol number does OSPF use for inter-router communication?
Explanation: OSPF uses protocol number 89.
2. How many packet types does OSPF use for inter-router communication?
- Three
- Four
- Five
- Six
- Seven
Explanation: OSPFv2 use five packet types for communication: hello, database description, link-state request, link-state update, and link-state acknowledgement.
3. What destination addresses does OSPF use, when feasible? (Choose two.)
- IP address 224.0.0.5
- IP address 224.0.0.10
- IP address 224.0.0.8
- MAC address 01:00:5E:00:00:05
- MAC address 01:00:5E:00:00:0A
Explanation: OSPF uses the multicast IP address 224.0.0.5 or MAC address 01:00:5e:00:00:05 for the AllSPFRouters group.
4. True or false: A router with an interface associated to Area 1 and Area 2 can inject routes learned from one area into another area.
Explanation: A router needs to have an interface in Area 0 so that it can be an ABR.
5. True or false: A member router contains a complete copy of the LSDBs for every area in the routing domain.
Explanation: An OSPF member router contains only a copy of the LSDB for the areas it participates in.
6. How many states does OSPF maintain when dealing with a neighbor adjacency?
Explanation: OSPF maintains eight states when dealing with a neighbor adjacency: down, attempt, init, 2-way, ExStart, Exchange, Loading, and Full.
7. True or false: The OSPF process ID must match for routers to establish a neighbor adjacency.
Explanation: The OSPF process ID is locally significant and is not required to match for neighbor adjacency.
8. True or false: OSPF is only enabled on a router interface by using the command network ip-address wildcard-mask area area-id under the OSPF router process.
Explanation: OSPF can also be enabled with the interface parameter command ip ospf process-id area area-id.
9. True or false: An advertised default route into OSPF always appears as an OSPF inter-area route.
Explanation: An OSPF advertised default route always appears as an external route. The exception is when OSPF stub areas are used.
10. True or false: The router with the highest IP address is the designated router when using a serial point-to-point link.
Explanation: Serial point-to-point links are automatically set as the OSPF point-to-point network type, which does not have a designated router.
11. What command is configured to prevent a router from becoming the designated router for a network segment?
- The interface command ip ospf priority 0
- The interface command ip ospf priority 255
- The command dr-disable interface-id under the OSPF process
- The command passive interface interface-id under the OSPF process
- The command dr-priority interface-id 255 under the OSPF process
Explanation: Setting the interface priority to 0 removes that interface from the DR election process.
12. What is the advertised network for the loopback interface with IP address 10.123.4.1/30?
- 10.123.4.1/24
- 10.123.4.0/30
- 10.123.4.1/32
- 10.123.4.0/24
Explanation: The loopback address is classified as an OSPF loopback interface type, which is always advertised as a /32 address, regardless of the subnet mask.
13. The OSPF dead interval defaults to how many times the hello interval?
Explanation: The OSPF dead interval defaults to four times the hello interval.
14. True or false: Enabling OSPF authentication for an area consists of setting the OSFP authentication type under the OSPF process and placing the password on all area interfaces.
Explanation: You can enable OSPF authentication on all interfaces for an area by configuring the area authentication in the OSPF process and then configuring the password for an interface under each member interface.



