Chapter 1 – Sections & Objectives
- 1.1 WAN Technologies Overview
- Explain WAN access technologies available to small to medium-sized business networks.
- 1.2 Selecting a WAN Technology
- Select WAN access technologies to satisfy business requirements.
1.1 WAN Technologies Overview
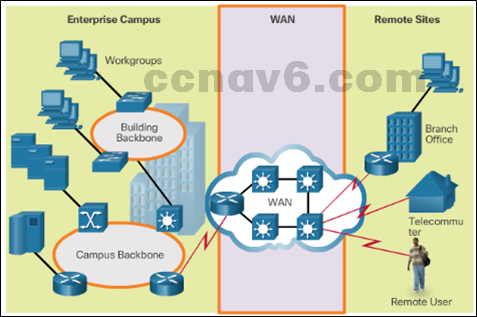
Purpose of WANs
- WANs connect LANs
- WANs are used to connect remote sites to the enterprise network.
- WANs connect home users to the Internet.
- Enterprise networks are using security and privacy solutions over the Internet to connect remote sites and users.
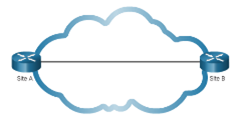
Common WAN topologies are:
- Point-to-Point – Typically a dedicated leased-line connection such as T1/E1
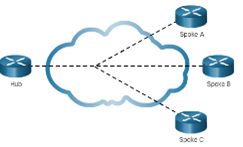
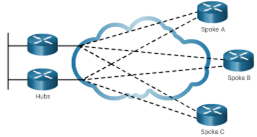
- Hub-and-Spoke – A single-homed, point-to-multipoint topology where a single interface on the hub router can be shared with multiple spoke routers through the use of virtual interfaces
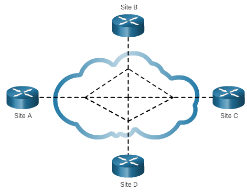
- Full Mesh – Each router has a connection to every other router; requires a large number of virtual interfaces
- Dual-homed – Provides redundancy for a single-homed, hub-and-spoke topology by providing a second hub to connect to spoke routers
- As businesses grow, the topologies and WAN strategies change:
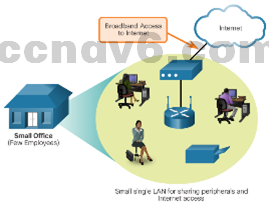
- Small Office – These businesses typically consist of one LAN at one location that connects to the Internet through a broadband technology.
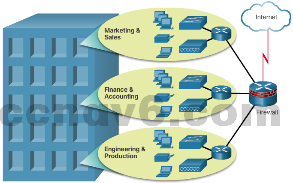
- Campus Network – A small- to medium-sized business with one location and multiple LANs uses specialized equipment and technologies to connect to the Internet.
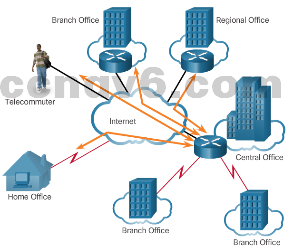
- Branch Networks – As the business grows, it adds more branch offices, each with its own campus network. WAN contracts to connect the remote networks are negotiated.
- Distributed Network – A multinational business has a network distributed across the globe. These businesses have complex WAN strategies to securely connect to regional offices, branch offices, partners, and telecommuters.
- Small Office – These businesses typically consist of one LAN at one location that connects to the Internet through a broadband technology.
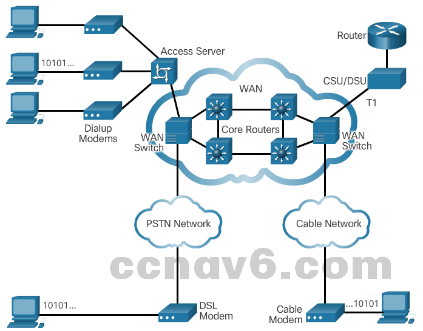
WAN Technologies Overview WAN Operations
-
- WAN operations focus primarily on the physical layer (OSI Layer 1) and the data link layer (OSI Layer 2).
- Layer 1 protocols describe how to provide electrical, mechanical, operational, and functional connections
- Layer 2 protocols define how data is encapsulated
- WAN Terms include:
- Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) – owned by the business or leased from the service provider.
- Data Communications Equipment (DCE) – provides an interface to connect subscribers to a communication link on the WAN cloud.
- Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) – connects to the local loop through the DCE.
- Demarcation Point – separates customer equipment from service provider equipment and is the place where the responsibility for the connection changes from the user to the service provider.
- Local Loop – cable that connects the CPE to the CO of the service provider (last mile).
- Central Office (CO) – local service provider facility or building that connects the CPE to the provider network.
- Toll network – all the cabling and equipment inside the WAN provider network.
- WAN operations focus primarily on the physical layer (OSI Layer 1) and the data link layer (OSI Layer 2).

- WAN devices include:
-
- Dialup modem – legacy WAN technology that converts digital signals into voice frequencies to be transmitted over the analog lines of the public telephone network.
- Access server – legacy WAN technology that coordinates dial-in and dial-out user communications.
- Broadband modem – used with high-speed DSL or cable Internet service
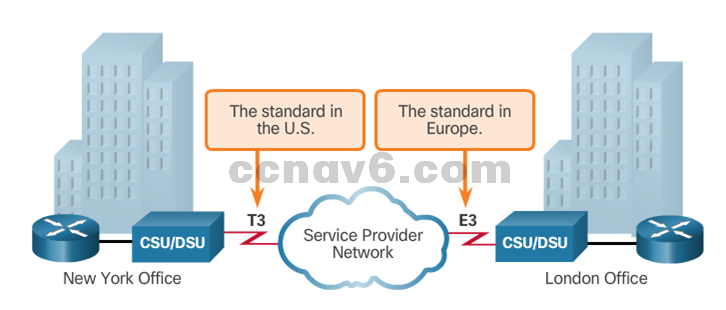
- CSU/DSU – used to convert digital, leased-line signals into frames that the LAN can interpret and vice versa.
- WAN switch – multiport internetworking device used in service provider networks
- Router – provides internetworking and WAN access interface ports to connect to the service provider network
- Core router/Multilayer switch – resides within the backbone of the WAN, supports multiple interfaces, and forwards IP packets at full line speed
-
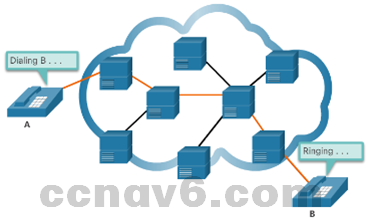
- WANs can operate as circuit-switched or packet-switched networks:
- Circuit-switched Networks – establish a dedicated circuit between source and destination before the users may communicate, such as making a telephone call
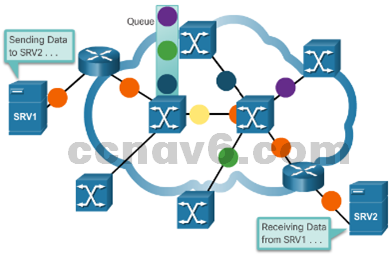
- Packet-Switched Networks – split traffic into packets that are routed over a shared network and do not require a dedicated circuit between source and destination
- Circuit-switched Networks – establish a dedicated circuit between source and destination before the users may communicate, such as making a telephone call
1.2 Selecting a WAN Technology
WAN Services
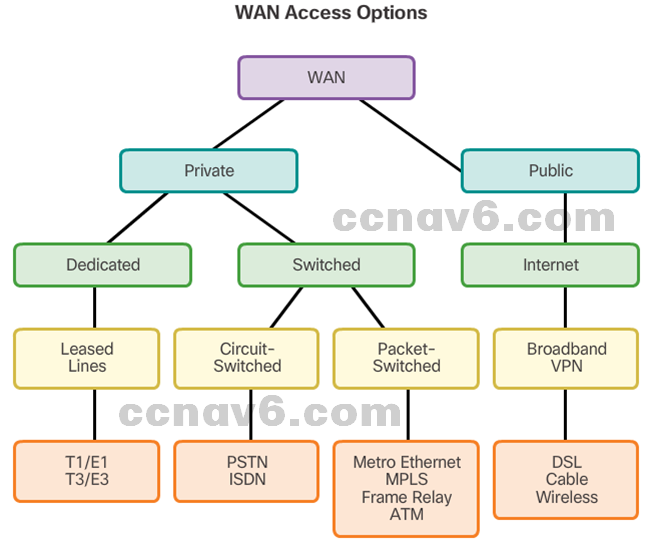
Two way that a business can get WAN access:
-
- Private WAN Infrastructure
– The business negotiates for dedicated or switched WAN access with a service provider. - Public WAN Infrastructure
– WAN access is achieved through the Internet using broadband connections. VPNs secure the connections.
- Private WAN Infrastructure
-
- This topology illustrates some of these WAN access technologies.
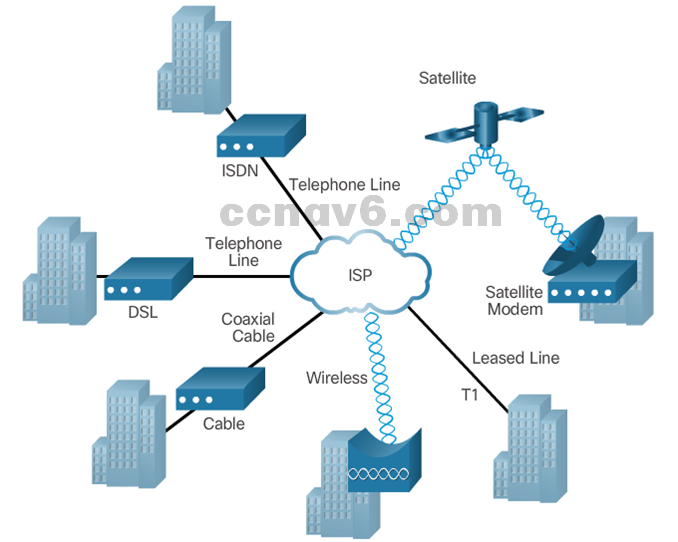
Private WAN Infrastructures
-
-
- Dialup
- Advantages:
- Simplicity
- Quality
- Availability
- Disadvantages:
- Cost
- Limited flexibility
- Advantages:
- Dialup
-
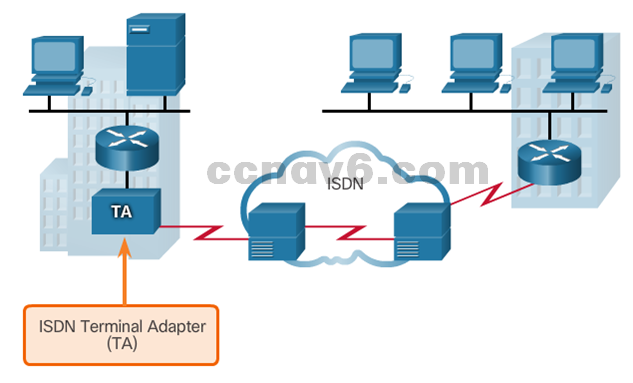
- ISDN
- Sample ISDN Topology
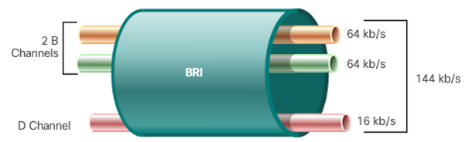
- ISDN BRI
- ISDN PRI
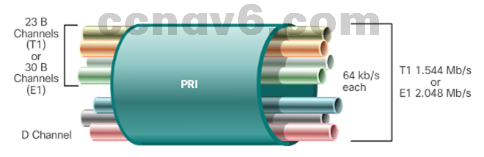
- Sample ISDN Topology
- Frame Relay
-
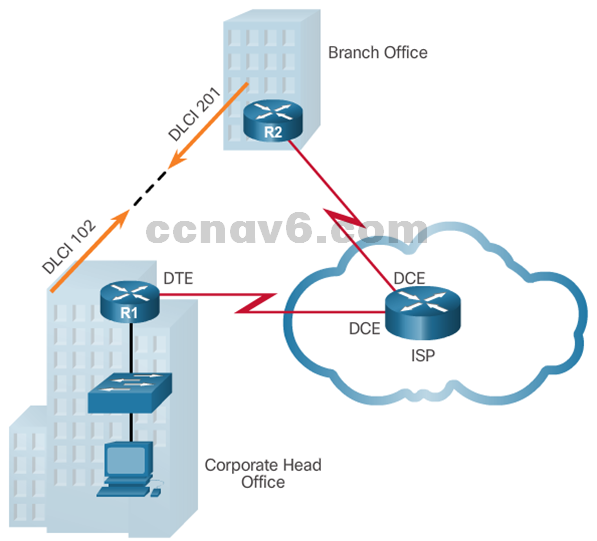
- PVCs carry both voice and data traffic.
- PVCs are uniquely identified by a data-link connection identifier (DLCI).
- PVCs and DLCIs ensure bidirectional communication from one DTE device to another.
- R1 uses DLCI 102 to reach R2 while R2 uses DLCI 201 to reach R1.
-
- ATM
- Built on a cell-based architecture, rather than on a frame-based architecture. ATM cells are always a fixed length of 53 bytes.
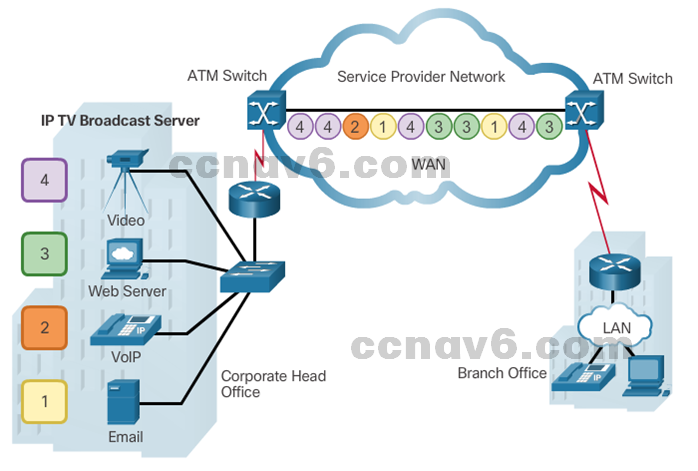
- Built on a cell-based architecture, rather than on a frame-based architecture. ATM cells are always a fixed length of 53 bytes.
- Ethernet WANFeatures and Benefits of Ethernet WAN include:
- Reduced expenses and administration
- Easy integration with existing networks
- Enhanced business productivity
- Service providers now offer Ethernet WAN service using fiber-optic cabling.
- Known as Metropolitan Ethernet (MetroE), Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS), and Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS).
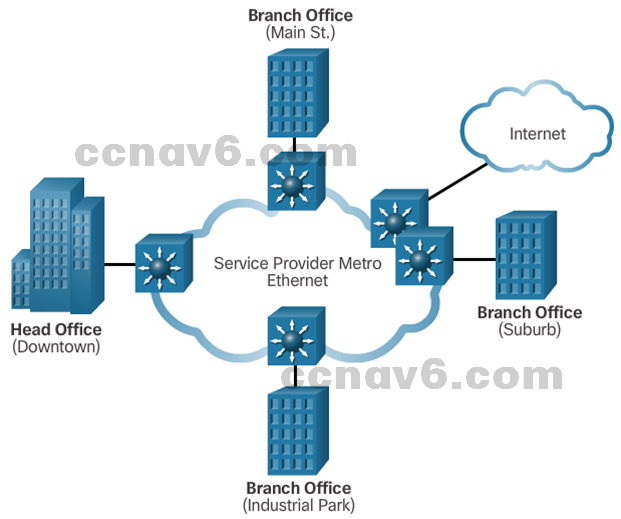
Note: Commonly used to replace the traditional Frame Relay and ATM WAN links.
- MPLSMultiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a multiprotocol high-performance WAN technology that directs data from one router to the next, based on short path labels rather than IP network addresses.
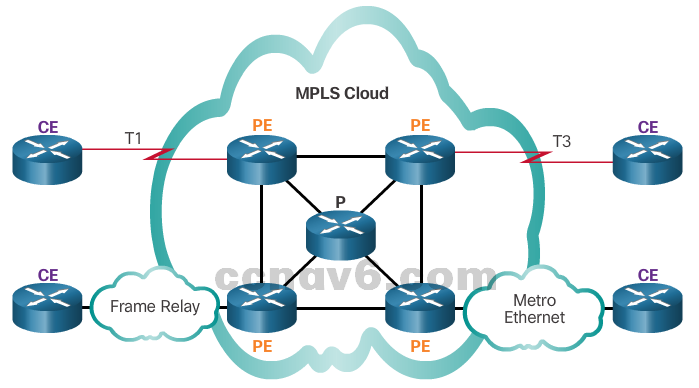
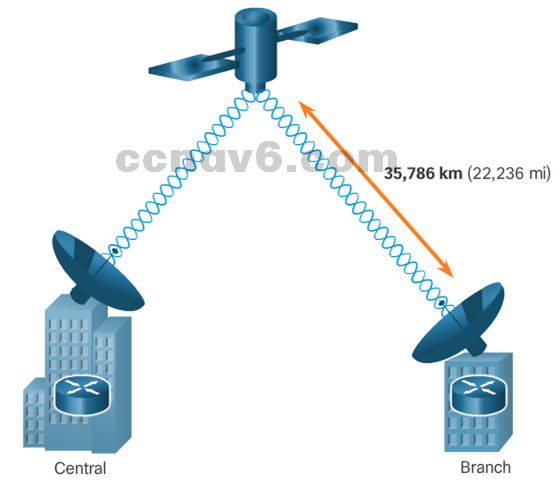
- VSATVery small aperture terminal (VSAT) – a solution that creates a private WAN using satellite communications.
Public WAN Infrastructures
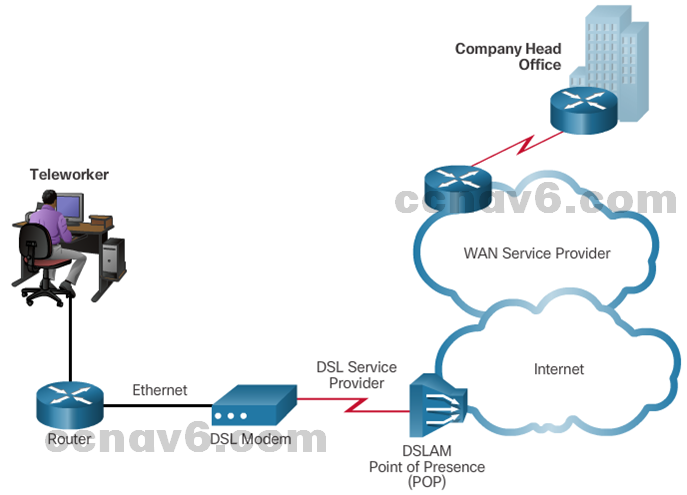
- DSL
-
- Always-on connection technology that uses existing twisted-pair telephone lines to transport high-bandwidth data, and provides IP services to subscribers.
- A DSL modem converts an Ethernet signal from the user device to a DSL signal, which is transmitted to the central office.
-
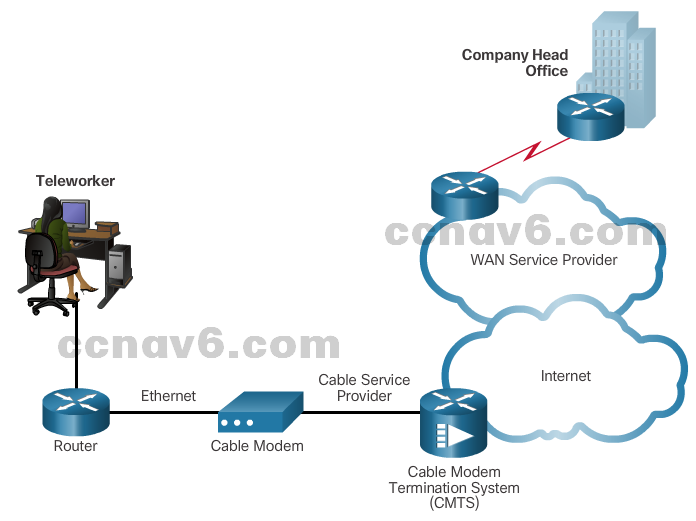
- Cable
-
- Network access is available from some cable television networks.
- Cable modems provide an always-on connection and a simple installation.
-
- Wireless
-
- New developments in broadband wireless technology:
- Municipal Wi-Fi – Many cities have begun setting up municipal wireless
- WiMAX – Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) is a new technology that is just beginning to come into use.
- Satellite Internet – Typically used by rural users where cable and DSL are not available.
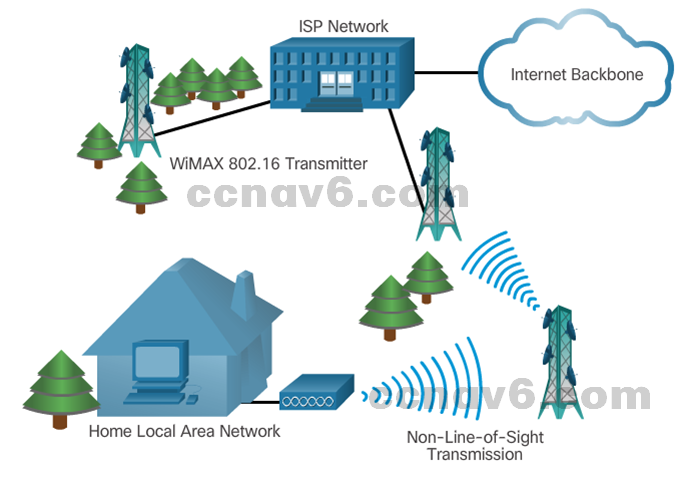
-
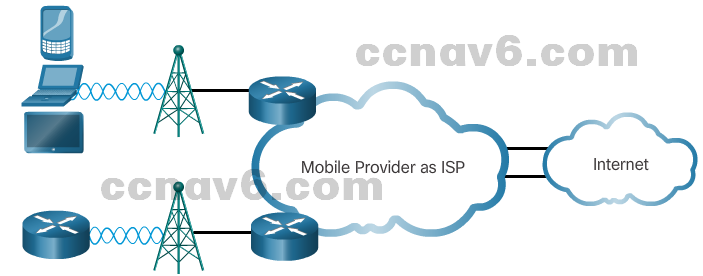
- 3G/4GCommon cellular industry terms include:
-
- 3G/4G Wireless – Abbreviation for 3rd generation and 4th generation cellular access. These technologies support wireless Internet access.
- Long-Term Evolution (LTE) – A newer and faster technology, considered to be part of the 4th generation (4G) technology.
- Public WANs rely on VPNs for securing data between private networks as it crosses a public network, such as the Internet.
- Benefits:
- Cost savings
- Security
- Scalability
- Compatibility with broadband technology
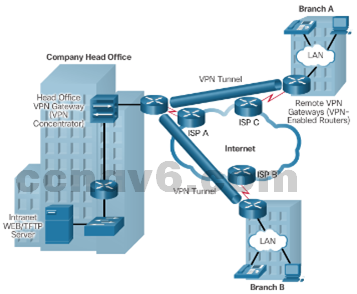
- Two types of VPN:
- Site-to-site VPNs
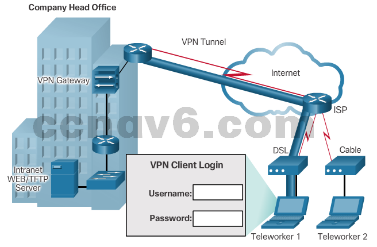
- Remote-access VPNs
- Site-to-site VPNs
-
Selecting WAN Services
Answer the following questions when choosing a WAN Connection:


1.3 Summary
Summary
- WAN access standards operate at Layers 1 and 2 of the OSI model.
- Permanent, dedicated point-to-point connections are provided by using leased lines.
- Private WAN connections include:
- Dialup
- ISDN
- Frame Relay
- ATM
- Metro Ethernet
- MPLS
- VSAT
- Public WAN connections include:
- DSL
- Cable
- Wireless
- Cellular
- Security over public infrastructure connections can be provided by using remote-access or site-to-site Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).
