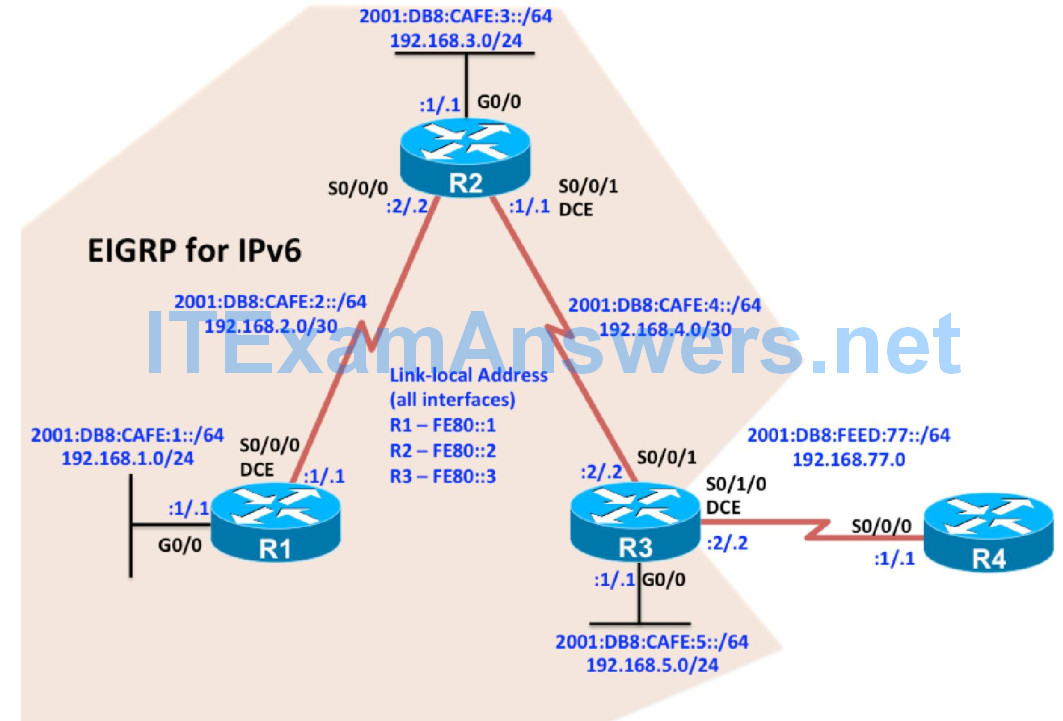
Topology
Objectives
- Configure Named EIGRP for IPv4 and IPv6.
- Verify Named EIGRP configuration.
- Configure and verify passive routes Named EIGRP configuration.
- Configure and verify default route using Named EIGRP configuration.
Background
What is known as “classic” EIGRP requires separate EIGRP configuration modes and commands for IPv4 and IPv6. Each process is configured separately, router eigrp as-number for IPv4 and ipv6 router eigrp as-number for IPv6.
Named EIGRP uses the address family (AF) feature to unify the configuration process when implementing both IPv4 and IPv6. In this lab, you will configure named EIGRP for IPv4 and IPv6.
Note: This lab uses Cisco 1941 routers with Cisco IOS Release 15.4 with IP Base. The switches are Cisco WSC2960-24TT-L with Fast Ethernet interfaces, therefore the router will use routing metrics associated with a 100 Mb/s interface. Depending on the router or switch model and Cisco IOS Software version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in this lab.
Required Resources
- 4 routers (Cisco IOS Release 15.2 or comparable)
- 3 switches (LAN interfaces)
- Serial and Ethernet cables
Step 0: Suggested starting configurations.
a. Apply the following configuration to each router along with the appropriate hostname. The exec-timeout 0 0 command should only be used in a lab environment.
Router(config)# no ip domain-lookup Router(config)# line con 0 Router(config-line)# logging synchronous Router(config-line)# exec-timeout 0 0
Step 1: Configure the addressing and serial links.
a. Using the topology, configure the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses on the interfaces of each router.
R1(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1/64 R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface Serial0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.252 R1(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::1/64 R1(config-if)# clock rate 64000 R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local R2(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:CAFE:3::1/64 R2(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface Serial0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local R2(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::2/64 R2(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface Serial0/0/1 R2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.4.1 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local R2(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::1/64 R2(config-if)# clock rate 64000 R2(config-if)# no shutdown
R3(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local R3(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:CAFE:5::1/64 R3(config-if)# no shutdown R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface Serial0/0/1 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.4.2 255.255.255.252 R3(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local R3(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::2/64 R3(config-if)# no shutdown R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface Serial0/1/0 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.77.2 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local R3(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:FEED:77::2/64 R3(config-if)# clock rate 64000 R3(config-if)# no shutdown R3(config-if)#
R4(config)# interface Serial0/0/0 R4(config-if)# ip address 192.168.77.1 255.255.255.0 R4(config-if)# ipv6 address FE80::4 link-local R4(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:DB8:FEED:77::1/64 R4(config-if)# no shutdown R4(config-if)# exit R4(config)# ipv6 route 2001:DB8:CAFE::/48 2001:DB8:FEED:77::2 R4(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.77.2 R4(config)#
b. Verify connectivity by pinging across each of the local networks connected to each router.
c. Issue the show ip interface brief and show ipv6 interface brief commands on each router. This command displays a brief listing of the interfaces, their status, and their IP addresses. Router R1 is shown as an example.
R1# show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/0/0 192.168.2.1 YES manual up up
Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
R1# show ipv6 interface brief
Em0/0 [administratively down/down]
unassigned
GigabitEthernet0/0 [up/up]
FE80::1
2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1
GigabitEthernet0/1 [administratively down/down]
unassigned
Serial0/0/0 [up/up]
FE80::1
2001:DB8:CAFE:2::1
Serial0/0/1 [administratively down/down]
unassigned
R1#
Step 2: Configure Named EIGRP for IPv4 on R1.
a. Named EIGRP is organized in an hierarchical manner. Configuration for each routing protocol, EIGRP for IPv4 and EIGRP for IPv6 is done within its own address family. To configure named EIGRP configuration use the router eigrp virtual-instance-name command in global configuration mode. The virtual-instance-names do not have to match between neighbors.
Note: IPv6 unicast routing must be enabled prior to configuring the IPv6 address family.
R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R1(config)# router eigrp DUAL-STACK R1(config-router)#
b. EIGRP doesn’t start until at least one address family has been defined (IPv4 or IPv6). The address family command starts the EIGRP protocol (IPv4 or IPv6) for the defined autonomous system.
To configure the IPv4 address family and autonomous system you use the address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system command. This command puts you into the address family configuration mode. Issue the address-family ? command see the two address families available. After configuring the IPv4 address family for EIGRP use the ? to see what commands available in address family configuration mode such as the af-interface, eigrp, and network commands.
R1(config-router)# address-family ? ipv4 Address family IPv4 ipv6 Address family IPv6 R1(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 4 R1(config-router-af)# ? Address Family configuration commands: af-interface Enter Address Family interface configuration default Set a command to its defaults eigrp EIGRP Address Family specific commands exit-address-family Exit Address Family configuration mode help Description of the interactive help system maximum-prefix Maximum number of prefixes acceptable in aggregate metric Modify metrics and parameters for address advertisement neighbor Specify an IPv4 neighbor router network Enable routing on an IP network no Negate a command or set its defaults shutdown Shutdown address family timers Adjust peering based timers topology Topology configuration mode R1(config-router-af)#
c. In address family configuration mode you can enable EIGRP for specific interfaces and define other general parameters such as the router ID and stub routing. Issue the eigrp ? to see the available options configured using the eigrp command. Use the eigrp router-id command to configure the EIGRP router ID for the IPv4 address family.
R1(config-router-af)# eigrp ? default-route-tag Default Route Tag for the Internal Routes log-neighbor-changes Enable/Disable EIGRP neighbor logging log-neighbor-warnings Enable/Disable EIGRP neighbor warnings router-id router id for this EIGRP process stub Set address-family in stubbed mode R1(config-router-af)# eigrp router-id 1.1.1.1 R1(config-router-af)#
d. While still in the address family configuration mode for IPv4, use the network command to enable EIGRP on the interfaces. These are the same network commands used in “classic” EIGRP for IPv4.
R1(config-router-af)# network 192.168.1.0 R1(config-router-af)# network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router-af)#
e. Exit the IPv4 address family configuration mode using the exit-address-family command or the shorter exit command. Notice that you are still in named EIGRP configuration mode.
R1(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R1(config-router)#
Step 3: Configure Named EIGRP for IPv6 on R1.
a. Configure the IPv6 address family using the autonomous system (process ID) of 6. Use the ? the view the command options available under each mode and for some of the commands. There is no requirement for the AS numbers to match between the IPv4 and IPv6 address families, but they must match their neighbors’ AS. In this example, routers R2 and R3 must use AS 4 for the IPv4 address family and AS 6 for the IPv6 address family.
R1(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 6 R1(config-router-af)#
b. Use the eigrp router-id command to configure the EIGRP router ID for the IPv4 address family. The IPv6 router ID does not have to match the a router ID configured for IPv4.
R1(config-router-af)# eigrp router-id 1.1.1.1 R1(config-router-af)#
c. By default, all IPv6 interfaces are automatically enabled for EIGRP for IPv6. This will be explored further in the next step.
In this scenario, is the eigrp router-id command required to configure a router ID for the IPv4 AF? Is it required for the IPv6 AF? What would happen if the router ID was not configured using the eigrp router-id command? ______________________________________________________________________
Step 4: Configure Named EIGRP on R2 and R3.
a. Configure named EIGRP on R2 for the IPv4 address family. The IPv6 unicast routing is enabled in preparation for configuring the IPv6 address family.
R2(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R2(config)# router eigrp DUAL-STACK R2(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 4 R2(config-router-af)# eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2 R2(config-router-af)# network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.3 *Jul 25 20:11:37.643: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 4: Neighbor 192.168.2.1 (Serial0/0/0) is up: new adjacency R2(config-router-af)# network 192.168.3.0 R2(config-router-af)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.3 R2(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R2(config-router)#
Notice that the adjacency between R1 and R2 is established after enabling EIGRP for IPv4 on the serial 0/0/0 interface.
b. Configure the IPv6 address family for EIGRP on R2.
R2(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 6 *Jul 25 20:19:05.435: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv6 6: Neighbor FE80::1 (Serial0/0/0) is up: new adjacency R2(config-router-af)# eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2 R2(config-router-af)#
Notice that the IPv6 adjacency with R1 comes up immediately after configuring the IPv6 AF. This is because by default, all IPv6 interfaces are enabled automatically.
c. On R3, configure named EIGRP on R3 for both the IPv4 and IPv6 address families. After the appropriate commands are configured the IPv4 and IPv6 EIGRP adjacencies are established between R2 and R3. The serial link between R3 and R4 is also automatically enabled in EIGRP for IPv6. This link is not suppose to be included and will be disabled in EIGRP for IPv6 later in step 6.
R3(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R3(config)# router eigrp DUAL-STACK R3(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 4 R3(config-router-af)# eigrp router-id 3.3.3.3 R3(config-router-af)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.3 *Jun 26 13:11:41.343: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 4: Neighbor 192.168.4.1 (Serial0/0/1) is up: new adjacency R3(config-router-af)# network 192.168.5.0 R3(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R3(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 6 *Jun 26 13:12:22.819: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv6 6: Neighbor FE80::2 (Serial0/0/1) is up: new adjacency R3(config-router-af)# eigrp router-id 3.3.3.3 R3(config-router-af)#
Step 5: Configure passive interfaces for named EIGRP.
a. Within each IPv4 and IPv6 AF is the address family interface configuration mode. This mode is used to configure EIGRP specific parameters on an interface, such as the hello timer and summarization. From address family configuration mode, use the af-interface interface-type interface-number command to enter address family interface configuration mode. The following output shows the sequence of commands starting from global configuration mode.
R1(config)# router eigrp DUAL-STACK R1(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 4 R1(config-router-af)# af-interface gigabitethernet 0/0 R1(config-router-af-interface)#
b. Issue the ? to see the commands available in address family interface configuration mode. Notice various commands to configure interface specific parameters such as the hello interval, hold timer, passive interfaces, and summarization.
R1(config-router-af-interface)# ? Address Family Interfaces configuration commands: add-paths Advertise add paths authentication authentication subcommands bandwidth-percent Set percentage of bandwidth percentage limit bfd Enable Bidirectional Forwarding Detection dampening-change Percent interface metric must change to cause update dampening-interval Time in seconds to check interface metrics default Set a command to its defaults exit-af-interface Exit from Address Family Interface configuration mode hello-interval Configures hello interval hold-time Configures hold time next-hop-self Configures EIGRP next-hop-self no Negate a command or set its defaults passive-interface Suppress address updates on an interface shutdown Disable Address-Family on interface split-horizon Perform split horizon summary-address Perform address summarization R1(config-router-af-interface)#
The interface configuration mode commands are similar for both the IPv4 and IPv6 address families. Commands issued are specific for an interface within the address family, IPv4 or IPv6.
c. Using the passive-interface command, configure G0/0 interface as passive for both the IPv4 and IPv6 EIGRP address families.
R1(config-router-af-interface)# passive-interface R1(config-router-af-interface)# exit-af-interface R1(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R1(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 6 R1(config-router-af)# af-interface gigabitethernet 0/0 R1(config-router-af-interface)# passive-interface R1(config-router-af-interface)# exit-af-interface R1(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R1(config-router)#
d. Configure R2’s G0/0 interface as passive for both the IPv4 and IPv6 address families.
R2(config)# router eigrp DUAL-STACK R2(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 4 R2(config-router-af)# af-interface gigabitethernet 0/0 R2(config-router-af-interface)# passive-interface R2(config-router-af-interface)# exit-af-interface R2(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R2(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 6 R2(config-router-af)# af-interface gigabitethernet 0/0 R2(config-router-af-interface)# passive-interface R2(config-router-af-interface)# exit R2(config-router-af)# exit R2(config-router)#
e. Configure R3’s G0/0 interface as passive for both the IPv4 and IPv6 address families.
R3(config)# router eigrp DUAL-STACK R3(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 4 R3(config-router-af)# af-interface gigabitethernet 0/0 R3(config-router-af-interface)# passive-interface R3(config-router-af-interface)# exit-af-interface R3(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R3(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 6 R3(config-router-af)# af-interface gigabitethernet 0/0 R3(config-router-af-interface)# passive-interface R3(config-router-af-interface)# exit R3(config-router-af)# exit R3(config-router)#
Notice the exit command was used as the shorter method for the exit-af-interface and exit-address-family commands.
Step 6: Disable named EIGRP on a specific IPv6 interface.
a. By default, all IPv6 interfaces are enabled for EIGRP for IPv6. This happens when enabling the IPv6 address family with the address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system command. Issue the show ipv6 protocols command on R3 to verify that all three of its IPv6 interfaces are enabled for EIGRP for IPv6. Notice that the Serial 0/1/0 interface is also included.
R3# show ipv6 protocols
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "connected"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "application"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ND"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "eigrp 6"
EIGRP-IPv6 VR(DUAL-STACK) Address-Family Protocol for AS(6)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0 K6=0
Metric rib-scale 128
Metric version 64bit
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 3.3.3.3
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 16
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Total Prefix Count: 6
Total Redist Count: 0
Interfaces:
Serial0/0/1
Serial0/1/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 (passive)
Redistribution:
None
R3#
b. As shown in the topology, R3’s S0/1/0 interface does not need to be included in the EIGRP updates. A default route will be configured later in this lab for reachability beyond the EIGRP routing domain. When we configured the IPv4 AF we excluded the network command for this interface. However, the same interface is automatically included when configuring the IPv6 AF. The shutdown address family interface command is used to disable EIGRP on a specific interface. This does not disable the physical interface, but only removes it from participating in EIGRP.
R3(config)# router eigrp DUAL-STACK R3(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 6 R3(config-router-af)# af-interface serial 0/1/0 R3(config-router-af-interface)# shutdown R3(config-router-af-interface)# end R3#
How can you verify that the IPv6 interface is still active, in the “up and up” state?
___________________________________________________________________
c. Using the show ipv6 protocols command, verify that R3 is no longer including S0/1/0 in EIGRP for IPv6.
R3# show ipv6 protocols
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "connected"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "application"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ND"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "eigrp 6"
EIGRP-IPv6 VR(DUAL-STACK) Address-Family Protocol for AS(6)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0 K6=0
Metric rib-scale 128
Metric version 64bit
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 3.3.3.3
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 16
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Total Prefix Count: 5
Total Redist Count: 0
Interfaces:
Serial0/0/1
GigabitEthernet0/0 (passive)
Redistribution:
None
R3#
Does the shutdown command used on S0/1/0 within the IPv6 AF also have the same affect for that interface within the IPv4 AF?
___________________________________________________________________
Step 7: Configure and distribute a default static route in named EIGRP.
a. On R3 configure IPv4 and IPv6 default static routes using an R4 as the next-hop router.
Note: With the use of CEF (Cisco Express Forwarding) it is recommended practice that a next-hop IP address is used instead of an exit-interface. There is a bug in IOS 15.4 that prevents an IPv6 static route with only a nexthop address from being redistributed. A fully specified static route with both an exit-interface and a next-hop address is used in the example.
R3(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.77.1 R3(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 serial0/1/0 2001:db8:feed:77::1 R3(config)#
a. Redistribution of static routes in named EIGRP is done in topology configuration mode. Topology configuration mode is a subset of an address family. By default, EIGRP has a base topology for each address family. Additional topologies can be configured for Multitopology Routing (MTR) which is used to enable an EIGRP process for a specified topology. MTR is beyond the scope of CCNP.
For each address family, issue the topology base command to enter the base EIGRP topology. In topology configuration mode use the redistribute static command to redistribute the default static route into EIGRP.
R3(config)# router eigrp DUAL-STACK R3(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 4 R3(config-router-af)# topology base R3(config-router-af-topology)# ? Address Family Topology configuration commands: auto-summary Enable automatic network number summarization default Set a command to its defaults default-information Control distribution of default information default-metric Set metric of redistributed routes distance Define an administrative distance distribute-list Filter entries in eigrp updates eigrp EIGRP specific commands exit-af-topology Exit from Address Family Topology configuration mode maximum-paths Forward packets over multiple paths metric Modify metrics and parameters for advertisement no Negate a command or set its defaults offset-list Add or subtract offset from EIGRP metrics redistribute Redistribute IPv4 routes from another routing protocol snmp Modify snmp parameters summary-metric Specify summary to apply metric/filtering timers Adjust topology specific timers traffic-share How to compute traffic share over alternate paths variance Control load balancing variance
R3(config-router-af-topology)# redistribute static R3(config-router-af-topology)# exit-af-topology R3(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R3(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 6 R3(config-router-af)# topology base R3(config-router-af-topology)# redistribute static R3(config-router-af-topology)# exit-af-topology R3(config-router-af)# exit-address-family R3(config-router)#
b. Issue the show ip protocols and show ipv6 protocols commands to verify that EIGRP is redistributing the static route.
R3# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "application"
Sending updates every 0 seconds
Invalid after 0 seconds, hold down 0, flushed after 0
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Maximum path: 32
Routing for Networks:
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 4)
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 4"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks not flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks not accepted from incoming updates
Redistributing: static
EIGRP-IPv4 VR(DUAL-STACK) Address-Family Protocol for AS(4)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0 K6=0
Metric rib-scale 128
Metric version 64bit
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 3.3.3.3
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Total Prefix Count: 5
Total Redist Count: 1
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.4.0/30
192.168.5.0
Passive Interface(s):
GigabitEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.4.1 90 02:07:02
Distance: internal 90 external 170
R3# show ipv6 protocols
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "connected"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "application"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ND"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "eigrp 6"
EIGRP-IPv6 VR(DUAL-STACK) Address-Family Protocol for AS(6)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0 K6=0
Metric rib-scale 128
Metric version 64bit
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 3.3.3.3
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 16
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Total Prefix Count: 6
Total Redist Count: 1
Interfaces:
Serial0/0/1
GigabitEthernet0/0 (passive)
Redistribution:
Redistributing protocol static
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "static"
R3#
Why does the show ip protocols command indicate that automatic summarization is disabled?
_____________________________________________________________________
c. Examine the IPv4 and IPv6 routing tables on R1 to verify that it is receiving the default static route using EIGRP.
R1# show ip route eigrp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.2.2 to network 0.0.0.0
D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/34036062] via 192.168.2.2, 00:03:23, Serial0/0/0
192.168.4.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.4.0 [90/23796062] via 192.168.2.2, 01:28:22, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.5.0/24 [90/23847262] via 192.168.2.2, 01:28:15, Serial0/0/0
R1# show ipv6 route eigrp
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 9 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, H - NHRP, I1 - ISIS L1
I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP
EX - EIGRP external, ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination
NDr - Redirect, O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1
OE2 - OSPF ext 2, ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
a - Application
EX ::/0 [170/34036062]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
D 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::/64 [90/23796062]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
D 2001:DB8:CAFE:5::/64 [90/23847262]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
D 2001:DB8:CAFE:99::/64 [90/23796702]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
R1#
Step 8: Verify named EIGRP.
a. Although named EIGRP unifies configuration for EIGRP for IPv4 and IPv6, the neighbor tables, topology tables and EIGRP routing processes are still separate. Use the show ip protocols and show ipv6 protocols command to verify both EIGRP for IPv4 and IPv6 processes. Below is the output displayed for R2.
R2# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "application"
Sending updates every 0 seconds
Invalid after 0 seconds, hold down 0, flushed after 0
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Maximum path: 32
Routing for Networks:
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 4)
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 4"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP-IPv4 VR(DUAL-STACK) Address-Family Protocol for AS(4)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0 K6=0
Metric rib-scale 128
Metric version 64bit
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 2.2.2.2
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Total Prefix Count: 6
Total Redist Count: 0
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.2.0/30
192.168.3.0
192.168.4.0/30
Passive Interface(s):
GigabitEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.2.1 90 00:04:54
192.168.4.2 90 00:04:54
Distance: internal 90 external 170
R2#
R2# show ipv6 protocols
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "connected"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "application"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ND"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "eigrp 6"
EIGRP-IPv6 VR(DUAL-STACK) Address-Family Protocol for AS(6)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0 K6=0
Metric rib-scale 128
Metric version 64bit
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 2.2.2.2
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 16
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Total Prefix Count: 6
Total Redist Count: 0
Interfaces:
Serial0/0/0
Serial0/0/1
GigabitEthernet0/0 (passive)
Redistribution:
None
R2#
b. Issue the show ip eigrp neighbors and show ipv6 eigrp neighbors command on R1 to verify the neighbor adjacencies with R2.
R1# show ip eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 VR(DUAL-STACK) Address-Family Neighbors for AS(4)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 192.168.2.2 Se0/0/0 13 03:56:20 31 186 0 8
R1# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv6 VR(DUAL-STACK) Address-Family Neighbors for AS(6)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 Link-local address: Se0/0/0 13 00:09:14 669 4014 0 21
FE80::2
R1#
c. Examine R1’s EIGRP topology tables for IPv4 and IPv6 using the show ip eigrp topology and show ipv6 eigrp topology commands.
R1# show ip eigrp topology
EIGRP-IPv4 VR(DUAL-STACK) Topology Table for AS(4)/ID(1.1.1.1)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 192.168.2.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 1735175958
via Connected, Serial0/0/0
P 192.168.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 13107200
via Connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
P 0.0.0.0/0, 1 successors, FD is 4356615958
via 192.168.2.2 (4356615958/3045895958), Serial0/0/0
P 192.168.4.0/30, 1 successors, FD is 3045895958
via 192.168.2.2 (3045895958/1735175958), Serial0/0/0
P 192.168.5.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 3052449558
via 192.168.2.2 (3052449558/1741729558), Serial0/0/0
R1# show ipv6 eigrp topology
EIGRP-IPv6 VR(DUAL-STACK) Topology Table for AS(6)/ID(1.1.1.1)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 2001:DB8:CAFE:5::/64, 1 successors, FD is 3052449558
via FE80::2 (3052449558/1741729558), Serial0/0/0
P 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::/64, 1 successors, FD is 3045895958
via FE80::2 (3045895958/1735175958), Serial0/0/0
P 2001:DB8:CAFE:99::/64, 1 successors, FD is 3045977878
via FE80::2 (3045977878/1735257878), Serial0/0/0
P 2001:DB8:CAFE:2::/64, 1 successors, FD is 1735175958
via Connected, Serial0/0/0
P ::/0, 1 successors, FD is 4356615958
via FE80::2 (4356615958/3045895958), Serial0/0/0
P 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/64, 1 successors, FD is 13107200
via Connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
R1#
d. Verify that R1 has all the IPv4 and IPv6 routes shown in the topology with the exclusion of R2’s LAN by using the show ip route eigrp and show ipv6 route eigrp commands.
R1# show ip route eigrp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.2.2 to network 0.0.0.0
D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/34036062] via 192.168.2.2, 00:10:25, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/13607262] via 192.168.2.2, 00:48:46, Serial0/0/0
192.168.4.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.4.0 [90/23796062] via 192.168.2.2, 00:48:33, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.5.0/24 [90/23847262] via 192.168.2.2, 00:38:12, Serial0/0/0
R1# show ipv6 route eigrp
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 9 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, H - NHRP, I1 - ISIS L1
I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP
EX - EIGRP external, ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination
NDr - Redirect, O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1
OE2 - OSPF ext 2, ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
a - Application
EX ::/0 [170/34036062]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
D 2001:DB8:CAFE:3::/64 [90/13607262]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
D 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::/64 [90/23796062]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
D 2001:DB8:CAFE:5::/64 [90/23847262]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
R1#
e. As a final verification of end-to-end reachability, from R1 ping the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses on R5’s LAN.
R1# ping 192.168.5.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.5.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/56/56 ms R1# ping 2001:db8:cafe:5::1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:DB8:CAFE:5::1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 52/55/56 ms R1#
f. Examine the named EIGRP configuration showing both the IPv4 and IPv6 address families with the show running-config | section router eigrp command. The output for R3 is displayed below.
R3# show running-config | section router eigrp router eigrp DUAL-STACK ! address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 4 ! af-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 passive-interface exit-af-interface ! topology base redistribute static exit-af-topology network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.5.0 eigrp router-id 3.3.3.3 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 unicast autonomous-system 6 ! af-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 passive-interface exit-af-interface ! af-interface Serial0/1/0 shutdown exit-af-interface ! topology base redistribute static exit-af-topology eigrp router-id 3.3.3.3 exit-address-family R3#
