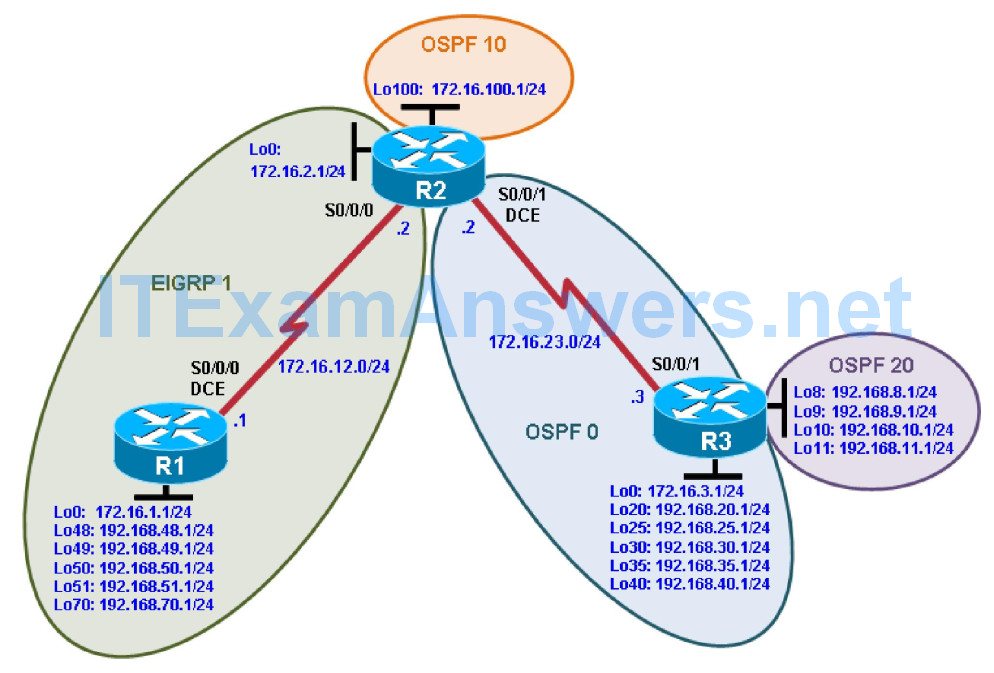
Topology
Objectives
- Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration.
- Summarize routes in EIGRP.
- Summarize in OSPF at an ABR.
- Redistribute into EIGRP.
- Redistribute into OSPF.
- Summarize in OSPF at an ASBR.
Background
Two online booksellers, Example.com and Example.net, have merged and now need a short-term solution to inter-domain routing. Since these companies provide client services to Internet users, it is essential to have minimal downtime during the transition.
Example.com is running EIGRP while Example.net is running a multi-area OSPF. Because it is imperative that the two booksellers continuously deliver Internet services, you should bridge these two routing domains without interfering with each router’s path through its own routing domain to the Internet.
The CIO determines that it is preferable to keep the two protocol domains shown in the diagram during the transition period, because the network engineers on each side need to understand the other’s network before deploying a long-term solution. Redistribution will be a short-term solution.
In this scenario, R1 and R2 are running EIGRP while R2 is the OSPF autonomous system border router
(ASBR) consisting of areas 0, 10, and 20. You need to configure R2 to enable these two routing protocols to interact to allow full connectivity between all networks.
In this lab, R1 is running EIGRP and R3 is running multi-area OSPF. Your task is to configure redistribution on R2 to enable these two routing protocols to interact, allowing full connectivity between all networks.
Note: This lab uses Cisco 1941 routers with Cisco IOS Release 15.2 with IP Base. Depending on the router or switch model and Cisco IOS Software version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in this lab.
Required Resources
- 3 routers (Cisco IOS Release 15.2 or comparable)
- Serial and Ethernet cables
Step 1: Configure loopbacks and assign addresses.
a. Configure all loopback interfaces on the three routers in the diagram. Configure the serial interfaces with the IP addresses, bring them up, and set a DCE clock rate where appropriate.
R1(config)# interface Loopback0 R1(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface Loopback48 R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.48.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface Loopback49 R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.49.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface Loopback50 R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.50.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface Loopback51 R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.51.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface Loopback70 R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.70.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface Serial0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address 172.16.12.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# clock rate 64000 R1(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config)# interface Loopback0 R2(config-if)# ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface loopback 100 R2(config-if)# ip address 172.16.100.1 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface Serial0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address 172.16.12.2 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R2(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface Serial0/0/1 R2(config-if)# ip address 172.16.23.2 255.255.255.0 R2(config-if)# clock rate 64000 R2(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R2(config-if)# no shutdown
R3(config)# interface Loopback0 R3(config-if)# ip address 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface loopback 8 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.8.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface loopback 9 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.9.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface loopback 10 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface loopback 11 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface Loopback20 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface Loopback25 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.25.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface Loopback30 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface Loopback35 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.35.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface Loopback40 R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.40.1 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface Serial0/0/1 R3(config-if)# ip address 172.16.23.3 255.255.255.0 R3(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R3(config-if)# no shutdown
b. Verify that you can ping across the serial links when you are finished. Use the following Tcl script to check full and partial connectivity throughout this lab.
R1# tclsh
foreach address {
172.16.1.1
192.168.48.1
192.168.49.1
192.168.50.1
192.168.51.1
192.168.70.1
172.16.12.1
172.16.12.2
172.16.2.1
172.16.100.1
172.16.23.2
172.16.23.3
172.16.3.1
192.168.8.1
192.168.9.1
192.168.10.1
192.168.11.1
192.168.20.1
192.168.25.1
192.168.30.1
192.168.35.1
192.168.40.1
} { ping $address }
Which pings are successful and why?
_____________________________________________________________________
Step 2: Configure EIGRP.
a. Configure R1 and R2 to run EIGRP in autonomous system 1. On R1, add in all connected interfaces either with classful network commands or with wildcard masks. Use a classful network statement on R2 and disable automatic summarization.
R1(config)# router eigrp 1 R1(config-router)# no auto-summary R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.48.0 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.49.0 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.50.0 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.51.0 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.70.0
or
R1(config)# router eigrp 1 R1(config-router)# no auto-summary R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 R2(config)# router eigrp 1 R2(config-router)# no auto-summary R2(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
b. Verify the EIGRP configuration using the show ip eigrp neighbors and show ip route eigrp commands on R1.
R1# show ip eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(1)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 172.16.12.2 Se0/0/0 10 00:00:22 42 2340 0 3
R1#
R1# show ip route eigrp
<Output omitted>
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 7 subnets, 2 masks
D 172.16.2.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.2, 00:00:31, Serial0/0/0
D 172.16.23.0/24 [90/41024000] via 172.16.12.2, 00:00:31, Serial0/0/0
D 172.16.100.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.2, 00:00:31, Serial0/0/0
R1#
c. Verify the EIGRP configuration on R2.
R2# show ip eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(1)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 172.16.12.1 Se0/0/0 11 00:04:14 35 2340 0 3
R2#
R2# show ip route eigrp
<Output omitted>
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 9 subnets, 2 masks
D 172.16.1.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:01:40, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.48.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:01:40, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.49.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:01:40, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.50.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:01:40, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.51.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:01:40, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.70.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:01:40, Serial0/0/0
R2#
d. Verify that R1 and R2 can reach all of the networks in the EIGRP routing domain using the following Tcl script.
R1# tclsh
foreach address {
172.16.1.1
192.168.48.1
192.168.49.1
192.168.50.1
192.168.51.1
192.168.70.1
172.16.12.1
172.16.12.2
172.16.2.1
} { ping $address }
All pings should be successful. Troubleshoot if necessary.
Step 3: Manually summarize with EIGRP.
To make routing updates more efficient and ultimately reduce the size of routing tables, contiguous EIGRP routes can be summarized out an interface by using the ip summary-address eigrp as network mask interface configuration command.
a. On R1, advertise one supernet route summarizing the networks of loopback 48 and 49 to R2.
R1(config)# interface Serial0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.48.0 255.255.254.0 R1(config-if)# *Oct 26 15:46:36.839: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 172.16.12.2 (Serial0/0/0) is resync: summary configured R1(config-if)# exit R1#
b. Verify the routing table of R1 using the show ip route eigrp command.
R1# show ip route eigrp
<Output omitted>
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 6 subnets
D 172.16.23.0 [90/41024000] via 172.16.12.2, 00:45:21, Serial0/0/0
D 172.16.2.0 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.2, 00:45:21, Serial0/0/0
D 172.16.100.0 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.2, 00:08:12, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.48.0/23 is a summary, 04:27:07, Null0
R1#
Notice how EIGRP now has a route to the summarized address going to the Null 0 interface in the routing table.
c. Verify the specifics for the summarized routes using the show ip route 192.168.48.0 255.255.254.0 command on R1.
R1# show ip route 192.168.48.0 255.255.254.0
Routing entry for 192.168.48.0/23, supernet
Known via "eigrp 1", distance 5, metric 128256, type internal
Redistributing via eigrp 1
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* directly connected, via Null0
Route metric is 128256, traffic share count is 1
Total delay is 5000 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is 10000000 Kbit
Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1514 bytes
Loading 1/255, Hops 0
Notice the low administrative distance (AD) for this route. Why does EIGRP add the summarized route
pointing to the Null 0 interface with a low AD?
_____________________________________________________________________
d. Verify the routing table of R2 using the show ip route eigrp command.
R2# show ip route eigrp
<Output omitted>
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 9 subnets, 2 masks
D 172.16.1.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:09:49, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.48.0/23 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:09:49, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.50.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:09:49, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.51.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:09:49, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.70.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.1, 00:09:49, Serial0/0/0
R2#
Notice how the routing table is slightly smaller as the entry to 192.168.49.0/24 is now missing. However, 192.168.49.1 is still reachable due to the summarized route to 192.168.48.0/23. Verify by pinging the loopback 49 interface from R2.
R2# ping 192.168.49.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.49.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/28/28 ms R2#
Step 4: Configure OSPF.
By default, loopback interfaces are advertised as a host route with a /32 mask. To advertise them as network routes, the loopback interface network type must be changed point-to-point. In this step, you will advertise the loopback interfaces as point-to-point and configure multi-area OSPF between R2 and R3.
a. On R2, configure the loopback 100 interface as a point-to-point network.
R2(config)# interface Loopback100 R2(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)#
b. Next advertise serial link connecting to R3 in area 0 and the loopback 100 network is area 10.
R2(config)# router ospf 1 R2(config-router)# network 172.16.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R2(config-router)# network 172.16.100.0 0.0.0.255 area 10
c. On R3, change the network type for the 10 loopback interfaces to point-to-point so that they are
advertised with the correct subnet mask (/24 instead of /32). Start with loopback 0.
R3(config)# interface Loopback0 R3(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point R3(config-if)# exit
d. Although we could manually configure all 9 other interface individually, we can also use the interface range command to simultaneously configure several interfaces. Loopback interfaces are contiguous and therefore configured by using a hyphen. The remainder of the interfaces are separated using a comma.
R3(config)# interface range lo 8 - 11 R3(config-if-range)# ip ospf network point-to-point R3(config-if-range)# exit R3(config)# R3(config)# interface range lo 20, lo 25, lo 30, lo 35, lo 40 R3(config-if-range)# ip ospf network point-to-point R3(config-if-range)# exit R3(config)#
e. On R3, include the serial link and all loopback interfaces in area 0 and the loopbacks in area 20.
R3(config)# router ospf 1 R3(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.8.0 0.0.3.255 area 20 R3(config-router)# *Jul 27 08:22:05.503: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 172.16.100.1 on Serial0/0/1 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done R3(config-router)#
f. Verify that your adjacencies come up with the show ip ospf neighbor command, and make sure that you have routes from OSPF populating the R2 routing table using the show ip route ospf command.
R2# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
192.168.40.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:39 172.16.23.3 Serial0/0/1
R2#
R2# show ip route ospf
<Output omitted>
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 10 subnets, 2 masks
O 172.16.3.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
O IA 192.168.8.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
O IA 192.168.9.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
O IA 192.168.10.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
O IA 192.168.11.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.20.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.25.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.30.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.35.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.40.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:04:24, Serial0/0/1
R2#
g. Verify that your adjacencies and routing table of R3.
R3# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
172.16.100.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:39 172.16.23.2 Serial0/0/1
R3#
R3# show ip route ospf
<Output omitted>
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
O IA 172.16.100.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.2, 00:07:02, Serial0/0/1
R3#
h. Verify that R1 and R2 can reach all of the networks in the OSPF routing domain using the following Tcl script.
R1# tclsh
foreach address {
172.16.100.1
172.16.23.2
172.16.23.3
172.16.3.1
192.168.8.1
192.168.9.1
192.168.10.1
192.168.11.1
192.168.20.1
192.168.25.1
192.168.30.1
192.168.35.1
192.168.40.1
} { ping $address }
All pings should be successful. Troubleshoot if necessary.
Step 5: Summarize OSPF areas at the ABR.
Review the R2 routing table. Notice the inter-area routes (O IA) for the R3 loopbacks in area 20. Where can you summarize in OSPF?
______________________________________________________________________
a. These four routes can be summarized into a single inter-area route using the area area range network mask command on the ABR, R3.
R3(config)# router ospf 1 R3(config-router)# area 20 range 192.168.8.0 255.255.252.0
b. On R2, verify the summarization with the show ip route ospf command on R2.
R2#show ip route ospf
<Output omitted>
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 10 subnets, 2 masks
O 172.16.3.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:37:42, Serial0/0/1
O IA 192.168.8.0/22 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:01:26, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.20.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:37:42, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.25.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:37:42, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.30.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:37:42, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.35.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:37:42, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.40.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.3, 00:37:42, Serial0/0/1
R2#
Compare and contrast OSPF and EIGRP in terms of where summarization takes place.
______________________________________________________________________
Step 6: Configure mutual redistribution between OSPF and EIGRP.
Notice that R2 is the only router with knowledge of all routes (EIGRP and OSPF) in the topology at this point, because it is involved with both routing protocols. Next you will redistribute the EIGRP routes into OSPF and the OSPF routes into EIGRP.
a. To redistribute the EIGRP routes into OSPF, on R2 issue the redistribute eigrp 1 subnets command. The subnets command is necessary because, by default, OSPF only redistributes classful networks and supernets.
R2(config)# router ospf 1 R2(config-router)# redistribute eigrp 1 subnets R2(config-router)# exit
A default seed metric is not required for OSPF. Redistributed routes are assigned a metric of 20 by default.
b. To redistribute the OSPF routes into EIGRP, on R2 issue the redistribute ospf 1 metric 10000 100 255 1 1500 command. Unlike OSPF, EIGRP must specify the metric associated to the redistributed routes. The command tells EIGRP to redistribute OSPF process 1 with these metrics: bandwidth of 10000, delay of 100, reliability of 255/255, load of 1/255, and a MTU of 1500. EIGRP requires a seed metric.
R2(config)# router eigrp 1 R2(config-router)# redistribute ospf 1 metric 10000 100 255 1 1500 R2(config-router)# exit
Alternatively, you can also set a default seed metric with the default-metric command.
R2(config-router)# default-metric 10000 100 255 1 1500 R2(config-router)# redistribute ospf 1 R2(config-router)# end
c. Issue the show ip protocols command on the redistributing router, R2. Compare your output with the following output.
R2# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
<Output omitted>
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
Redistributing: ospf 1
EIGRP-IPv4 Protocol for AS(1)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 172.16.100.1
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
172.16.0.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
172.16.12.1 90 02:00:24
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 172.16.100.1
It is an area border and autonomous system boundary router
Redistributing External Routes from,
eigrp 1, includes subnets in redistribution
Number of areas in this router is 2. 2 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
172.16.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
172.16.100.0 0.0.0.255 area 10
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.40.1 110 00:37:06
Distance: (default is 110)
R2#
d. Display the routing table on R1 to verify the redistributed routes. Redistributed OSPF routes display on R1 as D EX, which means that they are external EIGRP routes.
R1# show ip route
<Output omitted>
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 8 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.16.1.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
L 172.16.1.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
D 172.16.2.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.2, 02:08:18, Serial0/0/0
D EX 172.16.3.0/24 [170/40537600] via 172.16.12.2, 00:04:41, Serial0/0/0
C 172.16.12.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
L 172.16.12.1/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
D 172.16.23.0/24 [90/41024000] via 172.16.12.2, 02:08:18, Serial0/0/0
D 172.16.100.0/24 [90/40640000] via 172.16.12.2, 02:08:18, Serial0/0/0
D EX 192.168.8.0/22 [170/40537600] via 172.16.12.2, 00:04:41, Serial0/0/0
D EX 192.168.20.0/24 [170/40537600] via 172.16.12.2, 00:04:41, Serial0/0/0
D EX 192.168.25.0/24 [170/40537600] via 172.16.12.2, 00:04:41, Serial0/0/0
D EX 192.168.30.0/24 [170/40537600] via 172.16.12.2, 00:04:41, Serial0/0/0
D EX 192.168.35.0/24 [170/40537600] via 172.16.12.2, 00:04:41, Serial0/0/0
D EX 192.168.40.0/24 [170/40537600] via 172.16.12.2, 00:04:41, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.48.0/23 is a summary, 02:04:14, Null0
192.168.48.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.48.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback48
L 192.168.48.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback48
192.168.49.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.49.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback49
L 192.168.49.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback49
192.168.50.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.50.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback50
L 192.168.50.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback50
192.168.51.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.51.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback51
L 192.168.51.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback51
192.168.70.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.70.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback70
L 192.168.70.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback70
R1#
e. Display the routing table on R3 to see the redistributed routes. Redistributed EIGRP routes are tagged in the R3 routing table as O E2, which means that they are OSPF external type 2. Type 2 is the default OSPF external type.
R3# show ip route
<Output omitted>
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 8 subnets, 2 masks
O E2 172.16.1.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:08:18, Serial0/0/1
O E2 172.16.2.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:08:18, Serial0/0/1
C 172.16.3.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
L 172.16.3.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
O E2 172.16.12.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:08:18, Serial0/0/1
C 172.16.23.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
L 172.16.23.3/32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
O IA 172.16.100.0/24 [110/1563] via 172.16.23.2, 00:43:53, Serial0/0/1
O 192.168.8.0/22 is a summary, 00:43:53, Null0
192.168.8.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.8.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback8
L 192.168.8.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback8
192.168.9.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.9.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback9
L 192.168.9.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback9
192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback10
L 192.168.10.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback10
192.168.11.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback11
L 192.168.11.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback11
192.168.20.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback20
L 192.168.20.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback20
192.168.25.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.25.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback25
L 192.168.25.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback25
192.168.30.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.30.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback30
L 192.168.30.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback30
192.168.35.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.35.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback35
L 192.168.35.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback35
192.168.40.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.40.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback40
L 192.168.40.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback40
O E2 192.168.48.0/23 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:08:18, Serial0/0/1
O E2 192.168.50.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:08:18, Serial0/0/1
O E2 192.168.51.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:08:18, Serial0/0/1
O E2 192.168.70.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:08:18, Serial0/0/1
R3#
f. Verify full connectivity with the following Tcl script:
R1# tclsh
foreach address {
172.16.1.1
192.168.48.1
192.168.49.1
192.168.50.1
192.168.51.1
192.168.70.1
172.16.12.1
172.16.12.2
172.16.2.1
172.16.100.1
172.16.23.2
172.16.23.3
172.16.3.1
192.168.8.1
192.168.9.1
192.168.10.1
192.168.11.1
192.168.20.1
192.168.25.1
192.168.30.1
192.168.35.1
192.168.40.1
} { ping $address }
All pings should now be successful. Troubleshoot as necessary.
Step 7: Summarize external routes into OSPF at the ASBR.
You cannot summarize routes redistributed into OSPF using the area range command. This command is effective only on routes internal to the specified area. Instead, use the OSPF summary-address network mask command.
a. Before you make any changes, display the R3 the OSPF routes in the routing table and list only those routes that have a E2 type metric.
R3# show ip route ospf | include E2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
O E2 172.16.1.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:16:22, Serial0/0/1
O E2 172.16.2.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:16:22, Serial0/0/1
O E2 172.16.12.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:16:22, Serial0/0/1
O E2 192.168.48.0/23 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:16:22, Serial0/0/1
O E2 192.168.50.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:16:22, Serial0/0/1
O E2 192.168.51.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:16:22, Serial0/0/1
O E2 192.168.70.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:16:22, Serial0/0/1
R3#
Notice the external routes for the R1 loopback interfaces 48, 50 and 51. Loopbacks 48 and 49 were previously summarized in EIGRP, they will be included when redistributing the EIGRP into OSPF.
Which mask should you use to summarize all loopbacks 48, 50, and 51 to one prefix?
____________________________________________________________________
b. You can summarize this all into one supernet on R2 using the following commands.
R2(config)# router ospf 1 R2(config-router)# summary-address 192.168.48.0 255.255.252.0 R2(config-router)#
c. Verify this action in the R3 routing table.
R3# show ip route ospf | include E2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
O E2 172.16.1.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:21:44, Serial0/0/1
O E2 172.16.2.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:21:44, Serial0/0/1
O E2 172.16.12.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:21:44, Serial0/0/1
O E2 192.168.48.0/22 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:00:07, Serial0/0/1
O E2 192.168.70.0/24 [110/20] via 172.16.23.2, 00:21:44, Serial0/0/1
R3#
What would happen if loopback 50 on R1 were to become unreachable by R2?
____________________________________________________________________
Would data destined for 192.168.50.0/24 from R3 still be sent to R2?
____________________________________________________________________
Would data destined for 192.168.50.0/24 from R2 continue to be sent to R1?
_____________________________________________________________________
d. If you are unsure of the outcome, shut down the interface on R1. Issue the ICMP traceroute command to 192.168.50.1 from R3 and then from R2. Check your output against the output and analysis in Appendix A. Remember to issue the no shutdown command when you are finished checking.
Is this a desirable outcome? Explain.
_____________________________________________________________________
The resulting configuration is required for Lab 4-2
