Lab Objective:
The objective of this lab exercise is for you to learn how to implement IP floating static route functionality on a Cisco router.
Lab Purpose:
Configuring a floating static route will allow your Cisco router to have a backup route to a destination in case the primary route fails. As a Cisco engineer, as well as in the Cisco CCNA exam, you will be expected to know how to implement IP floating static route functionality.
Certification Level:
This lab is suitable for CCENT certification exam preparation.
Lab Difficulty:
This lab has a difficulty rating of 6/10.
Readiness Assessment:
When you are ready for your certification exam, you should complete this lab in no more than 10 minutes.
Lab Topology:
Please use the following topology to complete this lab exercise:
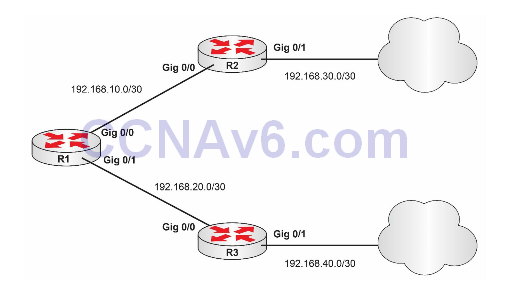
Note: Both R2 and R3 connect to the Internet, so R1 has two exit options to the Internet.
Task 1:
Configure the hostnames on R1, R2, and R3 as illustrated in the topology.
Task 2:
Configure the IP addresses on the Gig0/0 and Gig0/1 interfaces of R1, R2, and R3 as illustrated in the topology.
Note: R1 will always have the .1 IP in each of its Gig interfaces.
Note: R2 and R3 will have the .1 IP on the Gig0/1 interface.
Task 3:
Configure two default static routes on R1:
- The first one (primary one) will go to R2 with an administrative distance of 1.
- The secondary one will go to R3 with an administrative distance of 254.
Based on this, all traffic going to an unknown destination will be sent via R2.
Task 4:
Shut down the interface Gig0/0 of R1 and check via some show commands how the secondary route kicks in:
- show ip route
- show ip interface brief
Task 5:
Bring the interface Gig0/0 of R1 up again and check how it takes the primary role because of the lower administrative distance.
Run the same show commands and check the results.
Configuration and Verification
Task 1:
For reference information on configuring hostnames, please refer to earlier labs.
Task 2:
R1#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z. R1(config)#int gig0/0 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252 R1(config-if)#end R1(config)#int gig0/1 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.252 R1(config-if)#end R1# R2(config)#int gig0/0 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)#end R2(config)#int gig0/1 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)#end R2# R3(config)#int gig0/0 R3(config-if)#no shutdown R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.252 R3(config-if)#end R3(config)#int gig0/1 R3(config-if)#no shutdown R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.40.1 255.255.255.252 R3(config-if)#end R3#
Task 3:
R1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z. R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.10.2 R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.20.2 254
Task 4:
R1#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z.
R1(config)#int gig0/0
R1(config-if)#shutdown
R1#sh ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B – BGP,
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area,
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2,
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2,
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1,
L2 - IS-IS level2, ia - IS-IS inter area,
* - candidate default, U - per-user static, o - ODR,
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.20.2 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.20.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.20.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.20.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [254/0] via 192.168.20.2
R1#sh ip int brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.10.1 YES manual administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.20.1 YES manual up up
Task 5:
R1#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z.
R1(config)#int gig0/0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1#sh ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B – BGP,
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area,
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2,
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2,
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1,
L2 - IS-IS level2, ia - IS-IS inter area,
* - candidate default, U - per-user static,
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.10.2 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.10.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.10.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.20.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.20.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.20.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.10.2
R1#show ip int brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.10.1 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.20.1 YES manual up up
