New Version:
1. A network administrator enters the command copy running-config startup-config. Which type of memory will the startup configuration be placed into?
- flash
- RAM
- NVRAM
- ROM
2. Which packet-forwarding method does a router use to make switching decisions when it is using a forwarding information base and an adjacency table?
- fast switching
- Cisco Express Forwarding
- process switching
- flow process
3. Fill in the blank.
When a router receives a packet, it examines the destination address of the packet and looks in the ———- table to determine the best path to use to forward the packet.
Correct Answer: Routing
4. What are two functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- A router connects multiple IP networks
- It controls the flow of data via the use of Layer 2 addresses
- It determines the best path to send packets
- It provides segmentation at Layer 2
- It builds a routing table based on ARP requests
5. In order for packets to be sent to a remote destination, what three pieces of information must be configured on a host? (Choose three.)
- hostname
- IP address
- subnet mask
- default gateway
- DNS server address
- DHCP server address
6. Which software is used for a network administrator to make the initial router configuration securely?
- SSH client software
- Telnet client software
- HTTPS client software
- terminal emulation client software
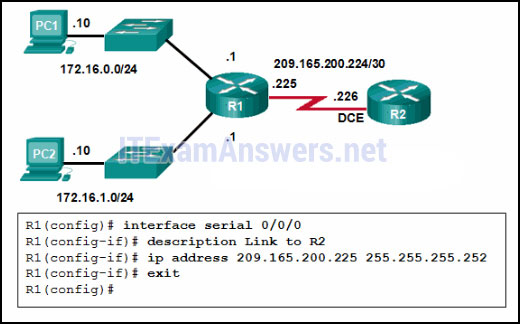
7. The exhibit consists of a network diagram that shows R1 with three network connections: two Ethernet segments and a WAN link. The WAN link connects R1 to a second router R2. R2 is the DCE on the WAN link. The configuration shown is as follows:
R1(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 R1(config-if)# description Link to R2 R1(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)#
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured R1 as shown. When the administrator checks the status of the serial interface, the interface is shown as being administratively down. What additional command must be entered on the serial interface of R1 to bring the interface up?
- IPv6 enable
- clockrate 128000
- end
- no shutdown
8. What is a characteristic of an IPv4 loopback interface on a Cisco IOS router?
- The no shutdown command is required to place this interface in an UP state
- It is a logical interface internal to the router
- Only one loopback interface can be enabled on a router
- It is assigned to a physical port and can be connected to other devices
9. What two pieces of information are displayed in the output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose two.)
- IP addresses
- MAC addresses
- Layer 1 statuses
- next-hop addresses
- interface descriptions
- speed and duplex settings
10. When a router receives a packet, what information must be examined in order for the packet to be forwarded to a remote destination?
- destination MAC address
- destination IP address
- source IP address
- source MAC address
11. Which two items are used by a host device when performing an ANDing operation to determine if a destination address is on the same local network? (Choose two.)
- destination IP address
- destination MAC address
- source MAC address
- subnet mask
- network number
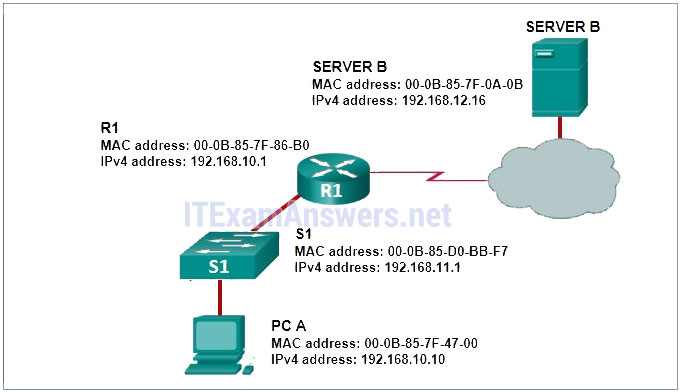
12. PC A is connected to switch S1, which in turn is connected to router R1. Router R1 is connected to a cloud, and the cloud is connected to Server B.
At one side of the PC is a label with the following information:
PC A
MAC address: 00-0B-85-7F-47-00
IPv4 address: 192.168.10.10At one side of the switch is a label with the following information:
S1
MAC address: 00-0B-85-D0-BB-F7
IPv4 address: 192.168.11.1At one side of the router is a label with the following information:
R1
MAC address: 00-0B-85-7F-86-B0
IPv4 address: 192.168.10.1At one side of the server is a label with the following information:
SERVER B
MAC address: 00-0B-85-7F-0A-0B
IPv4 address: 192.168.12.16
Refer to the exhibit. PC A sends a request to Server B. What IPv4 address is used in the destination field in the packet as the packet leaves PC A?
- 192.168.10.10
- 192.168.11.1
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.12.16
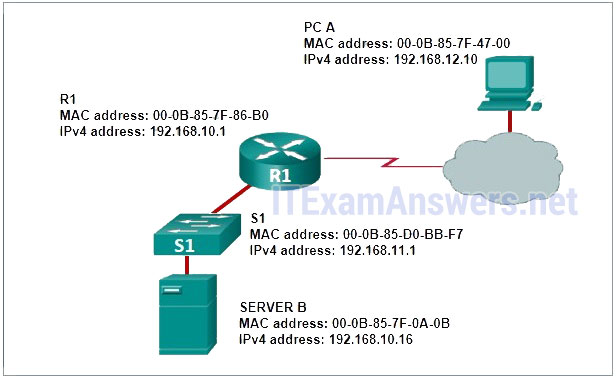
13. Server B is connected to switch S1, which in turn is connected to router R1. Router R1 is connected to a cloud, and the cloud is connected to PC A.
At one side of the server is a label with the following information:
SERVER B
MAC address: 00-0B-85-7F-0A-0B
IPv4 address: 192.168.10.16At one side of the switch is a label with the following information:
S1
MAC address: 00-0B-85-D0-BB-F7
IPv4 address: 192.168.11.1At one side of the router is a label with the following information:
R1
MAC address: 00-0B-85-7F-86-B0
IPv4 address: 192.168.10.1At one side of the PC is a label with the following information:
PC A
MAC address: 00-0B-85-7F-47-00
IPv4 address: 192.168.12.10
Refer to the exhibit. What does R1 use as the MAC address of the destination when constructing the frame that will go from R1 to Server B?
- If the destination MAC address that corresponds to the IPv4 address is not in the ARP cache, R1 sends an ARP request
- The packet is encapsulated into a PPP frame, and R1 adds the PPP destination address to the frame
- R1 uses the destination MAC address of S1
- R1 leaves the field blank and forwards the data to the PC
14. Refer to the exhibit. If PC1 is sending a packet to PC2 and routing has been configured between the two routers, what will R1 do with the Ethernet frame header attached by PC1?
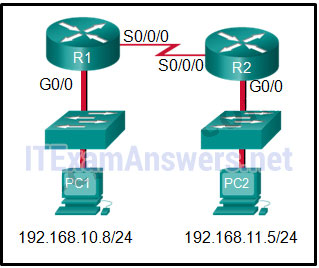
- nothing, because the router has a route to the destination network
- remove the Ethernet header and configure a new Layer 2 header before sending it out S0/0/0
- open the header and replace the destination MAC address with a new one
- open the header and use it to determine whether the data is to be sent out S0/0/0
15. The exhibit shows the following router output:
The gateway of last resort is 209.165.200.226 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 209.165.200.226
192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.10.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.11.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.11.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
209.165.200.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 209.165.200.224/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 209.165.200.225/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
Refer to the exhibit. What will the router do with a packet that has a destination IP address of 192.168.12.227?
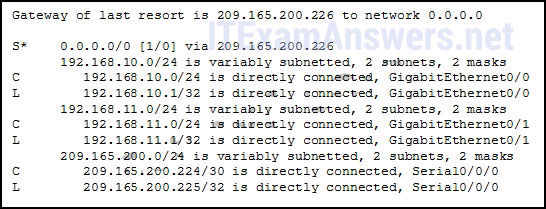
- Drop the packet
- Send the packet out the Serial0/0/0 interface
- Send the packet out the GigabitEthernet0/0 interface
- Send the packet out the GigabitEthernet0/1 interface
16. Which two statements correctly describe the concepts of administrative distance and metric? (Choose two.)
- Administrative distance refers to the trustworthiness of a particular route
- A router first installs routes with higher administrative distances
- The value of the administrative distance can not be altered by the network administrator
- Routes with the smallest metric to a destination indicate the best path
- The metric is always determined based on hop count
- The metric varies depending which Layer 3 protocol is being routed
17. Which two parameters are used by EIGRP as metrics to select the best path to reach a network? (Choose two.)
- hop count
- bandwidth
- jitter
- resiliency
- delay
- confidentiality
18. What route would have the lowest administrative distance?
- a directly connected network
- a static route
- a route received through the EIGRP routing protocol
- a route received through the OSPF routing protocol
19. Which two statements correctly describe the concepts of administrative distance and metric? (Choose two.)
- Administrative distance refers to the trustworthiness of a particular route
- A router first installs routes with higher administrative distances
- The value of the administrative distance cannot be altered by the network administrator
- Routes with the smallest metric to a destination indicate the best path
- The metric is always determined based on hop count
- The metric varies depending on which Layer 3 protocol is being routed
20. Consider the following routing table entry for R1:
D 10.1.1.0/24 [90/2170112] via 209.165.200.226, 00:00:05, Serial0/0/0
What is the significance of the Serial0/0/0?
- It is the interface on R1 used to send data that is destined for 10.1.1.0/24
- It is the R1 interface through which the EIGRP update was learned.
- It is the interface on the final destination router that is directly connected to the 10.1.1.0/24 network.
- It is the interface on the next-hop router when the destination IP address is on the 10.1.1.0/24 network.
21. The exhibit contains CLI output that says:
R1# show ipv6 routeC 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::/64 [0/0] via ::, FastEthernet0/0 L 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::54/128 [0/0] via ::, FastEthernet0/0 C 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 [0/0] via ::, FastEthernet0/1 L 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::12/128 [0/0] via ::, FastEthernet0/1 L FF00::/8 [0/0] via ::, Null0 R1#
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show ipv6 route command on R1. What two conclusions can be drawn from the routing table? (Choose two.)
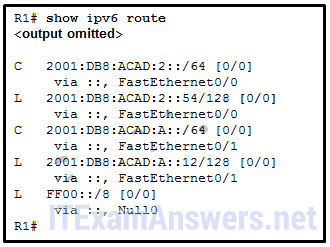
- R1 does not know a route to any remote networks
- The network FF00::/8 is installed through a static route command
- The interface Fa0/1 is configured with IPv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::12
- Packets that are destined for the network 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::/64 will be forwarded through Fa0/1
- Packets that are destined for the network 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::54/128 will be forwarded through Fa0/0
22. A network administrator configures the interface fa0/0 on the router R1 with the command ip address 172.16.1.254 255.255.255.0. However, when the administrator issues the command show ip route, the routing table does not show the directly connected network. What is the possible cause of the problem?
- The interface fa0/0 has not been activated
- The configuration needs to be saved first.
- No packets with a destination network of 172.16.1.0 have been sent to R1.
- The subnet mask is incorrect for the IPv4 address.
23. A network administrator configures a router by the command ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.226. What is the purpose of this command?
- to forward all packets to the device with IP address 209.165.200.226
- to add a dynamic route for the destination network 0.0.0.0 to the routing table
- to forward packets destined for the network 0.0.0.0 to the device with IP address 209.165.200.226
- to provide a route to forward packets for which there is no route in the routing table
24. What are two common types of static routes in routing tables? (Choose two)
- a default static route
- a built-in static route by IOS
- a static route to a specific network
- a static route shared between two neighboring routers
- a static route converted from a route that is learned through a dynamic routing protocol
25. What is the effect of configuring the ipv6 unicast-routing command on a router?
- to assign the router to the all-nodes multicast group
- to enable the router as an IPv6 router
- to permit only unicast packets on the router
- to prevent the router from joining the all-routers multicast group
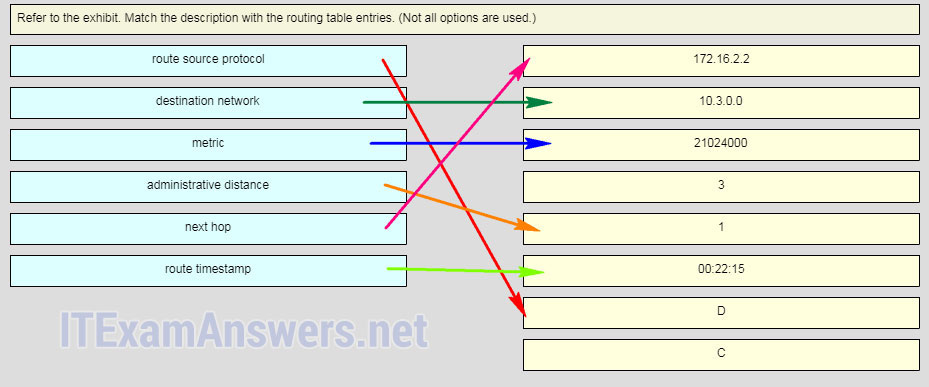
26. Refer to the exhibit. Match the description with the routing table entries. (Not all options are used.)
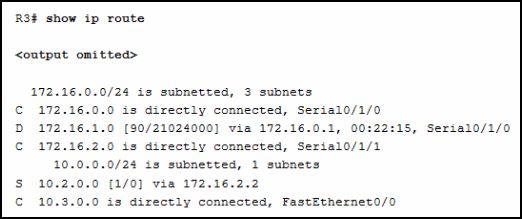
Graphic contains output of show ip route as follows:
R3# show ip route 172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets C 172.16.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/1/0 D 172.16.1.0 [90/21024000] via 172.16.0.1, 00:22:15, Serial0/1/0 C 172.16.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/1/0 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets S 10.2.0.0/24 [1/0] via 172.16.2.2 C 10.3.0.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
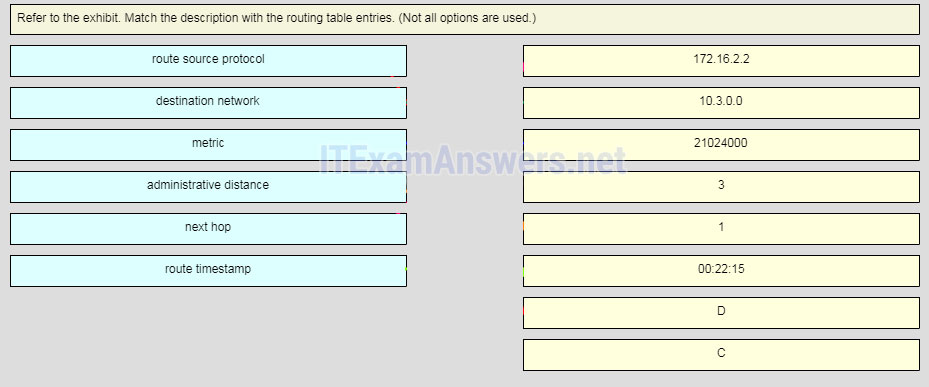
Question as presented:
Older Version:
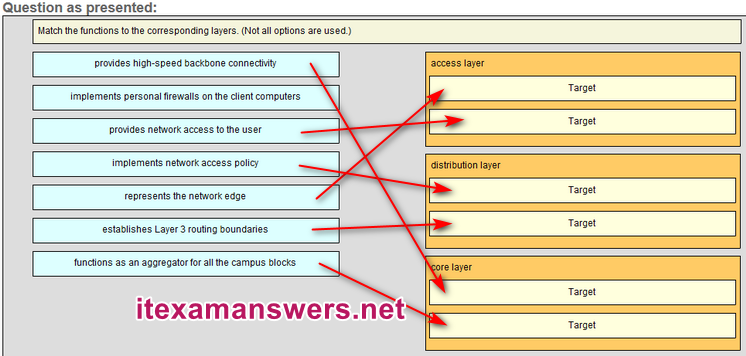
27. What is a basic function of the Cisco Borderless Architecture distribution layer?
- acting as a backbone
- aggregating all the campus blocks
- aggregating Layer 3 routing boundaries
- providing access to end user devices
28. A network designer must provide a rationale to a customer for a design which will move an enterprise from a flat network topology to a hierarchical network topology. Which two features of the hierarchical design make it the better choice? (Choose two.)
- lower bandwidth requirements
- reduced cost for equipment and user training
- easier to provide redundant links to ensure higher availability
- less required equipment to provide the same performance levels
- simpler deployment for additional switch equipment
29. What is a collapsed core in a network design?
- a combination of the functionality of the access and distribution layers
- a combination of the functionality of the distribution and core layers
- a combination of the functionality of the access and core layers
- a combination of the functionality of the access, distribution, and core layers
30. Which two previously independent technologies should a network administrator attempt to combine after choosing to upgrade to a converged network infrastructure? (Choose two.)
- user data traffic
- analog and VoIP phone traffic
- scanners and printers
- mobile cell phone traffic
- electrical system
31. What is a definition of a two-tier LAN network design?
- access and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the distribution layer on a separate tier
- access and distribution layers collapsed into one tier, and the core layer on a separate tier
- distribution and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the access layer on a separate tier
- access, distribution, and core layers collapsed into one tier, with a separate backbone layer
32. A local law firm is redesigning the company network so that all 20 employees can be connected to a LAN and to the Internet. The law firm would prefer a low cost and easy solution for the project. What type of switch should be selected?
- fixed configuration
- modular configuration
- stackable configuration
- StackPower
- StackWise
33. What are two advantages of modular switches over fixed-configuration switches? (Choose two.)
- lower cost per switch
- increased scalability
- lower forwarding rates
- need for fewer power outlets
- availability of multiple ports for bandwidth aggregation
34. Refer to the exhibit. Consider that the main power has just been restored. PC3 issues a broadcast IPv4 DHCP request. To which port will SW1 forward this request?
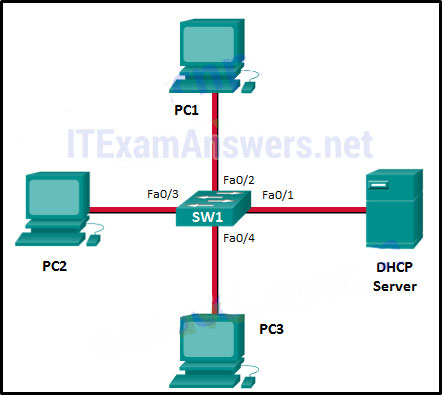
- to Fa0/1 only
- to Fa0/1 and Fa0/2 only
- to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 only
- to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, and Fa0/4
- to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/4 only
35. What is one function of a Layer 2 switch?
- forwards data based on logical addressing
- duplicates the electrical signal of each frame to every port
- learns the port assigned to a host by examining the destination MAC address
- determines which interface is used to forward a frame based on the destination MAC address
36. Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
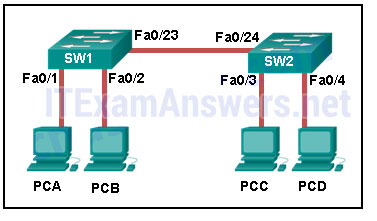
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
37. What two criteria are used by a Cisco LAN switch to decide how to forward Ethernet frames? (Choose two.)
- path cost
- egress port
- ingress port
- destination IP address
- destination MAC address
38. Which network device can be used to eliminate collisions on an Ethernet network?
- firewall
- hub
- router
- switch
39. Which type of address does a switch use to build the MAC address table?
- destination IP address
- source IP address
- destination MAC address
- source MAC address
40. What are two reasons a network administrator would segment a network with a Layer 2 switch? (Choose two.)
- to create fewer collision domains
- to enhance user bandwidth
- to create more broadcast domains
- to eliminate virtual circuits
- to isolate traffic between segments
- to isolate ARP request messages from the rest of the network
41. Refer to the exhibit. How many broadcast domains are displayed?
- 1
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 55
42. Which statement describes the microsegmentation feature of a LAN switch?
- Frame collisions are forwarded.
- Each port forms a collision domain.
- The switch will not forward broadcast frames.
- All ports inside the switch form one collision domain.
43. What is the destination address in the header of a broadcast frame?
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- 11-11-11-11-11-11
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
44. Fill in the blank.
A converged network is one that uses the same infrastructure to carry voice, data, and video signals.
45. Match the functions to the corresponding layers. (Not all options are used.)
Question
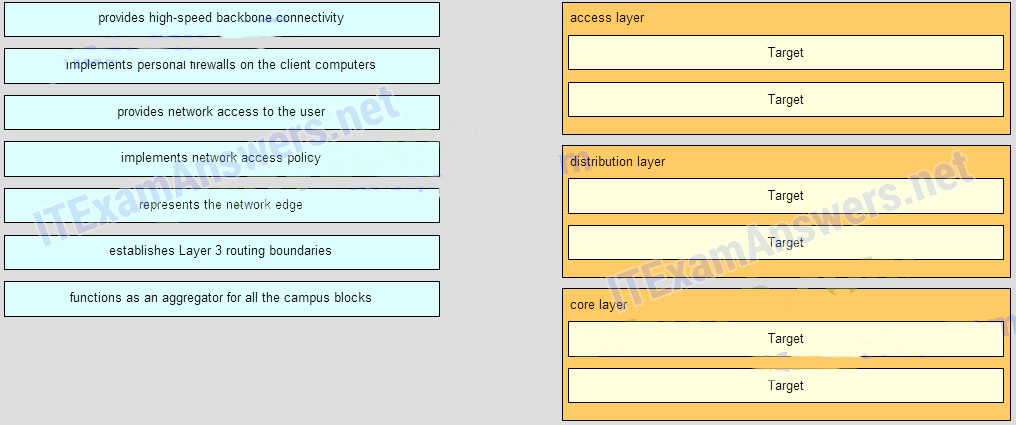
Answer
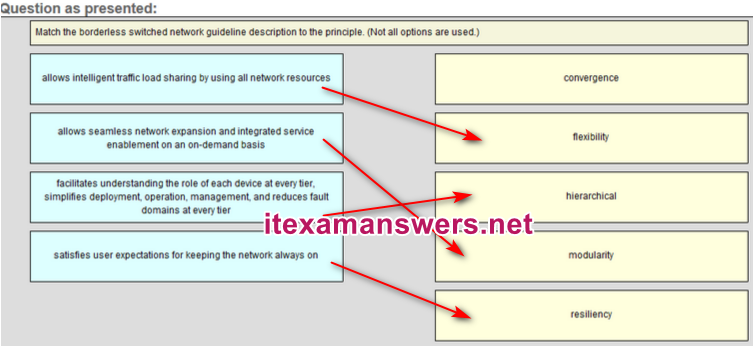
46. Match the borderless switched network guideline description to the principle. (Not all options are used.)
Question

Answer
47. Match the forwarding characteristic to its type. (Not all options are used.)
Question
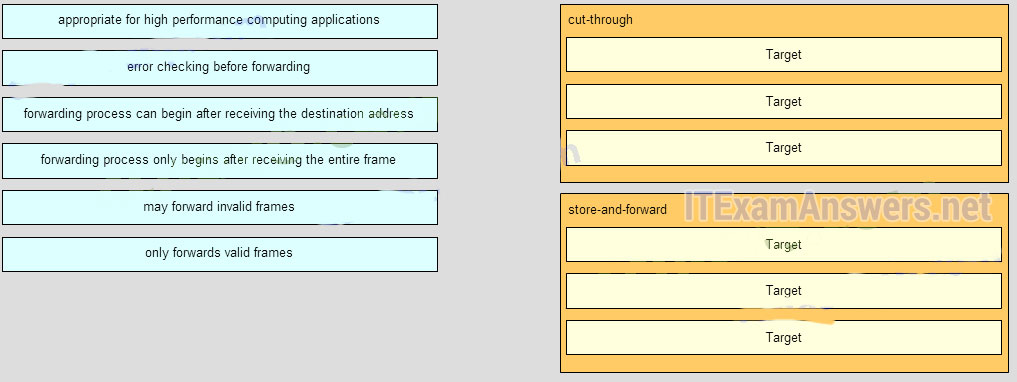
Answer
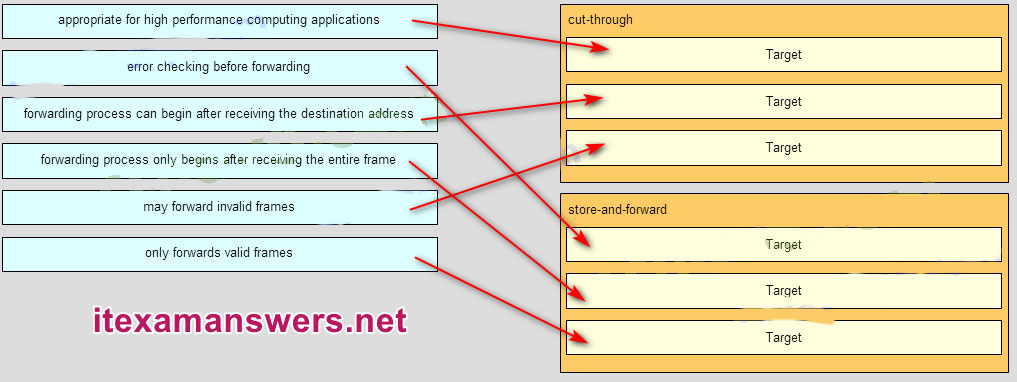
48. What is one advantage of using the cut-through switching method instead of the store-and-forward switching method?
- has a positive impact on bandwidth by dropping most of the invalid frames
- makes a fast forwarding decision based on the source MAC address of the frame
- has a lower latency appropriate for high-performance computing applications
- provides the flexibility to support any mix of Ethernet speeds
49. Refer to the exhibit. Consider that the main power has just been restored. PC1 asks the DHCP server for IPv4 addressing. The DHCP server sends it an IPv4 address. While PC2 is still booting up, PC3 issues a broadcast IPv4 DHCP request. To which port will SW1 forward this request?
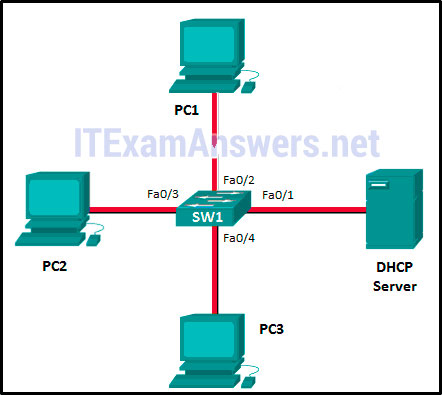
- to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/4 only
- to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, and Fa0/4
- to Fa0/1 and Fa0/2 only
- to Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3 only
- to Fa0/1 only
50. Refer to the exhibit. Fill in the blank.
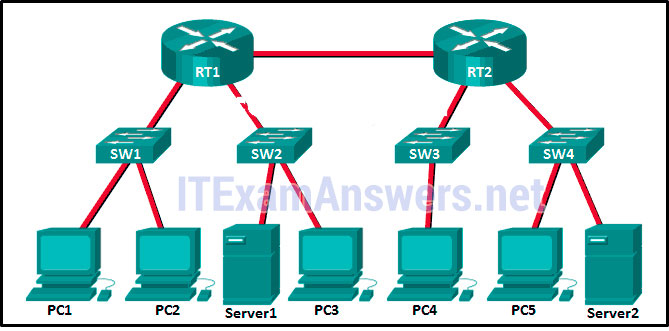
There are ” 12 ” collision domains in the topology.
51. ABC, Inc. has about fifty hosts in one LAN. The administrator would like to increase the throughput of that LAN. Which device will increase the number of collision domains and thereby increase the throughput of the LAN?
- hub
- host
- NIC
- switch
52. What does the term “port density” represent for an Ethernet switch?
- the numbers of hosts that are connected to each switch port
- the speed of each port
- the memory space that is allocated to each switch port
- the number of available ports
53. Which type of transmission does a switch use when the destination MAC address is not contained in the MAC address table?
- anycast
- unicast
- broadcast
- multicast
54. What information is added to the switch table from incoming frames?
- source MAC address and incoming port number
- destination MAC address and incoming port number
- destination IP address and incoming port number
- source IP address and incoming port number
55. An administrator purchases new Cisco switches that have a feature called StackPower. What is the purpose of this feature?
- It enables many switches to be connected with a special fiber-optic power cable to provide higher bandwidth.
- It enables the sharing of power among multiple stackable switches.
- It enables many switches to be connected to increase port density.
- It enables many switches to be physically stacked in an equipment rack.
- It enables AC power for a switch to be provided from a powered patch panel.
56. Which switch form factor should be used when large port density, fault tolerance, and low price are important factors?
- fixed-configuration switch
- modular switch
- stackable switch
- rackable 1U switch
57. Refer to the exhibit. Fill in the blank.
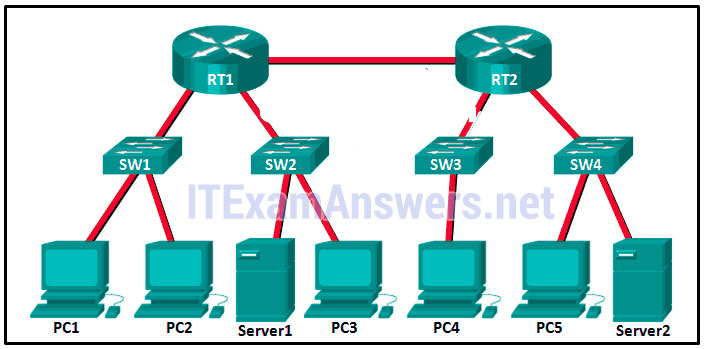
There are ” 5” broadcast domains in the topology.
58. What tool is important to consider for use when making hardware improvement decisions about switches?
- switched virtual interfaces
- authentication servers
- multilayer switching
- traffic flow analysis
59. What is the maximum wire speed of a single port on a 48-port gigabit switch?
- 1000 Mb/s
- 48 Mb/s
- 48 Gb/s
- 100 Mb/s
60. When the installation of a network infrastructure is being planned, which technology will allow power to be provided via Ethernet cabling to a downstream switch and its connected devices?
- PoE pass-through
- Gigabit Ethernet
- wireless APs and VoIP phones
- PoE
61. Match the function to the corresponding switch type. (Not all options are used.)
Layer 2 switches
[+] typically used in the access layer of a switched network
[+] forward traffic based on information in the Ethernet header
——
Multilayer switches
[#] can build a routing table
[#] supports a few routing protocols
62. Refer to the exhibit. Fill in the blank.
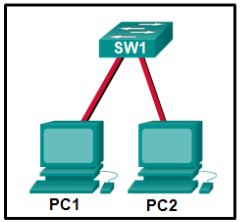
How many collision domains are shown in the topology? __2__
63. Match the borderless switched network guidline description to the principle (not all options used)

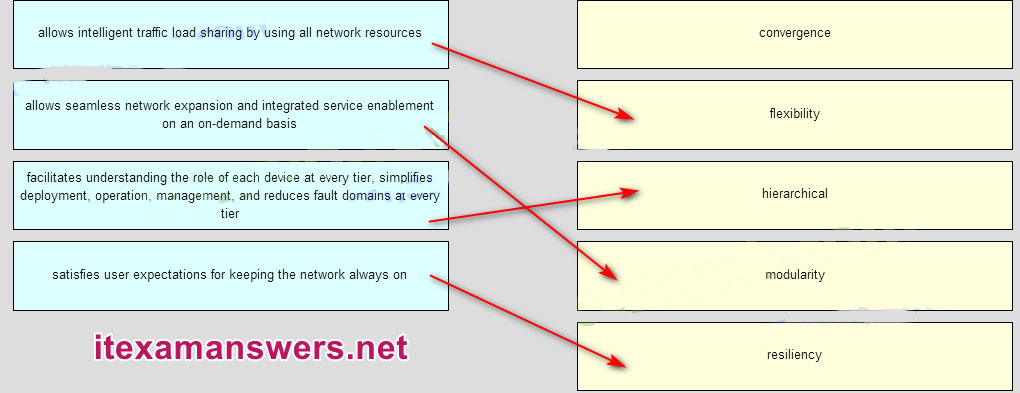
Place the options in the following order:
– allows intelligent traffic load sharing by using all network resources -> flexibility
– facilitates understanding the role of each device at every tier, simplifies deployment, operation, management, and reduces fault domains at every tier -> hierarchical
– allows seamless network expansion and integrated service enablement on an on-demand basis -> modularity
– satisfies user expectations for keeping the network always on -> resiliency
Download PDF File below:

please update 7.0
Hi Admin. will you update CCNA next year? i heard that there is new Exam 200-301 Certification
Sure! I will update new question for exam 200-301
Thank you
What are two functions of a router? (Choose two.)
It controls the flow of data via the use of Layer 2 addresses.
It builds a routing table based on ARP requests.
A router connects multiple IP networks.
It provides segmentation at Layer 2.
It determines the best path to send packets.
A router connects multiple IP networks.
It determines the best path to send packets.
thanks bro..taking the exam tomorrow…i’ll keep you updated
100% on test…just took it today. Thanks 👍
i will pass tomorrow!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Hi is that the really exam of 2018
YEAP