Network Addressing and Basic Troubleshooting: My Knowledge Check Answers
1. Why are two strands of fiber used for a single fiber optic connection?
- The two strands allow the data to travel for longer distances without degrading.
- They prevent crosstalk from causing interference on the connection.
- They increase the speed at which the data can travel.
- They allow for full-duplex connectivity.
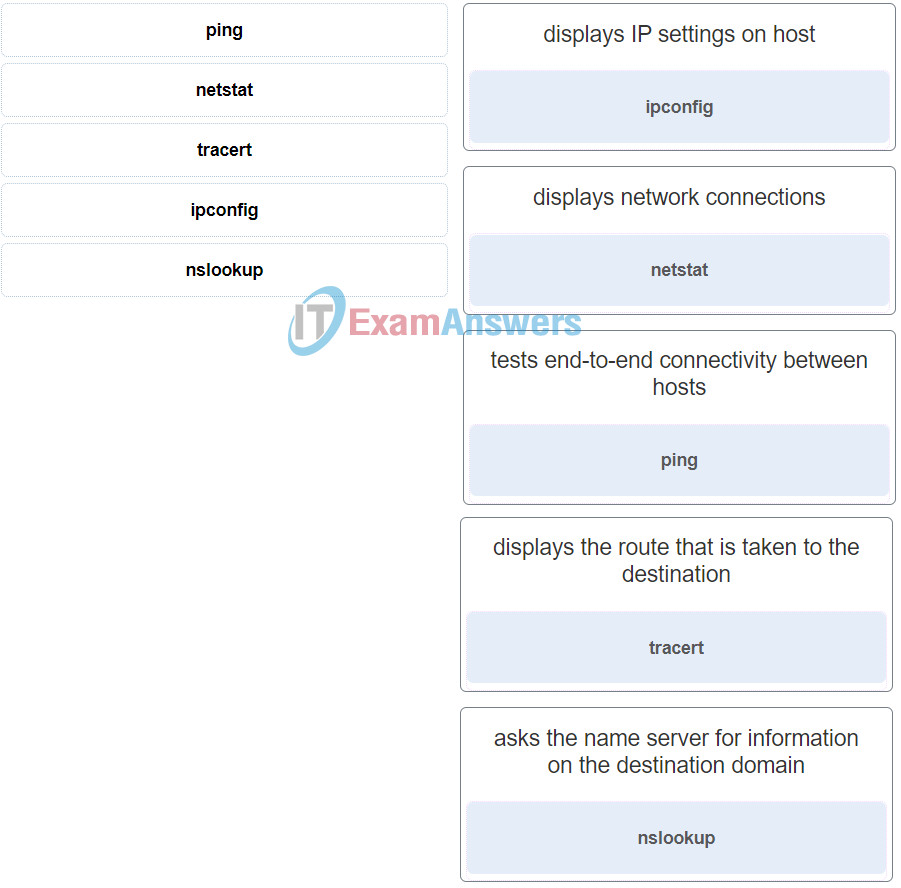
2. Match the command to the function.
3. On a point-to-point network, which communication type is used when two devices can both transmit and receive but not at the same time?
- controlled access
- deterministic
- full-duplex
- half-duplex
4. Which advantage does the store-and-forward switching method have compared with the cut-through switching method?
- collision detecting
- frame error checking
- faster frame forwarding
- frame forwarding using IPv4 Layer 3 and 4 information
5. Local workstations are unable to access web pages located on the www.cisco.com web server. Pings from the workstations to the server using the ping www.cisco.com command are successful. What settings should the administrator check to determine the cause of the problem?
- IP address settings
- firewall settings
- MAC address settings
- DNS server settings
6. A PC has sent an RS message to an IPv6 router attached to the same network. Which two pieces of information will the router send to the client? (Choose two.)
- administrative distance
- domain name
- prefix
- prefix length
- subnet mask in dotted decimal notation
- DNS server IP address
7. What type of Ethernet frame does an IPv6 host use to send a message in responding to an address resolution request?
- unicast
- anycast
- multicast
- broadcast
8. Which information does the show startup-config command display?
- the IOS image copied into RAM
- the bootstrap program in the ROM
- the contents of the current running configuration file in the RAM
- the contents of the saved configuration file in the NVRAM
9. A user can access a file share resource on a server located in the same office but cannot access the internet. What is the possible cause?
- The switch is malfunctioning.
- The DHCP server is disconnected.
- The default gateway address is misconfigured on the PC.
- The IPv4 address and subnet mask are misconfigured on the PC.
10. What address scope is used in the IPv6 frame to ensure that an IPv6 neighbor solicitation message would not be forwarded by routers?
- site-local scope
- link-local scope
- subnet-local scope
- interface-local scope
11. You are asked to document your school network. What type of topology diagram would you draw to show how devices are connected to the network?
- logical topology diagram
- physical topology diagram
12. The home computer of a user is working properly. However, the user cannot access the Internet. The Internet connection is provided through a cable company. The user cannot identify the cause of the problem. Who should the user contact for further help?
- the operating system vendor
- the help line of the cable company
- the help line of the computer manufacturer
- the support web site of the computer vendor
13. Refer to the exhibit. The PC is connected to the console port of the switch. All the other connections are made through FastEthernet links. Which types of UTP cables can be used to connect the devices?
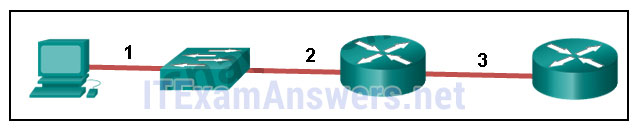
- 1 – rollover, 2 – crossover, 3 – straight-through
- 1 – rollover, 2 – straight-through, 3 – crossover
- 1 – crossover, 2 – straight-through, 3 – rollover
- 1 – crossover, 2 – rollover, 3 – straight-through
14. Users in a recently installed wireless network are complaining of slow data transfer and frequent loss of connectivity. The technician checks that the wireless security is correctly implemented, and there is no evidence of unauthorized users on the network. Which two problems might the technician suspect? (Choose two.)
- There is interference from outside sources.
- The DHCP server is faulty.
- The wireless signal is too weak.
- The antenna on the access point is too powerful.
- The network passwords need to be reissued to the users.
15. A technician is setting up a network in a new room. What is the best device to use to connect the PCs to each other and to the rest of the LAN?
- gateway
- firewall
- switch
- router
16. Refer to the exhibit. The command output is from a wireless DHCP host connected to a Linksys integrated router. What can be determined from the output?
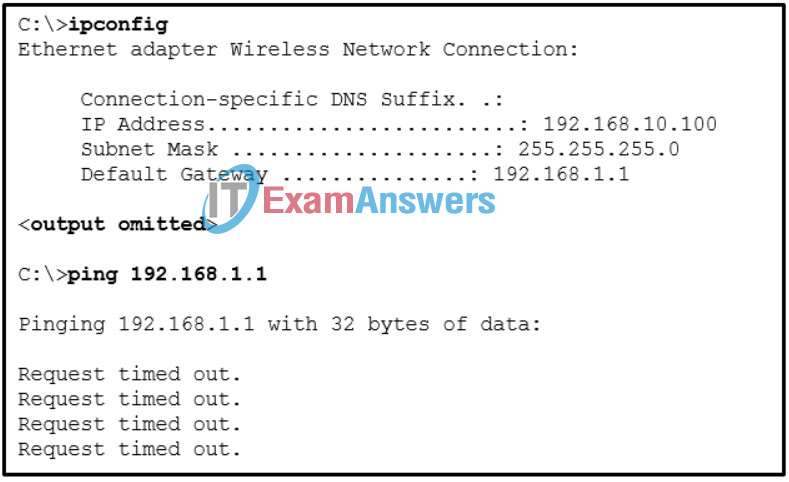
- A new wireless NIC needs to be installed.
- There is a DNS problem.
- The DHCP configuration needs to be checked.
- The connection to the SSID needs to be verified.
- An incorrect cable is being used between the host and the router.
17. An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::1. What is the target of this packet?
- the one IPv6 device on the link that has been uniquely configured with this address
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link or network
- only IPv6 DHCP servers
- only IPv6 configured routers
18. Which two types of signal interference are reduced more by STP than by UTP? (Choose two.)
- RFI
- white noise
- MDF
- dispersion
- EMI
19. Which two statements correctly describe the components of a router? (Choose two.)
- RAM permanently stores the configuration file used during the boot sequence.
- ROM contains diagnostics executed on hardware modules.
- NVRAM stores a backup copy of the IOS used during the boot sequence.
- Flash memory does not lose its contents during a reboot.
- ROM contains the most current and most complete version of the IOS.
- Flash contains boot system commands to identify the location of the IOS.
20. Which media access method requires that an end device send a notification across the media before sending data?
- CSMA/CA
- CSMA/CD
- deterministic
- token passing
21. What type of route is indicated by the code C in an IPv4 routing table on a Cisco router?
- static route
- default route
- directly connected route
- dynamic route that is learned through EIGRP
22. Which type of static route creates a gateway of last resort?
- default static route
- floating static route
- standard static route
- summary static route
23. Which statement describes the half-duplex mode of data transmission?
- Data that is transmitted over the network can only flow in one direction.
- Data that is transmitted over the network flows in one direction at a time.
- Data that is transmitted over the network flows in one direction to many different destinations simultaneously.
- Data that is transmitted over the network flows in both directions at the same time.
24. A network technician enters the command ipconfig /release followed by ipconfig /renew in order to ensure that the DHCP IP configuration on a workstation is updated. However, the workstation does not receive a valid IP configuration for the network. Which two problems may exist on the network? (Choose two.)
- There is a DHCP server issue.
- The DHCP lease time is misconfigured.
- The gateway router address needs to be updated.
- There is no network connectivity to the DHCP server.
- The ipconfig /all command must be issued to restore all IP configurations.
25. Following default settings, what is the next step in the router boot sequence after the IOS loads from flash?
- Perform the POST routine.
- Locate and load the startup-config file from NVRAM.
- Load the bootstrap program from ROM.
- Load the running-config file from RAM.
26. Which address is used to derive an IPv6 interface ID using the EUI-64 method?
- IPv4
- MAC
- multicast
- Layer 4
27. A computer can access devices on the same network but cannot access devices on other networks. What is the probable cause of this problem?
- The cable is not connected properly to the NIC.
- The computer has an invalid IP address.
- The computer has an incorrect subnet mask.
- The computer has an invalid default gateway address.
28. Refer to the exhibit. The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?
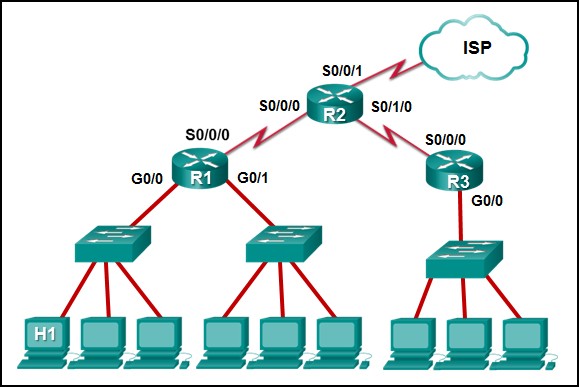
- R1: S0/0/0
- R2: S0/0/1
- R1: G0/0
- R2: S0/0/0
29. Which type of IPv6 address is not routable and used only for communication on a single subnet?
- global unicast address
- link-local address
- loopback address
- unique local address
- unspecified address
30. After several configuration changes are made to a router, the copy running-configuration startup-configuration command is issued. Where will the changes be stored?
- flash
- ROM
- NVRAM
- RAM
31. Match the ICMPv6 messages to the description.
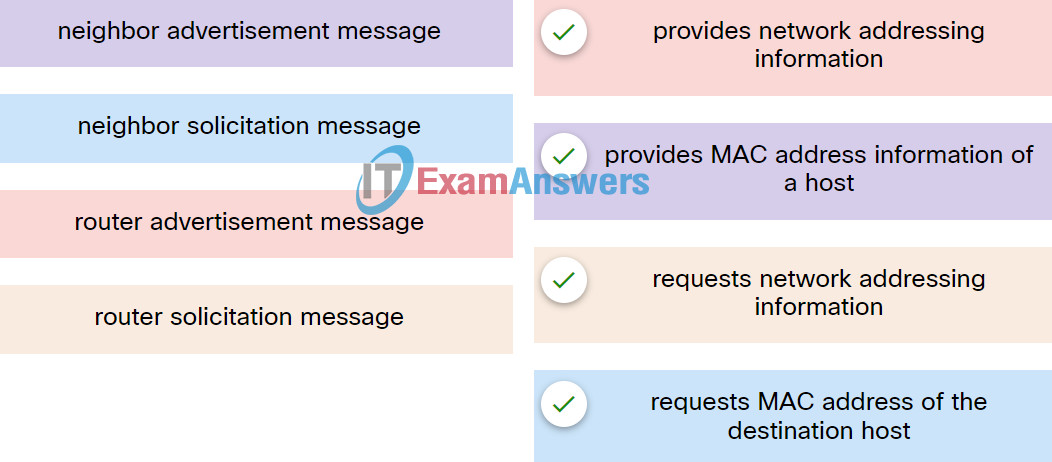
32. What type of address is automatically assigned to a Cisco router interface when an IPv6 global unicast address is assigned on that interface?
- broadcast
- link-local
- loopback
- unique local
33. What terms represent the maximum and actual speed that can be utilized by a device to transfer data?
- bandwidth; throughput
- throughput; bandwidth
- bandwidth; goodput
- throughput; goodput
34. What is an important function of the physical layer of the OSI model?
- It accepts frames from the physical media.
- It encapsulates upper layer data into frames.
- It defines the media access method performed by the hardware interface.
- It encodes frames into electrical, optical, or radio wave signals.
35. A router receives a packet from the Gigabit 0/0 interface and determines that the packet needs to be forwarded out the Gigabit 0/1 interface. What will the router do next?
- route the packet out the Gigabit 0/1 interface
- create a new Layer 2 Ethernet frame to be sent to the destination
- look into the ARP cache to determine the destination IP address
- look into the routing table to determine if the destination network is in the routing table
36. During the process of forwarding traffic, what will the router do immediately after matching the destination IP address to a network on a directly connected routing table entry?
- discard the traffic after consulting the route table
- look up the next-hop address for the packet
- switch the packet to the directly connected interface
- analyze the destination IP address
37. Which troubleshooting method begins by examining cable connections and wiring issues?
- top-down
- bottom-up
- substitution
- divide-and-conquer
38. Match the phases to the functions during the boot up process of a Cisco router.
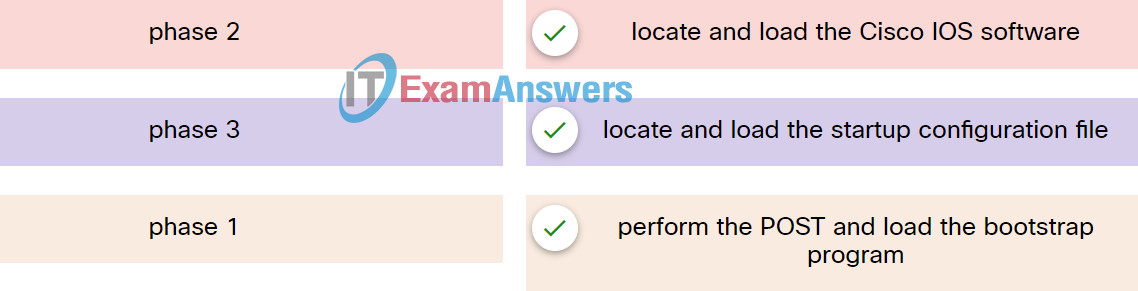
39. IPv6 host A is sending a neighbor solicitation message to IPv6 host B on the same Ethernet network. What address type is used in the Destination MAC field of the Ethernet frame header?
- unicast MAC address
- anycast MAC address
- multicast MAC address
- broadcast MAC address
40. A technician has been asked to develop a physical topology for a network that provides a high level of availability. Which physical topology requires that every node is attached to every other node on the network?
- bus
- hierarchical
- star
- mesh
- ring
41. Which pairs of wires change termination order between the 568A and 568B standards?
- green and orange
- green and brown
- blue and brown
- brown and orange
42. A network specialist has been hired to install a network in a company that assembles airplane engines. Because of the nature of the business, the area is highly affected by electromagnetic interference. Which type of network media should be recommended so that the data communication will not be affected by EMI?
- STP
- coaxial
- fiber optic
- UTP
43. IPv6 host A is communicating with a remote IPv6 host B. Which device would send ICMPv6 redirect messages to inform that a better next-hop device should be used?
- Host A
- Host B
- A router in the traffic path
- The switch connected to Host A
- The switch connected to Host B
44. Which address should be configured as the default gateway address of a client device?
- the Layer 2 address of the switch management interface
- the Layer 2 address of the switch port that is connected to the workstation
- the IPv4 address of the router interface that is connected to the same LAN
- the IPv4 address of the router interface that is connected to the internet
45. Which two characteristics describe the use of a logical topology? (Choose two.)
- describing the infrastructure
- identifying cable length requirements
- identifying the interconnection of routers and switches
- identifying the virtual connections between devices
- identifying the type of media access control used
- showing the physical connections of end devices
46. Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
47. What type of Ethernet cable would be used to connect one switch to another switch when neither switch supports the auto-MDIX feature?
- straight-through
- crossover
- coaxial
- rollover
48. What are two common causes of a physical layer network connectivity problem? (Choose two.)
- a monitor unplugged
- an Ethernet cable plugged into a wrong port
- an incorrect default gateway
- an unassigned IP address
- a faulty Ethernet cable
49. What are two services provided by IPv6 neighbor discovery protocol? (Choose two.)
- router discovery
- address resolution
- IPv6 dynamic routing
- domain name resolving
- maximum IPv6 packet size for end-to-end transmission
50. Following default settings, what two tasks are performed first in the router boot sequence? (Choose two.)
- Perform the POST routine.
- Locate and load the startup-config file from NVRAM.
- Load the bootstrap program from ROM.
- Load the running-config file from RAM.
- Locate and load the operating system.
51. A group of Windows PCs in a new subnet has been added to an Ethernet network. When testing the connectivity, a technician finds that these PCs can access local network resources but not the Internet resources. To troubleshoot the problem, the technician wants to initially confirm the IP address and DNS configurations on the PCs, and also verify connectivity to the local router. Which three Windows CLI commands and utilities will provide the necessary information? (Choose three.)
- arp -a
- ipconfig
- nslookup
- ping
- telnet
- tracert
52. At a minimum, which address is required on IPv6-enabled interfaces?
- link-local
- unique local
- site local
- global unicast
53. A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer
- data link layer
54. A dental office provides a WLAN in the waiting area for patients to access the Internet. The WLAN is equipped with a wireless router that connects to the Internet through a cable connection. Which data transmission mode is used by wireless devices?
- simplex
- half-duplex
- full-duplex
- multi-duplex
55. A router boots and enters setup mode. What is the reason for this?
- The IOS image is corrupt.
- Cisco IOS is missing from flash memory.
- The configuration file is missing from NVRAM.
- The POST process has detected hardware failure.
56. What is one advantage of using fiber-optic cabling rather than copper cabling?
- It is usually cheaper than copper cabling.
- It is able to be installed around sharp bends.
- It is easier to terminate and install than copper cabling.
- It is able to carry signals much farther than copper cabling.
57. Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is troubleshooting why PC1 cannot communicate with hosts in other networks. What is the problem?
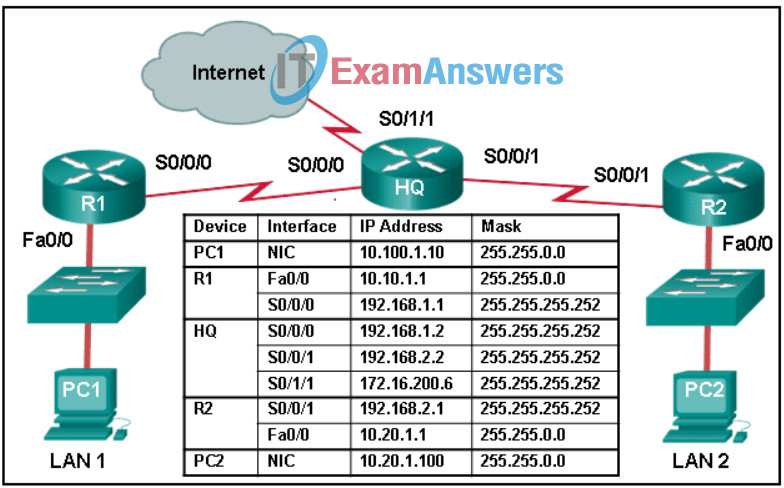
- The subnet mask that is configured on PC1 is the same as the mask that is configured on the router R1 interface.
- The IP address that is configured on PC1 is in a different network than the gateway address on router R1.
- A default route has not been configured on router R1.
- A default gateway IP address of 10.20.1.1 needs to be configured on PC1.
58. Which statement describes the ping and tracert commands?
- Tracert shows each hop, while ping shows a destination reply only.
- Tracert uses IP addresses; ping does not.
- Both ping and tracert can show results in a graphical display.
- Ping shows whether the transmission is successful; tracert does not.
59. Local workstations are unable to access web pages located on the www.cisco.com web server. Pings from the workstations to the server using the ping www.cisco.com command are successful. What settings should the administrator check to determine the cause of the problem?
- IP address settings
- firewall settings
- MAC address settings
- DNS server settings
60. What are IPv6 ULAs?
- a method of translating IPv6 addresses into IPv4 addresses
- a private IPv6 address range used for communication within a local site
- any device that can run both an IPv6 and an IPv4 protocol stack simultaneously
- tunneling protocols that allow two IPv6 networks to communicate across an IPv4 network
61. Which feature on a Cisco router permits the forwarding of traffic for which there is no specific route?
- next-hop
- gateway of last resort
- route source
- outgoing interface
62. Which statement describes an extended star topology?
- End devices connect to a central intermediate device, which in turn connects to other central intermediate devices.
- End devices are connected together by a bus and each bus connects to a central intermediate device.
- Each end system is connected to its respective neighbor via an intermediate device.
- All end and intermediate devices are connected in a chain to each other.
63. A network technician is attempting to connect an older device to a FastEthernet port on a Cisco switch. The technician has manually configured the device to full-duplex mode in order to enhance the network performance of the device. However, when the device is attached to the network, performance degrades and excessive collisions are detected on the switch. What is the likely cause of this problem?
- The host is configured in a different subnet from the subnet of the switch.
- There is a duplex mismatch between the device and switch port.
- The switch port is running at a different speed from the speed of the device NIC.
- The host has been configured with a default gateway that is different from that of the switch.
64. How do goodput, throughput, and bandwidth relate to network data transmissions?
- Goodput is always lower than throughput, which is generally lower than bandwidth.
- Throughput is always lower than bandwidth, which is generally lower than goodput.
- Goodput is always lower than bandwidth, which is generally lower than throughput.
- Throughput is always lower than goodput, which is generally lower than bandwidth.
65. What is a primary role of the Physical layer in transmitting data on the network?
- create the signals that represent the bits in each frame on to the media
- provide physical addressing to the devices
- determine the path packets take through the network
- control data access to the media
66. A user calls the help desk to report a workstation problem. Which three questions would produce the most helpful information for troubleshooting? (Choose three.)
- If you received an error message, what was it?
- What changes have you made to your workstation?
- Do you have the warranty for your workstation?
- What operating system version is running on your workstation?
- Have you used a network monitoring tool on your workstation?
- Have you performed a backup recently?
67. A customer called the cable company to report that the Internet connection is unstable. After trying several configuration changes, the technician decided to send the customer a new cable modem to try. What troubleshooting technique does this represent?
- top-down
- bottom-up
- substitution
- divide-and-conquer
68. Match the IPv6 address to the IPv6 address type.
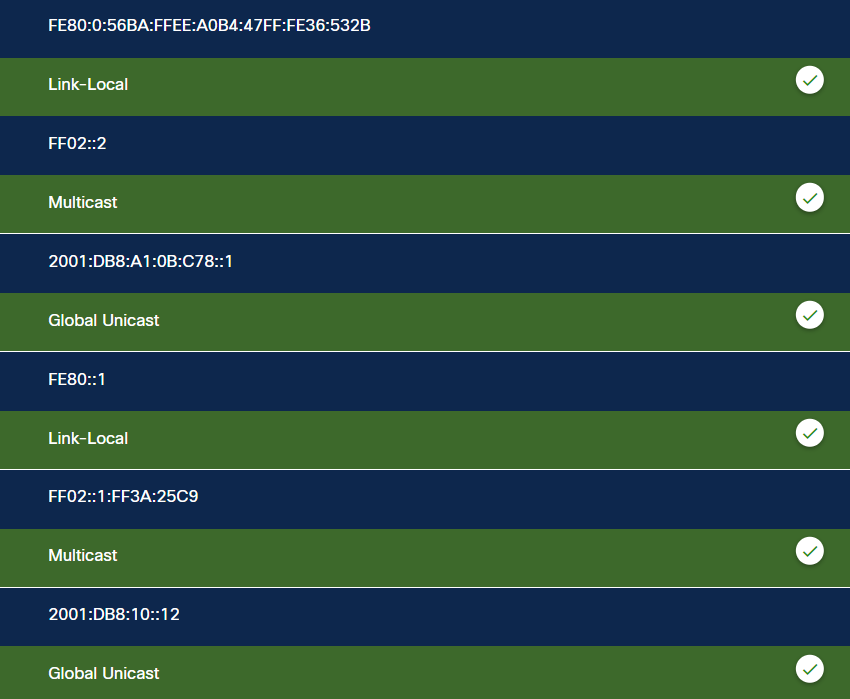
69. A laptop cannot connect to a wireless access point. Which two troubleshooting steps should be taken first? (Choose two.)
- Ensure that the wireless NIC is enabled.
- Ensure that the laptop antenna is attached.
- Ensure that the wireless SSID is chosen.
- Ensure that the correct network media is selected.
- Ensure that the NIC is configured for the proper frequency.
70. When troubleshooting network problems, where would a network administrator find the configuration information, such as the computer names and the IP addresses that are used?
- physical topology diagram
- DHCP server
- DNS server
- logical topology diagram
71. A production switch is reloaded and finishes with a Switch> prompt. What two facts can be determined? (Choose two.)
- POST occurred normally.
- The boot process was interrupted.
- There is not enough RAM or flash on this router.
- A full version of the Cisco IOS was located and loaded.
- The switch did not locate the Cisco IOS in flash, so it defaulted to ROM.
72. What are two advantages of using fiber-optic cabling to interconnect devices? (Choose two.)
- Fiber-optic cable is immune from EMI and RFI.
- Fiber-optic cables can extend several miles.
- Fiber-optic cables use extra shielding to protect copper wires.
- Fiber-optic cables are easy to install..
- Fiber-optic cables are commonly found in both homes and small businesses.
73. Which type of network cable contains multiple copper wires and uses extra shielding to prevent interference?
- STP
- UTP
- fiber-optic
- coax
74. Refer to the exhibit. An IT consulting firm is helping a mid-sized marketing and advertising company for updating the campus network. Which three network design features are covered in the diagram? (Choose three.)
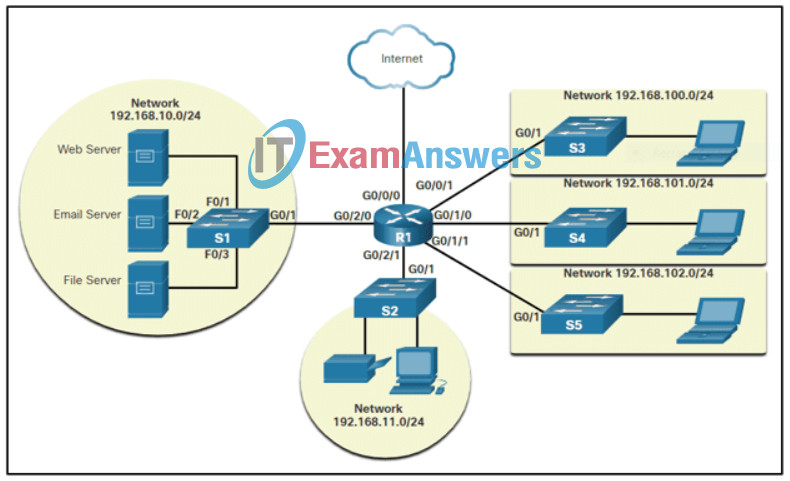
- flow of information in the network including addressing
- network devices that might be needed
- network segmentation
- data packet routing and protocol needs
- IP network subnetting consideration
- locations of network devices in the company
75. What is CSMA/CA on a network?
- an access method that is used by wireless technology to avoid duplicate SSIDs
- an access method that is used by any technology that has excessive collisions
- an access method that is used by wired Ethernet technology to avoid collisions
- an access method that is used by wireless technology to avoid collisions
76. An ISP help desk technician receives a call from a customer who reports that no one at their business can reach any websites or get their e-mail. After testing the communication line and finding everything fine, the technician instructs the customer to run nslookup from the command prompt. What does the technician suspect is causing the customer’s problem?
- improper IP address configuration on the host
- hardware failure of the ISR used to connect the customer to the ISP
- bad cables or connections at the customer site
- failure of DNS to resolve names to IP addresses
77. For the second time in a week, workstations on a LAN are not able to log into a specific server. The technician fixed the problem the first time, but cannot remember the steps taken to solve it. What aspect of the troubleshooting process has the technician neglected?
- identifying the problem
- asking questions of end users
- documenting the troubleshooting process
- using structured techniques to solve a problem
78. What is the first action in the boot sequence when a switch is powered on?
- load the default Cisco IOS software
- load boot loader software
- low-level CPU initialization
- load a power-on self-test program
79. Which string of hexadecimal numbers is an IPv6 GUA Interface ID probably created by using the EUI-64 process?
- 1272:23ff:eef0:1639
- fe99:47ff:fe75:cee0
- 52:74:fe:be:a8:7f
- 00:12:ff:eb:6b:40
80. A technician suspects that a new switch is the source of a network problem. While troubleshooting, the technician notices a blinking green activity LED on some of the ports. What does this indicate?
- There are no cables plugged into the ports.
- The power supply is the source of the problem.
- The ports are operational and are receiving traffic.
- The ports are operational, but no traffic is flowing.
81. Match the description to the IPv6 addressing component.
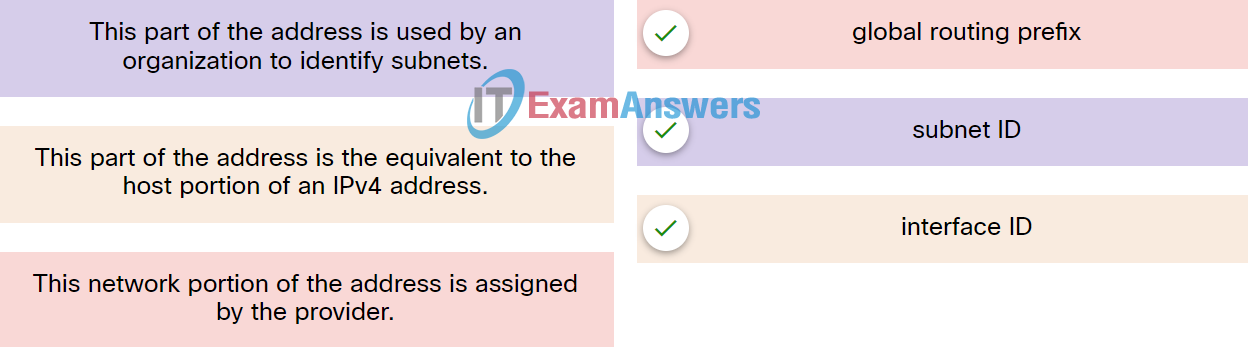
82. How many bits of an IPv6 address are used to identify the interface ID?
- 32
- 48
- 64
- 128
