Chapter 5 – Sections & Objectives
- 5.1 LAN Security
- Explain how to mitigate common LAN security.
- 5.2 SNMP
- Configure SNMP to monitor network operations in a small to medium-sized business network.
- 5.3 Cisco Switch Port Analyzer (SPAN)
- Troubleshoot a network problem using SPAN.
5.1 LAN Security
LAN Security Attacks
Common attacks against the Layer 2 LAN infrastructure include:
- CDP Reconnaissance Attacks
- Telnet Attacks
- MAC Address Table Flooding Attacks
- VLAN Attacks
- DHCP Attacks
LAN Security Best Practices
This topic covers several Layer 2 security solutions:
- Mitigating MAC address table flooding attacks using port security
- Mitigating VLAN attacks
- Mitigating DHCP attacks using DHCP snooping
- Securing administrative access using AAA
- Securing device access using 802.1X port authentication
LAN Security Best Practices
There are several strategies to help secure Layer 2 of a network:
- Always use secure variants of these protocols such as SSH, SCP, SSL, SNMPv3, and SFTP.
- Always use strong passwords and change them often.
- Enable CDP on select ports only.
- Secure Telnet access.
- Use a dedicated management VLAN where nothing but management traffic resides.
- Use ACLs to filter unwanted access.
5.2 SNMP
SNMP Operation
-
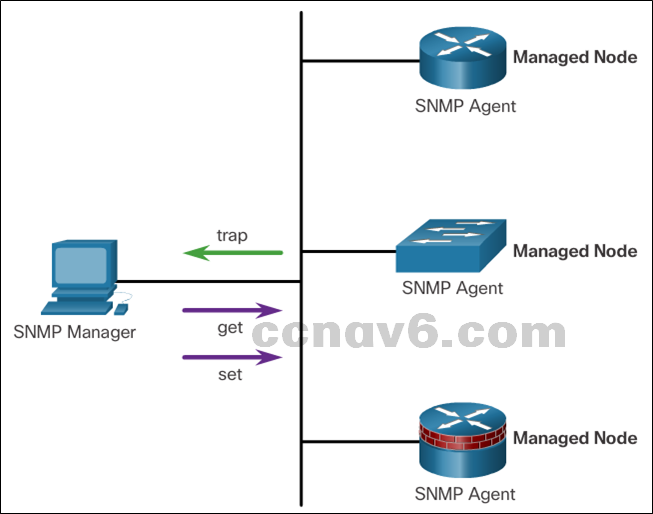
- SNMP allows administrators to manage and monitor devices on an IP network.
- SNMP Elements
- SNMP Manager
- SNMP Agent
- MIB
- SNMP Operation
- Trap
- Get
- Set
-
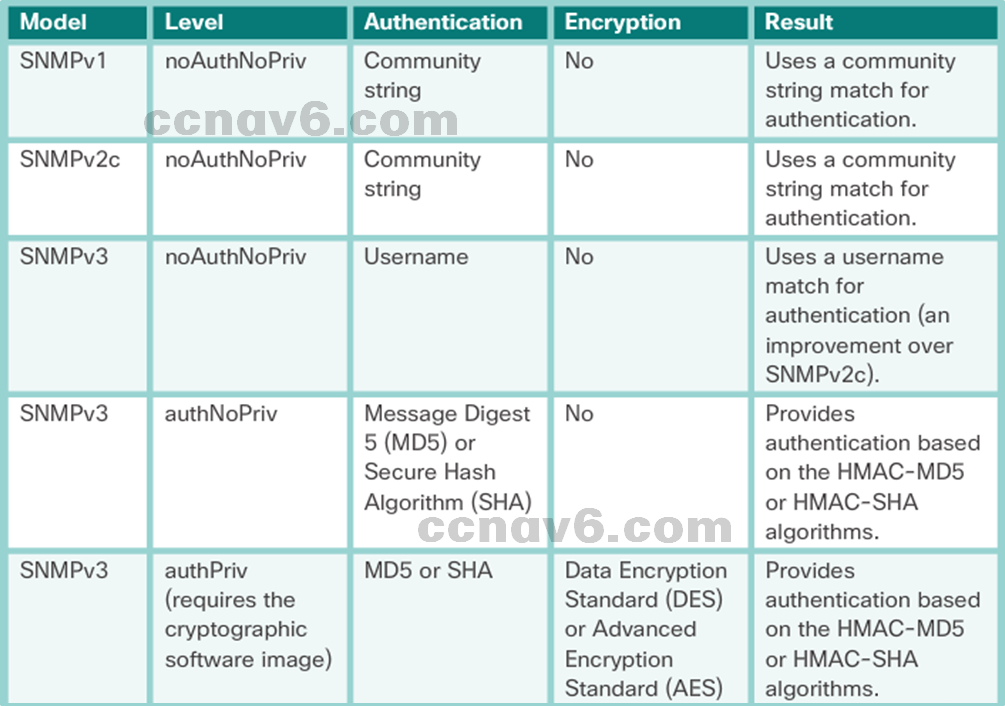
- SNMP Security Model and Levels
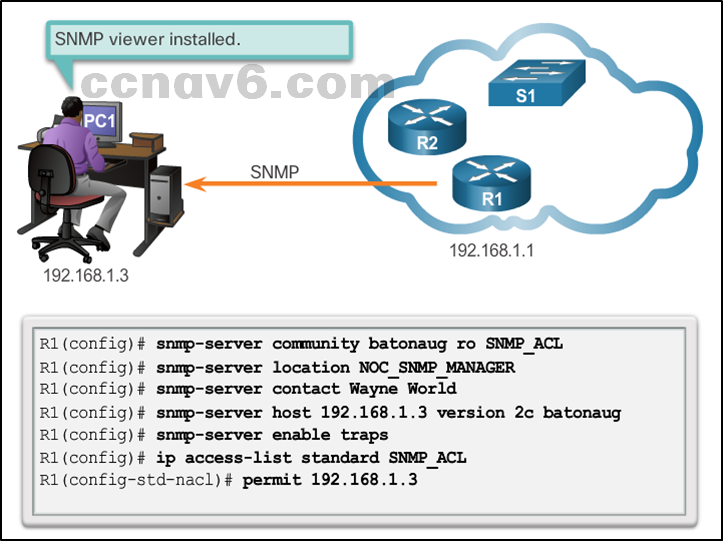
Configuring SNMP
- Configuration steps
- Configure community string
- Document location of device
- Document system contact
- Restrict SNMP Access
- Specify recipient of SNMP Traps
- Enable traps on SNMP agent
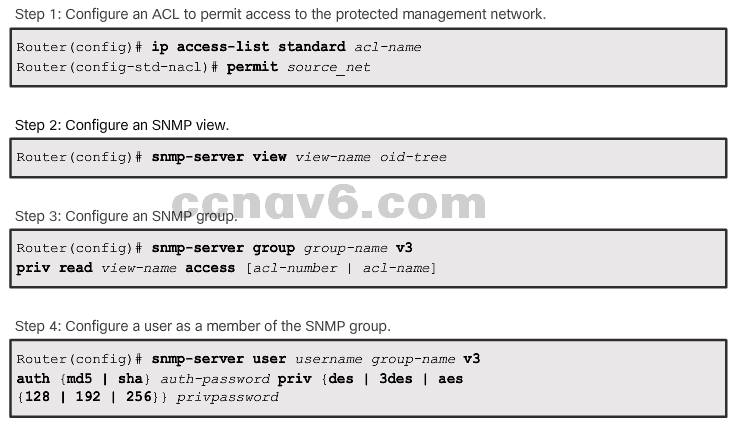
Securing SNMPv3
5.3 Cisco Switch Port Analyzer (SPAN)
SPAN Overview
Port mirroring
- The port mirroring feature allows a switch to copy and send Ethernet frames from specific ports to the destination port connected to a packet analyzer. The original frame is still forwarded in the usual manner.
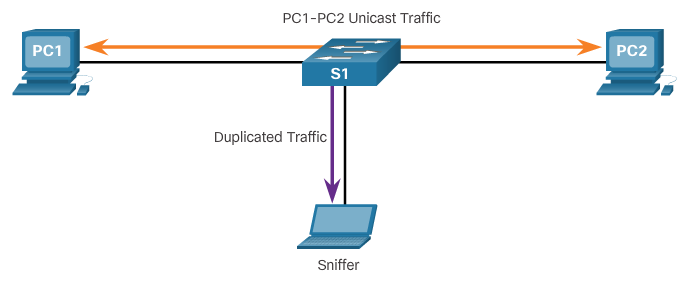
SPAN terminology
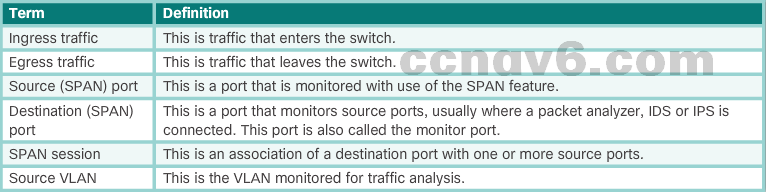
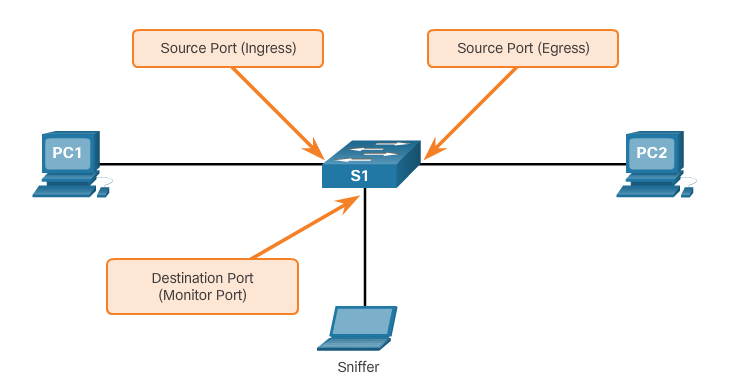
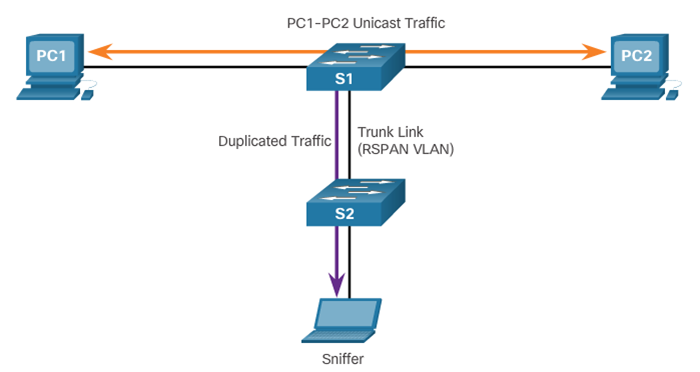
RSPAN terminology

SPAN Configuration
- Use monitor session global configuration command


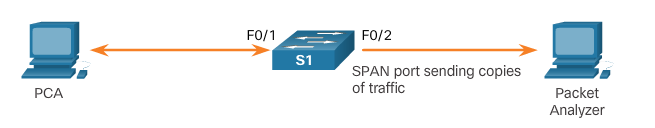

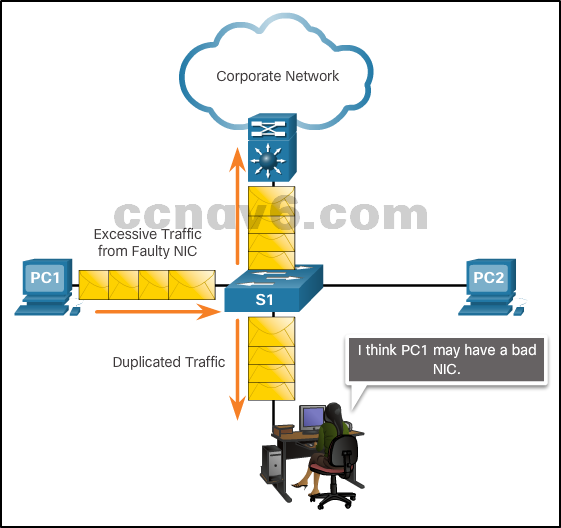
SPAN as a Troubleshooting Tool
-
- SPAN allows administrators to troubleshoot network issues
- Administrator can use SPAN to duplicate and redirect traffic to a packet analyzer
- Administrator can analyze traffic from all devices to troubleshoot sub-optimal operation of network applications
5.4 Chapter Summary
Summary
- At Layer 2, a number of vulnerabilities exist that require specialized mitigation techniques:
- MAC address table flooding attacks are addressed with port security.
- VLAN attacks are controlled by disabling DTP and following basic guidelines for configuring trunk ports.
- DHCP attacks are addressed with DHCP snooping.
- The SNMP protocol has three elements: the Manager, the Agent, and the MIB. The SNMP manager resides on the NMS, while the Agent and the MIB are on the client devices.
- The SNMP Manager can poll the client devices for information, or it can use a TRAP message that tells a client to report immediately if the client reaches a particular threshold. SNMP can also be used to change the configuration of a device.
- SNMPv3 is the recommended version because it provides security.
- SNMP is a comprehensive and powerful remote management tool. Nearly every item available in a show command is available through SNMP.
- Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) is used to mirror the traffic going to and/or coming from the host. It is commonly implemented to support traffic analyzers or IPS devices.
