15.1.6 Lab – Implement NAT (Answers)
Topology
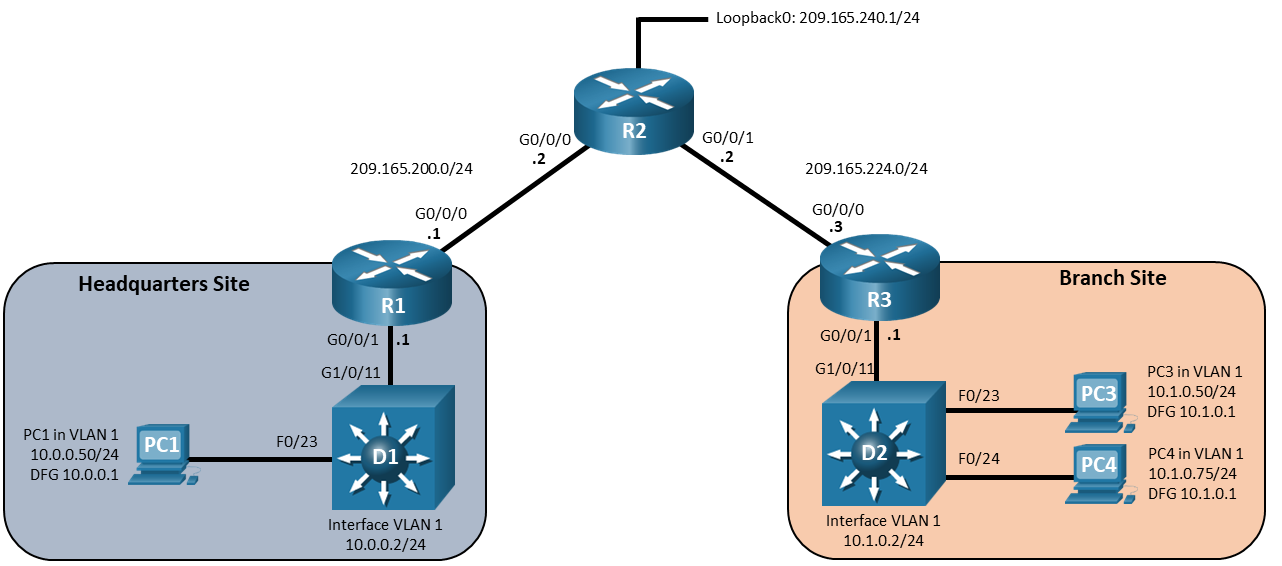
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0/0 | 209.165.200.1/24 | N/A |
| G0/0/1 | 10.0.0.1/24 | ||
| R2 | G0/0/0 | 209.165.200.2/24 | N/A |
| G0/0/1 | 209.165.224.2/24 | ||
| Loopback0 | 209.165.240.1/24 | ||
| R3 | G0/0/0 | 209.165.224.3/24 | N/A |
| G0/0/1 | 10.1.0.1/24 | ||
| D1 | VLAN 1 | 10.0.0.2/24 | N/A |
| D2 | VLAN 1 | 10.2.0.2/24 | N/A |
| PC1 | NIC | 10.0.0.50/24 | 10.0.0.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 10.1.0.50/24 | 10.1.0.1 |
| PC4 | NIC | 10.1.0.75/24 | 10.1.0.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 2: Configure and Verify Static Inside NAT
- Part 3: Configure and Verify Pooled NAT
- Part 4: Configure and Verify NAT Overload
Background / Scenario
The HQ and Branch sites must be configured to support NAT. Specifically, the HQ and Branch routers will be configured to provide inside LAN users with outside public addresses using NAT. The HQ router will also provide static NAT to access the email server from the outside network.
Note: This lab is an exercise in configuring and verifying various methods of NAT and does not reflect networking best practices.
Note: The routers and switches used with CCNP hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 and Cisco 3650, both with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs.
Note: Ensure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices
Required Resources
- 3 Routers (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 2 Switches (Cisco 3650 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 3 PCs (Choice of operating system with a terminal emulation program installed)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Configure basic settings for each device.
a. Console into each device, enter global configuration mode, and apply the basic settings. A command list for each device is provided below for the initial configurations.
Router R1
hostname R1 no ip domain lookup line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 password cisco123 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous login exit banner motd # This is R1, Implement NAT Lab # interface g0/0/0 ip address 209.165.200.1 255.255.255.0 no shut exit interface g0/0/1 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 no shut exit ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 g0/0/0 209.165.200.2
Router R2
hostname R2 no ip domain lookup line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 password cisco123 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous login exit banner motd # This is R2, Implement NAT Lab # interface g0/0/0 ip address 209.165.200.2 255.255.255.0 no shut exit interface g0/0/1 ip address 209.165.224.2 255.255.255.0 no shut exit interface loopback 0 ip address 209.165.240.1 255.255.255.0 no shut exit ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 g0/0/0 209.165.200.1 ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 g0/0/1 209.165.224.3
Router R3
hostname R3 no ip domain lookup line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 password cisco123 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous login exit banner motd # This is R3, Implement NAT Lab # interface g0/0/0 ip address 209.165.224.3 255.255.255.0 no shut exit interface g0/0/1 ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0 no shut exit ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 g0/0/0 209.165.224.2
Switch D1
hostname D1 no ip domain lookup line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 password cisco123 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous login exit banner motd # This is D1, Implement NAT Lab # interface range g1/0/1-24, g1/1/1-4 shutdown exit interface range g1/0/11, g1/0/23 no shutdown exit interface g1/0/23 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast exit interface vlan 1 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1
Switch D2
hostname D2 no ip domain lookup line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 password cisco123 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous login exit banner motd # This is D2, Implement NAT Lab # interface range g1/0/1-24, g1/1/1-4 shutdown exit interface range g1/0/11, g1/0/23-24 no shutdown exit interface range g1/0/23-24 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast exit interface vlan 1 ip address 10.1.0.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ip default-gateway 10.1.0.1
b. Set the clock on each device to UTC time.
c. Save the running configuration to startup-config.
Step 3: Verify reachability.
PC1 (10.0.0.50) should be able to ping PC3 (10.1.0.50), and PC4 (10.1.0.75) should be able to ping switch D1 (10.0.0.2). If not, notify your instructor so they may assist you in troubleshooting and correcting any incorrect configurations.
Part 2: Configure and Verify Static Inside NAT
In Part 2, you will configure and verify Static Inside NAT. The idea behind Static Inside NAT is to make an inside local address reachable via an outside global address. For this lab, we will make interface VLAN 1 on switch D1 appear as 209.165.200.99 on the outside network.
Step 1: On R1, configure Static Inside NAT.
Note: The following steps a and b do not have to be carried out in the order listed.
a. Configure R1 to translate the address on D1 Interface VLAN 1 to 209.165.200.99.
R1(config)# ip nat inside source static 10.0.0.2 209.165.200.99
b. On R1, specify the inside and outside interfaces for NAT purposes.
R1(config)# interface g0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip nat outside R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface g0/0/1 R1(config-if)# ip nat inside R1(config-if)# exit
Step 2: Verify the NAT process is occurring on R1.
a. On R1, issue the command show ip nat translations. In the output, you will see the static translation information.
R1# show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global --- 209.165.200.99 10.0.0.2 --- --- Total number of translations: 1
b. From the console of R2, send 10,000 pings to the destination address 209.165.200.99 using the command ping 209.165.200.99 repeat 10000. The pings should be successful.
c. On R1, issue the command show ip nat translations. In the output, you will see the static translation as well as the translation used for the ping.
R1# show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global --- 209.165.200.99 10.0.0.2 --- --- icmp 209.165.200.99:0 10.0.0.2:0 209.165.200.2:0 209.165.200.2:0 Total number of translations: 2
d. From the console of R2, stop the ping if it is still running and then telnet to 209.165.200.99. You should be able to connect and login to D1. Use cisco123 as the password when prompted.
e. While logged in to D1, issue the command show tcp brief. In the output, you will see the addresses involved in the communication from D1’s perspective.
D1# show tcp brief TCB Local Address Foreign Address (state) 054D9734 10.0.0.2.23 209.165.200.2.63955 ESTAB
f. On R1, issue the command show ip nat translations. In the output, you will see the static translation as well as the translation used for the telnet session.
R1# show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global --- 209.165.200.99 10.0.0.2 --- --- tcp 209.165.200.99:23 10.0.0.2:23 209.165.200.2:63955 209.165.200.2:63955 Total number of translations: 2
g. Disconnect the telnet session in preparation for the next part of the lab.
Part 3: Configure and Verify Pooled NAT
In Part 3, you will configure, examine, and verify pooled NAT. Pooled NAT uses a pool of available outside addresses to dynamically translate inside addresses on a one-to-one basis. The drawback to Pooled NAT is that if you do not have a pool of addresses that is at least the same size as the number of addresses that need to be translated, there will be inside hosts that cannot send traffic outside until a translation times out or is manually cleared.
Step 1: On R3, configure Pooled NAT.
Note: The following steps a, b, c, and d do not have to be carried out in the order listed.
a. On R3, create a standard access list that identifies the source addresses of traffic to be translated. Traffic with source addresses matching this access list are referred to as “interesting” and will be processed through the configured NAT rule. For this lab, specify the entire 10.1.0.0/24 network as interesting.
R3(config)# access-list 33 permit 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255
b. Next, create a pool of addresses to use for the interesting traffic translations. You should have authority to use these addresses, and outside networks should route traffic destined to these addresses to you. For this lab, we will use two addresses from the subnet connecting R3 and R2.
R3(config)# ip nat pool POOLEDNAT 209.165.224.5 209.165.224.6 prefix-length 24
c. Associate the interesting addresses with the NAT pool.
R3(config)# ip nat inside source list 33 pool POOLEDNAT
d. Establish the inside and outside interfaces on R3.
R3(config)# interface g0/0/0 R3(config-if)# ip nat outside R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface g0/0/1 R3(config-if)# ip nat inside R3(config-if)# exit
Step 2: Verify the NAT process is occurring on R3.
a. On R3, issue the command show ip nat translations. The output will indicate that there are no translations.
b. On R3, issue the command show ip nat pool name POOLEDNAT. The output will give you details about the pool that is available for translation.
R3# show ip nat pool name POOLEDNAT
NAT Pool Statistics
Pool name POOLEDNAT, id 1
Assigned Available
Addresses 0 2
UDP Low Ports 0 1024
TCP Low Ports 0 1024
UDP High Ports 0 129024
TCP High Ports 0 129024
(Low ports are less than 1024. High ports are greater than or equal to 1024.)
c. From the command prompt on PC3, start a continuous ping to the destination address 209.165.224.2. The pings should be successful.
d. On R3, issue the command show ip nat translations. In the output you will see the pooled translation as well as the translation used for the ping.
R3# show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global --- 209.165.224.5 10.1.0.50 --- --- icmp 209.165.224.5:1 10.1.0.50:1 209.165.224.2:1 209.165.224.2:1 Total number of translations: 2
e. From the command prompt on PC4, start a continuous ping to the destination address 209.165.224.2. The pings should be successful.
f. On R3, issue the command show ip nat translations. In the output you will see the pooled translations as well as the translation used for the ping.
R3# show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global --- 209.165.224.6 10.1.0.75 --- --- --- 209.165.224.5 10.1.0.50 --- --- icmp 209.165.224.6:6740 10.1.0.75:6740 209.165.224.2:6740 209.165.224.2:6740 icmp 209.165.224.5:1 10.1.0.50:1 209.165.224.2:1 209.165.224.2:1 Total number of translations: 4
g. From the console of D2, send 10,000 pings to the destination address 209.165.224.2 using the command ping 209.165.224.2 repeat 10000. The pings should fail.
h. On R3, you should see the following syslog message being repeated:
*Jan 25 16:52:01.498: %IOSXE-6-PLATFORM: R0/0: cpp_cp: QFP:0.0 Thread:000 TS:00000053243712630396 %NAT-6-ADDR_ALLOC_FAILURE: Address allocation failed; pool 1 may be exhausted [2]
We purposely created a pool of addresses that was too small to demonstrate one of the shortcomings of Pooled NAT. Verify the pool is exhausted by examining the output of the command show ip nat pool name POOLEDNAT.
R3# show ip nat pool name POOLEDNAT
NAT Pool Statistics
Pool name POOLEDNAT, id 1
Assigned Available
Addresses 2 0
UDP Low Ports 0 1024
TCP Low Ports 0 1024
UDP High Ports 0 129024
TCP High Ports 0 129024
(Low ports are less than 1024. High ports are greater than or equal to 1024.)
i. Stop the pings on D2, PC3, and PC4. (Note: To stop the ping, press Ctr+Shift+6.)
j. In preparation for the next part of the lab, remove the pool and mapping commands. Leave the ACL and the interface specifications.
R3(config)# do clear ip nat translation * R3(config)# no ip nat pool POOLEDNAT 209.165.224.5 209.165.224.6 prefix-length 24 R3(config)# no ip nat inside source list 33 pool POOLEDNAT
Part 4: Configure and Verify NAT Overload
In Part 4, you will configure and examine NAT Overload, which is also called Port Address Translation or PAT. PAT overloads on an interface address or on a pool of addresses by associating each traffic session with a unique set of port numbers. The advantage, especially for smaller networks, is that everyone can get out of the network by leveraging a single outside IP address. The drawback to PAT is that you have a limit of about 65,000 to the number of translations possible via a single address. The impact of this limit is felt in large networks, where you must have multiple outside IP addresses to overload onto to ensure everyone can communicate.
As a reminder, R3 still has interfaces setup as outside and inside, and still has access list 33 specifying the LAN network address. You will leverage those existing configurations to complete this part of the lab.
For this lab, R3 will overload on the interface specified as outside, which is g0/0/0.
a. Configure the NAT statement directing the router to translate addresses matching access list 33 to the outside interface IP address, keying on port numbers.
R3(config)# ip nat inside source list 33 interface g0/0/0 overload
b. On R3, issue the command show ip nat translations. The output will indicate that there are no translations.
c. From the command prompt on PC3, start a continuous ping to the destination address 209.165.224.2. The pings should be successful.
d. On R3, issue the command show ip nat translations. In the output you will see the PAT translation used for the ping.
R3# show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global icmp 209.165.224.3:1 10.1.0.50:1 209.165.224.2:1 209.165.224.2:1 Total number of translations: 1
e. From the command prompt on PC4, start a continuous ping to the destination address 209.165.224.2. From the console of D2, send 100,000 pings to the same address. The pings should be successful.
f. On R3, issue the command show ip nat translations. In the output you will see the PAT translations as well as the translation used for the ping from D2 and PC4.
R3# show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global icmp 209.165.224.3:6791 10.1.0.75:6791 209.165.224.2:6791 209.165.224.2:6791 icmp 209.165.224.3:1 10.1.0.50:1 209.165.224.2:1 209.165.224.2:1 icmp 209.165.224.3:6784 10.1.0.2:1 209.165.224.2:1 209.165.224.2:6784 Total number of translations: 3
e. Stop the continuous pings on D2, PC3, and PC4.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 4221 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 4300 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
Device Configs – Final
Router R1
R1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 3665 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode none ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 209.165.200.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat outside negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside negotiation auto ! interface Serial0/1/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface Serial0/1/1 no ip address shutdown ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http authentication local ip http secure-server ip nat inside source static 10.0.0.2 209.165.200.99 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 GigabitEthernet0/0/0 209.165.200.2 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C This is R1, Implement NAT Lab ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 logging synchronous login ! end
Router R2
R2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 3633 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode none ! interface Loopback0 ip address 209.165.240.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 209.165.200.2 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 209.165.224.2 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http authentication local ip http secure-server ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/0/0 209.165.200.1 ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 GigabitEthernet0/0/1 209.165.224.3 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C This is R2, Implement NAT Lab ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 logging synchronous login ! end
Router R3
R3# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 3762 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R3 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode none ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 209.165.224.3 255.255.255.0 ip nat outside negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside negotiation auto ! interface Serial0/1/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface Serial0/1/1 no ip address shutdown ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http secure-server ip nat inside source list 33 interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 overload ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 GigabitEthernet0/0/0 209.165.224.2 ! access-list 33 permit 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C This is R3, Implement NAT Lab ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 logging synchronous login ! end
Switch D1
D1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 6664 bytes ! version 16.9 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec ! Call-home is enabled by Smart-Licensing. service call-home no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname D1 ! vrf definition Mgmt-vrf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! no aaa new-model switch 1 provision ws-c3650-24ps ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! license boot level ipservicesk9 ! diagnostic bootup level minimal ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode sso ! transceiver type all monitoring ! class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control description Topology control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING class-map match-any system-cpp-default description Inter FED, EWLC control, EWLC data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFLSAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth description Punt Webauth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control description L2 LVX control packets class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station description MCAST END STATION class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control description L2 control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth description DOT1X Auth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control description Stackwise Virtual class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control description Routing control and Low Latency class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping description Protocol snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping description DHCP snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical description System Critical and Gold Pkt ! policy-map system-cpp-policy ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf no ip address negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/9 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/11 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/12 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/17 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/18 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/19 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/20 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/21 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/3 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/4 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http secure-server ! control-plane service-policy input system-cpp-policy ! banner motd ^C This is D1, Implement NAT Lab ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 logging synchronous login line vty 5 15 login ! end
Switch D2
D2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 6712 bytes! ! version 16.9 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec ! Call-home is enabled by Smart-Licensing. service call-home no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname D2 ! vrf definition Mgmt-vrf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! no aaa new-model switch 1 provision ws-c3650-24ps ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! license boot level ipservicesk9 ! diagnostic bootup level minimal ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode sso ! transceiver type all monitoring ! class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control description Topology control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING class-map match-any system-cpp-default description Inter FED, EWLC control, EWLC data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFLSAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth description Punt Webauth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control description L2 LVX control packets class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station description MCAST END STATION class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control description L2 control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth description DOT1X Auth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control description Stackwise Virtual class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control description Routing control and Low Latency class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping description Protocol snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping description DHCP snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical description System Critical and Gold Pkt ! policy-map system-cpp-policy ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf no ip address negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/9 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/11 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/12 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/17 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/18 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/19 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/20 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/21 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 switchport mode access shutdown spanning-tree portfast ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/3 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/4 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 ip address 10.1.0.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip default-gateway 10.1.0.1 ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http secure-server ! control-plane service-policy input system-cpp-policy ! banner motd ^C This is D2, Implement NAT Lab ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 logging synchronous login line vty 5 15 login ! end
