13. What additional information is contained in the 12-bit extended system ID of a BPDU?
- MAC address
- VLAN ID
- IP address
- port ID
14. Refer to the exhibit. Which switch will be the root bridge after the election process is complete?
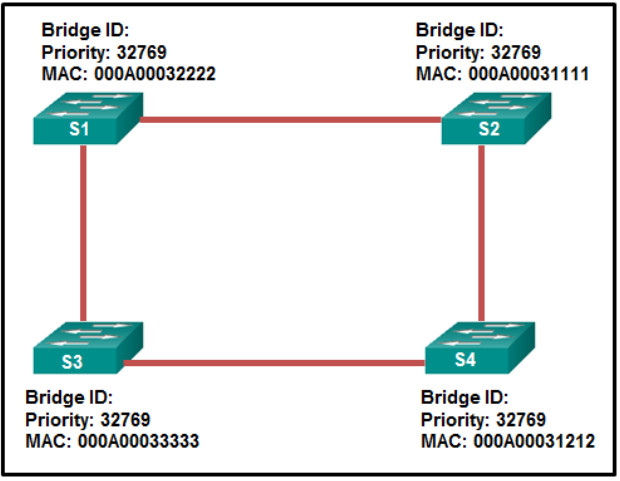
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
15. Which STP port type is permitted to forward traffic, but is not the port closest to the root bridge?
- root port
- backup port
- alternate port
- designated port
16. What is the value used to determine which port on a non-root bridge will become a root port in a STP network?
- the highest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the lowest MAC address of all the ports in the switch
- the VTP revision number
- the path cost
17. What is the purpose of STP?
- STP blocks redundant paths to prevent Layer 2 loops.
- It prevents unauthorized users from accessing a wireless network.
- It is used to automatically create trunk links between two devices.
- It ensures that only a specific number of devices can be connected to a port.
18. Which RSTP ports are connected to end devices?
- trunk ports
- designated ports
- root ports
- edge ports
19. If no bridge priority is configured in PVST, which criteria is considered when electing the root bridge?
- lowest IP address
- lowest MAC address
- highest IP address
- highest MAC address
20. In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
- blocking
- disabled
- forwarding
- learning
- listening
21. An administrator is troubleshooting a switch and wants to verify if it is a root bridge. What command can be used to do this?
- show spanning-tree
- show running-config
- show startup-config
- show vlan
22. Which port role will be assigned to all active trunk switch ports on the root bridge of a Layer 2 switched domain?
- root port
- designated port
- alternate port
- disabled port
23. During the implementation of Spanning Tree Protocol, all switches are rebooted by the network administrator. What is the first step of the spanning-tree election process?
- Each switch with a lower root ID than its neighbor will not send BPDUs.
- All the switches send out BPDUs advertising themselves as the root bridge.
- Each switch determines the best path to forward traffic.
- Each switch determines what port to block to prevent a loop from occurring.
24. Which three port states are used by Rapid PVST+? (Choose three.)
- discarding
- blocking
- trunking
- listening
- learning
- forwarding
25. By default, how often does a Cisco switch that is using RSTP send out BPDU frames?
- every 2 seconds
- every 4 seconds
- every 5 seconds
- every 10 seconds
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. How many different BPDU types are there?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
2. What attributes are used to elect a root bridge?
- Switch port priority
- Bridge priority
- Switch serial number
- Path cost
3. The original 802.1D specification assigns what value to a 1 Gbps interface?
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 19
4. All of the ports on a root bridge are assigned what role?
- Root port
- Designated port
- Superior port
- Master port
5. Using default settings, how long does a port stay in the listening state?
- 2 seconds
- 5 seconds
- 10 seconds
- 15 seconds
6. Upon receipt of a configuration BPDU with the topology change flag set, how do the downstream switches react?
- By moving all ports to a blocking state on all switches
- By flushing out all MAC addresses from the MAC address table
- By temporarily moving all non-root ports to a listening state
- By flushing out all old MAC addresses from the MAC address table
- By updating the Topology Change version flag on the local switch database
7. Which of the following is not an RSTP port state?
- Blocking
- Listening
- Learning
- Forwarding
8. True or false: In a large Layer 2 switch topology, the infrastructure must fully converge before any packets can be forwarded.
- True
- False
9. True or false: In a large Layer 2 switch topology that is running RSTP, the infrastructure must fully converge before any packets can be forwarded.
- True
- False
