5.5.2 Packet Tracer – Challenge Spanning Tree Protocol Answers
Topology
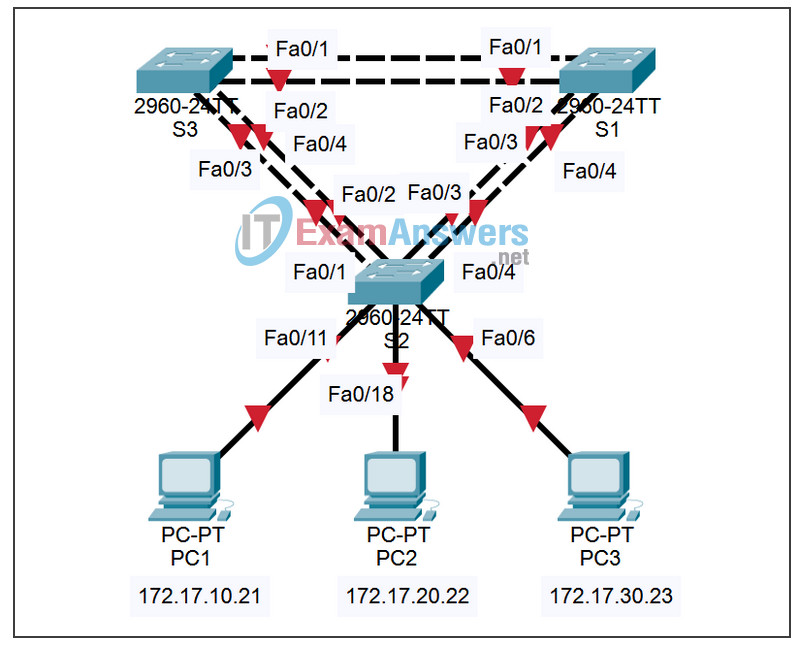
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | VLAN 99 | 172.17.99.11 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S2 | VLAN 99 | 172.17.99.12 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S3 | VLAN 99 | 172.17.99.13 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| PC1 | NIC | 172.17.10.21 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.17.30.12 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.17.20.22 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.17.30.12 |
| PC3 | NIC | 172.17.30.23 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.17.30.12 |
Port Assignments – S2
| Ports | Assignment | Network |
|---|---|---|
| Fa0/1 – 0/5 | 802.1q Trunks (Native VLAN 99) | 172.17.99.0 /24 |
| Fa0/6 – 0/10 | VLAN 30 – Guest (Default) | 172.17.30.0 /24 |
| Fa0/11 – 0/17 | VLAN 10 – Faculty/Staff | 172.17.10.0 /24 |
| Fa0/18 – 0/24 | VLAN 20 – Students | 172.17.20.0 /24 |
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
- Cable a network according to the topology diagram
- Erase the startup configuration and reload the default configuration, setting a switch to the default state
- Perform basic configuration tasks on a switch
- Configure VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on all switches
- Observe and explain the default behavior of Spanning Tree Protocol (STP, 802.1D)
- Modify the placement of the spanning tree root
- Observe the response to a change in the spanning tree topology
- Explain the limitations of 802.1D STP in supporting continuity of service
- Configure Rapid STP (802.1W)
- Observe and explain the improvements offered by Rapid STP
Introduction
In this activity, you will perform basic switch configurations, configure addressing on PCs, configure VLANs, examine the Spanning Tree Protocol and learn how to optimize it.
Task 1: Perform Basic Switch Configurations
Configure the S1, S2, and S3 switches according to the following guidelines and save all your configurations:
- Configure the switch hostname as indicated on the topology.
- Disable DNS lookup.
- Configure an EXEC mode password of class.
- Configure a password of cisco for console connections.
- Configure a password of cisco for vty connections.
Switch>enable Switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#hostname S1 S1(config)#enable secret class S1(config)#no ip domain-lookup S1(config)#line console 0 S1(config-line)#password cisco S1(config-line)#login S1(config-line)#line vty 0 15 S1(config-line)#password cisco S1(config-line)#login S1(config-line)#end %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console S1#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? Building configuration... [OK]
Task 2: Configure the Ethernet Interfaces on the Host PCs
Configure the Ethernet interfaces of PC1, PC2, and PC3 with the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway indicated in the addressing table.
Task 3: Configure VLANs
Step 1. Enable the user ports on S2 in access mode.
Refer to the topology diagram to determine which switch ports on S2 are activated for end-user device access. These three ports will be configured for access mode and enabled with the no shutdown command.
S2(config)#interface fa0/6 S2(config-if)#switchport mode access S2(config-if)#no shutdown S2(config-if)#interface fa0/11 S2(config-if)#switchport mode access S2(config-if)#no shutdown S2(config-if)#interface fa0/18 S2(config-if)#switchport mode access S2(config-if)#no shutdown
Step 2. Configure VTP.
Configure VTP on the three switches using the following table. Remember that VTP domain names and passwords are case-sensitive. The default operating mode is server.
| Switch Name | VTP Operating Mode | VTP Domain | VTP Password |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Server | Lab5 | cisco |
| S2 | Client | Lab5 | cisco |
| S3 | Client | Lab5 | cisco |
S1(config)#vtp mode server Device mode already VTP SERVER. S1(config)#vtp domain Lab5 Changing VTP domain name from NULL to Lab5 S1(config)#vtp password cisco Setting device VLAN database password to cisco S1(config)#end S2(config)#vtp mode client Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode S2(config)#vtp domain Lab5 Changing VTP domain name from NULL to Lab5 S2(config)#vtp password cisco Setting device VLAN database password to cisco S2(config)#end S3(config)#vtp mode client Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode S3(config)#vtp domain Lab5 Changing VTP domain name from NULL to Lab5 S3(config)#vtp password cisco Setting device VLAN database password to cisco S3(config)#end
Step 3. Configure Trunk Links and Native VLAN.
Configure trunking ports and native VLAN. For each switch, configure ports Fa0/1 through Fa0/5 as trunking ports. Designate VLAN 99 as the native VLAN for these trunks. When this activity was started, these ports were disabled and must be re-enabled now using the no shutdown command.
Only the commands for the FastEthernet0/1 interface on each switch are shown, but the commands should be applied up to the FastEthernet0/5 interface.
S1(config)#interface fa0/1 S1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk S1(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1(config-if)#no shutdown S1(config)#end S2(config)#interface fa0/1 S2(config-if)#switchport mode trunk S2(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2(config-if)#no shutdown S2(config-if)#end S3(config)#interface fa0/1 S3(config-if#switchport mode trunk S3(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3(config-if)#no shutdown S3(config-if-#end
Step 4. Configure the VTP server with VLANs.
VTP allows you to configure VLANs on the VTP server and have those VLANs populated to the VTP clients in the domain. This ensures consistency in the VLAN configuration across the network.
Configure the following VLANS on the VTP server:
| VLAN | VLAN Name |
|---|---|
| VLAN 99 | management |
| VLAN 10 | faculty-staff |
| VLAN 20 | students |
| VLAN 30 | guest |
S1(config)#vlan 99 S1(config-vlan)#name management S1(config)#vlan 10 S1(config-vlan)#name faculty-staff S1(config)#vlan 20 S1(config-vlan)#name students S1(config)#vlan 30 S1(config-vlan)#name guest S1(config-vlan)#end
Step 5. Verify the VLANs.
Use the show vlan brief command on S2 and S3 to verify that all four VLANs have been distributed to the client switches.
S2#show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -----------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/4, Fa0/5
Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9
Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12,Fa0/13
Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16,Fa0/17
Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20,Fa0/21
Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1
Gi0/2
10 faculty/staff active
20 students active
30 guest active
99 management active
S3#show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -----------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/4, Fa0/5
Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9
Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12,Fa0/13
Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16,Fa0/17
Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20,Fa0/21
Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1
Gi0/2
1002 fddi-default active
1003 token-ring-default active
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trnet-default active
Step 6. Configure the management interface address on all three switches.
S1(config)#interface vlan99 S1(config-if)#ip address 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2(config)#interface vlan99 S2(config-if)#ip address 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3(config)#interface vlan99 S3(config-if)#ip address 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
Verify that the switches are correctly configured by pinging between them. From S1, ping the management interface on S2 and S3. From S2, ping the management interface on S3.
Were the pings successful?
yes
If not, troubleshoot the switch configurations and try again.
Step 7. Assign switch ports to the VLANs.
Port assignments are listed in the table at the beginning of the activity. However, since Packet Tracer 4.11 does not support the interface range command, only assign the first port from each range.
S2(config)#interface fa0/6 S2(config-if)#switchport access vlan 30 S2(config-if)#interface fa0/11 S2(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10 S2(config-if)#interface fa0/18 S2(config-if)#switchport access vlan 20 S2(config-if)#end S2#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? [enter] Building configuration... [OK] S2#
Task 4: Configure Spanning Tree
Step 1. Examine the default configuration of 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
On each switch, display the spanning tree table with the show spanning-tree command. The output is shown for S1 only. Root selection varies depending on the default BID of each switch. In this activity S3 is currently the root.
S1#show spanning-tree
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32769
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 0050.0F68.146E
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32778
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 0050.0F68.146E
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
VLAN0020
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32788
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32788 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 20)
Address 0050.0F68.146E
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
VLAN0030
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32798
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32798 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 30)
Address 0050.0F68.146E
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
VLAN0099
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32867
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32867 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 99)
Address 0050.0F68.146E
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Note that there are five instances of STP on each switch.
Examine the VLAN 99 spanning tree for all three switches:
S1#show spanning-tree vlan 99
VLAN0099
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32867
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32867 (priority 32966 sys-id-ext 99)
Address 0050.0F68.146E
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
S2#show spanning-tree vlan 99
VLAN0099
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32867
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32867 (priority 32966 sys-id-ext 99)
Address 00E0.F7AE.7258
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/4 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
S3#show spanning-tree vlan 99
VLAN0099
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32867
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32867 (priority 32966 sys-id-ext 99)
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Step 2. Examine the output.
1. What is the bridge ID priority for switches S1, S2, and S3 on VLAN 99?
a. S1 _______32867 (32768 + 99)
b. S2 _______32867 (32768 + 99)
c. S3 _______32867 (32768 + 99)
2. What is the bridge ID priority for S1 on VLANs 10, 20, 30, and 99?
a. VLAN 10 _____ 32778 (32768 +10)
b. VLAN 20______32788 (32768 +20)
c. VLAN 30______32798 (32768 +30)
d. VLAN 99______32867 (32768 +99)
3. Which switch is the root for the VLAN 99 spanning tree?
S1 (may vary)
4. On VLAN 99, which spanning tree ports are in the blocking state on the root switch?
none
5. On VLAN 99, which spanning tree ports are in the blocking state on the non-root switches?
varies, but using default settings, one port is blocking on one nonroot switch, and three ports are blocking on the other non-root switch
6. How does STP elect the root switch?
lowest bridge ID
7. Since the bridge priorities are all the same, what else does the switch use to determine the root?
switch MAC address
Task 5: Optimizing STP
Because there is a separate instance of the spanning tree for every active VLAN, a separate root election is conducted for each instance. If the default switch priorities are used in root selection, the same root is elected for every spanning tree, as we have seen. This could lead to an inferior design. Some reasons to control the selection of the root switch include:
- The root switch is responsible for generating BPDUs in STP 802.1D and is the focal point for spanning tree control traffic. The root switch must be capable of handling this additional load.
- The placement of the root defines the active switched paths in the network. Random placement is likely to lead to suboptimal paths. Ideally the root is in the distribution layer.
- Consider the topology used in this activity. Of the six trunks configured, only three are carrying traffic. While this prevents loops, it is a waste of resources. Because the root can be defined on the basis of the VLAN, you can have some ports blocking for one VLAN and forwarding for another. This is demonstrated below.
In this example, it has been determined that the root selection using default values has led to under-utilization of the available switch trunks. Therefore, it is necessary to force another switch to become the root switch for VLAN 99 to impose some load-sharing on the trunks.
In the example output below, the default root switch for all VLANs is S3.
Selection of the root switch is accomplished by changing the spanning-tree priority for the VLAN. The default priority, as you have observed, is 32768 plus the VLAN ID. The lower number indicates a higher priority for root selection. Set the priority for VLAN 99 on S3 to 4096.
S1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 99 priority 4096 S1(config)#exit
Give the switches a little time to recalculate the spanning tree and then check the tree for VLAN 99 on switch S3 (the original VLAN 99 root) and switch S1 (the non-root switch selected to become the new VLAN 99 root).
S3#show spanning-tree vlan 99
VLAN0099
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 4195
Address 0050.0F68.146E
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32867 (priority 32966 sys-id-ext 99)
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
S1#show spanning-tree vlan 99
VLAN0099
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 4195
Address 0050.0F68.146E
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 4195 (priority 4294 sys-id-ext 99)
Address 0050.0F68.146E
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Which switch is the root for VLAN 99?
S3
Which ports are blocking VLAN 99 traffic on the new root?
none
Which ports are now blocking VLAN 99 traffic on the old root?
fa0/2 (may vary)
Compare the S1 VLAN 99 spanning tree above with the S1 VLAN 10 spanning tree.
S1#show spanning-tree vlan 10
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32778
Address 0030.F20D.D6B1
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32788 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 0050.0F68.146E
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Note that S1 can now use all four ports for VLAN 99 traffic as long as they are not blocked at the other end of the trunk. However, the original spanning tree topology, with one of four S1 ports in blocking mode, is still in place for the four other active VLANs. By configuring groups of VLANs to use different trunks as their primary forwarding path, we retain the redundancy of failover trunks, without having to leaves trunks totally unused.
