Chapter 2 – Sections & Objectives
- 2.1 Serial Point-to-Point Overview
- Configure HDLC encapsulation.
- 2.2 PPP Operation
- Explain how PPP operates across a point-to-point serial link.
- 2.3 PPP Implementation
- Configure PPP encapsulation.
- 2.4 Troubleshoot WAN Connectivity
- Troubleshoot PPP.
2.1 Serial Point-to-Point Overview
Serial Communications
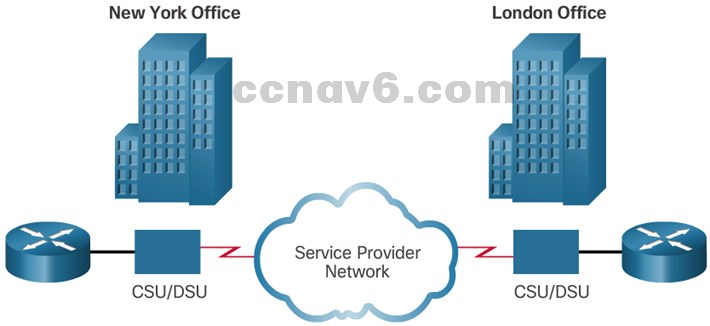
- Point-to-point connections are used to connect LANs to service provider WANs, and to connect LAN segments within an enterprise network.
- A point-to-point link can connect two geographically distant sites, such as a corporate office in New York and a regional office in London.
- Serial connection bandwidths can be incrementally increased to accommodate the need for faster transmission.
HDLC Encapsulation
- On each WAN connection, data is encapsulated into frames before crossing the WAN link.
- HDLC is the default encapsulation type on point-to-point connections, dedicated links, and circuit-switched connections when the link uses two Cisco devices.
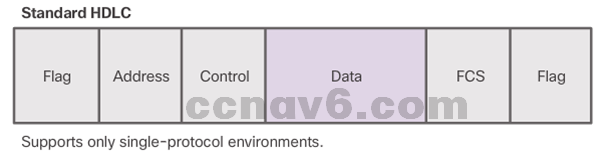
- HDLC defines a Layer 2 framing structure that allows for flow control and error control through the use of acknowledgments.
- HDLC uses a frame delimiter, or flag, to mark the beginning and the end of each frame
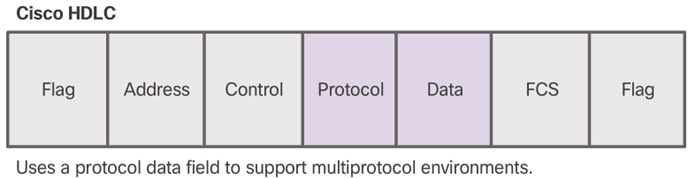
- Cisco HDLC frames contain a field for identifying the network protocol being encapsulated.
- There are two steps to re-enable HDLC encapsulation:
- Step 1. Enter the interface configuration mode of the serial interface.
- Step 2. Enter the encapsulation hdlc command to specify the encapsulation protocol on the interface.
- The show interfaces serial command returns one of six possible states:
- Serial x is up, line protocol is up
- Serial x is down, line protocol is down
- Serial x is up, line protocol is down
- Serial x is up, line protocol is up (looped)
- Serial x is up, line protocol is down (disabled)
- Serial x is administratively down, line protocol is down
- The show controllers command is another important diagnostic tool when troubleshooting serial lines.
- The output indicates the state of the interface channels and whether a cable is attached to the interface.
2.2 PPP Operation
Benefits of PPP
- Use PPP encapsulation to connect a Cisco router to a non-Cisco router.
- PPP Advantages
- The link quality management feature monitors the quality of the link. If too many errors are detected, PPP takes the link down.
- PPP supports PAP and CHAP authentication.

LCP and NCP
- PPP Layered Architecture
- PPP and OSI share the same physical layer, but PPP distributes the functions of LCP and NCP differently.
- The only absolute requirement imposed by PPP is a full-duplex circuit, either dedicated or switched, that can operate in an asynchronous or synchronous bit-serial mode.
- Most of the work done by PPP happens at the data link and network layers, by LCP and NCPs.
- Link Control Protocol
- LCP establishes the point-to-point link.
- LCP also negotiates and sets up control options on the WAN data link, which are handled by the NCPs.
- After the link is established, PPP also uses LCP to agree automatically on encapsulation formats such as authentication, compression, and error detection
- Network Control Protocol
- PPP permits multiple network layer protocols to operate on the same communications link.
- For every network layer protocol used, PPP uses a separate NCP
- Each NCP manages the specific needs required by its respective network layer protocols.
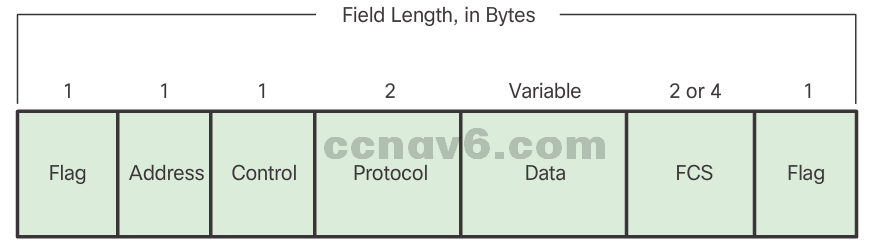
- A PPP frame consists of six fields:
PPP Sessions
- There are three phases of establishing a PPP session
- Phase 1: Link establishment and configuration negotiation
- Phase 2: Link quality determination (optional)
- Phase 3: Network layer protocol configuration negotiation
- LCP operation uses three classes of LCP frames to accomplish the work of each of the LCP phases:
- Link-establishment frames establish and configure a link.
- Link-maintenance frames manage and debug a link.
- Link-termination frames terminate a link.
- PPP can be configured to support optional functions:
- Authentication
- Compression
- Multilink
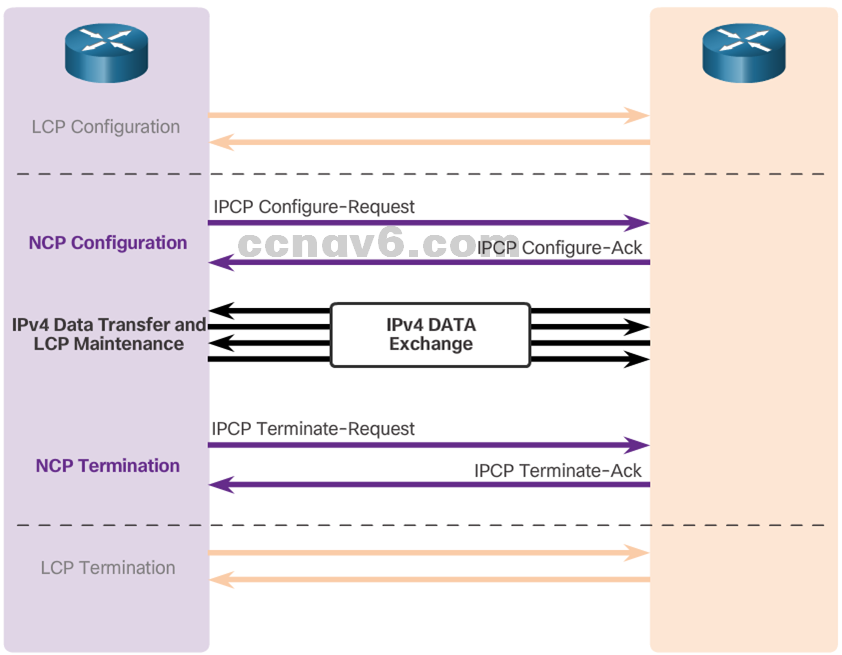
- After LCP has established the link, the routers exchange IPCP messages
- Compression
- IPv4-Address
2.3 PPP Implementation
Configure PPP
- PPP may include several LCP options:
- Authentication, Compression, Error detection, PPP Callback, and Multilink
- To set PPP as the encapsulation method used by a serial interface, use the encapsulation ppp interface configuration command.
- Point-to-point software compression on serial interfaces can be configured after PPP encapsulation is enabled with the compress command.
- The ppp quality percentage command ensures that the link meets the quality requirement set; otherwise, the link closes down.
Configure PPP
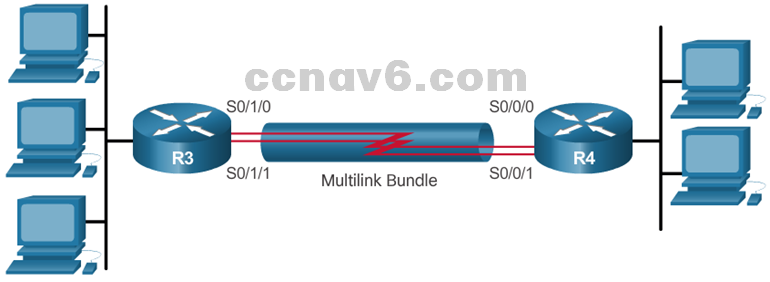
- MPPP allows packets to be fragmented and sends these fragments simultaneously over multiple point-to-point links to the same remote address.
- Configuring MPPP requires two steps:
- Step 1. Create a multilink bundle.
- Step 2. Assign interfaces to the multilink bundle.
- Use the show interfaces serial command to verify proper configuration of HDLC or PPP encapsulation
Configure PPP Authentication
- RFC 1334, PPP Authentication Protocols, defines two protocols for authentication, PAP and CHAP.
- PAP is a very basic two-way process. There is no encryption. The username and password are sent in plaintext.
- CHAP is more secure than PAP. It involves a three-way exchange of a shared secret.
- To specify the order in which the CHAP or PAP protocols are requested on the interface, use the ppp authentication interface configuration command. Use the no form of the command to disable this authentication.
- The PAP username and password that each router sends must match those specified with the username name password password command of the other router.
2.4 Troubleshoot WAN Connectivity
Troubleshoot PPP
- A debug output displays information about various router operations, related traffic generated or received by the router, and any error messages.
- Debug ppp
- Use the debug ppp command to display information about the operation of PPP.
- A good command to use when troubleshooting serial interface encapsulation is the debug ppp packet command.
- The debug ppp negotiation command enables the network administrator to view the PPP negotiation transactions, identify the problem or stage when the error occurs, and develop a resolution.
- The debug ppp error command is used to display protocol errors and error statistics associated with PPP connection negotiation and operation.
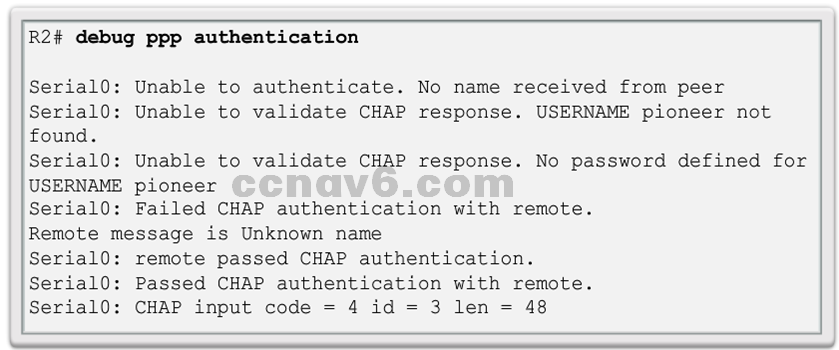
- Debug PPP Authentication
- Always verify your configuration with the show interfaces serial command, in the same way as you did without authentication.
- Never assume your authentication configuration works without testing it using the previously covered show commands
- For debugging PPP authentication, use the debug ppp authentication command.
2.4 Chapter Summary
Summary
- Serial transmissions sequentially send one bit at a time over a single channel. A serial port is bidirectional. Synchronous serial communications require a clocking signal.
- Point-to-Point links are usually more expensive than shared services; however, the benefits may outweigh the costs. Constant availability is important for some protocols, such as VoIP.
- SONET is an optical network standard that uses STDM for efficient use of bandwidth. In the United States, OC transmission rates are standardized specifications for SONET.
- The bandwidth hierarchy used by carriers is different in North America (T-carrier) and Europe (E-carrier). In North America, the fundamental line speed is 64 kbps, or DS0. Multiple DS0s are bundled together to provide higher line speeds.
- The demarcation point is the point in the network where the responsibility of the service provider ends and the responsibility of the customer begins. The CPE, usually a router, is the DTE device. The DCE is usually a modem or CSU/DSU.
- Cisco HDLC is a bit-oriented synchronous data link layer protocol extension of HDLC and is used by many vendors to provide multiprotocol support. This is the default encapsulation method used on Cisco synchronous serial lines.
- Synchronous PPP is used to connect to non-Cisco devices, to monitor link quality, provide authentication, or bundle links for shared use. PPP uses HDLC for encapsulating datagrams. LCP is the PPP protocol used to establish, configure, test, and terminate the data link connection. LCP can optionally authenticate a peer using PAP or CHAP. A family of NCPs are used by the PPP protocol to simultaneously support multiple network layer protocols. Multilink PPP spreads traffic across bundled links by fragmenting packets and simultaneously sending these fragments over multiple links to same remote address, where they are reassembled.
- PPP optionally supports authentication using PAP, CHAP, or both PAP and CHAP protocols. PAP sends authentication data in plaintext. CHAP uses a 3-way handshake, periodic challenge messaging, and a one-way hash that helps protect against playback attacks.
