9.1.2 Lab – Implement Multiarea OSPFv3 (Answers)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
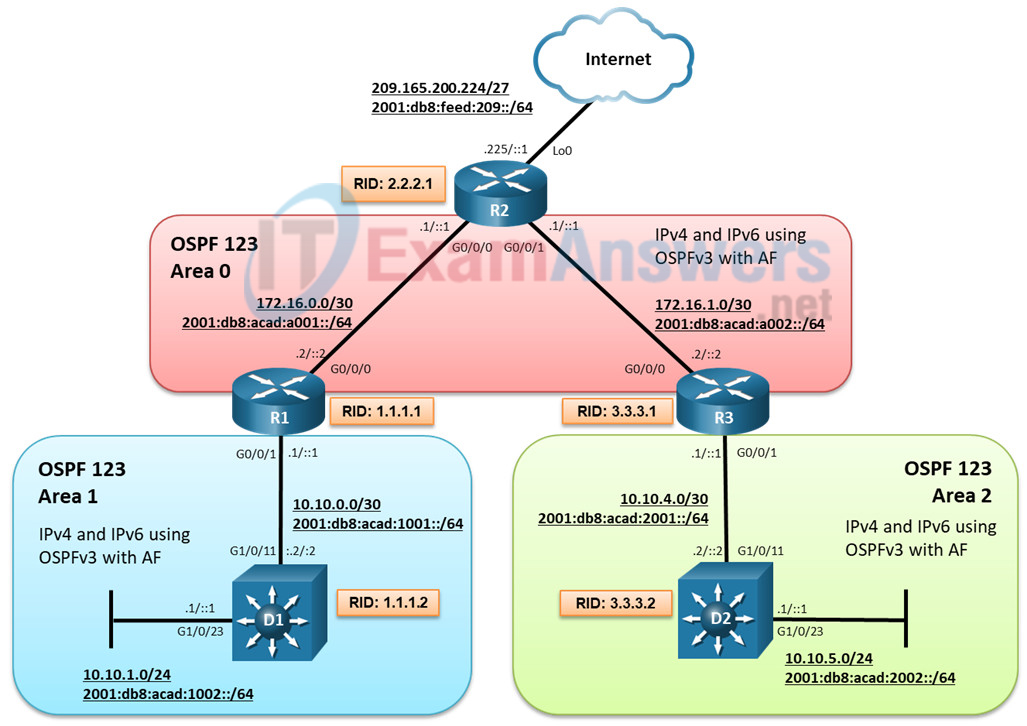
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IPv4 Address | IPv6 Address | IPv6 Link-Local |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0/0 | 172.16.0.2/30 | 2001:db8:acad:a001::2/64 | fe80::1:2 |
| G0/0/1 | 10.10.0.1/30 | 2001:db8:acad:1001::1/64 | fe80::1:1 | |
| R2 | Lo0 | 209.165.200.225/27 | 2001:db8:feed:209::1/64 | fe80::2:3 |
| G0/0/0 | 172.16.0.1/30 | 2001:db8:acad:a001::1/64 | fe80::2:1 | |
| G0/0/1 | 172.16.1.1/30 | 2001:db8:acad:a002::1/64 | fe80::2:2 | |
| R3 | G0/0/0 | 172.16.1.2/30 | 2001:db8:acad:a002::2/64 | fe80::3:2 |
| G0/0/1 | 10.10.4.1/30 | 2001:db8:acad:2001::1/64 | fe80::3:1 | |
| D1 | G1/0/11 | 10.10.0.2/30 | 2001:db8:acad:1001::2/64 | fe80::d1:2 |
| G1/0/23 | 10.10.1.0/24 | 2001:db8:acad:1002::1/64 | fe80::d1:1 | |
| D2 | G1/0/11 | 10.10.4.2/30 | 2001:db8:acad:2001::2/64 | fe80::d2:2 |
| G1/0/23 | 10.10.5.1/24 | 2001:db8:acad:2002::1/64 | fe80::d2:1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Topology and Configure Basic Device Settings and IP Addressing
- Part 2: Configure Traditional OSPFv3 for IPv6 on D1
- Part 3: Configure OSPFv3 for Address Families (AF) IPv4 and AF IPv6
- Part 4: Verify OSPFv3 AF
- Part 5: Tune OSPFv3 AF
Background / Scenario
In this lab, you will configure the network with multiarea OSPFv3 routing using the AF feature for both IPv4 and IPv6 in OSPF areas 0, 1 and 2. This lab was specifically designed to use three routers and two Layer 3 switches that support OSPFv3 using AF.
It should be noted that OSPFv3 runs on top of IPv6 and uses IPv6 link local addresses for OSPFv3 control packets. Therefore, it is required that IPv6 be enabled on an OSPFv3 link, although the link may not be participating in any IPv6 AFs. Additionally, OSPFv3 AF for IPv4 unicast is not backwards compatible with OSPFv2.
Note: The routers used with CCNP hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs.
Note: The switches used with CCNP hands-on labs are Cisco Catalyst 3650s with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). Other switches and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs.
Note: Ensure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
• 3 Routers (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
• 2 Switches (Cisco 3650 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
• Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
• Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings and Interface Addressing
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings and interface addressing on routers and switches.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Configure basic settings for each router.
a. Console into each device, enter global configuration mode, and apply the basic settings and interface addressing using the following startup configurations for each device.
Router R1
hostname R1 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging sync exec-time 0 0 exit interface g0/0/0 ip add 172.16.0.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:a001::2/64 ipv6 add fe80::1:2 link-local no shut exit interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:1001::1/64 ipv6 add fe80::1:1 link-local no shut exit
Router R2
hostname R2 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging sync exec-time 0 0 exit interface g0/0/0 ip add 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:a001::1/64 ipv6 add fe80::2:1 link-local no shut exit interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:a002::1/64 ipv6 add fe80::2:2 link-local no shut exit int lo0 ip add 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 ipv6 add 2001:db8:feed:209::1/64 ipv6 add fe80::2:3 link-local exit
Router R3
hostname R3 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging sync exec-time 0 0 exit interface g0/0/0 ip add 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:a002::2/64 ipv6 add fe80::3:2 link-local no shut exit interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 10.10.4.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:2001::1/64 ipv6 add fe80::3:1 link-local no shut exit
Switch D1
hostname D1 no ip domain lookup line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit interface g1/0/11 no switchport ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:1001::2/64 ipv6 add fe80::d1:2 link-local no shutdown exit interface g1/0/23 no switchport ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:1002::1/64 ipv6 add fe80::d1:1 link-local no shutdown exit
Switch D2
host D2 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging sync exec-time 0 0 exit interface gi1/0/11 no switchport ip address 10.10.4.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:2001::2/64 ipv6 add fe80::d2:2 link-local no shut exit interface gi1/0/23 no switchport ip address 10.10.5.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad:2002::1/64 ipv6 add fe80::d2:1 link-local no shut exit
b. Save the running configuration to startup-config.
Part 2: Configure Traditional OSPFv3 for IPv6 on D1
Step 1: Configure traditional OSPFv3 on D1.
Traditional OSPFv3 implements OSPF routing for IPv6. In this part of the lab, you will configure traditional OSPFv3 for routing IPv6 on D1, which is in the IPv6-only area.
a. OSPFv3 messages are sourced from the router’s IPv6 link-local address. Earlier in this lab, IPv6 GUA and link-local addresses were statically configured on each router’s interface. The link-local addresses were statically configured to make these addresses more recognizable than being automatically created using EUI-64. Issue the show ipv6 interface brief command to verify the GUA and link-local addresses on the router’s interfaces.
D1# show ipv6 interface brief
<output omitted>
GigabitEthernet1/0/11 [up/up]
FE80::D1:2
2001:DB8:ACAD:1001::2
<output omitted>
GigabitEthernet1/0/23 [up/up]
FE80::D1:1
2001:DB8:ACAD:1002::1
<output omitted>
b. IPv6 routing is disabled by default. Enable IPv6 routing using the ipv6 unicast-routing command in global configuration mode.
D1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
c. Most Cisco IOS versions have IPv6 CEF enabled by default when IPv6 routing is enabled. Use the show ipv6 cef command to verify whether IPv6 CEF is enabled. If you need to enable IPv6 CEF, use the ipv6 cef command. If IPv6 CEF is disabled you will see the an IOS message similar to “%IPv6 CEF not running”.
D1# show ipv6 cef ::/0 no route ::/127 discard 2001:DB8:ACAD:1001::/64 attached to GigabitEthernet1/0/11 2001:DB8:ACAD:1001::2/128 receive for GigabitEthernet1/0/11 2001:DB8:ACAD:1002::/64 attached to GigabitEthernet1/0/23 2001:DB8:ACAD:1002::1/128 receive for GigabitEthernet1/0/23 FE80::/10 receive for Null0 FF00::/8 multicast FF02::/16 receive
d. Configure the OSPFv3 process on D1. Similar to OSPFv2, the process ID does not have to match other routers to form neighbor adjacencies, although that is considered best practice. Configure the 32-bit OSPFv3 router ID on each router. Enable OSPFv3 directly on the interfaces using the interface ipv6 ospf pid area area command.
D1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing D1(config)# ipv6 router ospf 123 D1(config-rtr)# router-id 1.1.1.2 D1(config-rtr)# exit D1(config)# interface g1/0/11 D1(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 123 area 1 D1(config-if)# exit D1(config)# interface g1/0/23 D1(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 123 area 1 D1(config-if)# exit
e. The show ipv6 ospf command can be used to verify the OSPF router ID. If the OSPFv3 router ID is uses a 32-bit value other than the one specified by the router-id command, you can reset the router ID by using the clear ipv6 ospf pid process command and re-verify using the command show ipv6 ospf.
D1# show ipv6 ospf
Routing Process "ospfv3 123" with ID 1.1.1.2
Supports NSSA (compatible with RFC 3101)
Supports Database Exchange Summary List Optimization (RFC 5243)
Event-log enabled, Maximum number of events: 1000, Mode: cyclic
Router is not originating router-LSAs with maximum metric
Initial SPF schedule delay 50 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 200 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 5000 msecs
Initial LSA throttle delay 50 msecs
Minimum hold time for LSA throttle 200 msecs
Maximum wait time for LSA throttle 5000 msecs
Minimum LSA arrival 100 msecs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
Retransmission limit dc 24 non-dc 24
EXCHANGE/LOADING adjacency limit: initial 300, process maximum 300
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Graceful restart helper support enabled
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
RFC1583 compatibility enabled
Area 1
Number of interfaces in this area is 2
SPF algorithm executed 5 times
Number of LSA 12. Checksum Sum 0x0486C1
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
f. The show ipv6 protocols command can be used to verify general OSPFv3 information such as areas and enabled interfaces.
D1# show ipv6 protocols
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "connected"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ND"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ospf 123"
Router ID 1.1.1.2
Number of areas: 1 normal, 0 stub, 0 nssa
Interfaces (Area 1):
GigabitEthernet1/0/23
GigabitEthernet1/0/11
Redistribution:
None
Part 3: Configure OSPFv3 for AF IPv4 and AF IPv6
OSPFv3 with the address family (AF) unifies OSPF configuration for both IPv4 and IPv6. Each OSPFv3 AF is a single process, so you may have two processes per interface, but only one process per AF. OSPFv3 messages are sent over IPv6 which requires that IPv6 routing is enabled and that the interface has a link-local IPv6 address. This is the requirement even if only the IPv4 AF is configured.
In this section you will configure OSPFv3 with AF for the IPv4 and IPv6 address families on R1, R2, R3, D1 and D2.
Step 1: Configure OSPFv3 with AF on R1.
a. After enabling IPv6 unicast routing, configure OSPFv3 with AF on R1 using the router ospfv3 pid command. Use the ? to see the address families available.
R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R1(config)# router ospfv3 123 R1(config-router)# address-family ? ipv4 Address family ipv6 Address family
b. Next, specify the AF for IPv4 and use the ? to see the available options.
R1(config-router)# address-family ipv4 ? unicast Address Family modifier vrf Specify parameters for a VPN Routing/Forwarding instance <cr>
c. Enter the AF for IPv4 unicast using the command address-family ipv4 unicast. Use the ? to examine the options in AF configuration mode. Some of the more common configuration commands are highlighted. Use the router-id command to configure the router ID for the IPv4 AF.
R1(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast
R1(config-router-af)# ?
Router Address Family configuration commands:
adjacency Control adjacency formation
area OSPF area parameters
authentication Authentication parameters
auto-cost Calculate OSPF interface cost according to bandwidth
auto-cost-determination Calculate OSPF interface cost according to bandwidth
bfd BFD configuration commands
compatible Compatibility list
default Set a command to its defaults
default-information Control distribution of default information
default-metric Set metric of redistributed routes
discard-route Enable or disable discard-route installation
distance Define an administrative distance
distribute-list Filter networks in routing updates
event-log Event Logging
exit-address-family Exit from Address Family configuration mode
graceful-restart Graceful-restart options
help Description of the interactive help system
ignore Do not complain about specific event
interface-id Source of the interface ID
limit Limit a specific OSPF feature
local-rib-criteria Enable or disable usage of local RIB as route
criteria
log-adjacency-changes Log changes in adjacency state
manet Specify MANET OSPF parameters
max-lsa Maximum number of non self-generated LSAs to accept
max-metric Set maximum metric
maximum-paths Forward packets over multiple paths
mpls MPLS Traffic Engineering configs
no Negate a command or set its defaults
passive-interface Suppress routing updates on an interface
prefix-suppression Enable prefix suppression
process-min-time Percentage of quantum to be used before releasing
CPU
queue-depth Hello/Router process queue depth
redistribute Redistribute information from another routing
protocol
router-id router-id for this OSPF process
shutdown Shutdown the router process
snmp Modify snmp parameters
statistics Enable or disable OSPF statistics options
summary-address Configure IP address summaries
summary-prefix Configure IP address summaries
timers Adjust routing timers
R1(config-router-af)#
R1(config-router-af)# router-id 1.1.1.1
d. Exit the IPv4 AF configuration mode and enter the AF IPv6 configuration mode. The exit-address-family (or a shorter version of exit) command is used exit address family configuration mode. Issue the address-family ipv6 unicast command to enter the IPv6 AF. For the IPv6 AF, use the router-id command to configure the router ID. It isn’t necessary to configure a different router ID for IPv6 AF but it is a valid option. The exit command is used to return to global configuration mode.
R1(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R1(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast R1(config-router-af)# router-id 1.1.1.1 R1(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R1(config-router)# exit
e. OSPFv3 is enabled directly on the interfaces for both IPv4 and IPv6 AFs using the ospfv3 pid [ ipv4 | ipv6 ] area area-id interface command. Use this command to enable OSPFv3 on both of R1’s interfaces.
R1(config)# interface g0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 0 R1(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 0 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface g0/0/1 R1(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 1 R1(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 1
Step 2: Configure OSPFv3 with AF IPv4 and AF IPv6 on R2.
Enable IPv6 unicast routing and configure the OSPFv3 with AF for both IPv4 and IPv6 on R2, similar to the configuration for R1.
R2(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R2(config)# router ospfv3 123 R2(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast R2(config-router-af)# router-id 2.2.2.1 R2(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R2(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast R2(config-router-af)# router-id 2.2.2.1 R2(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R2(config-router)# exit R2(config)# interface g0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 0 R2(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 0 R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface g0/0/1 R2(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 0 R2(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 0
Step 3: Configure OSPFv3 with IPv4 AF and IPv6 AF on R3.
Enable IPv6 unicast routing and configure the OSPFv3 with AF for both IPv4 and IPv6 on R3, similar to the configurations for R1 and R2. On R3, set the router ID for both IPv4 AF and IPv6 AF with a single command as shown.
R3(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R3(config)# router ospfv3 123 R3(config-router)# router-id 3.3.3.1 R3(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast R3(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R3(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast R3(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R3(config-router)# exit R3(config)# interface g0/0/0 R3(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 0 R3(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface g0/0/1 R3(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 2 R3(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 2
Step 4: Configure OSPFv3 with AF on D2.
a. Enter the following command to enable routing for IPv4. (This may not be required on depending on model and IOS.)
D2(config)# ip routing
b. Enter the following command to enable routing for IPv6. (This may not be required on depending on model and IOS.)
D2(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
Note: By default, the 3650 supports IPv6 interface configuration.
c. Configure the OSPFv3 with AF for both IPv4 and IPv6 on D2, similar to the configurations for R1, R2 and R3.
D2(config)# router ospfv3 123 D2(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast D2(config-router-af)# router-id 3.3.3.2 D2(config-router-af)# exit-address-family D2(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast D2(config-router-af)# router-id 3.3.3.2 D2(config-router-af)# exit-address-family D2(config-router)# exit D2(config)# interface g1/0/11 D2(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 2 D2(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 2 D2(config-if)# exit D2(config)# interface g 1/0/23 D2(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 2 D2(config-if)# ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 2
Part 4: Verify OSPFv3
The commands to verify traditional OSPFv3 and OSPFv3 with AF may differ. This is because OSPFv3 with AF commands include information for both IPv4 and IPv6 address families, whereas traditional OSPFv3 is for IPv6 only.
Step 1: Verifying neighbor adjacencies.
a. Use the show ipv6 ospf neighbor command on D1 to display OSPFv3 neighbors. This is a command used for routers configured with traditional OSPFv3. The equivalent command for OSPFv2 would be show ip ospf neighbor.
D1# show ipv6 ospf neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.2) (Process ID 123)
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
1.1.1.1 1 FULL/DR 00:00:39 6 GigabitEthernet1/0/11
b. This same command on a router running OSPFv3 with AF would generate similar output. For example, on R1 issue the same show ipv6 ospf neighbor command. Notice the output is only OSPFv3 for the IPv6 AF.
R1# show ipv6 ospf neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 123)
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
2.2.2.1 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:31 5 GigabitEthernet0/0/0
1.1.1.2 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:38 471 GigabitEthernet0/0/1
c. Now, issue the show ospfv3 neighbor command on R1. This is a command used for routers configured for OSPFv3 with AF. Notice the output includes neighbors for both IPv4 and IPv6 address families.
R1# show ospfv3 neighbor
OSPFv3 123 address-family ipv4 (router-id 1.1.1.1)
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
2.2.2.1 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:38 5 GigabitEthernet0/0/0
OSPFv3 123 address-family ipv6 (router-id 1.1.1.1)
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
2.2.2.1 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:32 5 GigabitEthernet0/0/0
1.1.1.2 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:30 471 GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Traditional OSPFv3 commands are similar to those for OSPFv2, except ipv6 is used as an argument instead of ip, for example show ip ospf neighbor and show ipv6 ospf neighbor. OSPFv3 with AF uses the argument ospfv3 which includes both OSPF for IPv4 and IPv6 AFs. For example, show ospfv3 neighbor.
Traditional OSPFv3 commands can be used when a router is configured for OSPFv3 with AF, but the OSPFv3 AF router will only show OSPF for IPv6 AF information. OSPFv3 with AF commands cannot be used on routers configured with traditional OSPFv3.
To summarize the show command arguments:
• OSPFv2: Use show ip ospf (IPv4 only)
• Traditional OSPFv3: Use show ipv6 ospf (IPv6 only)
• OSPFv3 with AF: Use show ospfv3 (IPv4 and IPv6 AF) or show ipv6 ospf (IPv6 only)
Question:
Why does the show ipv6 ospf neighbor command only display OSPFv3 neighbors in the IPv6 AF?
The show ipv6 ospf neighbor command is used to display OSPFv3 neighbor adjacencies, specifically for IPv6 indicated by the ipv6 keyword in the command. The router ID 1.1.1.6 and 3.3.3.6 are associated with the IPv6 AF.
Step 2: Examining the IP routing tables.
a. Use the show ipv6 route ospf command on D1 to display OSPFv3 routing entries in the IPv6 routing table.
D1# show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 9 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, H - NHRP, I1 - ISIS L1
I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP
EX - EIGRP external, ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination
NDr - Redirect, RL - RPL, O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter
OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2, ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1
ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2, la - LISP alt, lr - LISP site-registrations
ld - LISP dyn-eid, lA - LISP away, le - LISP extranet-policy
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:2001::/64 [110/4]
via FE80::1:1, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:2002::/64 [110/5]
via FE80::1:1, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:A001::/64 [110/2]
via FE80::1:1, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:A002::/64 [110/3]
via FE80::1:1, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
Display the routes using the show ip route ospf. Why are there no routes displayed using this command?
D1 is in an IPv6-only area. D1 is only implementing traditional OSPFv3 for IPv6 and has not been configured for OSPFv2 for IPv4.
b. Understanding the difference between commands associated with OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 can seem challenging at times. The show ip route ospfv3 command is used to view OSPFv3 routes in the IPv4 routing table. The show ipv6 route ospf command is used to view OSPFv3 routes in the IPv6 routing table. The show ipv6 route ospf command is the same command used with traditional OSPFv3 for IPv6.
R1# show ip route ospf
R1# show ip route ospfv3
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 3 masks
O IA 10.10.4.0/30 [110/3] via 172.16.0.1, 00:17:34, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
O IA 10.10.5.0/24 [110/4] via 172.16.0.1, 00:17:34, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
O 172.16.1.0/30 [110/2] via 172.16.0.1, 00:17:34, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
R1# show ipv6 route ospfv3
^
% Invalid input detected at '^' marker.
R1# show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 9 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, H - NHRP, I1 - ISIS L1
I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP
EX - EIGRP external, ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination
NDr - Redirect, RL - RPL, O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter
OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2, ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1
ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2, a - Application
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:1002::/64 [110/2]
via FE80::D1:2, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:2001::/64 [110/3]
via FE80::2:1, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:2002::/64 [110/4]
via FE80::2:1, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:A002::/64 [110/2]
via FE80::2:1, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Why doesn’t the show ip route ospf command display any routes on R1?
The show ip route ospf command is used to display OSPFv2 routes in the IPv4 routing table. R1 is implementing OSPFv3.
Step 3: Examining the OSPF LSDB.
a. D1 is running traditional OSPFv3. The show ipv6 ospf database command is used to display a summary of the OSPFv3 LSDB.
D1# show ipv6 ospf database
OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.2) (Process ID 123)
Router Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Fragment ID Link count Bits
1.1.1.1 1096 0x80000009 0 1 B
1.1.1.2 1110 0x80000005 0 1 None
Net Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Rtr count
1.1.1.1 1152 0x80000001 6 2
Inter Area Prefix Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Prefix
1.1.1.1 1096 0x80000003 2001:DB8:ACAD:A001::/64
1.1.1.1 1096 0x80000003 2001:DB8:ACAD:A002::/64
1.1.1.1 833 0x80000005 2001:DB8:ACAD:2001::/64
1.1.1.1 1497 0x80000002 2001:DB8:ACAD:2002::/64
Link (Type-8) Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Interface
1.1.1.2 1150 0x80000001 39 Gi1/0/23
1.1.1.1 1096 0x80000006 6 Gi1/0/11
1.1.1.2 1151 0x80000001 38 Gi1/0/11
Intra Area Prefix Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Ref-lstype Ref-LSID
1.1.1.1 1152 0x80000001 6144 0x2002 6
1.1.1.2 1150 0x80000003 0 0x2001 0
b. R1 is running OSPFv3 with AF. The show ospfv3 database command is used to display a summary of the OSPFv3 LSDB for both the IPv4 and IPv6 AFs.
R1# show ospfv3 database
OSPFv3 123 address-family ipv4 (router-id 1.1.1.1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Fragment ID Link count Bits
1.1.1.1 532 0x80000005 0 1 None
2.2.2.1 508 0x80000008 0 2 None
3.3.3.1 507 0x80000006 0 1 B
Net Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Rtr count
2.2.2.1 539 0x80000001 5 2
3.3.3.1 512 0x80000001 5 2
Inter Area Prefix Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Prefix
3.3.3.1 553 0x80000001 10.10.4.0/30
3.3.3.1 513 0x80000001 10.10.5.0/24
Link (Type-8) Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Interface
1.1.1.1 579 0x80000001 5 Gi0/0/0
2.2.2.1 579 0x80000001 5 Gi0/0/0
Intra Area Prefix Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Ref-lstype Ref-LSID
2.2.2.1 539 0x80000001 5120 0x2002 5
3.3.3.1 512 0x80000001 5120 0x2002 5
Router Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Fragment ID Link count Bits
1.1.1.1 602 0x80000001 0 0 None
OSPFv3 123 address-family ipv6 (router-id 1.1.1.1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Fragment ID Link count Bits
1.1.1.1 530 0x80000005 0 1 B
2.2.2.1 508 0x80000009 0 2 None
3.3.3.1 508 0x80000006 0 1 B
Net Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Rtr count
2.2.2.1 539 0x80000001 5 2
3.3.3.1 511 0x80000001 5 2
Inter Area Prefix Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Prefix
1.1.1.1 579 0x80000001 2001:DB8:ACAD:1001::/64
1.1.1.1 559 0x80000001 2001:DB8:ACAD:1002::/64
3.3.3.1 551 0x80000001 2001:DB8:ACAD:2001::/64
3.3.3.1 512 0x80000001 2001:DB8:ACAD:2002::/64
Link (Type-8) Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Interface
1.1.1.1 578 0x80000002 5 Gi0/0/0
2.2.2.1 578 0x80000002 5 Gi0/0/0
Intra Area Prefix Link States (Area 0)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Ref-lstype Ref-LSID
2.2.2.1 539 0x80000001 5120 0x2002 5
3.3.3.1 511 0x80000001 5120 0x2002 5
Router Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Fragment ID Link count Bits
1.1.1.1 553 0x80000006 0 1 B
1.1.1.2 552 0x80000025 0 1 None
Net Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Rtr count
1.1.1.2 560 0x80000001 38 2
Inter Area Prefix Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Prefix
1.1.1.1 578 0x80000001 2001:DB8:ACAD:A001::/64
1.1.1.1 538 0x80000001 2001:DB8:ACAD:A002::/64
1.1.1.1 506 0x80000001 2001:DB8:ACAD:2002::/64
1.1.1.1 506 0x80000001 2001:DB8:ACAD:2001::/64
Link (Type-8) Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Interface
1.1.1.1 559 0x8000000C 6 Gi0/0/1
1.1.1.2 598 0x80000002 38 Gi0/0/1
Intra Area Prefix Link States (Area 1)
ADV Router Age Seq# Link ID Ref-lstype Ref-LSID
1.1.1.2 481 0x80000016 0 0x2001 0
1.1.1.2 560 0x80000001 38912 0x2002 38
What would the show ipv6 route database command display on R1, if anything?
The show ipv6 ospf database command can also be used on R1, but it will only display OSPFv3 IPv6 AF information.
Part 5: Tune OSPFv3
Step 1: Configuring a passive interface.
a. To configure a passive interface in traditional OSPFv3, use the passive-interface command in OSPFv3 router mode.
D1(config)# ipv6 router ospf 123 D1(config-rtr)# passive-interface g1/0/23
b. To configure a passive interface in OSPFv3 with AF, you can use the passive-interface command in OSPFv3 router mode to configure the passive interface for both IPv4 and IPv6 AFs.
D2(config)# router ospfv3 123 D2(config-router)# passive-interface g1/0/23
c. As an alternative, you can use the passive-interface command within AF configuration mode to configure the passive interface for a specific AFs.
D2(config-router)# no passive-interface g1/0/23 D2(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast D2(config-router-af)# passive-interface g1/0/23 D2(config-router-af)# exit-address-family D2(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast D2(config-router-af)# passive-interface g1/0/23 D2(config-router-af)# exit-address-family
Step 2: Configuring summarization.
a. The area area range ipv6-summary-address command is used to summarize prefixes from one are into another. The area is the area from which the prefixes are summarized.
R1(config)# router ospfv3 123 R1(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast R1(config-router-af)# area 1 range 2001:db8:acad:1000::/52 R3(config)# router ospfv3 123 R3(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast R3(config-router-af)# area 2 range 2001:db8:acad:2000::/52
b. Notice that R2 is now receiving the summarized prefixes.
R2# show ipv6 route ospf
<output omitted>
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:1000::/52 [110/3]
via FE80::1:2, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:2000::/52 [110/3]
via FE80::3:2, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
Why is prefix summarization considered desirable? How does it stabilize routing?
It reduces the number of routes in the routing table and stabilizes routing performance. As long as at least one subnet is still available within the summarized prefix, the aggregated route will continue to be advertised.
Step 3: Modifying the network type.
a. OSPFv3 supports the same network types as OSPFv2. Notice that the Ethernet interfaces between R2 and R1, and R2 and R3, elect a DR and a BDR. This is because Ethernet is a multiaccess network. However, these are point-to-point links and there is no need for a DR or BDR.
R2# show ospfv3 interface brief Interface PID Area AF Cost State Nbrs F/C Gi0/0/1 123 0 ipv4 1 BDR 1/1 Gi0/0/0 123 0 ipv4 1 DR 1/1 Gi0/0/1 123 0 ipv6 1 BDR 1/1 Gi0/0/0 123 0 ipv6 1 DR 1/1
b. These connections can be changed to point-to-point using the ospfv3 network point-to-point interface command. This command needs to be configured one both sides of the point to point interface.
R2(config)# interface g0/0/1 R2(config-if)# ospfv3 network point-to-point R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface g0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ospfv3 network point-to-point R1(config)# interface g0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ospfv3 network point-to-point R3(config)# interface g0/0/0 R3(config-if)# ospfv3 network point-to-point
c. Notice that the links have now change to P2P.
R2# show ospfv3 interface brief Interface PID Area AF Cost State Nbrs F/C Gi0/0/1 123 0 ipv4 1 P2P 1/1 Gi0/0/0 123 0 ipv4 1 P2P 1/1 Gi0/0/1 123 0 ipv6 1 P2P 1/1 Gi0/0/0 123 0 ipv6 1 P2P 1/1
What is the effect on the state of the interface when changing a broadcast network to point-to-point?
There is no longer a DR or BDR on the multiaccess network.
Step 4: Advertising a default route.
a. Similar to OSPFv2, an ASBR in OSPFv3 advertises using the default-information command. Configure a static default route for IPv4 and IPv6 on R2.
Note: Without a default route in the routing table, OSPF would require the default-information originate always command to advertise a default route.
R2(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 lo0 R2(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 lo0 R2(config)# router ospfv3 123 R2(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast R2(config-router-af)# default-information originate R2(config-router-af)# exit R2(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast R2(config-router-af)# default-information originate R2(config-router-af)# exit
b. Verify D1 is receiving an IPv6 default route via OSPFv3.
D1# show ipv6 route ospf
<output omitted>
OE2 ::/0 [110/1], tag 123
via FE80::1:1, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:2000::/52 [110/5]
via FE80::1:1, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:A001::/64 [110/2]
via FE80::1:1, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
OI 2001:DB8:ACAD:A002::/64 [110/3]
via FE80::1:1, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
c. Verify D2 is receiving an IPv4 default route via OSPFv3.
D2# show ip route ospfv3
<output omitted>
Gateway of last resort is 10.10.4.1 to network 0.0.0.0
O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 10.10.4.1, 00:01:13, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
172.16.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
O IA 172.16.0.0 [110/3] via 10.10.4.1, 00:02:55, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
O IA 172.16.1.0 [110/2] via 10.10.4.1, 00:20:22, GigabitEthernet1/0/11
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 4221 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 4300 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
Device Configs – Final
Router R1
R1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 3836 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! ipv6 unicast-routing multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode none ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 172.16.0.2 255.255.255.252 negotiation auto ipv6 address FE80::1:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A001::2/64 ospfv3 network point-to-point ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 0 ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 no ip address negotiation auto ipv6 address FE80::1:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1001::1/64 ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 1 ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 1 ! interface Serial0/1/0 ! interface Serial0/1/1 ! router ospfv3 123 ! address-family ipv4 unicast router-id 1.1.1.1 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 unicast router-id 1.1.1.1 area 1 range 2001:DB8:ACAD:1000::/52 exit-address-family ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http authentication local ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login ! end
Router R2
R2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 4068 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! ipv6 unicast-routing multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode none ! interface Loopback0 ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 ipv6 address FE80::2:3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:FEED:209::1/64 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.252 negotiation auto ipv6 address FE80::2:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A001::1/64 ospfv3 network point-to-point ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 0 ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252 negotiation auto ipv6 address FE80::2:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A002::1/64 ospfv3 network point-to-point ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 0 ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 0 ! router ospfv3 123 ! address-family ipv4 unicast default-information originate router-id 2.2.2.1 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 unicast default-information originate router-id 2.2.2.1 exit-address-family ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server ip http secure-server ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Loopback0 ! ipv6 route ::/0 Loopback0 ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login ! end
Router R3
R3# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 3859 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R3 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! ipv6 unicast-routing multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode none ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.252 negotiation auto ipv6 address FE80::3:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A002::2/64 ospfv3 network point-to-point ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 0 ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 10.10.4.1 255.255.255.252 negotiation auto ipv6 address FE80::3:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2001::1/64 ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 2 ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 2 ! interface Serial0/1/0 ! interface Serial0/1/1 ! router ospfv3 123 router-id 3.3.3.1 ! address-family ipv4 unicast exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 unicast area 2 range 2001:DB8:ACAD:2000::/52 exit-address-family ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http authentication local ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login ! end
Switch D1
D1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 6542 bytes ! version 16.9 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec ! Call-home is enabled by Smart-Licensing. service call-home no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname D1 ! vrf definition Mgmt-vrf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! no aaa new-model switch 1 provision ws-c3650-24ps ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ipv6 unicast-routing ! license boot level ipservicesk9 ! diagnostic bootup level minimal ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode sso ! transceiver type all monitoring ! class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control description Topology control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING class-map match-any system-cpp-default description Inter FED, EWLC control, EWLC data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFLSAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth description Punt Webauth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control description L2 LVX control packets class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station description MCAST END STATION class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control description L2 control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth description DOT1X Auth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control description Stackwise Virtual class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control description Routing control and Low Latency class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping description Protocol snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping description DHCP snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical description System Critical and Gold Pkt ! policy-map system-cpp-policy ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf no ip address negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/9 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/11 no switchport no ip address ipv6 address FE80::D1:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1001::2/64 ipv6 ospf 123 area 1 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/12 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/17 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/18 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/19 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/20 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/21 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 no switchport no ip address ipv6 address FE80::D1:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1002::1/64 ipv6 ospf 123 area 1 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/1 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/3 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/4 ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http secure-server ! ipv6 router ospf 123 router-id 1.1.1.2 passive-interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 ! control-plane service-policy input system-cpp-policy ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login line vty 5 15 login ! end
Switch D2
D2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 8968 bytes ! version 16.9 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service call-home no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname D2 ! ! vrf definition Mgmt-vrf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! ! no aaa new-model switch 1 provision ws-c3650-24ps ! ip routing ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ipv6 unicast-routing ! license boot level ipservicesk9 ! diagnostic bootup level minimal ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode sso ! transceiver type all monitoring ! class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control description Topology control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING class-map match-any system-cpp-default description Inter FED, EWLC control, EWLC data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFLSAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth description Punt Webauth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control description L2 LVX control packets class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station description MCAST END STATION class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control description L2 control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth description DOT1X Auth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control description Stackwise Virtual class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control description Routing control and Low Latency class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping description Protocol snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping description DHCP snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical description System Critical and Gold Pkt ! policy-map system-cpp-policy ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf no ip address negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/9 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/11 no switchport ip address 10.10.4.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address FE80::D2:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2001::2/64 ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 2 ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 2 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/12 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/17 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/18 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/19 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/20 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/21 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 no switchport ip address 10.10.5.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address FE80::D2:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2002::1/64 ospfv3 123 ipv4 area 2 ospfv3 123 ipv6 area 2 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/1 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/3 ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/4 ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! router ospfv3 123 ! address-family ipv4 unicast passive-interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 router-id 3.3.3.2 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 unicast passive-interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 router-id 3.3.3.2 exit-address-family ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http secure-server ! control-plane service-policy input system-cpp-policy ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login line vty 5 15 login ! end
