24.1.5 Lab – Implement SPAN Technologies (Answers)
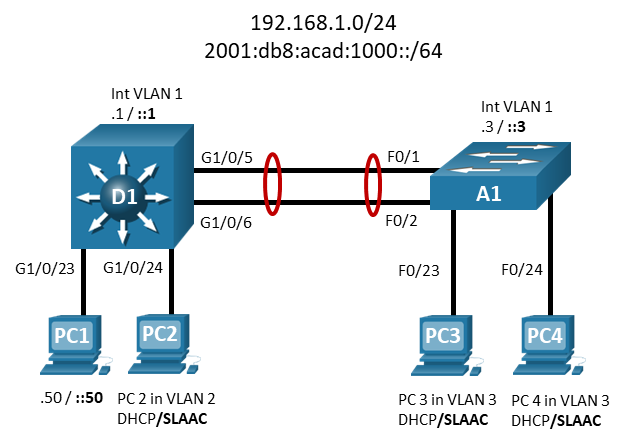
Topology
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | IPv6 Address | IPv6 Link Local |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.1/24 | 2001:db8:acad:1000::1/64 | fe80::d1:1 |
| VLAN 2 | 192.168.2.1/24 | 2001:db8:acad:2000::1/64 | fe80::d1:2 | |
| VLAN 3 | 192.168.3.1/24 | 2001:db8:acad:3000::1/64 | fe80::d1:3 | |
| A1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.3/24 | 2001:db8:acad:1000::3/64 | fe80::a1:1 |
| PC1 | NIC | 192.168.1.50/24 | 2001:db8:acad:1000::50/64 | EUI-64 |
| PC2 | NIC (VLAN 2) | Assigned by DHCP | Assigned by SLAAC | EUI-64 |
| PC3 | NIC (VLAN 3) | Assigned by DHCP | Assigned by SLAAC | EUI-64 |
| PC4 | NIC (VLAN 3) | Assigned by DHCP | Assigned by SLAAC | EUI-64 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings and Interface Addressing
- Part 2: Configure and Verify Local SPAN
- Part 3: Configure and Verify RSPAN
Background / Scenario
The Switch Port Analyzer (SPAN) feature allows you to instruct a switch to send copies of packets seen on one port, multiple ports, or an entire VLAN, to another port on the same switch. The Remote SPAN (RSPAN) feature takes the SPAN feature beyond a single switch to a network, allowing you to remotely capture traffic on different switches in the network. This is extremely useful in campus networks where a sniffer may not be located at the desired traffic capture point. In addition, this allows you to permanently place a sniffer in the campus network to SPAN traffic as necessary or when troubleshooting situations arise.
Note: This lab is an exercise in configuring options available for SPAN and does not necessarily reflect network troubleshooting best practices.
Instructor Note: This lab may not work as intended if you are using NETLAB with a control switch.
Note: The switches used in the CCNP hands-on labs are Cisco Catalyst 3650s with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image) and Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other switches and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs.
Note: Make sure that the switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Note: The default Switch Database Manager (SDM) template on a Catalyst 2960 does not support IPv6. You must change the default SDM template to the dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 default template using the sdm prefer dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 default global configuration command. Changing the template will require a reboot.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 1 Switch (Cisco 3650 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 4 PCs (Choice of operating system with terminal emulation program and with a packet capture utility)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings and Interface Addressing
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings and interface addressing on switches.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Configure basic settings for each device.
a. Console into each device, enter global configuration mode, and apply the basic settings. The startup configurations for each device are provided below.
Switch D1
config t hostname D1 no ip domain lookup ip routing ipv6 unicast-routing banner motd # D1, Implement SPAN Technologies # line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco123 login exit vlan 2 name SECOND_VLAN exit vlan 3 name THIRD_VLAN exit interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::d1:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1000::1/64 no shutdown exit interface vlan 2 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::d1:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:2000::1/64 no shutdown exit interface vlan 3 ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::d1:3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:3000::1/64 no shutdown exit interface range g1/0/23 spanning-tree portfast switchport mode access no shutdown exit interface range g1/0/24 spanning-tree portfast switchport mode access switchport access vlan 2 no shutdown exit interface range g1/0/5-6 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active no shutdown exit interface range g1/0/1-4, g1/0/7-22, g1/1/1-4 shutdown exit ip dhcp pool SECOND_VLAN_POOL network 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.2.1 exit ip dhcp pool THIRD_VLAN_POOL network 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.3.1 exit end
Switch A1
config t hostname A1 no ip domain lookup ipv6 unicast-routing banner motd # A1, Implement SPAN Technologies # line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous exit line vty 0 4 privilege level 15 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco123 login exit vlan 2 name SECOND_VLAN exit vlan 3 name THIRD_VLAN exit interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address fe80::a1:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1000::3/64 no shutdown exit interface range f0/1-2 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active no shutdown exit interface range f0/23 - 24 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 3 spanning-tree portfast no shutdown exit interface range f0/3-22, g0/1-2 shutdown exit end
b. Set the clock on each device to UTC time.
c. Save the running configuration to startup-config.
d. Configure IPv4 and IPv6 addresses on all hosts as shown in the addressing table.
e. Verify that the PCs can ping their default gateways and each other.
Part 2: Configure and Verify Local SPAN
In this part you will configure and verify a local SPAN on D1, configuring it so that PC1 is able to capture traffic from PC2, even though it is in a different VLAN.
Step 1: Configure Local SPAN.
a. Create a Local SPAN session with a source of g1/0/24 and a destination of g1/0/23. The monitor session number is locally significant only, so you can use any number IOS XE allows you to. Note that there is a limit to the number of sessions that can run simultaneously, and that the SPAN can consume significant resources.
D1(config)# monitor session 1 source interface g1/0/24 D1(config)# monitor session 1 destination interface g1/0/23
b. Verify the configuration by issuing the show monitor session # or show monitor session local command.
D1# show monitor session local
Session 1
---------
Type : Local Session
Source Ports :
Both : Gi1/0/24
Destination Ports : Gi1/0/23
Encapsulation : Native
Ingress : Disabled
Step 2: Verify that the SPAN is operational.
a. On PC 1, open Wireshark and start capturing on the Ethernet interface. Add the capture filter icmp.
b. On PC 2, ping 192.168.1.1. Send 3 packets of 300 bytes.
On a Windows PC, the command is ping -n 3 -l 300 192.168.1.1
On a Linux PC, the command is ping -s 300 -c 3 192.168.1.1
c. On PC 1, stop the Wireshark capture and examine the output.
d. Remove the monitor session using the no monitor session 1 command.
Part 3: Configure and Verify RSPAN
In this part, you will configure and verify a Remote SPAN (RSPAN). RSPAN allows the source and destination ports to be on different switches. For this to work, it uses a VLAN configured only for remote-span functionality. The source port then places the transmitted or received data onto the remote-span VLAN. The remote-span VLAN is carried across trunks. The receiving switch takes the data sourced from the remote-span VLAN and sends it to the destination port that is running the protocol analyzer.
VLAN 500 will be created on D1 and A1 to be used as the remote-span VLAN. PC 1 will again take on the capture role, this time it will be interested in traffic coming from VLAN 2 on Switch A1.
Step 1: Configure RSPAN VLAN.
a. Create the RSPAN VLAN on D1 and A1 using the vlan 500 command from global configuration mode.
D1# config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. D1(config)# vlan 500 D1(config-vlan)# name Remote_SPAN D1(config-vlan)# remote-span D1(config-vlan)# exit
b. Use the show vlan remote-span command to verify VLAN 500 is configured correctly and is designated as the remote-span vlan. Use the show interface trunk command to ensure the RSPAN VLAN is allowed on the trunks. The RSPAN VLAN should not be a DATA VLAN. Its purpose is strictly for carrying the monitored traffic across trunk links from one switch to another.
D1# show vlan remote-span Remote SPAN VLANs ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 500 D1# show interface trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Po1 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Po1 1-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Po1 1-3,500 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Po1 1-3,500
c. Now configure the monitor session on A1 with a source interface of vlan 2 and a destination of remote vlan 500. Because the captured traffic must traverse the local switch to a remote switch, we must use the remote VLAN as the destination.
A1(config)# monitor session 2 source vlan 3 A1(config)# monitor session 2 destination remote vlan 500 %Note: ingoring the reflector port configuration
Note: The ignoring the reflector port message is an artifact of an older OS and can be safely ignored.
d. Verify the configuration using the show monitor session 2 command.
A1# show monitor session 2
Session 2
---------
Type : Remote Source Session
Source VLANs :
Both : 3
Dest RSPAN VLAN : 500
e. Move to the D1 switch and configure it to collect the desired traffic. The source port on D1 will be the remote-span vlan 500 and the destination port will be the client connected to G1/0/23.
D1(config)# monitor session 2 source remote vlan 500 D1(config)# monitor session 2 destination interface g1/0/23
Note that the session numbers do not have to match at either end of the session.
f. Verify the configuration using the show monitor session 2 command on D1.
D1# show monitor session 2
Session 2
---------
Type : Remote Destination Session
Source RSPAN VLAN : 500
Destination Ports : Gi1/0/23
Encapsulation : Native
Ingress : Disabled
Step 2: Verify that the SPAN is operational.
a. On PC 1, open Wireshark and start capturing on the Ethernet interface.
b. On PC3 and PC4 (the hosts on A1), ping 192.168.1.1. Send 3 packets of 300 bytes.
On a Windows PC, the command is ping -n 3 -l 300 192.168.1.1
On a Linux PC, the command is ping -s 300 -c 3 192.168.1.1
c. On PC 1, stop the Wireshark capture and examine the output. You should see pings sourced from PC3 and PC4, along with responses to those pings.
d. Remove the monitor session using the no monitor session 2 command on A1 and D1.
Device Configs – Final
Switch D1
D1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 9628 bytes ! version 16.9 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec ! Call-home is enabled by Smart-Licensing. service call-home no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname D1 ! vrf definition Mgmt-vrf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! no aaa new-model switch 1 provision ws-c3650-24ts ! ip routing ! no ip domain lookup ! ip dhcp pool SECOND_VLAN_POOL network 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.2.1 ! ip dhcp pool THIRD_VLAN_POOL network 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.3.1 ! login on-success log ipv6 unicast-routing ! license boot level ipservicesk9 ! diagnostic bootup level minimal ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode sso ! transceiver type all monitoring ! class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control description Topology control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING class-map match-any system-cpp-default description Inter FED, EWLC control, EWLC data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFL SAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth description Punt Webauth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control description L2 LVX control packets class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station description MCAST END STATION class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control description L2 control class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth description DOT1X Auth class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control description Stackwise Virtual class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control description Routing control and Low Latency class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping description Protocol snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping description DHCP snooping class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical description System Critical and Gold Pkt ! policy-map system-cpp-policy ! interface Port-channel1 switchport mode trunk ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf no ip address shutdown negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/9 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/11 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/12 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/13 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/14 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/16 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/17 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/18 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/19 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/20 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/21 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/22 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/23 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 switchport access vlan 2 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/2 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/3 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1/4 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address FE80::D1:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1000::1/64 ! interface Vlan2 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address FE80::D1:2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2000::1/64 ! interface Vlan3 ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address FE80::D1:3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:3000::1/64 ! ip forward-protocol nd ip http server ip http authentication local ip http secure-server ! ! control-plane service-policy input system-cpp-policy ! banner motd ^C D1, Implement SPAN Technologies ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 login line vty 5 15 login ! end
Switch A1
A1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 3698 bytes ! version 15.2 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname A1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup ipv6 unicast-routing ! spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! interface Port-channel1 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active ! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport mode trunk channel-group 1 mode active ! interface FastEthernet0/3 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/7 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/19 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 switchport access vlan 3 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast ! interface FastEthernet0/24 switchport access vlan 3 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address FE80::A1:1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1000::3/64 ! ip http server ip http secure-server ! banner motd ^C A1, Implement SPAN Technologies ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronous line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 privilege level 15 password cisco123 login line vty 5 15 login ! end
