15.1.3 Lab – Implement HSRP (Answers)
Topology
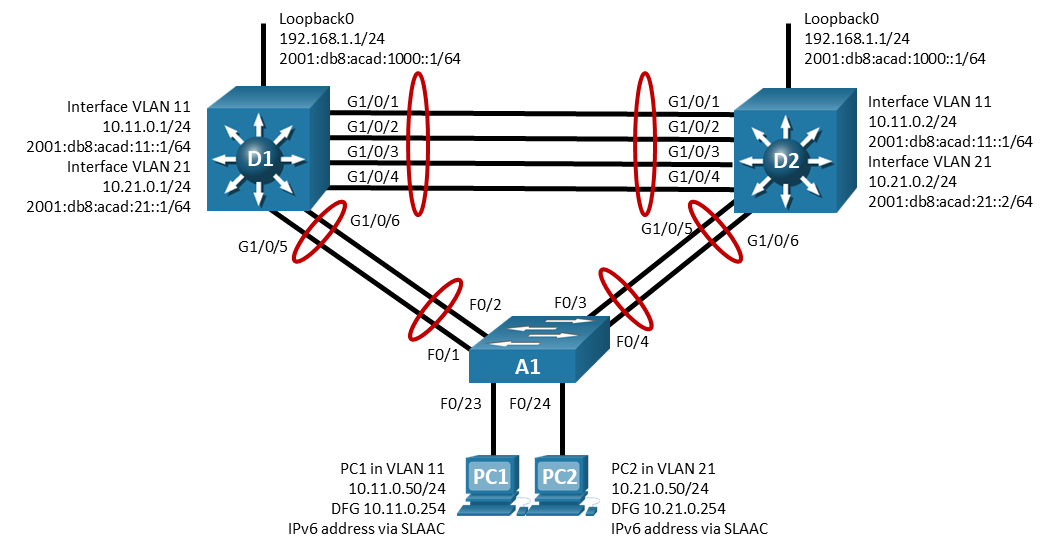
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Lo 0 | 192.168.1.1/24 | N/A |
| Lo 0 | 2001:db8:acad:1000::1/64 | N/A | |
| VLAN 11 | 10.11.0.1/24 | N/A | |
| VLAN 11 | 2001:db8:acad:11::1/64 | N/A | |
| VLAN 21 | 10.21.0.1/24 | N/A | |
| VLAN 21 | 2001:db8:acad:21::1/64 | N/A | |
| D2 | Lo 0 | 192.168.1.1/24 | N/A |
| Lo 0 | 2001:db8:acad:1000::1/64 | N/A | |
| VLAN 11 | 10.11.0.2/24 | N/A | |
| VLAN 11 | 2001:db8:acad:11::1/64 | N/A | |
| VLAN 21 | 10.21.0.2/24 | N/A | |
| VLAN 21 | 2001:db8:acad:21::2/64 | N/A | |
| PC1 | NIC | 10.11.0.50/24 | 10.11.0.254 |
| NIC | IPv6 SLAAC | ||
| PC2 | NIC | 10.21.0.50/24 | 10.21.0.254 |
| NIC | IPv6 SLAAC |
Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings and Interface Addressing
- Part 2: Configure and Observe HSRP for IPv4 and IPv6
- Part 3: Configure and Observe HSRP Authentication
- Part 4: Configure and Observe HSRP Object Tracking
Background / Scenario
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a Cisco-proprietary redundancy protocol for establishing a fault-tolerant default gateway. It is described in RFC 2281. HSRP provides a transparent failover mechanism to the end stations on the network. This provides users at the access layer with uninterrupted service to the network if the primary gateway becomes inaccessible.
Note: This lab is an exercise in deploying and verifying HSRP and does not necessarily reflect networking best practices.
Note: The switches used with CCNP hands-on labs are Cisco 3650 with Cisco IOS XE release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image) and Cisco 2960 with IOS release 15.2 (lanbase image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs.
Note: Ensure that the switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Note: The default Switch Database Manager (SDM) template on a Catalyst 3650 running IOS XE supports dual-stacked operations and requires no additional configuration for our purposes.
If you are using a device, such as Cisco 2960, running Cisco IOS, check the SDM template with the privileged EXEC command show sdm prefer.
S1# show sdm prefer
The default bias template used by the Switch Database Manager (SDM) does not provide IPv6 address capabilities. Verify that SDM is using either the dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 template or the lanbase-routing template. The new template will be used after reboot even if the configuration is not saved.
Use the following commands to assign the dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 template as the default SDM template.
S1# configure terminal S1(config)# sdm prefer dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 default S1(config)# end S1# reload
Required Resources
- 2 Switches (Cisco 3650 with Cisco IOS XE release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 1 PC (Choice of operating system with a terminal emulation program installed)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings and Interface Addressing
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings and interface addressing.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Configure basic settings for each switch.
a. Console into each switch, enter global configuration mode, and apply the basic settings. A command list for each switch is provided below for initial configurations.
Switch D1
hostname D1 ip routing ipv6 unicast-routing no ip domain lookup banner motd # D1, Implement HSRP # line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 password cisco123 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous login exit interface range g1/0/1-24, g1/1/1-4, g0/0 shutdown exit interface range g1/0/1-6 switchport mode trunk no shutdown exit interface range g1/0/1-4 channel-group 12 mode active exit interface range g1/0/5-6 channel-group 1 mode active exit vlan 11 name FIRST_VLAN exit vlan 21 name SECOND_VLAN exit interface vlan 11 ip address 10.11.0.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::d1:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:11::1/64 no shutdown exit interface vlan 21 ip address 10.21.0.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::d1:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:21::1/64 no shutdown exit interface loopback 0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::d1:3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1000::1/64 no shutdown exit
Switch D2
hostname D2 ip routing ipv6 unicast-routing no ip domain lookup banner motd # D2, Implement HSRP # line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 password cisco123 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous login exit interface range g1/0/1-24, g1/1/1-4, g0/0 shutdown exit interface range g1/0/1-6 switchport mode trunk no shutdown exit interface range g1/0/1-4 channel-group 12 mode active exit interface range g1/0/5-6 channel-group 2 mode active exit vlan 11 name FIRST_VLAN exit vlan 21 name SECOND_VLAN exit interface vlan 11 ip address 10.11.0.2 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::d2:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:11::2/64 no shutdown exit interface vlan 21 ip address 10.21.0.2 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::d2:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:21::2/64 no shutdown exit interface loopback 0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::d2:3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1000::1/64 no shutdown exit
Switch A1
hostname A1 banner motd # A1, Implement HSRP # line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 password cisco123 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous login exit interface range f0/1-24, g0/1-2 shutdown exit interface range f0/1-4 switchport mode trunk no shutdown exit interface range f0/1-2 channel-group 1 mode active exit interface range f0/3-4 channel-group 2 mode active exit vlan 11 name FIRST_VLAN exit vlan 21 name SECOND_VLAN exit interface f0/23 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 11 spanning-tree portfast no shutdown exit interface f0/24 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 21 spanning-tree portfast no shutdown exit interface vlan 11 ip address 10.11.0.3 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::a1:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:11::3/64 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 10.11.0.254
b. Set the clock on each switch to UTC time.
c. Save the running configuration to startup-config.
Step 3: Configure the PCs for network connectivity.
Configure PC1 and PC2 with the IPv4 address, subnet mask, and default gateway specified in the topology diagram. The IPv6 address and default gateway information for each PC will come from SLAAC.
Part 2: Configure and Observe HSRP for IPv4 and IPv6.
In Part 2, you will configure and test HSRPv2 in support of IPv4 and IPv6.
HSRP provides redundancy in the network. The traffic can be load-balanced by using the standby group priority priority command.
IP routing is enabled on D1 and D2. Each route processor can route between the SVIs configured on its switch. In addition to the real IP address assigned to each switch SVI, assign a third IP address in each subnet to be used as a virtual gateway address. HSRP negotiates and determines which switch accepts information forwarded to the virtual gateway IP address.
The standby command configures the IP address of the virtual gateway, sets the priority for each group, and configures the router for preemption. Preemption allows the router with the higher priority to become the active router after a network failure has been resolved. Notice that the abbreviation HSRP is not used in the command syntax to implement HSRP. HSRP version 2 must be implemented to support IPv6. This is accomplished by using the standby version 2 command on every interface required.
The standby x ipv6 autoconfig command, where x is the assigned HSRP group number, is used to assign the group an automatically generated virtual ipv6 address. Note that the group number used for IPv6 on an interface must be different than the group used for IPv4.
In this lab, the group numbers will be 11 and 21 for IPv4, and 116 and 216 for IPv6.
In the following configurations, the priority for VLAN 11 on D1 is set to 150, making it the active router for VLAN 11. VLAN 21 has the default priority of 100 on D1, making D1 the standby router for VLAN 21. D2 is configured to be the active router for VLAN 21 with a priority of 150, and the standby router for VLAN 11 with a default priority of 100.
Note: It is recommended that the HSRP group number be mapped to VLAN number.
Step 1: Configure HSRPv2 on Switch D1.
a. Configure standby group 11 on interface VLAN 11 for HSRP version 2, a standby IP address of 10.11.0.254, a priority of 150, and preemption.
D1(config)# interface vlan 11 D1(config-if)# standby version 2 D1(config-if)# standby 11 ip 10.11.0.254 D1(config-if)# standby 11 priority 150 D1(config-if)# standby 11 preempt
b. Configure standby group 116 on interface vlan 11 for ipv6 autoconfig command, a priority of 150, and preemption.
D1(config-if)# standby 116 ipv6 autoconfig D1(config-if)# standby 116 priority 150 D1(config-if)# standby 116 preempt
c. Configure standby group 21 on interface VLAN 21 for HSRP version 2, a standby IP address of 10.21.0.254, and preemption.
D1(config)# interface vlan 21 D1(config-if)# standby version 2 D1(config-if)# standby 21 ip 10.21.0.254 D1(config-if)# standby 21 preempt
d. Configure standby group 216 on interface vlan 21 for ipv6 autoconfig command and preemption.
D1(config-if)# standby 216 ipv6 autoconfig D1(config-if)# standby 216 preempt
Step 2: Verify HSRPv2 is operational on Switch D1.
a. Verify that HSRP is active and operating on Switch D1 with the show standby brief command.
D1# show standby brief
P indicates configured to preempt.
|
Interface Grp Pri P State Active Standby Virtual IP
Vl11 11 150 P Active local unknown 10.11.0.254
Vl11 116 150 P Active local unknown FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:74
Vl21 21 100 P Active local unknown 10.21.0.254
Vl21 216 100 P Active local unknown FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:D8
b. Interface Loopback0 on D1 and D2 represent a destination on the internet. From PC1 and PC2, ping the IPv4 and IPv6 address of interface Loopack0 on D1. A successful ping verifies that the gateway router is working.
Step 3: Configure HSRPv2 on Switch D2.
a. Configure standby group 11 on interface VLAN 11 for HSRP version 2, a standby IP address of 10.11.0.254, and preemption.
D2(config)# interface vlan 11 D2(config-if)# standby version 2 D2(config-if)# standby 11 ip 10.11.0.254 D2(config-if)# standby 11 preempt
b. Configure standby group 116 on interface vlan 11 for ipv6 autoconfig command, and preemption.
D2(config-if)# standby 116 ipv6 autoconfig D2(config-if)# standby 116 preempt
c. Configure standby group 21 on interface VLAN 21 for HSRP version 2, a standby IP address of 10.21.0.254, a priority of 150, and preemption.
D2(config)# interface vlan 21 D2(config-if)# standby version 2 D2(config-if)# standby 21 ip 10.21.0.254 D2(config-if)# standby 21 priority 150 D2(config-if)# standby 21 preempt
d. Configure standby group 216 on interface vlan 21 for ipv6 autoconfig command, a priority of 150, and preemption.
D2(config-if)# standby 216 ipv6 autoconfig D2(config-if)# standby 216 priority 150 D2(config-if)# standby 216 preempt
Step 4: Verify HSRPv2 is operational on Switch D2.
a. Verify that HSRP is active and operating on Switch D2 with the show standby brief command. Based on the configuration, D2 should be the active switch for VLAN 21 only.
D2# show standby brief
P indicates configured to preempt.
|
Interface Grp Pri P State Active Standby Virtual IP
Vl11 11 100 P Standby 10.11.0.1 local 10.11.0.254
Vl11 116 100 P Standby FE80::D1:1 local FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:74
Vl21 21 150 P Active local 10.21.0.1 10.21.0.254
Vl21 216 150 P Active local FE80::D1:2 FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:D8
b. Interface Loopback0 on D1 and D2 represent a destination on the internet. From PC1 and PC2, ping the IPv4 and IPv6 address of interface Loopack0 on D1. A successful ping verifies that the gateway router is working.
Step 5: Observe and validate HSRPv2 operation.
The whole point of HSRP is to help maintain gateway reachability in case of an outage. In this step, we will simulate an outage to show how HSRP achieves this objective.
a. On PC1, start a continuous ping to 192.168.1.1 and 2001:db8:acad:1000::1.
b. On Switch D1, issue the shutdown command on interface VLAN 11. Note that D2 takes over the active role, and there is very little traffic loss in the running pings.
c. On Switch D1, issue the no shutdown command on interface VLAN 11. Note that D1 takes back over as the active router, and once again there is very little traffic loss experienced.
d. Stop the continuous ping running on PC1.
Step 6: Tune HSRPv2 operation.
We have validated the operation of HSRP for both IPv4 and IPv6, and our gateways are now redundant. But in some cases, the default amount of time taken to detect and react to an outage is too slow. By default, HSRP uses a 3-second hello timer and a 10-second hold timer. If 10 seconds is too slow for your organization or traffic scenario, you can tune the HSRP timers to speed things up. This should only be done on a stable network, and this will cause more HSRP traffic to be sent between the configured switches, so you should take those factors into account before changing the timers on a production network.
a. On both switches, issue the shutdown command on interface VLAN 11 and VLAN 21.
b. On both switches, configure the timers for standby group 11 and standby group 21 so that the hello time is 250 milliseconds and the hold time is 750 milliseconds.
D1(config)# interface vlan 11 D1(config-if)# standby 11 timers msec 250 msec 750 D1(config-if)# exit D1(config)# interface vlan 21 D1(config-if)# standby 21 timers msec 250 msec 750 D1(config-if)# exit
c. On both switches, issue the no shutdown command on interface VLAN 11 and VLAN 21 and let HSRP initialize. Verify that it is operating as designed by issuing the show standby brief command on switch D1. You should see D1 as active for VLAN 11 and standby for VLAN 21.
d. On PC1, start a continuous ping to 192.168.1.1 and 2001:db8:acad:1000::1
e. On Switch D1, issue the shutdown command on interface VLAN 11. Note that that D2 takes over the active role almost immediately, and there is almost no traffic loss in the running pings.
f. On Switch D1, issue the no shutdown command on interface VLAN 11. Note that D1 takes back over as the active router, and once again there is almost no traffic loss experienced.
g. Stop the continuous ping running on PC1.
Part 3: Configure and Observe HSRP Authentication
In this part of the lab, you will secure the HSRP communication between member devices. HSRP authentication prevents rogue routers on the network from joining the HSRP group. Without authentication, a rogue router could join the group and claim the active role. The attacker would then be able to capture all the traffic forwarded to attacker’s device. HSRP authentication can be configured using plaintext, an MD5-hashed key-string, or an MD5-hashed key chain. Using key chains offers more options and security because you can have lifetime parameters associated with the different keys. For simplicity, we will configure HSRP authentication using the key string option.
a. On D1, configure authentication for group 11 and group 21 using the key-string Super53cret.
D1(config)# interface vlan 11 D1(config-if)# standby 11 authentication md5 key-string Super53cret D1(config-if)# exit D1(config)# interface vlan 21 D1(config-if)# standby 21 authentication md5 key-string Super53cret D1(config-if)# exit D1(config)# end
b. Notice as soon as this command was entered on D1 that we received a “bad authentication” message display to the console screen. HSRP authentication is not yet configured on D2 therefore we expect for the HSRP process to be disrupted. The output of the show standby brief command below confirms that D2 is no longer the standby router for group 11. The standby router shows unknown.
*Jan 19 01:10:13.167: %HSRP-4-BADAUTH2: Bad authentication from 10.11.0.2
D1# show standby brief
P indicates configured to preempt.
|
Interface Grp Pri P State Active Standby Virtual IP
Vl11 11 150 P Active local unknown 10.11.0.254
Vl11 116 150 P Active local FE80::D2:1 FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:74
Vl21 21 100 P Active local unknown 10.21.0.254
Vl21 216 100 P Standby FE80::D2:2 local FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:D8
c. On D2, configure authentication for group 11 and group 21 using the key-string Super53cret.
D2(config)# interface vlan 11 D2(config-if)# standby 11 authentication md5 key-string Super53cret D2(config-if)# exit D2(config)# interface vlan 21 D2(config-if)# standby 21 authentication md5 key-string Super53cret D2(config-if)# exit D2(config)# end
d. As soon as the key string was entered, HSRP started working again. Verify this by examining the output of show standby brief on D1 and you will see that D2 is now listed as the standby router for group 11.
D1# show standby brief
P indicates configured to preempt.
|
Interface Grp Pri P State Active Standby Virtual IP
Vl11 11 150 P Active local 10.11.0.2 10.11.0.254
Vl11 116 150 P Active local FE80::D2:1 FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:74
Vl21 21 100 P Standby 10.21.0.2 local 10.21.0.254
Vl21 216 100 P Standby FE80::D2:2 local FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:D8
Part 4: Configure and Observe HSRP Object Tracking
HSRP can perform object and interface tracking. Either of these tracking methods enables the priority of a standby group router to be automatically adjusted, based on the status of the tracked entity. When a tracked entity becomes unavailable, the HSRP priority of the router is decreased. With preemption configured on the HSRP group, this might cause another router to take over as the active router for a group based on its higher priority value. When properly configured, the HSRP tracking feature ensures that a router with an unavailable key interface will relinquish the active router role.
Step 1: Create a tracked object.
Create an object on Switch D1 and D2 that tracks the line-protocol of interface Loopback 0.
D1(config)# track 4 interface loopback 0 line-protocol D1(config-track)# exit D2(config)# track 4 interface loopback 0 line-protocol D2(config-track)# exit
Step 2: Configure HSRP to track the object status.
On D1, configure standby groups 11 and 116 to track the status of track 4. On D2, configure standby groups 21 and 216 to track the status of track 4. When the tracked object has failed, decrement the system priority by 60.
D1(config)# interface vlan 11 D1(config-if)# standby 11 track 4 decrement 60 D1(config-if)# standby 116 track 4 decrement 60 D1(config-if)# exit D2(config)# interface vlan 21 D2(config-if)# standby 21 track 4 decrement 60 D2(config-if)# standby 216 track 4 decrement 60 D2(config-if)# exit
Step 3: Verify the HSRP configuration.
Issue the command show standby on Switch D1. This is the full version of the command, and in the output, you can see all the adjustments that have been made to this point.
D1# show standby
Vlan11 - Group 11 (version 2)
State is Active
5 state changes, last state change 00:07:30
Virtual IP address is 10.11.0.254
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c9f.f00b (MAC In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c9f.f00b (v2 default)
Hello time 250 msec, hold time 750 msec
Next hello sent in 0.240 secs
Authentication MD5, key-string
Preemption enabled
Active router is local
Standby router is 10.11.0.2, priority 100 (expires in 0.816 sec)
Priority 150 (configured 150)
Track object 4 state Up decrement 60
Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-11" (default)
Vlan11 - Group 116 (version 2)
State is Active
1 state change, last state change 00:04:53
Link-Local Virtual IPv6 address is FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:74 (conf auto EUI64)
Active virtual MAC address is 0005.73a0.0074 (MAC In Use)
Local virtual MAC address is 0005.73a0.0074 (v2 IPv6 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 1.216 secs
Preemption enabled
Active router is local
Standby router is FE80::D2:1, priority 100 (expires in 11.024 sec)
Priority 150 (configured 150)
Track object 4 state Up decrement 60
Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-116" (default)
<output omitted>
Step 4: Verify HSRP complies with the configuration.
a. On D1, shut down interface Loopback 1. Switch D2 should take over as active for group 11. Verify D1’s current priority value and D2’s status with the show standby brief command.
D1(config)# interface loopback 0
D1(config-if)# shutdown
D1(config-if)#
*Jan 19 16:10:52.041: %TRACK-6-STATE: 4 interface Lo0 line-protocol Up -> Down
D1(config-if)#
*Jan 19 16:10:52.168: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan11 Grp 11 state Active -> Speak
*Jan 19 16:10:53.035: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan11 Grp 11 state Speak -> Standby
D1(config-if)#
*Jan 19 16:10:53.037: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan11 Grp 116 state Active -> Speak
D1(config-if)#
*Jan 19 16:10:54.040: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to down
D1(config-if)#
*Jan 19 16:10:54.041: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Loopback0, changed state to administratively down
*Jan 19 16:10:59.047: %HSRP-5-STATECHANGE: Vlan11 Grp 116 state Speak -> Standby
D1(config-if)# end
D1#
D1# show standby brief
P indicates configured to preempt.
|
Interface Grp Pri P State Active Standby Virtual IP
Vl11 11 90 P Standby 10.11.0.2 local 10.11.0.254
Vl11 116 90 P Standby FE80::D2:1 local FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:74
Vl21 21 100 P Standby 10.21.0.2 local 10.21.0.254
Vl21 216 100 P Standby FE80::D2:2 local FE80::5:73FF:FEA0:D8
b. Examine the priority information in detail in the output of the show standby command.
D1# show standby
Vlan11 - Group 11 (version 2)
State is Standby
<output omitted>
Active router is 10.11.0.2, priority 100 (expires in 0.720 sec)
MAC address is 7069.5a9f.5654
Standby router is local
Priority 90 (configured 150)
Track object 4 state Down decrement 60
Group name is "hsrp-Vl11-11" (default)
Device Configs – Final
Switch D1
D1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 5434 bytes ! version 16.9 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname D1 ! vrf definition Mgmt-vrf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! no aaa new-model switch 1 provision ws-c3650-24ps ! ip routing ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ipv6 unicast-routing ! license boot level ipservicesk9 ! diagnostic bootup level minimal ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode sso ! transceiver type all monitoring ! track 4 interface Loopback0 line-protocol ! class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control description Topology control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING class-map match-any system-cpp-default description Inter FED, EWLC control, EWLC data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFLSAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth description Punt Webauth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control description L2 LVX control packets class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station description MCAST END STATION class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control description L2 control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth description DOT1X Auth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control description Stackwise Virtual class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control description Routing control and Low Latency class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping description Protocol snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping description DHCP snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical description System Critical and Gold Pkt ! policy-map system-cpp-policy ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 shutdown ipv6 address FE80::D1:3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1000::1/64 ! interface Port-channel1 switchport mode trunk ! interface Port-channel12 switchport mode trunk ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf no ip address shutdown negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport mode trunk channel-group 12 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 switchport mode trunk channel-group 12 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3 switchport mode trunk channel-group 12 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4 switchport mode trunk channel-group 12 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/9 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/11 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/12 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/17 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/18 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/19 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/20 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/21 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/3 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/4 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! interface Vlan11 ip address 10.11.0.1 255.255.255.0 standby version 2 standby 11 ip 10.11.0.254 standby 11 timers msec 250 msec 750 standby 11 priority 150 standby 11 preempt standby 11 authentication md5 key-string Super53cret standby 11 track 4 decrement 60 standby 116 ipv6 autoconfig standby 116 priority 150 standby 116 preempt standby 116 track 4 decrement 60 ipv6 address FE80::D1:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:11::1/64 ! interface Vlan21 ip address 10.21.0.1 255.255.255.0 standby version 2 standby 21 ip 10.21.0.254 standby 21 timers msec 250 msec 750 standby 21 preempt standby 21 authentication md5 key-string Super53cret standby 216 ipv6 autoconfig standby 216 preempt ipv6 address FE80::D1:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:21::1/64 ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http secure-server ! control-plane service-policy input system-cpp-policy ! banner motd ^C D1, Implement HSRP ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 logging synchronous login line vty 5 15 login ! end
Switch D2
D2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 10167 bytes ! version 16.9 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec ! Call-home is enabled by Smart-Licensing. service call-home no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname D2 ! vrf definition Mgmt-vrf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! no aaa new-model switch 1 provision ws-c3650-24ps ! ip routing ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ipv6 unicast-routing ! license boot level ipservicesk9 ! diagnostic bootup level minimal ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode sso ! transceiver type all monitoring ! track 4 interface Loopback0 line-protocol ! class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control description Topology control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING class-map match-any system-cpp-default description Inter FED, EWLC control, EWLC data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFLSAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth description Punt Webauth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control description L2 LVX control packets class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station description MCAST END STATION class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control description L2 control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth description DOT1X Auth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control description Stackwise Virtual class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control description Routing control and Low Latency class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping description Protocol snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping description DHCP snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical description System Critical and Gold Pkt ! policy-map system-cpp-policy ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address FE80::D2:3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1000::1/64 ! interface Port-channel2 switchport mode trunk ! interface Port-channel12 switchport mode trunk ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf no ip address shutdown negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport mode trunk channel-group 12 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 switchport mode trunk channel-group 12 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3 switchport mode trunk channel-group 12 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4 switchport mode trunk channel-group 12 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5 switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6 switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/9 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/11 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/12 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/17 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/18 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/19 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/20 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/21 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/3 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/4 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! interface Vlan11 ip address 10.11.0.2 255.255.255.0 standby version 2 standby 11 ip 10.11.0.254 standby 11 timers msec 250 msec 750 standby 11 preempt standby 11 authentication md5 key-string Super53cret standby 116 ipv6 autoconfig standby 116 preempt ipv6 address FE80::D2:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:11::2/64 ! interface Vlan21 ip address 10.21.0.2 255.255.255.0 standby version 2 standby 21 ip 10.21.0.254 standby 21 timers msec 250 msec 750 standby 21 priority 150 standby 21 preempt standby 21 authentication md5 key-string Super53cret standby 21 track 4 decrement 60 standby 216 ipv6 autoconfig standby 216 priority 150 standby 216 preempt standby 216 track 4 decrement 60 ipv6 address FE80::D2:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:21::2/64 ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http serverip http secure-server ! control-plane service-policy input system-cpp-policy ! banner motd ^C D2, Implement HSRP ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 logging synchronous login line vty 5 15 login ! end
Switch A1
A1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2319 bytes ! version 15.2 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname A1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! interface Port-channel1 switchport mode trunk ! interface Port-channel2 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active ! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode active ! interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport mode trunk channel-group 2 mode active ! interface FastEthernet0/5 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/7 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/19 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 switchport access vlan 11 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast edge ! interface FastEthernet0/24 switchport access vlan 21 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast edge ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! interface Vlan11 ip address 10.11.0.3 255.255.255.0 ! ip default-gateway 10.11.0.254 ip http server ip http secure-server ! banner motd ^C A1, Implement HSRP ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 logging synchronous login line vty 5 15 login ! end
