6.4.2 Packet Tracer – Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Answers
Topology
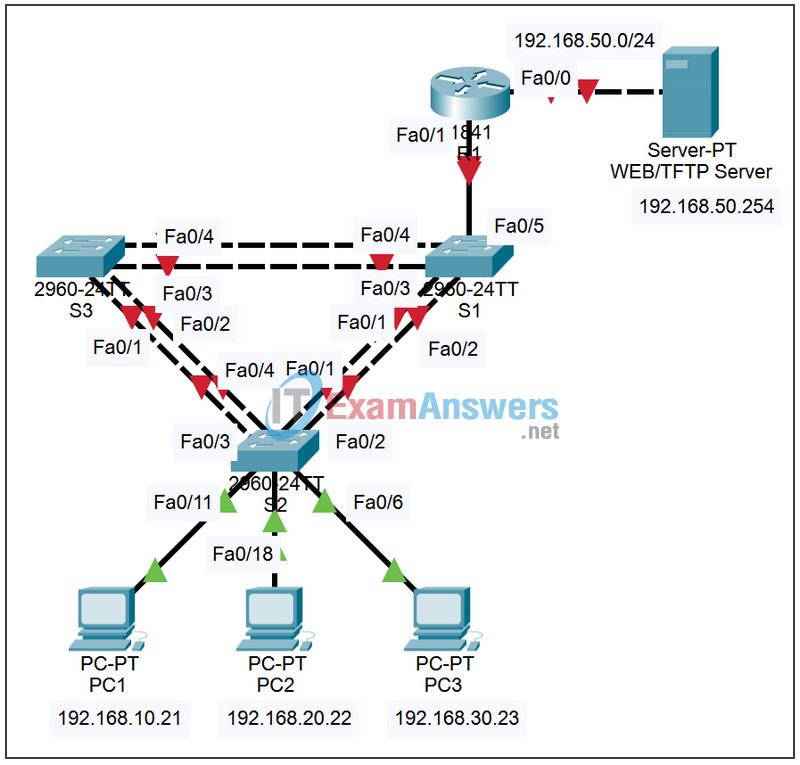
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | VLAN 99 | 192.168.99.11 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.99.1 |
| S2 | VLAN 99 | 192.168.99.12 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.99.1 |
| S3 | VLAN 99 | 192.168.99.13 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.99.1 |
| R1 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.50.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | See Subinterface Configuration Table | N/A | ||
| PC1 | NIC | 192.168.10.21 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.10.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 192.168.20.22 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.20.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.30.23 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.30.1 |
| Server | NIC | 192.168.50.254 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.50.1 |
Port Assignments – S2
| Ports | Assignment | Network |
|---|---|---|
| Fa0/1-0/5 | 802.1q Trunks (Native VLAN 99) | 192.168.99.0 /24 |
| Fa0/6-0/10 | VLAN 30 – Sales | 192.168.30.0 /24 |
| Fa0/11 – 0/17 | VLAN 10 – R&D | 192.168.10.0 /24 |
| Fa0/18 – 0/24 | VLAN 20 – Engineering | 192.168.20.0 /24 |
Subinterface Configuration Table – R1
| Router Interface | Assignment | IP Address |
|---|---|---|
| F0/0.1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.1 |
| Fa0/0.10 | VLAN 10 | 192.168.10.1 |
| Fa0/0.20 | VLAN 20 | 192.168.20.1 |
| Fa0/0.30 | VLAN 30 | 192.168.30.1 |
| Fa0/0.99 | VLAN 99 | 192.168.99.1 |
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to to:
- Cable a network according to the topology diagram
- Clear configurations and reload a switch and a router to the default state
- Perform basic configuration tasks on a switched LAN and a router
- Configure VLANs and VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on all switches
- Configure a router to support 802.1q trunking on a Fast Ethernet interface
- Configure a router with subinterfaces corresponding to the configured VLANs
- Demonstrate inter-VLAN routing
Task 1: Prepare the Network
Step 1: Cable a network that is similar to the one in the topology diagram.
The output shown in this lab is based on 2960 switches and an 1841 router. You can use any current switches or routers in your lab as long as they have the required interfaces shown in the topology diagram. Other device types may produce different output. Note that Ethernet (10Mb) LAN interfaces on routers do not support trunking, and Cisco IOS software earlier than version 12.3 may not support trunking on Fast Ethernet router interfaces.
Set up console connections to all three switches and to the router.
Step 2: Clear any existing configurations on the switches.
Clear NVRAM, delete the vlan.dat file and reload the switches. Refer to Lab 2.2.1 if necessary for the procedure. After the reload is complete, use the show vlan command to confirm that only default VLANs exist and that all ports are assigned to VLAN 1.
S1#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports ---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------- 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4 Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8 Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12 Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15,Fa0/16 Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19,Fa0/20 Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23,Fa0/24 Gig1/1, Gig1/2 1002 fddi-default active 1003 token-ring-default active 1004 fddinet-default active 1005 trnet-default active
Step 3: Disable all ports using the shutdown command.
Ensure that the initial switch port states are inactive by disabling all ports. Use the interface-range command to simplify this task.
S1(config)#interface range fa0/1-24 S1(config-if-range)#shutdown S1(config-if-range)#interface range gi0/1-2 S1(config-if-range)#shutdown S2(config)#interface range fa0/1-24 S2(config-if-range)#shutdown S2(config-if-range)#interface range gi0/1-2 S2(config-if-range)#shutdown S3(config)#interface range fa0/1-24 S3(config-if-range)#shutdown S3(config-if-range)#interface range gi0/1-2 S3(config-if-range)#shutdown
Step 4: Re-enable the active user ports on S2 in access mode.
Enable ports Fa0/6, Fa0/11, and Fa0/18 on S2 using the no shutdown command, and configure them as access ports.
S2(config)#interface fa0/6 S2(config-if)#switchport mode access S2(config-if)#no shutdown S2(config-if)#interface fa0/11 S2(config-if)#switchport mode access S2(config-if)#no shutdown S2(config-if)#interface fa0/18 S2(config-if)#switchport mode access S2(config-if)#no shutdown
Task 2: Perform Basic Switch Configurations
Configure the S1, S2, and S3 switches according to the addressing table and the following guidelines:
- Configure the switch hostname.
- Disable DNS lookup.
- Configure an EXEC mode password of class.
- Configure a password of cisco for console connections.
- Configure a password of cisco for vty connections.
- Configure the default gateway on each switch.
(Output for S1 shown)
Switch>enable Switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#hostname S1 S1(config)#enable secret class S1(config)#no ip domain-lookup S1(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.99.1 S1(config)#line console 0 S1(config-line)#password cisco S1(config-line)#login S1(config-line)#line vty 0 15 S1(config-line)#password cisco S1(config-line)#login S1(config-line)#end %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console S1#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? Building configuration...
Task 3: Configure the Ethernet Interfaces on the Server and Host PCs
Configure the Ethernet interfaces of PC1, PC2, PC3 and the remote TFTP/Web Server with the IP addresses from the addressing table. Connect these devices using the correct cables and interfaces.
Task 4: Configure VTP on the Switches
Step 1: Configure VTP on the three switches.
Use the following table to configure the switches. Remember that VTP domain names and passwords are case-sensitive.
| Switch Name | VTP Operating Mode | VTP Domain | VTP Password |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Server | Lab6 | cisco |
| S2 | Client | Lab6 | cisco |
| S3 | Client | Lab6 | cisco |
S1:
S1(config)#vtp mode server Device mode already VTP SERVER. S1(config)#vtp domain Lab6 Changing VTP domain name from NULL to Lab6 S1(config)#vtp password cisco Setting device VLAN database password to cisco S1(config)#end
S2:
S2(config)#vtp mode client Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode S2(config)#vtp domain Lab6 Changing VTP domain name from NULL to Lab6 S2(config)#vtp password cisco Setting device VLAN database password to cisco S2(config)#end
S3:
S3(config)#vtp mode client Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode S3(config)#vtp domain Lab6 Changing VTP domain name from NULL to Lab6 S3(config)#vtp password cisco Setting device VLAN database password to cisco S3(config)#end
Step 2: Configure trunking ports and designate the native VLAN for the trunks.
Configure Fa0/1 through Fa0/5 as trunking ports, and designate VLAN 99 as the native VLAN for these trunks. Use the interface range command in global configuration mode to simplify this task.
S1(config)#interface range fa0/1-4 S1(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S1(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1(config-if-range)#no shutdown S1(config-if-range)#end S2(config)# interface range fa0/1-4 S2(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S2(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2(config-if-range)#no shutdown S2(config-if-range)#end S3(config)# interface range fa0/1-4 S3(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S3(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3(config-if-range)#no shutdown S3(config-if-range)#end
Step 3: Configure VLANs on the VTP server.
Configure the following VLANS on the VTP server.
| VLAN | VLAN Name |
|---|---|
| VLAN 99 | Management |
| VLAN 10 | R&D |
| VLAN 20 | Engineering |
| VLAN 30 | Sales |
S1(config)#vlan 99 S1(config-vlan)#name Management S1(config-vlan)#exit S1(config)#vlan 10 S1(config-vlan)#name R&D S1(config-vlan)#exit S1(config)#vlan 20 S1(config-vlan)#name Engineering S1(config-vlan)#exit S1(config)#vlan 30 S1(config-vlan)#name Sales S1(config-vlan)#exit
Verify that the VLANs have been created on S1 with the show vlan brief command.
Step 4: Verify that the VLANs created on S1 have been distributed to S2 and S3.
Use the show vlan brief command on S2 and S3 to verify that the four VLANs have been distributed to the client switches.
S2#show vlan brief VLAN Name Status Ports ---- -------------------------------- --------- ----------------------------- 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/4, Fa0/5 Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9 Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12,Fa0/13 Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16,Fa0/17 Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20,Fa0/21 Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1 Gi0/2 10 R&D active 20 Engineering active 30 Sales active 99 Management active
Step 5: Configure the Management interface address on all three switches.
Refer to the addressing table at the beginning of the lab to assign the management IP address on all three switches.
S1(config)#interface vlan 99 S1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S1(config-if)#no shutdown S2(config)#interface vlan 99 S2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S2(config-if)#no shutdown S3(config)#interface vlan 99 S3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 S3(config-if)#no shutdown
Verify that the switches are correctly configured by pinging between them. From S1, ping the Management interface on S2 and S3. From S2, ping the Management interface on S3.
Were the pings successful?
All pings should be successful.
If not, troubleshoot the switch configurations and resolve.
Step 6: Assign switch ports to VLANs on S2.
Refer to the port assignment table at the beginning of the lab to assign ports to VLANs on S2.
S2(config)#interface range fa0/5-10 S2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 30 S2(config-if-range)#interface range fa0/11-17 S2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 10 S2(config-if-range)#interface range fa0/18-24 S2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 20 S2(config-if-range)#end S2#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? [enter] Building configuration... [OK]
Step 7: Check connectivity between VLANs.
Open command windows on the three hosts connected to S2. Ping from PC1 (192.168.10.21) to PC2 (192.168.20.22). Ping from PC2 to PC3 (192.168.30.23).
Are the pings successful?
No
If not, why do these pings fail?
Each host is in a different VLAN. Because each VLAN is in a separate Layer 3 domain, packets need to be routed at Layer 3 between VLANS. We have not yet configured the devices with L3 capability.
Task 5: Configure the Router
Step 1: Clear the configuration on the router and reload.
Router#erase nvram: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files! Continue? [confirm] Erase of nvram: complete Router#reload System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: n
Step 2: Create a basic configuration on the router.
- Configure the router with hostname R1.
- Disable DNS lookup.
- Configure an EXEC mode password of class.
- Configure a password of cisco for console connections.
- Configure a password of cisco for vty connections.
Step 3: Configure the trunking interface on R1.
Configure the Fa0/1 interface on R1 with five subinterfaces, one for each VLAN identified in the Subinterface Configuration Table at the beginning of the lab. Configure these subinterfaces with dot1q encapsulation, and use the first address in each VLAN subnet on the router subinterface. Specify VLAN 99 as the native VLAN on its subinterface. Do not assign an IP address to the physical interface, but be sure to enable it. Document your subinterfaces and their respective IP addresses in the subinterface table.
R1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/1.1 R1(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 1 R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/1.10 R1(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 10 R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/1.20 R1(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 20 R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/1.30 R1(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 30 R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/1.99 R1(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 99 native R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0
Step 4: Configure the server LAN interface on R1.
Refer to the addressing table and configure Fa0/0 with the correct IP address and mask.
R1(config)# interface FastEthernet0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.50.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#description server interface R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#end
Step 5: Verify the routing configuration.
At this point, there should be six networks configured on R1. Verify that you can route packets to all six by checking the routing table on R1.
R1#show ip route
<output omitted>
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.0.0/24 is subnetted, 6 subnets
C 192.168.50.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 192.168.30.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1.30
C 192.168.20.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1.20
C 192.168.10.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1.10
C 192.168.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1.1
C 192.168.99.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1.99
If your routing table does not show all six networks, troubleshoot your configuration and resolve the problem before proceeding.
Step 6: Verify inter-VLAN routing
From PC1, verify that you can ping the remote server (192.168.50.254) and the other two hosts (192.168.20.22 and 192.168.30.23). It may take a couple of pings before the end-to-end path is established.
Are the pings successful?
These pings should be successful.
If not, troubleshoot your configuration. Check to make sure the default gateways have been set on all PCs and all switches. If any of the hosts have gone into hibernation, the connected interface may go down.
At this point, you should be able to ping any node on any of the six networks configured on your LAN, including the switch management interfaces.
Task 6: Clean Up
Erase the configurations and reload the switches. Disconnect and store the cabling. For PC hosts that are normally connected to other networks (such as the school LAN or to the Internet), reconnect the appropriate cabling and restore the TCP/IP settings.
Final Configurations
Router 1 Configuration
hostname R1
!
enable secret class
!
no ip domain lookup
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.50.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1.1
encapsulation dot1Q 1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/1.10
encapsulation dot1Q 10
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/1.20
encapsulation dot1Q 20
ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/1.30
encapsulation dot1Q 30
ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FastEthernet0/1.99
encapsulation dot1Q 99 native
ip address 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0
!
<output omitted - serial interfaces not configured>
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
Switch 1 Configuration
!
hostname S1
!
enable secret class
!
no ip domain lookup
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/2
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/3
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/4
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/5
shutdown
!
<output omitted - all remaining ports in shutdown>
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
!
interface Vlan99
ip address 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
!
ip default-gateway 192.168.99.1
ip http server
!
line con 0
logging synchronous
line vty 0 4
no login
line vty 5 15
no login
!
end
Switch 2 Configuration
!
hostname S2
!
enable secret class
!
no ip domain lookup
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/2
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/3
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/4
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/5
switchport access vlan 30
switchport mode access
!
interface FastEthernet0/6
switchport access vlan 30
switchport mode access
!
interface FastEthernet0/7
switchport access vlan 30
!
interface FastEthernet0/8
switchport access vlan 30
!
interface FastEthernet0/9
switchport access vlan 30
!
interface FastEthernet0/10
switchport access vlan 30
!
interface FastEthernet0/11
switchport access vlan 10
switchport mode access
!
interface FastEthernet0/12
switchport access vlan 10
!
interface FastEthernet0/13
switchport access vlan 10
!
interface FastEthernet0/14
switchport access vlan 10
!
interface FastEthernet0/15
switchport access vlan 10
!
interface FastEthernet0/16
switchport access vlan 10
!
interface FastEthernet0/17
switchport access vlan 10
!
interface FastEthernet0/18
switchport access vlan 20
!
interface FastEthernet0/19
switchport access vlan 20
!
interface FastEthernet0/20
switchport access vlan 20
!
interface FastEthernet0/21
switchport access vlan 20
!
interface FastEthernet0/22
switchport access vlan 20
!
interface FastEthernet0/23
switchport access vlan 100
!
interface FastEthernet0/24
switchport access vlan 20
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
!
interface Vlan99
ip address 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
!
ip default-gateway 192.168.99.1
ip http server
!
line con 0
password cisco
logging synchronous
login
line vty 0 4
password cisco
login
line vty 5 15
password cisco
login
!
end
Switch 3 Configuration
!
hostname S3
!
enable secret class
!
no ip domain lookup
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/2
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/3
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/4
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport mode trunk
!
interface FastEthernet0/5
shutdown
!
<output omitted - all remaining ports in shutdown>
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
!
interface Vlan99
ip address 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
!
ip default-gateway 192.168.99.1
ip http server
!
control-plane
!
!
line con 0
password cisco
login
line vty 0 4
password cisco
login
line vty 5 15
password cisco
login
!
end
