Packet Tracer – Troubleshooting Serial Interfaces (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
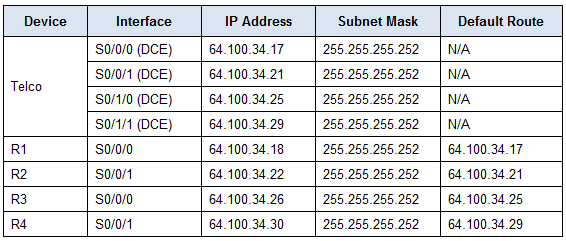
Addressing Table
Objectives
Part 1: Diagnose and Repair the Physical Layer
Part 2: Diagnose and Repair the Data Link Layer
Part 3: Diagnose and Repair the Network Layer
Scenario
You have been asked to troubleshoot WAN connections for a local telephone company (Telco). The Telco router should communicate with four remote sites, but none of them are working. Use your knowledge of the OSI model and a few general rules to identify and repair the errors in the network.
Part 1: Diagnose and Repair the Physical Layer
Step 1: Diagnose and repair the cabling.
a. Examine the Addressing Table to determine the location of the DCE connections.
b. Each serial connection has a DCE and a DTE connection. To determine if each Telco interface is using the correct end of the cable look on the third line of output following the show controllers command.
Telco# show controllers [interface_type interface_num]
c. Reverse any cables that are incorrectly connected.
Note: Cable between Telco and R4 should be reversed and clock rate set on Telco. Serial Cable on R4 should connect to S0/0/1.
Note: In real network settings, the DCE (which sets the clock rate) is typically a CSU/DSU.
Step 2: Diagnose and repair incorrect port connections.
a. Examine the Addressing Table to match each router port with the correct Telco port.
b. Hold the mouse over each wire to ensure that the wires are connected as specified. If not, correct the connections.
Step 3: Diagnose and repair ports that are shutdown.
a. Show a brief interface summary of each router. Ensure that all of the ports that should be working are not administratively down.
b. Enable the appropriate ports that are administratively down:
R3(config)# interface s0/0/0 R3(config-if)# no shutdown
Part 2: Diagnose and Repair the Data Link Layer
Step 1: Examine and set clock rates on DCE equipment.
a. All of the DCE cables should be connected to Telco. Show the running configuration of Telco to verify that a clock rate has been set on each interface.
b. Set the clock rate of any serial interfaces that requires it:
Telco(config)# interface s0/0/0 Telco(config-if)# clock rate 4000000 Telco(config-if)# interface s0/1/1 Telco(config-if)# clock rate 4000000
Step 2: Examine the encapsulation on DCE equipment.
a. All of the serial interfaces should be using HDLC as the encapsulation type. Examine the protocol setting of the serial interfaces.
Telco# show interface [interface_type interface_num]
b. Change the encapsulation type to HDLC for any interface that is set otherwise:
R4(config)# interface s0/0/1 R4(config-if)# encapsulation hdlc
Part 3: Diagnose and Repair the Network Layer
Step 1: Verify the IP addressing.
a. Show a brief interface summary of each router. Check the IP addresses against the Addressing Table and ensure that they are in the correct subnet with their connecting interface.
b. Correct any IP addresses that overlap, or are set to the host or broadcast address:
R1(config)# interface s0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address 64.100.34.18 255.255.255.252

Thank you, well explained with the flow