Chapter 1 – Sections & Objectives
1.1 Campus Wired LAN Designs
Explain why it is important to design a scalable hierarchical network.
1.2 Selecting Network Devices
Select network devices based on feature compatibility and network requirements.
1.1 Campus Wired LAN Designs
Cisco Validated Designs
- The Need to Scale the Network
- All enterprise networks must: support critical applications, support converged network traffic, support diverse business needs, and provide centralized administrative control.
- Campus network designs include small networks that use a single LAN switch, up to very large networks with thousands of connections.
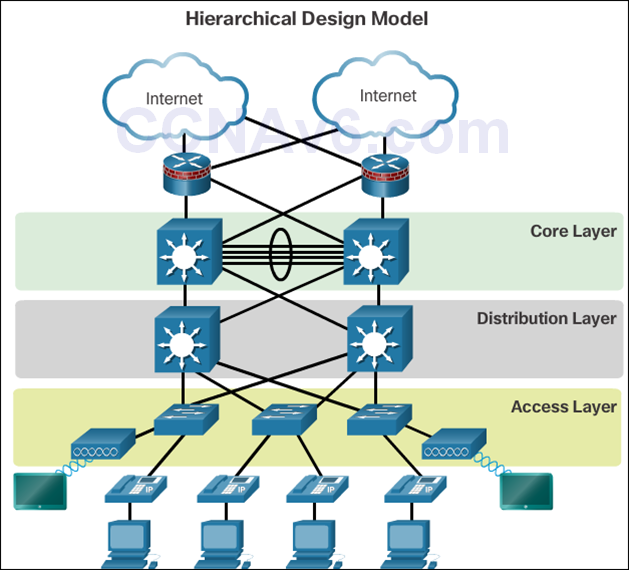
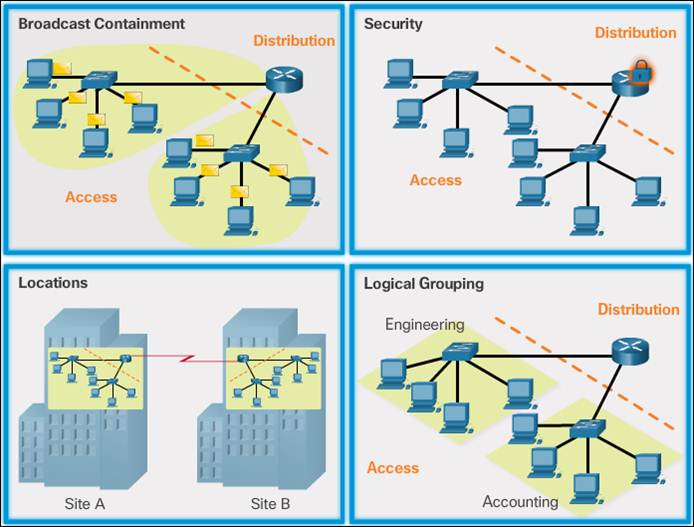
- A hierarchical LAN design includes
- The access, distribution, and core layers:
- The access layer provides endpoints and users direct access to the network.
- The distribution layer aggregates access layers and provides connectivity to services.
- The core layer provides connectivity between distribution layers for large LAN environments.
Expanding the Network
- To support a large, medium or small network, the network designer must develop a strategy to enable the network to be available and to scale effectively and easily.
- One method of implementing redundancy is by installing duplicate equipment and providing failover services for critical devices. Another method of implementing redundancy is redundant paths.
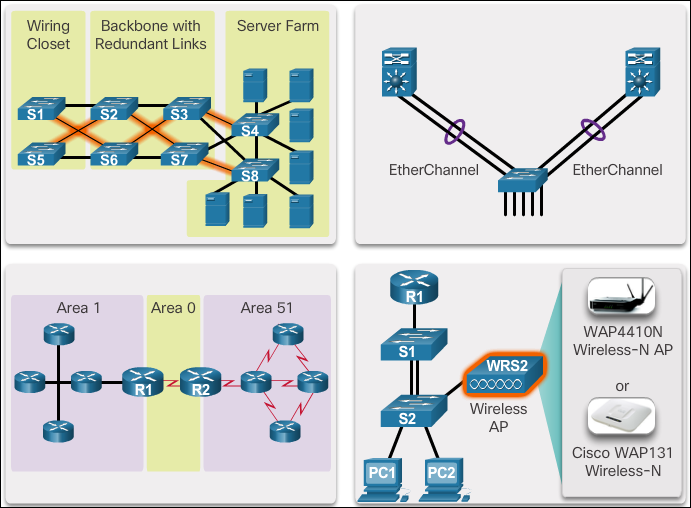
- A failure domain is the area of a network that is impacted when a critical device or network service experiences problems. Smaller failure domains reduce the impact of a failure on company productivity.
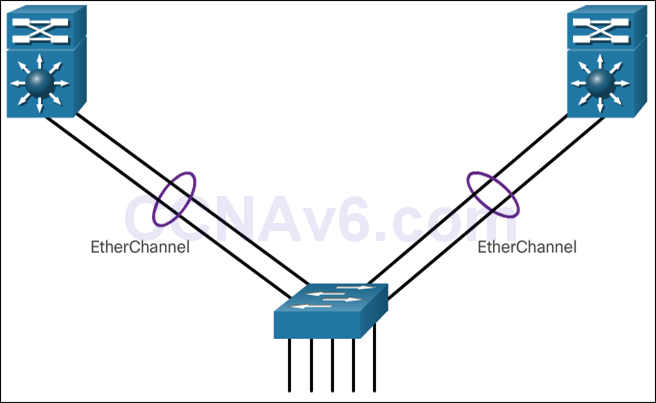
- Link aggregation allows an administrator to increase the amount of bandwidth between devices by creating one logical link made up of several physical links. EtherChannel is a form of link aggregation used in switched networks.
- To communicate wirelessly, end devices require a wireless NIC that incorporates a radio transmitter/receiver and the required software driver to make it operational. Additionally, a wireless router or a wireless access point (AP) is required for users to connect.
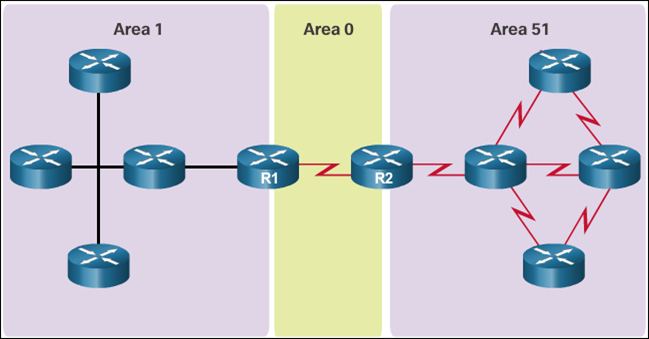
- Link-state routing protocols, such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), works well for larger hierarchical networks where fast convergence is important. OSPF routers establish and maintain neighbor adjacency or adjacencies, with other connected OSPF routers.
1.2 Selecting Network Devices
Switch Hardware
- There are five categories of switches for enterprise networks: Campus LAN, Data Center, Cloud-Managed, Service Provider, and Virtual Networking.
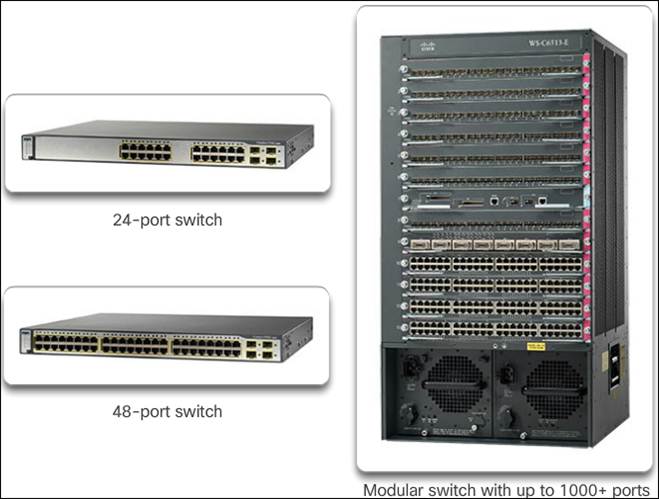
- The port density of a switch refers to the number of ports available on a single switch. Fixed configuration switches typically support up to 48 ports on a single device. Modular switches can support very high-port densities through the addition of multiple switch port line cards.

- Forwarding rates define the processing capabilities of a switch by rating how much data the switch can process per second.
- Wire speed is the data rate that each Ethernet port on the switch is capable of attaining. Data rates can be 100 Mb/s, 1 Gb/s, 10 Gb/s, or 100 Gb/s.
- Less expensive, lower performing switches can be used at the access layer, and more expensive, higher performing switches can be used at the distribution and core layers, where the forwarding rate has a greater impact on network performance.

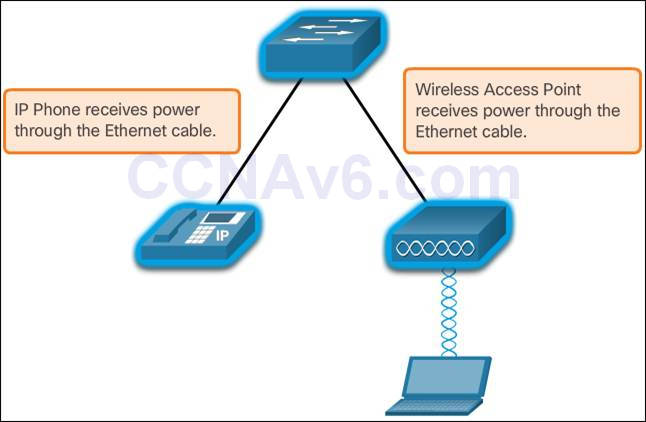
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) allows the switch to deliver power to a device over the existing Ethernet cabling.
- Multilayer switches are typically deployed in the core and distribution layers of an organization’s switched network. Multilayer switches are characterized by their ability to build a routing table, support a few routing protocols, and forward IP packets at a rate close to that of Layer 2 forwarding.
Router Hardware
- Routers play a critical role in networking by connecting homes and businesses to the Internet, interconnecting multiple sites within an enterprise network, providing redundant paths, and connecting ISPs on the Internet. They also act as a translator between different media types and protocols.
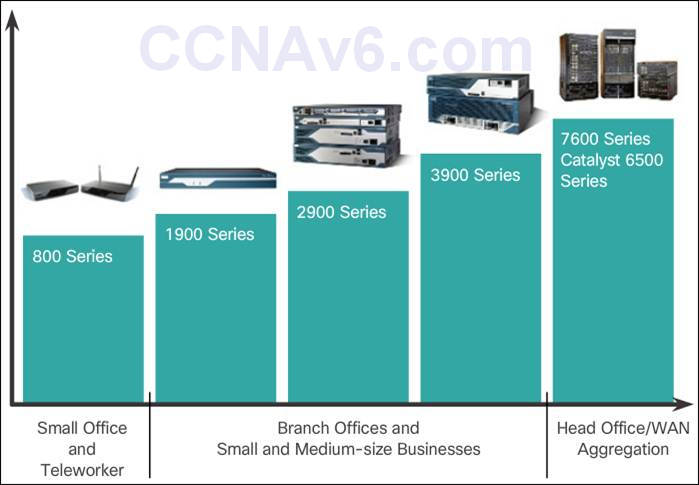
- There are three categories of routers: Branch, Network Edge, and Service Provider.
- Routers also come in many form factors. Network administrators in an enterprise environment should be able to support a variety of routers, from a small desktop router to a rack-mounted or blade model.
Managing Devices
- IOS refers to the package of routing, switching, security, and other internetworking technologies integrated into a single multitasking operating system.
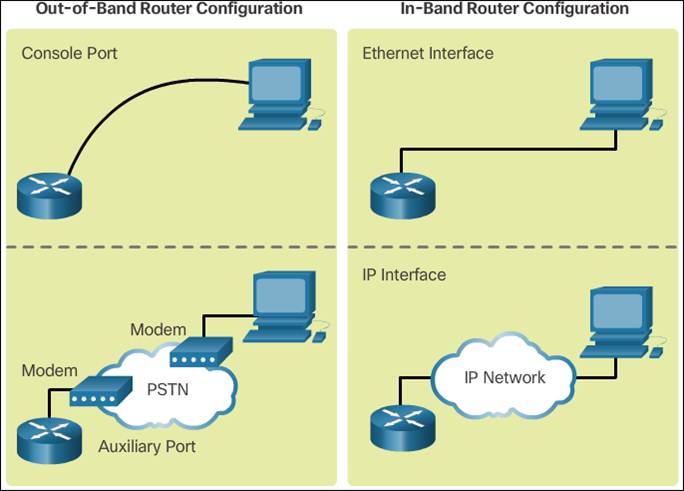
- Out-of-band management is used for initial configuration or when a network connection is unavailable.
- In-band management is used to monitor and make configuration changes to a network device over a network connection.
- A basic router configuration includes the hostname for identification, passwords for security, assignment of IP addresses to interfaces for connectivity, and basic routing. Verify and save configuration changes using the copy running-config startup-config command. To clear the router configuration, use the erase startup-config command and then the reload command.
- Some of the most commonly used IOS commands to display and verify the operational status of the router and related IPv4 network functionality are
- show ip protocols – Displays information about the routing protocols configured.
- show ip route – Displays routing table information, including: routing codes, known networks, administrative distance and metrics, how routes were learned, next hop, static routes, and default routes.
- show interfaces – Displays interfaces with line (protocol) status, bandwidth, delay, reliability, encapsulation, duplex, and I/O statistics.
- show ip interfaces – Displays interface information, including: protocol status, the IPv4 address, if a helper address is configured, and whether an ACL is enabled on the interface.
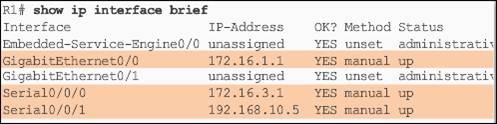
- show ip interface brief – Displays all interfaces with IPv4 addressing information and interface and line protocols status.
- show protocols – Displays information about the routed protocol that is enabled, and the protocol status of interfaces.
- A basic router configuration includes the hostname for identification, passwords for security, assignment of IP addresses to interfaces for connectivity, and basic routing.
- Verify and save configuration changes using the copy running-config startup-config command. To clear the router configuration, use the erase startup-config command and then the reload command.
- Some of the most commonly used IOS commands to display and verify the operational status of the router and related IPv4 network functionality are:
- show ip protocols
- show ip route
- show interfaces
- show ip interfaces
- show ip interface brief
- show protocols
- Verify and save the switch configuration using the copy running-config startup-config command. To clear the switch configuration, use the erase startup-config command and then the reload command. Erase any VLAN information using the command delete flash:vlan.dat. When switch configurations are in place, view the configurations using the show running-config command.
- Switches make use of common IOS commands for configuration, to check for connectivity and to display current switch status:
- show port-security
- show port-security address
- show interfaces
- show mac-address-table
- show cdp neighbors

