1.3.3 Packet Tracer – Troubleshooting a Small Network Answers
Topology
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
- Verify that a paper design meets stated network requirements
- Cable a network according to the topology diagram
- Erase the startup configuration and reload a router to the default state
- Load the routers with supplied scripts
- Discover where communication is not possible
- Gather information about the misconfigured portion of the network along with any other errors
- Analyze information to determine why communication is not possible
- Propose solutions to network errors
- Implement solutions to network errors
Scenario
In this lab, you are given a completed configuration for a small routed network. The configuration contains design and configuration errors that conflict with stated requirements and prevent end-to-end communication. You will examine the given design and identify and correct any design errors. You will then cable the network, configure the hosts, and load configurations onto the router. Finally, you will troubleshoot the connectivity problems to determine where the errors are occurring and correct them using the appropriate commands. When all errors have been corrected, each host should be able to communicate with all other configured network elements and with the other host.
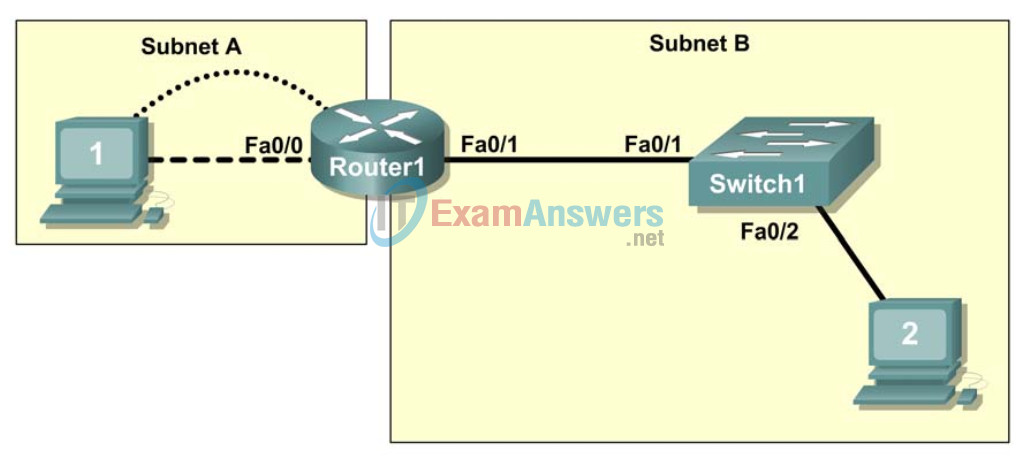
Task 1: Examine the Logical LAN Topology
The IP address block of 172.16.30.0 /23 is subnetted to meet the following requirements:
| Subnet | Number of Hosts |
|---|---|
| Subnet A | 174 |
| Subnet B | 60 |
Additional requirements and specifications:
- The 0 subnet is used.
- The smallest possible number of subnets that satisfy the requirements for hosts should be used, keeping the largest possible block in reserve for future use.
- Assign the first usable subnet to Subnet A.
- Host computers use the first usable IP address in the subnet. The network router uses the last usable network host address.
Based on these requirements, the following topology has been provided to you:
| Subnet A | |
|---|---|
| Specification | Value |
| IP mask (decimal) | 255.255.255.0 |
| IP address | 172.16.30.0 |
| First IP host address | 172.16.30.1 |
| Last IP host address | 172.16.30.254 |
| Subnet B | |
|---|---|
| Specification | Value |
| IP mask (decimal) | 255.255.255.128 (should be 255.255.255.192) |
| IP address | 172.16.31.0 |
| First IP host address | 172.16.31.1 |
| Last IP host address | 172.16.31.126 (should be 172.16.31.62 based on correct mask) |
Examine each of the values in the tables above and verify that this topology meets all requirements and specifications. Are any of the given values incorrect? _______
If yes, correct the values in the table above and write the corrected values below:
______________________________________________________
Create a configuration table similar to the one below using your corrected values:
| Device | IP address | Mask | Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Host1 | 172.16.30.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.30.254 |
| Router1–Fa0/0 | 172.16.30.254 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| Host2 | 172.16.31.1 | 255.255.255.128 (255.255.255.192) |
172.16.31.126 (172.16.31.62) |
| Router1–Fa0/1 | 172.16.31.126 (172.16.31.62) |
255.255.255.128 255.255.255.192 |
N/A |
Task 2: Cable, Erase, and Reload the Routers
Step 1: Cable the network.
Cable a network that is similar to the one in the topology diagram.
Step 2: Clear the configuration on each router.
Clear the configuration on the router using the erase startup-config command and then reload the router. Answer no if asked to save changes.
Task 3: Configure the Host Computers
Step 1: Configure host computers.
Configure the static IP address, subnet mask, and gateway for each host computer based on the configuration table created in Task 1. After configuring each host computer, display and verify the host network settings with the ipconfig /all command.
Task 4: Load the Router with the Supplied Scripts
[Instructor Note: Missing or misconfigured commands are shown in red]
enable ! config term ! hostname Router1 ! enable secret class ! no ip domain-lookup ! interface FastEthernet0/0 description connection to host1 ip address 172.16.30.1 255.255.255.0 (duplicate ip address – should be 172.16.30.254) duplex auto speed auto (missing command - no shutdown) ! interface FastEthernet0/1 description connection to switch1 ip address 192.16.31.1 255.255.255.192 (wrong ip address – should be 172.16.31.62) duplex auto speed auto (missing command - no shutdown) ! ! line con 0 password cisco login line vty 0 login line vty 1 4 password cisco login ! end
Task 5: Identify Connectivity Problems
Step 1: Use the ping command to test network connectivity.
Use the following table to test the connectivity of each network device.
| From | To | IP Address | Ping Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Host1 | NIC IP address | 172.16.30.1 | Should be successful. |
| Host1 | Router1, Fa0/0 | 172.16.30.254 | Should fail. |
| Host1 | Router1, Fa0/1 | 172.16.31.126 | Should fail. |
| Host1 | Host2 | 172.16.31.1 | Should fail. |
| Host2 | NIC IP address | 172.16.30.1 | Should be successful. |
| Host2 | Router1, Fa0/1 | 172.16.31.126 | Should fail. |
| Host2 | Router1, Fa0/0 | 172.16.30.254 | Should fail. |
| Host2 | Host1 | 172.16.30.1 | Should fail. |
Task 6: Troubleshoot Network Connections
Step 1: Begin troubleshooting at the host connected to the BRANCH router.
From host PC1, is it possible to ping PC2? No
From host PC1, is it possible to ping the router fa0/1 interface? No
From host PC1, is it possible to ping the default gateway? No
From host PC1, is it possible to ping itself? Yes
Where is the most logical place to begin troubleshooting the PC1 connection problems?
The first connection – PC1 to router interface fa0/0
Step 2: Examine the router to find possible configuration errors.
Begin by viewing the summary of status information for each interface on the router.
Are there any problems with the status of the interfaces?
Interfaces fa0/0 and fa0/1 are administratively down
If there are problems with the status of the interfaces, record any commands that are necessary to correct
the configuration errors.
config term; interface FastEthernet 0/0; no shutdown; FastEthernet 0/1; no shutdown
Step 3: Use the necessary commands to correct the router configuration.
Step 4: View a summary of the status information.
If any changes were made to the configuration in the previous step, view the summary of the status information for the router interfaces.
Does the information in the interface status summary indicate any configuration errors on Router1?
no
If the answer is yes, troubleshoot the interface status of the interfaces.
Has connectivity been restored? no
Step 5: Verify the logical configuration.
Examine the full status of Fa 0/0 and 0/1. Is the IP addresses and subnet mask information in the interface status consistent with the configuration table? no
If there are differences between the configuration table and the router interface configuration, record any commands that are necessary to correct the router configuration.
config term; interface FastEthernet 0/0; ip address 172.16.30.254 255.255.255.0; interface FastEthernet 0/1; ip address 172.16.31.62 255.255.255.192; end
Has connectivity been restored? yes
Why is it useful for a host to ping its own address?
Verifies the TCP/IP stack on the host
Task 7: Clean Up
Unless directed otherwise by your instructor, erase the configurations and reload the switches. Disconnect and store the cabling. For PC hosts that are normally connected to other networks (such as the school LAN or to the Internet), reconnect the appropriate cabling and restore the TCP/IP settings.
Corrected Router1 Configuration
Router1#show run <selective output omitted> ! hostname Router1 ! enable secret class ! interface FastEthernet0/0 description connection to host1 ip address 172.16.30.254 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/1 description connection to switch1 ip address 172.16.31.62 255.255.255.192 no shutdown ! ! line con 0 password cisco login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login ! end
